Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Seishiro*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Konsoryu, 37(1), p.79 - 85, 2023/03
Yamamoto, Seishiro*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okano, Yasushi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Ishizuka, Yoshihiro*; Geshi, Nobuo*; Furukawa, Ryuta*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-11) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2016/10
This paper describes mainly volcanic margin assessment methodology development in addition to the project overview. The volcanic tephra could potentially clog filters of air-intakes that need the decay heat removal. The filter clogging can be calculated by atmospheric concentration and fallout duration of the volcanic tephra and also suction flow rate of each component. In this paper, the margin was defined as a grace period to a filter failure limit. Consideration is needed only when the grace period is shorter than the fallout duration. The margin by component was calculated using the filter failure limit and the suction flow rate of each component. The margin by sequence was evaluated based on an event tree and the margin by component. An accident management strategy was also suggested to extend the margin; for instance, manual trip of the forced circulation operation, sequential operation of three air coolers, and covering with pre-filter.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okano, Yasushi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Ishizuka, Yoshihiro*; Geshi, Nobuo*; Furukawa, Ryuta*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2016/06
This paper describes mainly volcanic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) methodology development for sodium-cooled fast reactors in addition to the project overview. The volcanic ash could potentially clog air filters of air-intakes that are essential for the decay heat removal. The degree of filter clogging can be calculated by atmospheric concentration of ash and tephra fallout duration and also suction flow rate of each component. The atmospheric concentration can be calculated by deposited tephra layer thickness, tephra fallout duration and fallout speed. This study evaluated a volcanic hazard using a combination of tephra fragment size, layer thickness and duration. In this paper, each component functional failure probability was defined as a failure probability of filter replacement obtained by using a grace period to a filter failure limit. Finally, based on an event tree, a core damage frequency was estimated about 3 10
10 /year in total by multiplying discrete hazard probabilities by conditional decay heat removal failure probabilities. A dominant sequence was led by the loss of decay heat removal system due to the filter clogging after the loss of emergency power supply. A dominant volcanic hazard was 10
/year in total by multiplying discrete hazard probabilities by conditional decay heat removal failure probabilities. A dominant sequence was led by the loss of decay heat removal system due to the filter clogging after the loss of emergency power supply. A dominant volcanic hazard was 10 kg/m
kg/m of atmospheric concentration, 0.1 mm of tephra diameter, 50-75 cm of deposited tephra layer thickness, and 1-10 hr of tephra fallout duration.
of atmospheric concentration, 0.1 mm of tephra diameter, 50-75 cm of deposited tephra layer thickness, and 1-10 hr of tephra fallout duration.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Okano, Yasushi; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Takata, Takashi*
Earthquakes, Tsunamis and Nuclear Risks, p.111 - 121, 2016/01
The present study is developing risk assessment methodologies that include probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) and margin assessment methodologies against snow, tornado, strong wind, rain, volcanic eruption and forest fire mainly for a sodium-cooled fast reactor. The present paper describes briefly the project overview and then mainly the development of PRA and margin assessment methodologies against strong wind. In the strong wind PRA, the hazard curve was estimated using the Gumbel distributions based on weather data. Next, failure probabilities for components were calculated and event trees were developed. Using them, the strong wind PRA methodology was developed to quantify a core damage frequency. The present study also developed the wind margin assessment methodology that the margin was regarded as wind speed leading to the decay heat removal failure.
Ito, Takanori*; Mori, Masashi*; Inukai, Manabu*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Miyanaga, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ishida, Naoya*; Idemoto, Yasushi*
Photon Factory News, 33(1), p.18 - 24, 2015/05
The effect of the annealing on the crystal and local structures of doped zirconia was investigated by multi-probe technique using synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction, and first principles calculation. It was revealed that the annealing process enhances the periodic distortion of some zirconia compounds by Rietveld/ maximum entropy methods applied to the SR-X-ray and neutron diffractions. In addition, the combined X-ray absorption spectroscopy and first-principles calculations results showed the ZrO polyhedra in zirconia were distorted by the annealing. Those results indicate that the degradation of oxide ionic conductivity by the annealing was related to the periodic distortion in zirconia.
polyhedra in zirconia were distorted by the annealing. Those results indicate that the degradation of oxide ionic conductivity by the annealing was related to the periodic distortion in zirconia.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okano, Yasushi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Ishizuka, Yoshihiro*; Geshi, Nobuo*; Furukawa, Ryuta*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2015 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2015) (CD-ROM), p.454 - 465, 2015/05
This paper describes mainly strong wind PRA methodology development in addition to the project overview. In developing the strong wind PRA methodology, hazard curves were estimated by using Weibull and Gumbel distributions based on weather data recorded in Japan. The obtained hazard curves were divided into five discrete categories for event tree quantification. Next, failure probabilities for decay heat removal related components were calculated as a product of two probabilities: i.e., a probability for the missiles to enter the intake or outtake in the decay heat removal system, and fragility caused by the missile impacts. Finally, based on the event tree, the core damage frequency was estimated about 6 10
10 /year by multiplying the discrete hazard probabilities in the Gumbel distribution by the conditional decay heat removal failure probabilities. A dominant sequence was led by the assumption that the operators could not extinguish fuel tank fire caused by the missile impacts and the fire induced loss of the decay heat removal system.
/year by multiplying the discrete hazard probabilities in the Gumbel distribution by the conditional decay heat removal failure probabilities. A dominant sequence was led by the assumption that the operators could not extinguish fuel tank fire caused by the missile impacts and the fire induced loss of the decay heat removal system.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okano, Yasushi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Ishizuka, Yoshihiro*; Geshi, Nobuo*; Furukawa, Ryuta*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2015/05
This paper describes mainly snow margin assessment methodology development in addition to the project overview. For the snow margin assessment, the index is a combination of a snowfall rate and duration. Since snow removal can be expected during the snowfall, the developed snow margin assessment methodology is such that the margin was regarded as the snowfall duration up to the decay heat removal failure which was defined as when the snow removal rate was smaller than the snowfall rate.
Ito, Takanori*; Mori, Masashi*; Inukai, Manabu*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Miyanaga, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ishida, Naoya*; Idemoto, Yasushi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(16), p.8447 - 8458, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:50.75(Chemistry, Physical)The effects of the annealing process on the crystal and local structures of the doped zirconia were investigated by Rietveld refinements of synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction, maximum entropy method (MEM), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and first principles calculation (FPC). This study reveals that the crystal structures of the sintered and annealed ((Zr Y
Y )O
)O and (Zr
and (Zr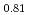 Sc
Sc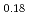 Ce
Ce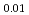 )O
)O ) are cubic with the space
) are cubic with the space  -3
-3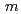 having large atomic displacement parameters (
having large atomic displacement parameters (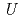 ). For the annealed (Zr
). For the annealed (Zr Y
Y )O
)O , the
, the 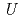 values reduce, and the electrons around the Zr/oxide ion sites gather at the center of each site. On the other hand, the annealed (Zr
values reduce, and the electrons around the Zr/oxide ion sites gather at the center of each site. On the other hand, the annealed (Zr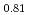 Sc
Sc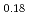 Ce
Ce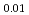 )O
)O shows the opposite tendency to that of the annealed (Zr
shows the opposite tendency to that of the annealed (Zr Y
Y )O
)O .
.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okano, Yasushi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Ishizuka, Yoshihiro*; Geshi, Nobuo*; Furukawa, Ryuta*; Nanayama, Futoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2014/12
This paper describes mainly snow probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) methodology development in addition to the project overview. In snow hazard category, the accident sequence was evaluated by producing event trees which consist of several headings representing the loss of decay heat removal. Snow removal action and manual operation of the air cooler dampers were introduced into the event tree as accident managements. The snow PRA showed less than 10 /reactor-year of core damage frequency.
/reactor-year of core damage frequency.
Endo, Kiyoshi*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Nakai, Kei*; Matsumura, Akira*; Sato, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Akihito; Koka, Masashi; Okubo, Takeru; Yamazaki, Akiyoshi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 86, 2012/01
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Uehara, Yasushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/10
In this paper, FY2009 results of the COMPASS code development are reported. Validation calculations for melt freezing and blockage formation, eutectic reaction of metal fuel, duct wall failure (thermal-hydraulic analysis), fuel pin failure and disruption and duct wall failure (structural analysis) are shown. Phase diagram calculations, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics were used to investigate physical properties of eutectic reactions: metallic fuel/steel and control rod material/steel. Basic studies for the particle method and SIMMER code calculations supported the COMPASS code development. COMPASS is expected to clarify the basis of experimentally-obtained correlations used in SIMMER. Combination of SIMMER and COMPASS will be useful for safety assessment of CDAs as well as optimization of the core design.
Isayama, Akihiko; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Furukawa, Masaru*; Matsunaga, Go; Yamazaki, Kozo*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tanaka, Kenji*; Tamura, Naoki*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(6), p.374 - 377, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Osakabe, Masaki*; Shinohara, Koji; Toi, Kazuo*; Todo, Yasushi*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tanaka, Kenji*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(12), p.839 - 842, 2009/12
no abstracts in English
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/09
Dispersion and freezing of molten core material was calculated by the COMPASS code to compare with the experimental data of GEYSER. Molten core material flowed up with freezing on the pipe inner surface. As a molten pool behavior, CABRI-TPA2 experiment was analyzed, where a sphere of solid steel was surrounded by solid fuel. Power was injected to cause melting and boiling of the steel sphere. SCARABEE-BE+3 test was analyzed by COMPASS as a validation of failure of duct walls.
Kobayashi, Yasushi; Yamada, Tsutomu; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Nishida, Takahiro*; Hironaga, Michihiko*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Daisuke*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-013, 70 Pages, 2009/06
Cementitious materials will be used to ensure construction and operational safety and work efficiency in a deep geological repository. The low alkaline cement has been developed to reduce uncertainties due to hyper alkaline for the long-term safety performance of the repository system. Functions of cementitious material required in each phase of repository construction, operation and closure were summarized in a separate report entitled "Application Study on Low Alkaline Cementitious Materials for Deep Geological Repository of High Level Radioactive Wastes (Phase I) "In this report, properties of low alkaline cement/concrete which have been developed both at home and abroad, and recipes of the low alkaline concrete taken account of application to the repository component have been investigated. Fresh and hardened properties of the low alkaline cement are equivalent to the OPC and the low alkaline cement has an advantage over OPC in terms of leaching resistance. The HFSC developed by JAEA, which belongs to a pozzolanic type low alkaline cement will be able to apply to the shotcrete and the lining concrete by choosing an adequate recipe. Clarification of influences of the chemical composition of groundwater on leachate properties of the hydrates, examination of pH measurement of cement leachate, evaluation of corrosion behavior of rebar embedded in the HFSC concrete are raised as open questions for future activities.
Uehara, Yasushi*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamamoto, Yuichi*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-17) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2009/06
A mesoscopic approach with the COMPASS code is expected to advance the understanding of key phenomena during event progression in core disruptive accidents. In this paper, the overall analysis of SCARABEE-BE+3 test with the SIMMER-III is described as well as the simulation with COMPASS, focusing on the duct wall failure in a small temporal and spatial window cut from the SIMMER-III analysis results.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2009/05
A computer code, named COMPASS, is developed for multi-physics analysis of core disruptive accidents of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). A meshless method, called MPS method, is employed since complex thermal-hydraulics and structural problems with various phase change processes have to be analyzed. Verification for separeted basic processes and validation for practical phenomena are carried out. COMPASS is also expected to investigate molten fuel discharge to avoid re-criticality in large size SFR cores. Both MOX and metal fuels are considered. Eutectic reactions between the metal fuel and the cladding material are investigated by phase diagram calculation, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics. Basic studies relevant to the numerical methods support the code development of COMPASS. Parallel processing is implemented by OpenMP to treat large-scale problems. A visualization tool is also prepared by using AVS.