Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 decay of
decay of 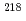 At
AtCubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Barzakh, A. E.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Day Goodacre, T.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(6), p.064317_1 - 064317_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:53.97(Physics, Nuclear)An  decay of
decay of 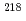 At was studied at the CERN-ISOLDE facility using a laser-ionization technique. Coincidence
At was studied at the CERN-ISOLDE facility using a laser-ionization technique. Coincidence  -
- data were collected for the first time and a more precise half-life value of T
data were collected for the first time and a more precise half-life value of T = 1.27(6) s was measured. A new
= 1.27(6) s was measured. A new  -decay scheme was deduced based on the fine-structure of the
-decay scheme was deduced based on the fine-structure of the  decay. The results lead to a preferred spin and parity assignment of J
decay. The results lead to a preferred spin and parity assignment of J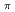 = (3
= (3 ) for the ground state of
) for the ground state of 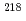 At; however, J
At; however, J = (2)
= (2) cannot be fully excluded.
cannot be fully excluded.
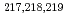 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero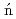 , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:77.09(Physics, Nuclear) -spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facility
-spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facilityJentschel, M.*; Blanc, A.*; de France, G.*; K ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.P11003_1 - P11003_33, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:84.92(Instruments & Instrumentation) -delayed fission of
-delayed fission of  Am
AmWilson, G. L.*; Takeyama, Mirei*; Andreyev, A. N.; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Catford, W. N.*; Ghys, L.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; He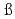 berger, F. P.*; Huang, M.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Huang, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044315_1 - 044315_7, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.01(Physics, Nuclear) T
T As
As (
( = Co,Ni)
= Co,Ni)Tam, D. M.*; Song, Y.*; Man, H.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Yin, Z.*; Lu, X.*; Wang, W.*; Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Gong, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(6), p.060505_1 - 060505_6, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Guguchia, Z.*; Khasanov, R.*; Morenzoni, E.*; Munsie, T. J. S.*; Hallas, A. M.*; Wilson, M. N.*; Cai, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 7, p.12519_1 - 12519_8, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:77.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Matthi , D.*; Ehresmann, B.*; Lohf, H.*; K
, D.*; Ehresmann, B.*; Lohf, H.*; K hler, J.*; Zeitlin, C.*; Appel, J.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Slaba, T. C.*; Martin, C.*; Berger, T.*; et al.
hler, J.*; Zeitlin, C.*; Appel, J.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Slaba, T. C.*; Martin, C.*; Berger, T.*; et al.
Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (Internet), 6, p.A13_1 - A13_17, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:93.52(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) on the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) has been measuring the radiation environment on the surface of Mars since August 6th 2012. In this work, several models such as GEANT4, PHITS, and HZETRN/OLTARIS are used to predict the radiation environment caused by galactic cosmic rays on Mars in order to compare and validate them with the experimental results. Although good agreement is found in many cases for GEANT4, PHITS and HZETRN/OLTARIS, some models still show large, sometimes order of magnitude, discrepancies in certain particle spectra. We have found that RAD data is helping make better choices of input parameters and physical models. These results help to predict dose rates for future manned missions as well as to perform shield optimization studies.
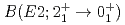 value in
value in  Kr
KrR gis, J.-M.*; Jolie, J.*; Saed-Samii, N.*; Warr, N.*; Pfeiffer, M.*; Blanc, A.*; Jentschel, M.*; K
gis, J.-M.*; Jolie, J.*; Saed-Samii, N.*; Warr, N.*; Pfeiffer, M.*; Blanc, A.*; Jentschel, M.*; K ster, U.*; Mutti, P.*; Soldner, T.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Mutti, P.*; Soldner, T.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 90(6), p.067301_1 - 067301_4, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:80.23(Physics, Nuclear)Savage, D.*; Soler, J. M.*; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Walker, C.; Honda, Akira; Inagaki, Manabu; Watson, C.*; Wilson, J.*; Benbow, S.*; Gaus, I.*; et al.
Applied Geochemistry, 26(7), p.1138 - 1152, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:48.49(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The use of cement and concrete as fracture grouting or as tunnel seals in a geological disposal facility for rad wastes creates potential issues concerning chemical reactivity. From a long term safety perspective, it is desirable to be able model these interactions and changes quantitatively. As part of the LCS (Long-term Cement Studies) project programme, a modelling inter-comparison has been conducted, involving the modelling of two experiments describing cement hadration and cement-rock reaction, with teams representing the NDA (UK), Posiva (Finland), and JAEA. This modelling exercise showed that the dominant reaction pathways in the two experiments are fairly well understood and are consistent between the different modelling teams, although significant differences existed amongst the precise parameterisation. Future modelling exercises of this type should focus on a suitable natural or industrial analogue that might aid assessing mineral-fluid reactions at these longer timescales.
Mayoral, M.-L.*; Bobkov, V.*; Colas, L.*; Goniche, M.*; Hosea, J.*; Kwak, J. G.*; Pinsker, R.*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Wukitch, S.*; Baity, F. W.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2011/03
For any given ICRF antenna design for ITER, the maximum achievable power strongly depends on the density profiles in the SOL. It has been suggested that gas injection can be used to modify the SOL profiles and thus minimize the sensitivity of the ICRF coupling to variations in the density at the edge of the confined plasma. Recently joint experiments coordinated by the ITPA were performed to characterize further this method. An increase in SOL density during gas injection led to improved coupling for all tokamaks in this multi-machine comparison. The effectiveness of using gas injection over a wide range of conditions, as a tool to tailor the edge density in front of the ICRF antennas, is documented for different gas inlet location and plasma configurations. In addition, any deleterious effects on the confinement and interaction with the antenna near-field are not investigated.
Fischer, U.*; Iida, Hiromasa; Li, Y.*; Loughlin, M.*; Sato, Satoshi; Serikov, A.*; Tsige-Tamirat, H.*; Tautges, T.*; Wilson, P. P.*; Wu, Y.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 56(2), p.702 - 709, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Several approaches have been recently developed to make available CAD geometry data for Monte Carlo calculations with the MCNP code. Among these are conversion tools for the automatic generation of geometry models in MCNP representation such as MCAM of China, McCad of Germany, and GEOMIT of JAEA, as well as the direct DAG-MCNPX approach developed by USA. An extensive benchmark exercise has been conducted on ITER between 2005 and 2007 with the objective to test and validate the different approaches and thereby check the maturity level for ITER design applications. The exercise encompassed the generation of a dedicated neutronics CATIA model based on available engineering CAD design data, the conversion into MCNP geometry, the verification of the converted models, and a number of calculations to compare the different approaches with regard to the performance and the validity of the results obtained. The paper briefly reviews the different approaches and provides a detailed description of the ITER benchmark effort, its results and conclusions. As a key issue, the recommendations are discussed that need to be followed when generating a neutronics CAD model for ITER design calculations. This is considered essential since the ITER quality assurance requirements will request the consistency of the analysis models and the underlying engineering CAD models.
Loughlin, M. J.*; Batistoni, P.*; Konno, Chikara; Fischer, U.*; Iida, Hiromasa; Petrizzi, L.*; Polunovskiy, E.*; Sawan, M.*; Wilson, P.*; Wu, Y.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 56(2), p.566 - 572, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:92.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is envisaged that ITER should produce as much as 700 MW of fusion power. This equates to the production of 2.48 10
10 14MeV neutrons/s which will give an uncollided flux at the first wall of approximately 4
14MeV neutrons/s which will give an uncollided flux at the first wall of approximately 4 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /s and a total with the addition of the collided to some 10
/s and a total with the addition of the collided to some 10 n/cm
n/cm /s. ITER is therefore a significant nuclear facility and it is essential that an efficient and coherent strategy for nuclear analysis is in place. This paper reviews the status of the methods applied to date and recommends the future strategy which ITER should adopt to address the continuing requirements and responsibilities. This is done by consideration of the application of radiation transport codes, the creation of suitable models, developments in information technology, and the management tools which will be required. Areas in which new codes and techniques need to be developed will be identified.
/s. ITER is therefore a significant nuclear facility and it is essential that an efficient and coherent strategy for nuclear analysis is in place. This paper reviews the status of the methods applied to date and recommends the future strategy which ITER should adopt to address the continuing requirements and responsibilities. This is done by consideration of the application of radiation transport codes, the creation of suitable models, developments in information technology, and the management tools which will be required. Areas in which new codes and techniques need to be developed will be identified.
Snyder, P. B.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085035_1 - 085035_8, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:170 Percentile:98.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The pressure at the top of the edge transport barrier impacts fusion performance, while large ELMs can constrain material lifetimes. Investigation of intermediate wavelength MHD mode has led to improved understanding of the pedestal height and the mechanism for ELMs. The combination of high resolution diagnostics and a suite of stability codes has made edge stability analysis routine, and contribute both to understanding, and to experimental planning and performance optimization. Here we present extensive comparisons of observations to predicted edge stability boundaries on several tokamaks, both for the standard (Type I) ELM regime, and for small ELM and ELM-free regimes. We further discuss a new predictive model for the pedestal height and width (EPED1), developed by self-consistently combining a simple width model with peeling-ballooning stability calculations. This model is tested against experimental measurements, and used in initial predictions of the pedestal height for ITER.
Snyder, P. B.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Investigation of intermediate wavelength MHD modes has led to improved understanding of important constraints on the pedestal height and the mechanism for ELMs. The combination of high resolution pedestal diagnostics and a suite of highly efficient stability codes, has made edge stability analysis routine on several major tokamaks, contributing both to understanding, and to experimental planning and performance optimization. Here we present extensive comparisons of observations to predicted edge stability boundaries on several tokamaks, both for the standard ELM regime, and for small ELM and ELM-free regimes. We further use the stability constraint on pedestal height to test models of the pedestal width, and self-consistently combine a simple width model with MHD stability calculations to develop a new predictive model (EPED1) for the pedestal height and width. This model is tested against experimental measurements, and used in initial predictions of the pedestal height for ITER.
Kirk, A.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Boedo, J. A.*; Beurskens, M.*; Counsell, G. F.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Herrmann, A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 123, p.012011_1 - 012011_10, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:97.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A comparison of the spatial and temporal evolution of the filamentary structures observed during type I ELMs is presented from a variety of diagnostics and machines. There is evidence that these filaments can be detected inside the LCFS prior to ELMs. The filaments do not have a circular cross section instead they are elongated in the perpendicular (poloidal) direction and this size appears to increase linearly with the minor radius of the machine. The filaments start rotating toroidally/poloidally with velocities close to that of the pedestal. This velocity then decreases as the filaments propagate radially. It is most likely that the filaments have at least their initial radial velocity when they are far out into the SOL. The dominant loss mechanism is through parallel transport and the transport to the wall is through the radial propagation of these filaments. Measurements of the filament energy content show that each filament contains up to 2.5 % of the energy released by the ELM.
Doyle, E. J.*; Houlberg, W. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mukhovatov, V.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Polevoi, A.*; Bateman, G.*; Connor, J. W.*; Cordey, J. G.*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S18 - S127, 2007/06
no abstracts in English
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Fujita, Takaaki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Chu, M. S.*; Snyder, P. B.*; Wilson, H. R.*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.010_1 - 010_8, 2007/04
Numerical method for the stability analysis of ideal MHD modes is invented by using the physical model based on the two-dimensional Newcomb equation in combination with the conventional ideal MHD model. The MARG2D code built on this numerical method realizes to analyze the stability of wide  range of ideal MHD modes. The validity of MARG2D has been confirmed with the benchmarking test with the DCON code by identifying the stability boundary of low-
range of ideal MHD modes. The validity of MARG2D has been confirmed with the benchmarking test with the DCON code by identifying the stability boundary of low- modes, and that with the ELITE code by comparing the growth rates of intermediate to high
modes, and that with the ELITE code by comparing the growth rates of intermediate to high  modes. With the MARG2D code, the edge stability of JT-60SA, the complementally experiment of ITER, is investigated.
modes. With the MARG2D code, the edge stability of JT-60SA, the complementally experiment of ITER, is investigated.
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Leonard, A. W.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Boedo, J. A.*; Becoulet, M.*; Counsell, G. F.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Herrmann, A.*; Horton, L. D.*; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A149 - A162, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:78.1(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This report summarizes Type I edge localized mode (ELM) dynamics measurements from a number of tokamaks. Several transport mechanisms are conjectured to be responsible for ELM transport, including convective transport due to filamentary structures ejected from the pedestal, parallel transport due to edge ergodization or magnetic reconnection and turbulent transport driven by the high edge gradients when the radial electric field shear is suppressed. The experimental observations are assessed for their validation, or conflict, with these ELM transport conjectures.
B coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An
coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An , J.-M.*; et al.
, J.-M.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12A), p.A93 - A113, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:91.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English