Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Ishida, Taku*; Nakano, Keita; Abe, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Spina, T.*; Ammigan, K.*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.138 - 143, 2022/03
To predict the operating lifetime of materials in high-energy radiation environments at proton accelerator facilities, Monte Carlo code are used to calculate the number of displacements per atom (dpa). However, there is no experimental data in the energy region above 30 GeV. In this presentation, we introduce our experimental plan for displacement cross sections with 120-GeV protons at Fermilab Test Beam Facility. Experiments will be performed for the US fiscal year 2022. We developed the sample assembly with four wire sample of Al, Cu, Nb and W with 250- m diameter and 4-cm length. The sample assembly will be maintained at around 4 K by using a cryocooler in a vacuum chamber. Then, changes in the electrical resistivity of samples will be obtained under 120-GeV proton irradiation. Recovery of the accumulated defects through isochronal annealing, which is related to the defect concentration in the sample, will also be measured after the cryogenic irradiation.
m diameter and 4-cm length. The sample assembly will be maintained at around 4 K by using a cryocooler in a vacuum chamber. Then, changes in the electrical resistivity of samples will be obtained under 120-GeV proton irradiation. Recovery of the accumulated defects through isochronal annealing, which is related to the defect concentration in the sample, will also be measured after the cryogenic irradiation.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Shima, Tatsushi*
Materials Science Forum, 1024, p.95 - 101, 2021/03
To predict the lifetime of target materials in high-energy radiation environments at spallation neutron sources, radiation transport codes such as PHITS are used to calculate the displacements per atom (DPA) value. In this work, to validate calculated DPA values of tungsten, we implemented 0.25-mm-diameter wire sample of tungsten in a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler and measured the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the displacement cross section using 389-MeV protons at 10 K. As well as our previous results for aluminum and copper, calculated results with defect production efficiencies provided good agreements with experimental data. Based on measurements of recovery of the defects through annealing, about 85% of the damage remained at 60 K, and the same tendency is observed in other experimental result for reactor neutron irradiation.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Kinomura, Atsushi*; Shima, Tatsushi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.061003_1 - 061003_5, 2020/02
To predict the lifetime of target materials in high-energy radiation environments at spallation neutron sources, radiation transport codes such as PHITS are used to calculate the displacements per atom (DPA) value. In this work, to validate calculated DPA values of tungsten, we implemented 0.25-mm-diameter wire sample of tungsten in a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler and measured the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the displacement cross section using 389-MeV protons at 10 K. In comparison with experimental data under 1.1 and 1.9 GeV proton irradiation, we found that damage rate of tungsten increases with proton energy due to increase the number of secondary particle s produced by nuclear reactions.
Kuwabara, Jun; Kinoshita, Naoki; Tobinai, Kazuhito; Matsuno, Satoru; Oyokawa, Atsushi; Seki, Takeo; Yabuuchi, Noriaki
Dai-28-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.77 - 79, 2015/12
A Tandetron AMS system (JAEA-AMS-MUTSU) at Mutsu Office, Aomori Research and Development Center, Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Waste Management, JAEA, installed in 1997, has composed of 3 MV tandem accelerator and two beam lines (carbon and iodine). Status of the JAEA-AMS-MUTSU and trouble of ion source caused by deterioration of optical fiber cable are reported.
Adachi, Taihei*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Strasser, P.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kojima, Kenji*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036017_1 - 036017_4, 2015/09
 Cu
Cu Al
Al bulk glassy alloy
bulk glassy alloyOnodera, Naoto*; Ishii, Akito*; Ishii, Koji*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Yokoyama, Yoshihiko*; Saito, Yuichi; Ishikawa, Norito; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Hori, Fuminobu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.122 - 124, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)It has been reported that heavy ion irradiation causes softening in some cases of Zr-based bulk metallic glass alloys. However, the fundamental mechanisms of such softening have not been clarified yet. In this study, Zr Cu
Cu Al
Al bulk glassy alloys were irradiated with heavy ions of 10 MeV I at room temperature. Positron annihilation measurements have performed before and after irradiation to investigate changes in free volume. We discuss the relationship between the energy loss and local open volume change after 10 MeV I irradiation compared with those obtained for 200 MeV Xe and 5 MeV Al. The energy loss analysis in ion irradiation for the positron lifetime has revealed that the decreasing trend of positron lifetime is well expressed as a function of total electronic energy deposition rather than total elastic energy deposition. It means that the positron lifetime change by the irradiation has a relationship with the inelastic collisions with electrons during heavy ion irradiation.
bulk glassy alloys were irradiated with heavy ions of 10 MeV I at room temperature. Positron annihilation measurements have performed before and after irradiation to investigate changes in free volume. We discuss the relationship between the energy loss and local open volume change after 10 MeV I irradiation compared with those obtained for 200 MeV Xe and 5 MeV Al. The energy loss analysis in ion irradiation for the positron lifetime has revealed that the decreasing trend of positron lifetime is well expressed as a function of total electronic energy deposition rather than total elastic energy deposition. It means that the positron lifetime change by the irradiation has a relationship with the inelastic collisions with electrons during heavy ion irradiation.
 Ge-
Ge- Ga positron source
Ga positron sourceMaekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 308, p.9 - 14, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sawada, Shinichi; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Yasunari
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 87, p.46 - 52, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:49.28(Chemistry, Physical)The location and size of nanoscale free-volume holes (nanoholes) in graft-type polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs), which were prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization (grafting) of styrene into crosslinked-polytetrafluoroethylene (cPTFE) films and subsequent sulfonation, was investigated using positron annihilation lifetime (PAL) spectroscopy. The PAL spectra of the PEMs indicated the existence of two types of ortho-positronium (o-Ps) species, corresponding to nanoholes with volumes of 0.11 and 0.38 nm , respectively. Comparison of the PAL data of the PEMs with that of the precursor original cPTFE and polystyrene-grafted films demonstrated the probability that the smaller holes were located in both the PTFE crystalline phases and the poly(styrene sulfonic acid) graft regions, whereas the larger holes are potentially localized in the PTFE amorphous phases.
, respectively. Comparison of the PAL data of the PEMs with that of the precursor original cPTFE and polystyrene-grafted films demonstrated the probability that the smaller holes were located in both the PTFE crystalline phases and the poly(styrene sulfonic acid) graft regions, whereas the larger holes are potentially localized in the PTFE amorphous phases.
 Cr
Cr N
NYabuuchi, Atsushi*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Zhou, Y.-K.*; Hasegawa, Shigehiko*; Asahi, Hajime*
Applied Physics Letters, 102(14), p.142406_1 - 142406_4, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.63(Physics, Applied)Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 430(1-3), p.190 - 193, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:85.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and 4
and 4 ferromagnets using polarized positrons
ferromagnets using polarized positronsKawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi
Physical Review B, 85(2), p.024417_1 - 024417_6, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:53.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We measured the Doppler broadening of annihilation radiation (DBAR) spectra of 3 (Fe, Co and Ni) and 4
(Fe, Co and Ni) and 4 (Gd, Tb and Dy) ferromagnets under magnetic field by using spin-polarized positrons from a
(Gd, Tb and Dy) ferromagnets under magnetic field by using spin-polarized positrons from a  Ge-
Ge- Ga source. The results showed that the DBAR spectra of these metals have notable different magnetic field dependences. The differences among Fe, Co and Ni reflect that the upper minority spin bands of Fe and Co are nearly empty, while those of Ni are still mostly occupied. For the rare-earth metals, instead of the inner 4
Ga source. The results showed that the DBAR spectra of these metals have notable different magnetic field dependences. The differences among Fe, Co and Ni reflect that the upper minority spin bands of Fe and Co are nearly empty, while those of Ni are still mostly occupied. For the rare-earth metals, instead of the inner 4 electrons, 5d electrons that mediate the exchange interaction of the 4
electrons, 5d electrons that mediate the exchange interaction of the 4 electrons, are primarily responsible for magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra. Furthermore, magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra of Gd, Tb and Dy vanished above the Curie temperatures of the magnetic phase transition for these metals.
electrons, are primarily responsible for magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra. Furthermore, magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra of Gd, Tb and Dy vanished above the Curie temperatures of the magnetic phase transition for these metals.
 ion implanted B2 type Fe-Al alloy using slow positron beam
ion implanted B2 type Fe-Al alloy using slow positron beamKomagata, Eiichi*; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Maekawa, Masaki; Batchuluun, C.*; Yasuda, Keisuke*; Ishigami, Ryoya*; Kume, Kyo*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Hori, Fuminobu*
Physics Procedia, 35, p.75 - 79, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.54(Physics, Particles & Fields)Fe48-at.% Al alloy were implanted with 50 keV H ions to the fluence of 3
ions to the fluence of 3 10
10 and 1
and 1 10
10 /cm
/cm at room temperature. Positron annihilation Doppler broadening and lifetime measurements for these alloys have been carried out using slow positron beam apparatus with an energy range of 0.2 to 30.2 keV. The positron annihilation S-parameter decreased by H
at room temperature. Positron annihilation Doppler broadening and lifetime measurements for these alloys have been carried out using slow positron beam apparatus with an energy range of 0.2 to 30.2 keV. The positron annihilation S-parameter decreased by H ion irradiation. Also the positron lifetimes for hydrogen deposited region in the alloy decreased by the irradiation. These results show that implanted H atoms were trapped by vacancy type defects.
ion irradiation. Also the positron lifetimes for hydrogen deposited region in the alloy decreased by the irradiation. These results show that implanted H atoms were trapped by vacancy type defects.
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 419(1-3), p.9 - 14, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:71.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To reveal vacancy formation during the stress corrosion cracking (SCC), three factors influencing SCC in Type 304 stainless steels - sensitization heat treatment, corrosion treatment and tensile plastic deformation - were investigated by means of positron annihilation spectroscopy. Vacancy defects induced by the sensitization heat treatment and by tensile deformation were identified as monovacancies. These monovacancies were annealed within the same temperature range in which light water reactors are operated (280-320  C). The above results allow us to conclude that such vacancy defects play an important role in high-temperature-water SCC crack propagation.
C). The above results allow us to conclude that such vacancy defects play an important role in high-temperature-water SCC crack propagation.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi
Physical Review B, 83(10), p.100406_1 - 100406_4, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:69.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The Doppler broadening of annihilation radiation (DBAR) spectra of Fe, Co, Ni and Gd polycrystals measured using spin-polarized positrons from a  Ge-
Ge- Ga source in magnetic fields exhibited clear asymmetry upon field reversal. The differential DBAR spectra between field-up and field-down conditions were qualitatively reproduced in calculations considering polarization of positrons and electrons. The magnitudes of the field-reversal asymmetry for the Fe, Co and Ni samples was approximately proportional to the effective magnetization. The magnetic field dependence of the DBAR spectrum for the Fe sample showed hysteresis that is similar to a magnetization curve. These results demonstrate that spin-polarized positron annihilation spectroscopy will be useful in studying magnetic substances.
Ga source in magnetic fields exhibited clear asymmetry upon field reversal. The differential DBAR spectra between field-up and field-down conditions were qualitatively reproduced in calculations considering polarization of positrons and electrons. The magnitudes of the field-reversal asymmetry for the Fe, Co and Ni samples was approximately proportional to the effective magnetization. The magnetic field dependence of the DBAR spectrum for the Fe sample showed hysteresis that is similar to a magnetization curve. These results demonstrate that spin-polarized positron annihilation spectroscopy will be useful in studying magnetic substances.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 176, 2011/01
We attempt to produce the  Ge-
Ge- Ga radioisotope as a highly spin-polarized positron source. We irradiated 20 MeV or 25 MeV proton beam for
Ga radioisotope as a highly spin-polarized positron source. We irradiated 20 MeV or 25 MeV proton beam for 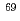 Ga targets. We confirmed the production of
Ga targets. We confirmed the production of  Ge-
Ge- Ga radioisotopes by a nuclear reaction of
Ga radioisotopes by a nuclear reaction of 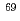 Ga(p,2n)
Ga(p,2n) Ge. From the magnetic field dependence of two-
Ge. From the magnetic field dependence of two- self-annihilation intensity of positronium in a fused silica, we determined the spin polarization of emitted positrons to be more than 80% as theoretically predicted using the positron helicity.
self-annihilation intensity of positronium in a fused silica, we determined the spin polarization of emitted positrons to be more than 80% as theoretically predicted using the positron helicity.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Hasegawa, Shigehiko*; Zhou, Y.-K.*; Asahi, Hajime*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 148, 2011/01
Vacancy defects in GaCrN grown by molecular beam epitaxy have been characterized by energy variable positron beam. Both positron lifetime and the Doppler broadening of annihilation  ray (DBAR) measurements show that the GaCrN film grown at low 540
ray (DBAR) measurements show that the GaCrN film grown at low 540 C contains vacancy defects. The observed vacancy defects are identified as eight-vacancy clusters. Although the Si doping reduces such vacancy clusters probably due to the occupation of Ga sites, another type of vacancy defects still survives. From the detailed theoretical calculation, the residual vacancy defects are attributable to SiGa-VN complexes.
C contains vacancy defects. The observed vacancy defects are identified as eight-vacancy clusters. Although the Si doping reduces such vacancy clusters probably due to the occupation of Ga sites, another type of vacancy defects still survives. From the detailed theoretical calculation, the residual vacancy defects are attributable to SiGa-VN complexes.
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 142, 2011/01
Recently, the SCC propagation model that the vacancy-type defects that accumulate in the crack tip play a role as crack nucleus was proposed. However, there is no information available on the generation or accumulation mechanism of such vacancies around the SCC crack tips. In this study, lattice defect spatial distributions around the SCC crack tip in an austenitic stainless steel have been evaluated probed by positron microbeam. As a result, the increase of S-parameter was observed around the SCC crack. To investigate what type of defect has caused the increase of this S parameter, the  -ray energy distribution spectrum obtained from the surrounding of the SCC crack was compared with the spectrum obtained from the tensile test specimen. From the comparison of these two spectra, it can be concluded that plastic deformation induced vacancies caused the increase of S-parameter near the SCC crack.
-ray energy distribution spectrum obtained from the surrounding of the SCC crack was compared with the spectrum obtained from the tensile test specimen. From the comparison of these two spectra, it can be concluded that plastic deformation induced vacancies caused the increase of S-parameter near the SCC crack.
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Entani, Shiro; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Yamamoto, Shunya
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 131, 2011/01
Ion implantation technique is expected to be useful in fabrication of diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMS) that require high concentration magnetic atom doping without a secondary phase formation. However, ion implantation surely introduces irradiation-induced vacancies into crystals. Recent calculation studies have suggested a presence of vacancies affect the magnetic properties in DMS. In this study, magnetic ions were implanted into compound semiconductor crystals by using ion implantation. N-type ZnO(0001) crystals were implanted with 380 keV maximum energy Cr ions to a dose of 1
ions to a dose of 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . After ion implantation, isochronal annealing in steps of 30 min/100
. After ion implantation, isochronal annealing in steps of 30 min/100  C was performed. From the measurement results, irradiation-induced vacancies were annealed out at 900
C was performed. From the measurement results, irradiation-induced vacancies were annealed out at 900  C. From XRD measurements after annealing at 1100
C. From XRD measurements after annealing at 1100  C, no secondary phase peaks were observed. However, from SQUID measurement, a clear magnetic hysteresis was not observed.
C, no secondary phase peaks were observed. However, from SQUID measurement, a clear magnetic hysteresis was not observed.
Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 262, p.012035_1 - 012035_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.52(Physics, Applied)Using spin-polarized positrons, the excess spins in magnetic substances can be detected. For efficient measurements with spin-polarized positrons, a strong enough source emitting highly polarized positrons is needed. For this purpose, we focus on a  Ge radioisotope. This radioisotope decays to
Ge radioisotope. This radioisotope decays to  Ga with a half-life of 280 days. The endpoint positron energy is 1.9 MeV and hence the theoretical longitudinal spin polarization is approximately 94%. This radioisotope can be produced though the nuclear reaction of
Ga with a half-life of 280 days. The endpoint positron energy is 1.9 MeV and hence the theoretical longitudinal spin polarization is approximately 94%. This radioisotope can be produced though the nuclear reaction of 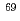 Ga (p,2n)
Ga (p,2n)  Ga. In this study, we report the production of
Ga. In this study, we report the production of  Ge by proton irradiation. We examined a metal form
Ge by proton irradiation. We examined a metal form 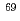 Ga stable isotope and a GaN substrate as target materials. When the metal
Ga stable isotope and a GaN substrate as target materials. When the metal  Ga targets were used, the production rates of
Ga targets were used, the production rates of  Ge were 0.16 and 0.14 MBq/
Ge were 0.16 and 0.14 MBq/ A/h for 20 and 25 MeV, respectively. Using the GaN target, it was 0.24 MBq/
A/h for 20 and 25 MeV, respectively. Using the GaN target, it was 0.24 MBq/ A/h. Thus,
A/h. Thus,  Ge radioisotopes were generated in both targets. The spin polarizations of positrons emitted from
Ge radioisotopes were generated in both targets. The spin polarizations of positrons emitted from  Ge and
Ge and  Na were estimated to be approximately 90% and 30%, respectively.
Na were estimated to be approximately 90% and 30%, respectively.
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Hasegawa, Shigehiko*; Zhou, Y. K.*; Asahi, Hajime*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 262(1), p.012066_1 - 012066_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English