Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arimori, Takao; Yamagata, Yuriko*
Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi, 102(11), p.303 - 312, 2011/11
Human NUDT5 hydrolyzes 8-oxo-dGDP into 8-oxo-dGMP and inorganic phosphate and prevents mutations caused by misincorporation of 8-oxoG into DNA. In addition, NUDT5 displays a broad substrate specificity for various modified nucleotides including 8-oxo-dADP, 8-oxo-GDP, and ADP-ribose. To understand the mechanisms of substrate recognition and catalysis by NUDT5, we have determined the crystal structure of NUDT5 complexed with 8-oxo-dGDP. A comparison of the structure with the previously reported NUDT5-ADP-ribose complex structure illustrated extremely different binding modes of these substrates. Especially, unexpectedly, the positions of two phosphates of substrate ( and
and  phosphates) in the 8-oxo-dGDP complex are completely inverted compared to those in the ADP-ribose complex, which indicates that either the catalytic residues or the nucleophilic substitution sites of substrates are different between hydrolysis reactions of these substrates. To further investigate the catalytic mechanisms, we next determined the site of nucleophilic substitution of water for 8-oxo-dGDP and ADP-ribose by the
phosphates) in the 8-oxo-dGDP complex are completely inverted compared to those in the ADP-ribose complex, which indicates that either the catalytic residues or the nucleophilic substitution sites of substrates are different between hydrolysis reactions of these substrates. To further investigate the catalytic mechanisms, we next determined the site of nucleophilic substitution of water for 8-oxo-dGDP and ADP-ribose by the 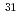 P NMR spectra of the reaction products in
P NMR spectra of the reaction products in  O-labeled water. The results clearly showed that the sites were different between these substrates, that is, 8-oxo-dGDP was attacked by a nucleophilic water at the P
O-labeled water. The results clearly showed that the sites were different between these substrates, that is, 8-oxo-dGDP was attacked by a nucleophilic water at the P , whereas ADP-ribose was at the P
, whereas ADP-ribose was at the P . Thus, we revealed the unique catalytic mechanism of NUDT5 as well as the multiple substrate recognition mechanism by structural and NMR analyses.
. Thus, we revealed the unique catalytic mechanism of NUDT5 as well as the multiple substrate recognition mechanism by structural and NMR analyses.
Arimori, Takao; Tamaoki, Haruhiko*; Nakamura, Teruya*; Kamiya, Hiroyuki*; Ikemizu, Shinji*; Takagi, Yasumitsu*; Ishibashi, Toru*; Harashima, Hideyoshi*; Sekiguchi, Mutsuo*; Yamagata, Yuriko*
Nucleic Acids Research, 39(20), p.8972 - 8983, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:52.02(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Hikuchi, Mariko; Ishida, Hisashi; Kitao, Akio*; Yamagata, Yuriko*; Go, Nobuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Arimori, Takao; Tamaoki, Haruhiko*; Nakamura, Teruya*; Kamiya, Hiroyuki*; Ikemizu, Shinji*; Takagi, Yasumitsu*; Ishibashi, Toru*; Harashima, Hideyoshi*; Sekiguchi, Mutsuo*; Yamagata, Yuriko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English