Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshioka, Kenichi*; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Gunji, Satoshi*; Kumanomido, Hironori*; Mitsuhashi, Ishi*; Umano, Takuya*; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(2), p.282 - 293, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed a void reactivity evaluation method by using modified conversion ratio measurements in a light water reactor (LWR) critical lattice. Assembly-wise void reactivity is evaluated from the "finite neutron multiplication factor", 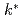 , deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and
, deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and 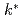 on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
Yoshioka, Kenichi*; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Gunji, Satoshi*; Kumanomido, Hironori*; Mitsuhashi, Ishi*; Umano, Takuya*; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(6), p.606 - 614, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed an intra-pellet neutron flux and conversion ratio distribution measurement method. A foil activation method with special foils was used for the neutron flux distribution measurement. A  -ray spectrum analysis method with special collimators was used for the conversion ratio distribution measurement. Using the developed methods, intra-pellet neutron flux distributions and conversion ratio distributions were measured in critical experiments on a reduced-moderation LWR. Measured values were analyzed with a deterministic method and a Monte Carlo method. The neutron flux distribution measurements and analyses agreed within the range of 1% to 2%. The conversion ratio distribution measurements and analyses were consistent with each other. We found that the measurement methods are useful for the validation of neutron behavior in a fuel pellet, which is known as micro reactor physics.
-ray spectrum analysis method with special collimators was used for the conversion ratio distribution measurement. Using the developed methods, intra-pellet neutron flux distributions and conversion ratio distributions were measured in critical experiments on a reduced-moderation LWR. Measured values were analyzed with a deterministic method and a Monte Carlo method. The neutron flux distribution measurements and analyses agreed within the range of 1% to 2%. The conversion ratio distribution measurements and analyses were consistent with each other. We found that the measurement methods are useful for the validation of neutron behavior in a fuel pellet, which is known as micro reactor physics.
Kitano, Akihiro; Teruyama, Hidehiko; Nishi, Hiroshi; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Moriki, Yasuyuki*; Nakagawa, Masatoshi*
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (15), p.1 - 16, 2002/06
None
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Kawashima, Masatoshi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; Takashita, Hirofumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 34(10), p.983 - 991, 1997/10
None
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Fujita, Reiko*
PNC TJ9164 97-002, 105 Pages, 1997/03
As a study on technology utilization of advanced fast reactors, a core study on burning technology of actinides and FPs by fast reactors is carried out together with a research on material characteristics of fuels and targets for Pu/FP Burning. In the core study, a Pu-burning fast reactor corc was studied which can also burn minor actinides and FPs based upon the 600MWe Pu-burning fast reactor core with high Pu enrichment ( 40%). The criteria of core design were no significant change of core specification and small sodium void reactivity, and so on. In the core, minor actinides and FPs are loaded in the following way. (a)Core region ; loading of Pu/Np (Oxide fuel, Pu enrichment of
40%). The criteria of core design were no significant change of core specification and small sodium void reactivity, and so on. In the core, minor actinides and FPs are loaded in the following way. (a)Core region ; loading of Pu/Np (Oxide fuel, Pu enrichment of  40%) (b)Outside of core region ; the first layer
40%) (b)Outside of core region ; the first layer  loading of Am/Cm/rate earths mixed with ZrH
loading of Am/Cm/rate earths mixed with ZrH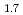 the second laycr
the second laycr  loading of Tc-99 mixed with ZrH
loading of Tc-99 mixed with ZrH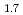 . The operation cycle length is 5 months and the averagc discharge burnup is about 80GWd/t. The burning capability of Pu, minor actinides and FPs is as follows ; (1)Pu burning rate ;
. The operation cycle length is 5 months and the averagc discharge burnup is about 80GWd/t. The burning capability of Pu, minor actinides and FPs is as follows ; (1)Pu burning rate ;  390kg/Year(
390kg/Year( 74kg/TWhe) (2)Burning rate of minor actinides;
74kg/TWhe) (2)Burning rate of minor actinides;  4.2%/Year(
4.2%/Year( 43kg/Year) (3)Burning rate of Tc-99;
43kg/Year) (3)Burning rate of Tc-99;  3.7%/Year(
3.7%/Year( 6.5kg/Year) The sodium void reactivity is very small. (0.1%
6.5kg/Year) The sodium void reactivity is very small. (0.1%  k/kk'=40cent) It is much smaller than that of the conventional fast reactors. This is the advantage of the core concept. The recent progress of material investigation of Pu, minor actinides and FP burning fuels was summaried. Also, basic characteristics of targets for FP burning was summalized, and the compatibility of the targets with ZrH
k/kk'=40cent) It is much smaller than that of the conventional fast reactors. This is the advantage of the core concept. The recent progress of material investigation of Pu, minor actinides and FP burning fuels was summaried. Also, basic characteristics of targets for FP burning was summalized, and the compatibility of the targets with ZrH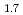 is evaluated.
is evaluated.
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Kawashima, Masatoshi*
PNC TJ9164 97-001, 185 Pages, 1997/03
To prepare unified library applicable to licensing calculation of the demonstration fast breeder reactor as well as base design calculation, the experimental data of the small reactor "JOYO" were re-evaluated and analyzed that had not been utilized in cross section adjustment before. The data of "JOYO" startup tests and operation were analyzed with cross section set based on the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL3.2 to provide integral data for cross section adjustment as power reactor data to supplement critical experiment data. The analysis is the first work that evaluated the core characteristics of "JOYO" MK-I and MK-II cores consistently. In the present work, errors and their correlation factors of both experiment and analysis data were evaluated for criticality, sodium void worth, fuel replacement worth and burnup coefficient. The recommended future work includes comparison of results with critical experiments, addition of experiment data to adjustment so as to reduce of dependency of prediction error upon core size.
*; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*
PNC TJ9164 98-011, 299 Pages, 1997/02
"MAGI" system renewal has been continued for improving the prediction accuracy for neutronic and thermal characteristics along with the core-upgrading to the MK-III core. Preparation of several modules was finished before the present work for neutron diffusion calculation of nomal/adjoint flux, gamma-source, and power distribution, as well as burnup calculation. The modules to calculate the gamma flux distribution based on diffusion theory and reactor kinetics parameters such as effective delayed neutron fraction and prompt neutron life time were made. Test calculation for each module was carried out to confirm the validity of calculation results. As for future works, it is required to make several modules for the evaluation of thermal characteristics, and preparation of effective cross section, in addition to the I/O interfaces and system control modules, for the further renewals of "MAGI" system.
*; Kawashima, Masatoshi*; *; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Fujita, Reiko*
PNC TJ9164 96-008, 189 Pages, 1996/12
In the first reactor, sodium void reactivity and and sodium coolant temperature reavtivity are increased, and Doppler coefficient is decreased when MA is recycled. It is important to improve these reactivities in terms of safety features. In the study, Analysis was conducted of the effect on the sodium void reduction without deteriorating the core performance by mixing nuclides that give large absorption reactions in the higher energy region, where neutrons are increased at the neutron spectrum is hardened. Effect of higher Pu isotopes was also analyzed with parameters for improving Doppler coefficient. In the analysis of reduced sodium void reactivity core usig the threshold reaction, dominant energy region was identified for the sodium void reactivity by analyzing the core neutron spectra with parameters of MA mixing and core size. Furthermore, effect on reducing void reactivity was analyzed with parameters of inventory amounts and kinds of absorber nuclides. As a result, it was found that the sodium void reactivity of the MOX core with oxide-17 was about half of that of the core with natural oxide. In the analysis of reduced Doppler reactivity core, effect of improving the Doppler effect was analyzed for the nitride fuel core with higher Pu isotopes and resonance absorbers. Applicability and properties required for core analysis were also examined for candidates of base inert material, and the properties of fuel with those materials were preliminary surveyed. As a result, it was found that characteristics including Doppler coefficients can be improved with nuclides of structure material as metal form.
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Kawashima, Masatoshi*
PNC TJ9164 96-007, 106 Pages, 1996/12
Some of fission products (FPs) in spent fuels have very long half lives as transuranic nuclides. Fast reactors have a potential to transmute these FPs into short-lived ones because of high neutron flux. As neutron capture cross sections of FPs increase in low energy region, one of the effective means to transmute them is to irradiate them using target assemblies that contain pins loaded with neutron moderating material such as ZrH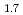 as well as FP loading Pins. In the work carried out in 1994, a study was performed on transmutation of long-lived FPs, assuming that FP target assemblies are loaded in the core region of fast reactors. As a result, it was found that neutron moderation tends to improve transmutation rate whereas it causes to significant power spike in the adjacent core fuel. So as to suppress the power spike, FPs' loading at the outer periphery of the core was suggested. In the present study, an analysis was carried out to transmute FPs in fast reactors, assuming that target assemblies containing ZrH
as well as FP loading Pins. In the work carried out in 1994, a study was performed on transmutation of long-lived FPs, assuming that FP target assemblies are loaded in the core region of fast reactors. As a result, it was found that neutron moderation tends to improve transmutation rate whereas it causes to significant power spike in the adjacent core fuel. So as to suppress the power spike, FPs' loading at the outer periphery of the core was suggested. In the present study, an analysis was carried out to transmute FPs in fast reactors, assuming that target assemblies containing ZrH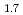 pins and Tc pins are loaded at the outer periphery of the core. The analysis was mainly performed using the continuous energy Monte Carlo code that is effective for rigorous trestment of rcsonance absorption of Tc99 in the target assembly with large heterogeneity. The results are shown below. (1)To increase absorption rate of Tc99, the neutron spectrum where absorption in the resonance region is more than in the thermal region is advantageous. This is because the spectrum helps to suppress absorption by structural material. Therefore, the appropriate loading mass of moderator depends upon the moderating power. (2)The target assembly selected from the survey indudes 19 ZrH
pins and Tc pins are loaded at the outer periphery of the core. The analysis was mainly performed using the continuous energy Monte Carlo code that is effective for rigorous trestment of rcsonance absorption of Tc99 in the target assembly with large heterogeneity. The results are shown below. (1)To increase absorption rate of Tc99, the neutron spectrum where absorption in the resonance region is more than in the thermal region is advantageous. This is because the spectrum helps to suppress absorption by structural material. Therefore, the appropriate loading mass of moderator depends upon the moderating power. (2)The target assembly selected from the survey indudes 19 ZrH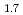 pins with large diameter and 36 Tc pins with small diameter. The transmutation rate of Tc99 is about 4-5%/year and the mass is about 15-20kg/year. (3)The effect of loading target assembly upon main core characteristics were analyzed. It was found that the ...
pins with large diameter and 36 Tc pins with small diameter. The transmutation rate of Tc99 is about 4-5%/year and the mass is about 15-20kg/year. (3)The effect of loading target assembly upon main core characteristics were analyzed. It was found that the ...
Wakabayashi, Toshio; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki;
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 154(3), p.239 - 250, 1995/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; *
PNC TJ9164 95-011, 115 Pages, 1995/03
Some of fission products (FPs) in spent fuels have very long half lives as transuranic nuclides. Fast reactors have a potential to transmute these FPs into short-lived ones because of high neutron flux. As neutron capture cross sections of FPs increase in low energy region, one of the effective means to transmute them is to irradiate them using target assemblies that contain pins loaded with neutron moderating material such as ZrHx as well as FP loading Pins. A study has been performed on transmutation of long-lived FPs, Tc99 and I129 in fast reactors usig target assemblies. The Monte Carlo method (MC method) with continuous-energy cross section was mainly employed to analyze rigorously resonance absorption of FPs in target assemblies with large heterogeneity. Specications of target assemblies were investigated with a aim to transmute FPs effectively. The target assemblies were assumed to be located in the core region. Also, comparison of calculation methods was carried out, where results from deterministic methods (diffusion and transport calculations) were compared with those from the MC method. Further, the effect of heterogeneity upon resonance absorption was analyzed. The results are as follows: (1)As the number of FP pins increases with total number of FP pins and ZrHx pins kept constant, transmutation rate decreases monotonously, whereas amount of transmutation decreases after it shows its peak value. The transmutation rate is about 1-2%/year at the case with maximum transmutation amount. (2)Heterogeneity effect upon transmutation rate is very large ; the rate for heterogeneous geometry is 30% smaller than that for homogeneous geometly with the same average composition. This is caused by heterogeneity effect upon resonance absorption. (3)Amount of transmutation vary by about 20-30% with arrangement variation of FP pins. Dispersing FP pins increases transmutation rate. (4)The difference between absorption rates from the MC method and the ...
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; *; Kawashima, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Reiko*
PNC TJ9164 95-009, 231 Pages, 1995/03
To enhance plutonium burning capability in fast reactors, one of the effective means is to use materials other than uranium for dilution of plutonium. A feasibility study was made to build a 600MWe-class core concept within the do-main of sodium-cooled fast reactors. The analysis covered core static and transient characteristics, including fuel material surveys. The candidate fuels were chosen as plutonium oxide with diluen materials, such as Al O
O and BeO, to keep the Doppler coefficients negative large enough, condisering the TOP-type transisnts results from the FY1993 study. Core nuclear analysis showed that use of fuel without uranium considerably increases burnup swing and power mismatch between fresh and burnt fuels, aiming at the long cycle length as the 600MWe MOX core design. The core characteristics under ULOF- and UTOP-transients were compared with those in the 600MWe-MOX core. The study showed that the 9-month cycle core burned 59% fissile plutonium with negative sodium void worth (-1 $) under the plant condition for sodium inlet 390 C-deg. and the outlet temperature 510 C-deg. This study revealed that core neutronic feasibility has shown for such an innovative core concept with selecting appropriate diluent fuel materials combining core specifications. This means that sodium-cooled fast reactor has additional larger flexibility associated with plutonium utilization in the future.
and BeO, to keep the Doppler coefficients negative large enough, condisering the TOP-type transisnts results from the FY1993 study. Core nuclear analysis showed that use of fuel without uranium considerably increases burnup swing and power mismatch between fresh and burnt fuels, aiming at the long cycle length as the 600MWe MOX core design. The core characteristics under ULOF- and UTOP-transients were compared with those in the 600MWe-MOX core. The study showed that the 9-month cycle core burned 59% fissile plutonium with negative sodium void worth (-1 $) under the plant condition for sodium inlet 390 C-deg. and the outlet temperature 510 C-deg. This study revealed that core neutronic feasibility has shown for such an innovative core concept with selecting appropriate diluent fuel materials combining core specifications. This means that sodium-cooled fast reactor has additional larger flexibility associated with plutonium utilization in the future.
; Hayashi, Hideyuki; ; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki; ; ;
PNC TN9410 93-162, 494 Pages, 1993/07
A design study on a large scale fast reactor was performed based on the results of the study on 600 MWe class "reactor vessel head access concept" plant in FY1990 1991. The objective of this study is to confirm quantitatively the applicability of "reactor vessel head access concept" to larger scale fast reactor plant as well as to establish the basic design such as core design, reactor structure, heat transport system, of 1300 MWe class "reactor vessel head access concept" plant and to evaluate its feasibility. In the former half period of FY1992, studies were performed aiming at evaluation of precision of core design, integrity of the structure and safety reflecting the final equipment design, feasibility of the concept of spent fuel storage, etc. While in the latter half period, added were the subjects on key technologies and plant concepts which enhance economy, safety, and social acceptance in order to ascertain the direction of a design study in the future and to contribute the realization of a commecial fast reactor.
1991. The objective of this study is to confirm quantitatively the applicability of "reactor vessel head access concept" to larger scale fast reactor plant as well as to establish the basic design such as core design, reactor structure, heat transport system, of 1300 MWe class "reactor vessel head access concept" plant and to evaluate its feasibility. In the former half period of FY1992, studies were performed aiming at evaluation of precision of core design, integrity of the structure and safety reflecting the final equipment design, feasibility of the concept of spent fuel storage, etc. While in the latter half period, added were the subjects on key technologies and plant concepts which enhance economy, safety, and social acceptance in order to ascertain the direction of a design study in the future and to contribute the realization of a commecial fast reactor.
; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki
PNC TN9410 93-123, 125 Pages, 1993/05
A heterogeneous MA-loading method, where a few number of subassemblies with concentrated MA fuel (target fuel subassemblies) are loaded in the core, can have an advantage in fabricating and managing the MA-loaded fuel since the number of the MA-loaded fuel subassemblies is smaller compared with the method loading MA homogeneously. A study has been carried out on the feasibility of the heterogeneous MA-loading in an oxide-fueled 1000MWe LMFBR core. Based on the experimental data on fuel properties of MA fuel published up to now, it was found that MA loading significantly reduces the linear power limit almost proportionally to the MA loading ratio because of degradation of the thermal conductivity and the melting point. Furthermore, core analyses showed that heterogeneous MA-loading leads to a significant power deformation in the core if the design of target fuel subassemblies is the same as that of the normal fuel subassemblies with no MA fuel loaded. These cause a serious thermal problem. An effort was made so as to make the heterogeneous method feasible. The fuel pin design and the loading pattern of the target fuel subassemblies were studied. It was found that reduction of the fuel pin diameter and the Pu enrichment is essential to reduce the power of MA-loaded fuel. It is concluded that the heterogeneous MA-loading method is feasible by optimizing fuel design, loading pattern and coolant flow of MA-loaded fuel subassemblies.
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki;
PNC TN9410 92-371, 94 Pages, 1992/12
TRU nuclides (Np, Am, and Cm) contained in the high level waste have extremely long-term radioactivity. They would be managed much more easily if transmuted in a short period. The present study deals with TRU transmutation by Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs). The results are summarized below. (1)Study on a 300MWe Super Long Life Core for TRU Transmutation An FBR core loaded with TRU has a large potentiality of extending operation cycle length. Making use of the potentiality, a super long life FBR core loaded with TRU was studied aiming at continuous operation without refueling during plant life and efficient reduction of TRU nuclides. Core parameters were optimized with the electric power of 300MWe and analyses of nuclear and thermal characteristics were carried out. As a result, the burnup reactivity change of the optimized core for 34 years is very small (2.5%  k/kk'). The power swing is also small, which resulted in satisfaction of the thermal design criteria. The amount of TRU transmuted during lifetime is about 5300Kg, which is equal to that 6 LWRs of 1000MWe produce during their lifetime. The Doppler coefficient (absolute value) is rather small because of TRU loading. Further study is needed on core kinetics from the view point of core safety and control. (2)Study on influence of uncertainties of TRU cross sections There are large uncertainties in TRU cross sections because of lack of experimental data. The influences of the uncertainties upon nuclear characteristics were evaluated for the super long life core and a large FBR core loaded with TRU of 5%. Sensitivity analysis on cross sections was carried out and uncertainties of nuclear characteristics were roughly evaluated. Based on the results, the TRU cross sections with large influences were identified.
k/kk'). The power swing is also small, which resulted in satisfaction of the thermal design criteria. The amount of TRU transmuted during lifetime is about 5300Kg, which is equal to that 6 LWRs of 1000MWe produce during their lifetime. The Doppler coefficient (absolute value) is rather small because of TRU loading. Further study is needed on core kinetics from the view point of core safety and control. (2)Study on influence of uncertainties of TRU cross sections There are large uncertainties in TRU cross sections because of lack of experimental data. The influences of the uncertainties upon nuclear characteristics were evaluated for the super long life core and a large FBR core loaded with TRU of 5%. Sensitivity analysis on cross sections was carried out and uncertainties of nuclear characteristics were roughly evaluated. Based on the results, the TRU cross sections with large influences were identified.
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki; Hayashi, Hideyuki
PNC TN9410 92-368, 75 Pages, 1992/12
A passive safety test phase IIB is planned at the FFTF (Fast Flux Test Facility) core to assess the reactivity feedback effect related to passive safety feature of FBRs, especially the effect due to core deformation. For pre-test analyses of the test, a bowing reactivity analysis has been carried out for FFTF core. The bowing reactivity is analyzed based on core displacement data evaluated postulating ULOF (Unprotected Loss of Flow) event at 30% rated flow. In the analysis, fuel reactivity worth distribution is expressed as function on the reference core without deformation and the bowing reactivity is calculated based on the first-order perturbation theory. This report summarizes the relationships between power to flow ratio and the bowing reactivity with clearance between subassembly load pads and that between the core and the core restraint system as parameters. Followings are main results. (1)As the power to flow ratio increases, a positive reactivity is added to the core by the core deformation until clearance between subassembly load pads doses. This is due to the inward displacement of active core caused by mechanical interactions of subassemblies. (2)After the closure of clearance between subassembly load pads, the active core begins to move outwards, and a negative reactivity is added to the core. (3)The deformation behavior of the outermost subassemblies of the core dominates the bowing reactivity since both the magnitude of deformation and the reactivity effect for unit displacement are large compared with those of others. For the analysis, a code for bowing reactivity calculation has been developed. The calculation method and the manual are also presented in this report.
; Hayashi, Hideyuki; ; ; ; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki;
PNC TN9410 92-353, 120 Pages, 1992/11
A design study on a large scale fast reactor was performed at OEC about 600MWe class plant which might be the lowest power scale as a commercial one. Results of the design study till the end of JFY1991 were summarized in a previous progress report of the design study on a large scale reactor (PNC ZN9410 92-137). In this report, the evaluation results of the construction cost of the 600MWe class plant are described and also the drawings of their various parts are summaried.
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki;
International Conference on Design and Safety of Advanced Nuclear Power Plants (ANP '92), 1, p.3.3-1 - 3.3-6, 1992/10
None
Yamaguchi, Akira; ; Shimakawa, Yoshio; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Aizawa, Kiyoto
International Conference on Design and Safety of Advanced Nuclear Power Plants (ANP '92), 3, p.30.4.1 - 30.4.9, 1992/10
None
Yoshida, Hiroshi; Naruse, Yuji; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; *; *; *
JAERI-M 92-088, 105 Pages, 1992/06
no abstracts in English