Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Watanabe, Masaya; Tsukada, Manabu*; Hoshino, Kazutoyo*; Hirai, Koki; Ikegami, Yuta*; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Hatakeyama, Yuichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-029, 36 Pages, 2024/03
At the Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF), the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220" was relocated from the 4th research building of the Nuclear Science Research Institute in FY2019, and the use of gamma ray irradiation has begun. Initially, Fuel Cycle Safety Research Group, Fuel Cycle Safety Research Division, Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, the owner of this device, conducted the tests as the main user, but since 2022, other users, including those outside the organization, have started using it. The gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220" is manufactured by Nordion International Inc. in Canada. Since it was purchased in 1989, the built-in 60Co radiation source has been updated once, and safety research related to nuclear fuel cycles, etc. It is still used for this purpose to this day. This report summarizes the equipment overview of the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220", its permits and licenses at WASTEF, usage status, maintenance and inspection, and future prospects.
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(2), p.172 - 181, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We developed a remote continuous air monitoring (RCAM) system. The RCAM system consisted of a personal air monitor and a robot. The personal air monitor (poCAMon, SARAD, Germany) had a 400 mm ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the
ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the  Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of
Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of 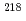 Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and
Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and  Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Narita, Takahiro; Usami, Hiroki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kojima, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.756 - 759, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Toshikazu*; Usami, Shin; Fujimura, Koji*; Takakuwa, Masayuki*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.560 - 566, 2015/09
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan has launched a national project entitled "technology development for the environmental burden reduction" in 2013. The present study is one of the studies adopted as the national project. The objective of the study is the efficient and safe transmutation and volume reduction of minor actinides with long-lived radioactivity and high decay heat contained in high level radioactive wastes by using sodium cooled fast reactors. We are developing MA transmutation core concepts which harmonize efficient MA transmutation with core safety. To accurately design the core concepts we have improved calculation methods for estimating the transmutation rate of individual MA nuclides, and estimating and reducing uncertainty of MA transmutation. The overview of the present project is first described. The method improvement is presented with numerical results for a minor-actinide transmutation fast reactor.
Uehara, Hiroyuki; Komuro, Kazuma; Usami, Koji; Nihei, Yasuo; Nakata, Masahito
Proceedings of 52nd Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling Working Group (HOTLAB 2015) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2015/09
For the accurate measurement of the released FP gas during RIA, Gas Chromatograph was improved with the hardware approach and the software one. As the hardware approach, PDD was added to the gas detector of GC and it can detect 50 times higher sensitivity compared with the TCD. As the software approach, ETG function was adopted to deconvolute the overlapped Kr peak from N one. With ETG estimation, Kr volume can be evaluated with the deconvolution from N
one. With ETG estimation, Kr volume can be evaluated with the deconvolution from N peak in neither the long measurement time nor the changing measurement condition.
peak in neither the long measurement time nor the changing measurement condition.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Narita, Takahiro; Nishiyama, Koichi; Usami, Hiroki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kasugai, Atsushi; Kojima, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.799 - 802, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Hamaguchi, Dai; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Ono, Katsuto; Matsui, Hiroki; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Dai, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 431(1-3), p.44 - 51, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.8(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To evaluate the lifetime of the beam window of an accelerator-driven transmutation system (ADS), post irradiation examination (PIE) of the STIP (SINQ target irradiation program, SINQ; Swiss spallation neutron source) specimens was carried out. The specimens tested in this study were made from the austenitic steel JPCA (Japan primary candidate alloy). The specimens were irradiated at SINQ Target 4 (STIP-II) with high-energy protons and spallation neutrons. The irradiation conditions were as follows: the proton energy was 580 MeV, irradiation temperatures ranged from 100 to 430 C, and displacement damage levels ranged from 7.1 to 19.5 dpa. Tensile tests were performed in air at room temperature (R.T.), 250
C, and displacement damage levels ranged from 7.1 to 19.5 dpa. Tensile tests were performed in air at room temperature (R.T.), 250 C and 350
C and 350 C. Fracture surface observation after the tests was done by SEM (Scanning electron microscope). Results of the tensile tests performed at R.T. showed the extra hardening of JPCA at higher dose compared to the fission neutron irradiated data. At the higher temperatures, 250
C. Fracture surface observation after the tests was done by SEM (Scanning electron microscope). Results of the tensile tests performed at R.T. showed the extra hardening of JPCA at higher dose compared to the fission neutron irradiated data. At the higher temperatures, 250 C and 350
C and 350 C, the extra hardening was not observed. Degradation of ductility bottomed around 10 dpa, and specimens kept their ductility until 19.5 dpa. All specimens fractured in ductile manner. The result from a microstructure observation on a specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420
C, the extra hardening was not observed. Degradation of ductility bottomed around 10 dpa, and specimens kept their ductility until 19.5 dpa. All specimens fractured in ductile manner. The result from a microstructure observation on a specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420 C indicates that some agglomeration of bubbles on grain boundaries was observed in the specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420
C indicates that some agglomeration of bubbles on grain boundaries was observed in the specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420 C. However the tensile specimen irradiated up to 18.4 dpa at 425
C. However the tensile specimen irradiated up to 18.4 dpa at 425 C still exhibited little loss of ductility. Since He/dpa was very high on SINQ target irradiations, the formation of highly dense small bubbles in the matrix consequently avoided the accumulation of He on grain boundaries, which might have resulted in avoiding grain boundary embrittlement.
C still exhibited little loss of ductility. Since He/dpa was very high on SINQ target irradiations, the formation of highly dense small bubbles in the matrix consequently avoided the accumulation of He on grain boundaries, which might have resulted in avoiding grain boundary embrittlement.
Toyokawa, Takuya; Usami, Koji; Shiina, Hidenori; Onozawa, Atsushi
Proceedings of 49th Conference on Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2012) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2012/09
Ioka, Ikuo; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Usami, Koji; Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.887 - 891, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-25Cr-35Ni EHP alloy was developed with conducting the countermeasure for IASCC. It is composed to adjust major elements, to remove harmful impurities and so on. The specimens were irradiated at 553 K for 25000h using JRR-3. The fluence was estimated to be 1.5 10
10 n/m
n/m . Type 304SS was also irradiated as a comparison material. SSRT test was conducted in oxygenated water at 561 K in 7.7 MPa. The fracture mode of EHP alloy was ductile. IGSCC was not observed in the fracture surface. On the other hand, the fraction of IGSCC on the fracture surface of type 304 was about 70%. Microstructural evolution of EHP and type 304 after irradiation was examined by TEM. The defects induced by irradiation mostly consisted of black dots and frank loops in both specimens. No void was also observed in grain and grain boundary of both specimens. There was a little difference in microstructure after irradiation. It is believed that EHP alloy is superior to type 304 in irradiation.
. Type 304SS was also irradiated as a comparison material. SSRT test was conducted in oxygenated water at 561 K in 7.7 MPa. The fracture mode of EHP alloy was ductile. IGSCC was not observed in the fracture surface. On the other hand, the fraction of IGSCC on the fracture surface of type 304 was about 70%. Microstructural evolution of EHP and type 304 after irradiation was examined by TEM. The defects induced by irradiation mostly consisted of black dots and frank loops in both specimens. No void was also observed in grain and grain boundary of both specimens. There was a little difference in microstructure after irradiation. It is believed that EHP alloy is superior to type 304 in irradiation.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Numata, Masami; Komiya, Tomokazu; Ichise, Kenichi; Nishi, Masahiro; Tomita, Takeshi; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Miyata, Seiichi; Kurosawa, Tatsuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-071, 34 Pages, 2010/03
As a part of maintenance technology of a large-sized glove box for handling of TRU nuclides, we developed replacement technology for front acrylic panels using the bag-in/bag-out method and applied this technology to replace the deteriorated front acrylic panels at Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF) in Nuclear Science Research Institute of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As a consequence, we could safely replace the front acrylic panels under the condition of continuous negative pressure only with partial decontamination of the glove box. We also demonstrated that the present technology is highly effective in points of safety, workability and cost as compared to the usual replacement technology for front acrylic panels of a glove box, where workers in an air-line suit replace directly the front acrylic panels in a green house.
Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Hamaguchi, Dai; Usami, Koji; Ishikawa, Akiyoshi; Nishino, Yasuharu; Endo, Shinya; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Dai, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 398(1-3), p.49 - 58, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In several institutes, R&D for an ADS have been progressed. Ferritic / martensitic (F/M) steels are the candidate material for the beam window. To obtain the irradiation data, the PIE work of the SINQ target irradiation program (STIP) specimens was carried out at JAEA. In this study, the results of PIE on F/M steel F82H and its welded joint will be reported. The results of tensile tests indicate that the irradiation hardening occurred with increasing dpa up to 10.1 dpa below 320 C irradiation. At higher dose (- 11.8 dpa) and higher temperature (- 380
C irradiation. At higher dose (- 11.8 dpa) and higher temperature (- 380 C), irradiation hardening and degradation of ductility relaxed. In this study, all specimens kept its ductility after irradiation and fractured in ductile manner. The fatigue life of F82H base metal is almost the same as that of unirradiated specimens. Though the number of specimen is limited, the fatigue life of F82H EB welded joints seems to increase after irradiation. The fracture surfaces of the specimens showed transgranular morphology. While F82H TIG welded specimens were not fractured by 10
C), irradiation hardening and degradation of ductility relaxed. In this study, all specimens kept its ductility after irradiation and fractured in ductile manner. The fatigue life of F82H base metal is almost the same as that of unirradiated specimens. Though the number of specimen is limited, the fatigue life of F82H EB welded joints seems to increase after irradiation. The fracture surfaces of the specimens showed transgranular morphology. While F82H TIG welded specimens were not fractured by 10 cycles.
cycles.
Saito, Shigeru; Hamaguchi, Dai; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Ono, Katsuto; Matsui, Hiroki; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Yong, D.*
Proceedings of 1st International Workshop on Technology and Components of Accelerator-driven Systems (TCADS-1) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2010/03
The research and development for an accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinide (MA) have been progressed. The target beam window of ADS submerged in the reactor will be subjected to high-energy proton and spallation neutron irradiation. To evaluate mechanical properties of irradiated materials, post irradiation examination (PIE) of the STIP (SINQ target irradiation program) specimens was carried out at JAEA. In the present study, PIE on austenitic steels JPCA and Alloy800H irradiated at SINQ target 4 (STIP-II) was conducted. Austenitic steels are preferable as the material for the target beam window of ADS from the view point of DBTT shift, which should be taken into consideration for ferritic / martensitic steels. The irradiation conditions were as follows: proton energy was 580 MeV, irradiation temperatures were ranged from 100 to 450 C, and displacement damage levels were ranged from 6.5 to 19.5 dpa. Tensile tests were performed in air at R.T. to 350
C, and displacement damage levels were ranged from 6.5 to 19.5 dpa. Tensile tests were performed in air at R.T. to 350 C. Results of the tensile tests performed at R.T. indicate that irradiation hardening occurred with increasing displacement damage level up to 10 dpa. At higher doses, irradiation hardening seemed to tend to saturate. Degradation of ductility was bottomed around 10 dpa and specimens kept its ductility until 19.5 dpa. All the specimens fractured in ductile manner.
C. Results of the tensile tests performed at R.T. indicate that irradiation hardening occurred with increasing displacement damage level up to 10 dpa. At higher doses, irradiation hardening seemed to tend to saturate. Degradation of ductility was bottomed around 10 dpa and specimens kept its ductility until 19.5 dpa. All the specimens fractured in ductile manner.
Endo, Shinya; Numata, Masami; Ichise, Kenichi; Nishi, Masahiro; Komiya, Tomokazu; Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Usami, Koji; Tomita, Takeshi
Proceedings of 46th Annual Meeting of "Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling" Working Group (HOTLAB 2009) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2009/09
For safety operation and maintenance of the large size glove box, the degraded acrylic panels of the box must be replaced by the new panels. As the conventional replacement technique, the decontamination of the glove box and installation of isolation tent are necessary to prevent the leak of contamination, because airtight condition of the box is broken down during replacement process. Therefore, the prerequisite works are required considerable manpower. The new replacement technique using bag-in / bag-out method was developed by JAEA. In this technique, for keeping the airtight condition of the box, the inside of degraded panel is covered with an airtight panel and the outside is covered over the large bag which is used to replace the acrylic panels. As the benefits of this technique, the prerequisite works are not required and the manpower is less than a third of the conventional technique.
 10
10 n/m
n/m
Nakano, Junichi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Usami, Koji; Tsukada, Takashi; Hide, Koichiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.281 - 285, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crack initiation and crack growth processes of irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking on stainless steels were studied by slow strain rate testing in oxygenated high temperature water at 561 K. In-situ observation was carried out during SSRT. Specimens of type 304 stainless steel were subjected to a solution annealing (SA), a thermally sensitization (TS), or a cold working (CW) and irradiated to 1.0 10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E  1 MeV) at 323 K in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). Crack initiations were observed before the maximum stress would be reached for the CW material in in-situ observation. In fracture surface examination, the TS material exhibited almost intergranular stress corrosion cracking while mixtures of transgranular stress corrosion cracking and ductile dimple fracture were observed for the SA and the CW materials.
1 MeV) at 323 K in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). Crack initiations were observed before the maximum stress would be reached for the CW material in in-situ observation. In fracture surface examination, the TS material exhibited almost intergranular stress corrosion cracking while mixtures of transgranular stress corrosion cracking and ductile dimple fracture were observed for the SA and the CW materials.
Endo, Shinya; Usami, Koji; Nakata, Masahito; Fukuda, Takuji*; Onozawa, Atsushi; Harada, Akio; Kizaki, Minoru; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki
HPR-366, Vol.1 (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Endo, Shinya; Usami, Koji; Nakata, Masahito; Fukuda, Takuji*; Numata, Masami; Kizaki, Minoru; Nishino, Yasuharu
Proceedings of 2005 JAEA-KAERI Joint Seminar on Advanced Irradiation and PIE Technologies, p.S2_7_1 - S2_7_11, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji; Usami, Koji; Ishikawa, Akiyoshi; Nishino, Yasuharu; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Dai, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.253 - 261, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A beam window of a spallation target will be subjected to proton/neutron irradiation, pressure wave and thermal stresses accompanied by high-energy proton beam injection. To obtain the irradiation data, the SINQ target irradiation program (STIP) was initiated in 1996 at Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and has been progressing. JAERI takes part in STIP and shares the PIE work. In this study, the results of tensile tests on austenitic stainless steels, JPCA and 316F SS, will be reported. The results indicate that the irradiation causes considerable hardening and degradation of ductility. The YS increases in this study are slightly large in comparison with those irradiated at fission reactor. Strain-to-necking (STN) values show sufficient large ductility of the irradiated JPCA-SA and 316F-SA. The trends of the STN decrease in this study are slightly abrupt in comparison with those irradiated at fission reactor. All specimens, including irradiated at embrittlement temperature for austenitic steels, fractured in ductile manner.
Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji; Usami, Koji; Ishikawa, Akiyoshi; Nishino, Yasuharu; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Dai, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.1093 - 1097, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In several institutes, research and development for an accelerator-driven spallation neutron source have been progressed. A beam window of a target will be subjected to proton/neutron irradiation, pressure wave and thermal stresses accompanied by high-energy proton beam injection. To obtain the irradiation data, the SINQ target irradiation program (STIP) at Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) has been progressing. JAERI takes part in STIP and shares the PIE work. The STIP specimens are very small so that we developed a new fatigue-testing machine with ceramic piezoelectric actuator. The results showed that the numbers of cycles to failure (Nf) on the irradiated specimens were less than that of unirradiated specimens. Dpa dependence of Nf was not clearly seen in the irradiation conditions. On the other hand, fracture surface varied with irradiation conditions. Specimens irradiated at low temperature fractured in ductile manner. However, interglanular fractured surface was observed for 316F SS irradiated up to 12.5 dpa at 360 C.
C.
Kikuchi, Kenji; Saito, Shigeru; Nishino, Yasuharu; Usami, Koji
Proceedings of 6th International Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerator Technology (AccApp '03), p.874 - 880, 2004/00
Specimens irradiated at SINQ were tested by tensile and fatigue. Speciemns were irradiated by 580MeV proton beams under spallation reaction during two years, transported to JAERI and tested at JAERI Hot Cell. Material is JPCA austenitic stainless steel. Strain-to-necking is over 8% at 250 C test temperature and are different from APT handbook database. Fatigue test was conducted at low stress regime of high cycle fatigue. The number of cycles to failure is reduced by factors five to ten. These data will help a design of spallation target in JPARC.
C test temperature and are different from APT handbook database. Fatigue test was conducted at low stress regime of high cycle fatigue. The number of cycles to failure is reduced by factors five to ten. These data will help a design of spallation target in JPARC.