Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 rays from a neutron-induced
rays from a neutron-induced  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Xe
XeOkudaira, Takuya*; Tani, Yuika*; Endo, Shunsuke; Doskow, J.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kameda, Kento*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Luxnat, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 107(5), p.054602_1 - 054602_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.16(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Yamamoto, Kento*; Akie, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya; Hosoyamada, Ryuji*
JAEA-Technology 2015-019, 110 Pages, 2015/10
In the direct disposal of used nuclear fuel (UNF), criticality safety evaluation is one of the important issues since UNF contains some amount of fissile material. The recent development of higher-enrichment fuel has enhanced the benefit of the application of Burnup Credit. In the present study, the effects of the several parameters on the reactivity of disposal canister model were evaluated for used PWR fuel. The parameters are relevant to the uncertainties of depletion calculation code, irradiation history, and axial and horizontal burnup distribution, which are known to be important effect in the criticality safety evaluation adopting burnup credit. The latest data or methodology was adopted in this evaluation, based on the various latest studies. The appropriate margin of neutron multiplication factor in the criticality safety evaluation for UNF can be determined by adopting the methodology described in the present study.
Yamamoto, Kento; Akie, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2015) (DVD-ROM), p.228 - 237, 2015/09
Japan has recently started to study the technical issues for the direct disposal of the used nuclear fuel (UNF) to prepare various disposal options. The criticality safety is important for the direct disposal because of the presence of certain amount of the fissile nuclides in UNF. This paper gives the outline of the research to be addressed in this field and the relevant studies in Japan. Especially, it presents the first result of the criticality safety evaluation for a disposal canister model adopting burnup credit. The uncertainties of effective neutron multiplication factor (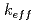 ) caused by the depletion calculation errors as well as the effect of the axial burnup profile and the horizontal burnup gradient on
) caused by the depletion calculation errors as well as the effect of the axial burnup profile and the horizontal burnup gradient on 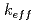 were also evaluated. It was found that the
were also evaluated. It was found that the 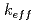 including these uncertainties and conservatism was below 0.95 for the representative used PWR fuel when the fuel assemblies and the disposal canister were assumed to keep intact.
including these uncertainties and conservatism was below 0.95 for the representative used PWR fuel when the fuel assemblies and the disposal canister were assumed to keep intact.
Yamamoto, Kento; Okumura, Keisuke; Kojima, Kensuke; Okamoto, Tsutomu
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.233 - 249, 2015/00
To improve the prediction accuracy of concentrations of activation products (APs) in the field of nuclear back-end, it is important to investigate the elements and the nuclear reactions leading to generation of APs. To clarify quantitatively the source elements and the nuclear reactions dominating generation of APs, sensitivity analyses of initial compositions and cross sections were conducted using ORIGEN2.2 code and ORLIBJ40, which is a set of the 1-group cross section libraries based on JENDL-4.0. Activations of cladding tubes, end-plugs and spacers of fuel assemblies and channel boxes in BWR, whose materials are zirconium alloy, stainless steel, and nickel-chromium-based alloy, were analyzed. The results clarified quantitatively the source elements and the nuclear reactions dominating generation of APs. It was remarkable that the dominant generation pathways were clarified even for the nuclides generated through complicated pathways. In conclusion, the results of sensitivity analyses could be utilized to select the objective of elements for measurements of impurities in the materials and of nuclear data for improvement of accuracy.
 U in UO
U in UO and MOX fuels
and MOX fuelsYamamoto, Kento; Okumura, Keisuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(4), p.568 - 573, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)To clarify the generation pathway of  U in burned fuels, which is an important nuclide for dose evaluation at various stages in fuel cycle, concentrations of
U in burned fuels, which is an important nuclide for dose evaluation at various stages in fuel cycle, concentrations of  U generated through various pathways were evaluated for UO
U generated through various pathways were evaluated for UO and MOX fuels at 45 GWd/t using the ORIGEN2.2 code. It was found that the difference of
and MOX fuels at 45 GWd/t using the ORIGEN2.2 code. It was found that the difference of  U concentrations in UO
U concentrations in UO and MOX fuel are mainly derived from the difference of the initial compositions of
and MOX fuel are mainly derived from the difference of the initial compositions of  U,
U,  U and
U and  U and the contribution of plutonium and americium isotopes in MOX fuels is not so large compared with that of uranium isotopes. The results clarified that the capture cross sections of
U and the contribution of plutonium and americium isotopes in MOX fuels is not so large compared with that of uranium isotopes. The results clarified that the capture cross sections of  Th,
Th, 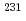 Pa,
Pa,  U and
U and  U and (
U and ( ,2
,2 ) cross sections of
) cross sections of  Np and
Np and  U have a large effect on generation of
U have a large effect on generation of  U. The additional investigation showed that not only time after irradiation but also time before irradiation has a strong effect on
U. The additional investigation showed that not only time after irradiation but also time before irradiation has a strong effect on  U concentration.
U concentration.
Yamamoto, Kento; Okumura, Keisuke; Kojima, Kensuke; Okamoto, Tsutomu
JAEA-Research 2013-038, 88 Pages, 2014/02
Accurate information on main generation pathways of activation products is important to improve the accuracy of predicting the concentrations of activation products. Using ORIGEN2 and ORLIBJ40, which is a set of the cross section libraries based on JENDL-4.0, the initial compositions and the cross sections which influence on the concentrations of activation products were clarified by executing the sensitivity analyses on them. Activations of cladding tubes, end-plugs and spacers of fuel assemblies and channel boxes, which were composed of Zircaloy, SUS304, and Inconel-718, were analyzed. The main generation pathways of some significant activation products were summarized from the results of sensitivity analyses.
Okumura, Keisuke; Hagura, Hiroyuki; Kojima, Kensuke; Yamamoto, Kento; Tanaka, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
A method of the activation sensitivity analysis was developed for the optimization of the inventory evaluation of radionuclides in the waste generated in the decommissioning of LWR plants. By applying the method to a BWR plant, we clarified the impurity nuclides in the structural materials and their nuclear reactions contributing the generation of about fifty radioactive nuclides important for the processing and disposal of radioactive wastes.

Suyama, Kenya; Akie, Hiroshi; Kataoka, Masaharu*; Yamamoto, Kento*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Ryohei*; Sugita, Kento*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Age-Momentum Correlation (AMOC) can observe the Doppler broadening of time-resolved annihilation gamma rays. The annihilation rate depends on the positron state, and it is possible to know if positrons are trapped in structural defects in a sample. Moreover, the Doppler broadening gives the information of impurities around the defects. Positrons from radioactive isotopes cannot penetrate a deep region of bulk material. The application of radioisotopes is difficult for the measurements under severe conditions such as in high pressure or a high temperature. Therefore, we have developed a GiAMOC (Gamma-ray induced AMOC) system, which is a measurement method for generating positrons in a sample using inverse Thomson scattered gamma rays in UVSOR-III. In addition, the developed measurement system was used to measure the reference material for positron lifetime measurement.
Taira, Yoshitaka*; Sugita, Kento*; Yamamoto, Ryohei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
We are developing gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation spectroscopy at UVSOR-III. This method enables defect analysis of the entire bulk sample with a thickness of several cm, which was difficult to measure with the conventional method using a positron radiation source. Currently, the user use of the positron lifetime measurement method is being developed, and in parallel with this, the coincidence Doppler broadening method, the age-momentum correlation measurement method, and the spin-polarized positron spectroscopy are being developed. Here, we will describe the development status of them.
Taira, Yoshitaka*; Sugita, Kento*; Yamamoto, Ryohei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Positron annihilation spectroscopy is a powerful analytical method to observe single-atom vacant defects in crystals and microvoids in insulating materials. UVSOR-III installed at the Institute of Molecular Science promotes the development and user use of Gamma-ray induced positron annihilation spectroscopy (GiPAS) by ultrashort pulse gamma rays. Since the ultrashort pulse gamma rays generate positrons inside the material by pair production, positron annihilation experiments of bulk materials with a thickness of several cm can be performed non-destructively. In addition, since the sample is irradiated with gamma rays from the outside, measurement can be performed in an environment such as high temperature, high pressure, and immersion. We report on the generation of ultrashort pulse gamma rays and the development status of the positron lifetime measurement, and the positron age-momentum correlation measurement.
Yamamoto, Ryohei*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Sugita, Kento*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Takashima, Yoshifumi*; Kato, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
Positron annihilation spectroscopy is a powerful analytical method that can observe single-atom vacant defects in crystals and microvoids in insulating materials. UVSOR-III installed at the Institute of Molecular Science is promoting the development and user use of Gamma-ray induced positron annihilation spectroscopy (GiPAS) by ultrashort pulse gamma rays. We have succeeded in positron lifetime measurement and lifetime momentum correlation measurement. This time, we succeeded in detecting the process of defect capture in the positron age-momentum correlation measurement of strained steel materials.