Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*; Heim, D. M.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Garbet, X.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Masatoshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 28(1), p.012304_1 - 012304_21, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This article demonstrates a data compression technique for the time series of five dimensional distribution function data based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Phase space bases and corresponding coefficients are constructed by PCA in order to reduce the data size and the dimensionality. It is shown that about 83% of the variance of the original five dimensional distribution can be expressed with 64 components. This leads to the compression of the degrees of freedom from 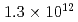 to
to 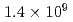 . One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
. One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Maeyama, Shinya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Nakata, Motoki*; Yagi, Masatoshi; Miyato, Naoaki; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Nunami, Masanori*
Physical Review Letters, 114(25), p.255002_1 - 255002_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:95.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Multiscale gyrokinetic turbulence simulations with the real ion-to-electron mass ratio and  value are realized for the first time, where the
value are realized for the first time, where the  value is given by the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure and characterizes electromagnetic effects on microinstabilities. Numerical analysis at both the electron scale and the ion scale is used to reveal the mechanism of their cross-scale interactions. Even with the real- mass scale separation, ion-scale turbulence eliminates electron-scale streamers and dominates heat transport, not only of ions but also of electrons. When the ion-scale modes are stabilized by finite-
value is given by the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure and characterizes electromagnetic effects on microinstabilities. Numerical analysis at both the electron scale and the ion scale is used to reveal the mechanism of their cross-scale interactions. Even with the real- mass scale separation, ion-scale turbulence eliminates electron-scale streamers and dominates heat transport, not only of ions but also of electrons. When the ion-scale modes are stabilized by finite- effects, the contribution of the electron-scale dynamics to the turbulent transport becomes non-negligible and turns out to enhance ion-scale turbulent transport.
effects, the contribution of the electron-scale dynamics to the turbulent transport becomes non-negligible and turns out to enhance ion-scale turbulent transport.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Seto, Yusuke*; Nagai, Takaya*; Utsumi, Wataru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 780, p.55 - 67, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)PLANET is a time-of-flight (ToF) neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature experiments. The large six-axis multi-anvil high-pressure press designed for ToF neutron diffraction experiments enables routine data collection at high pressures and high temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000 K, respectively. To obtain clean data, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators to eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell assembly. The high performance of the diffractometer for the resolution (
 /
/
 0.6%) and the accessible
0.6%) and the accessible  -spacing range (0.2-8.4
-spacing range (0.2-8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
 L. irradiated by
L. irradiated by  rays
raysKitano, Sayaka*; Miyagi, Atsuko*; Ono, Yutaka; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Yamaguchi, Masatoshi*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Kawai, Maki*
Metabolomics, 11(1), p.134 - 142, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:25.41(Endocrinology & Metabolism)Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi; Scott, B. D.*
Physics of Plasmas, 22(1), p.012103_1 - 012103_9, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:32.98(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two representations of fluid moments, which are called push-forward representations, are compared in the standard electrostatic gyrokinetic model. In the conventional representation the gyro-center part appears as the pull-back transformation of the gyro-center distribution function which contains scalar functions generating the gyro-center transformation. Usually only the lowest order solution of the generating function at first order is considered. This is true in explicitly deriving representations of scalar fluid moments with polarization terms. However, higher-order solutions are needed to derive finite Larmor radius terms of particle flux including the polarization flux from the conventional representation. On the other hand, the lowest order solution is sufficient for the other representation in which the gyro-center part is combined with the guiding-center one and the pull-back transformation of the distribution function does not appear.
Nuga, Hideo; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Yagi, Masatoshi; Fukuyama, Atsushi*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10, p.1203006_1 - 1203006_2, 2015/01
 n acoustic channel for ion energy in high-beta tokamak plasmas revisited with a linear gyrokinetic model (LIGKA)
n acoustic channel for ion energy in high-beta tokamak plasmas revisited with a linear gyrokinetic model (LIGKA)Bierwage, A.; Lauber, P.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 14th IAEA Technical Meeting on Energetic Particles in Magnetic Confinement Systems (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/00
Matsuyama, Akinobu; Yagi, Masatoshi; Kagei, Yasuhiro; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*
Nuclear Fusion, 54(12), p.123007_1 - 123007_14, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:48.45(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Bierwage, A.; Shinohara, Koji; Todo, Yasushi*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
Shiraishi, Junya; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083008_1 - 083008_8, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Toroidal rotation effects are self-consistently taken into account not only in the linear magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stability analysis but also in the equilibrium calculation. The MHD equilibrium computation is affected by centrifugal force due to the toroidal rotation. To study the toroidal rotation effects on resistive wall modes (RWMs), a new code has been developed. The RWMaC modules, which solve the electromagnetic dynamics in vacuum and the resistive wall, have been implemented in the MINERVA code, which solves the Frieman-Rotenberg equation that describes the linear ideal MHD dynamics in a rotating plasma. It is shown that modification of MHD equilibrium by the centrifugal force significantly reduces growth rates of RWMs. Moreover, it can open a stable window which does not exist under the assumption that the rotation affects only the linear dynamics.
Yagi, Masatoshi; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Miyato, Naoaki; Takizuka, Tomonori*
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 54(4-6), p.363 - 367, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Maeyama, Shinya; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Nakata, Motoki; Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 21(5), p.052301_1 - 052301_12, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:59.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Yagi, Masatoshi; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Takizuka, Tomonori*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9, p.3403030_1 - 3403030_4, 2014/04
Matsuyama, Akinobu; Yagi, Masatoshi; Kagei, Yasuhiro*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 1, p.015037_1 - 015037_4, 2014/03
no abstracts in English
Matsuyama, Akinobu; Yagi, Masatoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8, p.1403170_1 - 1403170_6, 2013/12
Honda, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Yoshida, Maiko; Yagi, Masatoshi; Fujita, Takaaki
Nuclear Fusion, 53(7), p.073050_1 - 073050_11, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:69.61(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 55(7), p.074011_1 - 074011_6, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.09(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*; Ishii, Yasutomo; Yagi, Masatoshi; Aiba, Nobuyuki
Nuclear Fusion, 53(6), p.063024_1 - 063024_11, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.34(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A mechanism for fast magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasma is studied for understanding sawtooth collapse in tokamak discharges. Explosive growth of the tearing mode driven by electron inertia is analytically estimated by using an energy principle with a nonlinear displacement map. Decrease of the potential energy in the nonlinear regime (where the island width exceeds the electron skin depth) is found to be steeper than in the linear regime, resulting in accelerated reconnection. Release of free energy by such ideal fluid motion leads to unsteady and strong convective flow, which is not deterred by the small dissipation effects in high-temperature tokamak plasmas. Direct numerical simulation in slab geometry substantiates the theoretical prediction of the nonlinear growth.
Shiraishi, Junya; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Effects of plasma toroidal rotation are self-consistently taken into account not only in the magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stability analysis but also in the equilibrium calculation. To study the effects of toroidal rotation on resistive wall modes (RWMs), a new code has been developed. The RWMaC modules, which solve the electromagnetic dynamics in vacuum and the resistive wall, have been implemented in the MINERVA code, which solves the Frieman-Rotenberg equation that describes the linear ideal MHD in a rotating plasma. It is shown for the first time that MHD equilibrium change induced by toroidal rotation significantly reduces the growth rates of RWMs. Moreover, it can open the stable window which does not exist under the assumption that the rotation affects only the linear dynamics. The rotation modifies the equilibrium pressure, current density, and mass density profiles, which results in the change of the potential energy including rotational effects.