Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Saiki, Seiichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Analytical Chemistry, 83(24), p.9600 - 9604, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:78.17(Chemistry, Analytical)Chemical reactions of a novel gauche-type spin trap, G-CYPMPO (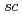 -5-(5,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-yl)-5-methy-1-pyrroline 1-oxide, torsion angle: O1-P1-C6-N1 of 52.8
-5-(5,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-yl)-5-methy-1-pyrroline 1-oxide, torsion angle: O1-P1-C6-N1 of 52.8 ), with reactive oxygen species were examined by pulse radiolysis technique with 35 MeV electron beam and electron spin resonance spectroscopy after
), with reactive oxygen species were examined by pulse radiolysis technique with 35 MeV electron beam and electron spin resonance spectroscopy after  Co
Co  -ray irradiation. The spin trapping reaction rate constants of G-CYPMPO toward hydroxyl radical and hydrated electron were estimated to be (4.2
-ray irradiation. The spin trapping reaction rate constants of G-CYPMPO toward hydroxyl radical and hydrated electron were estimated to be (4.2 0.1)
0.1) 10
10 and (11.8
and (11.8 0.2)
0.2) 10
10 M
M s
s , respectively. Half-lives of spin adducts, hydroxyl radical and perhydroxyl radical adducted G-CYPMPO were estimated to be
, respectively. Half-lives of spin adducts, hydroxyl radical and perhydroxyl radical adducted G-CYPMPO were estimated to be  35 and
35 and  90 min, respectively. A comparison of the results with earlier reports using different radical sources suggests that the purity of the solution and/or the radical generation technique may influence the stability of spin adducts.
90 min, respectively. A comparison of the results with earlier reports using different radical sources suggests that the purity of the solution and/or the radical generation technique may influence the stability of spin adducts.
Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Funtowiez, D.*; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Fujisaki, Kenta*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Kobayashi, Kensei*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Kawai, Hideyuki*; Mita, Hajime*; Narumi, Issei; Okudaira, Kyoko*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Fujisaki, Kenta*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Yamashita, Masamichi*; Yano, Hajime*; Okudaira, Kyoko*; Yoshimura, Yoshitaka*; Narumi, Issei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Fujisaki, Kenta*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Fushimi, Hidehiko*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Yamashita, Masamichi*; Yano, Hajime*; Okudaira, Kyoko*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 OH yield near the Bragg peak
OH yield near the Bragg peakMaeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Funtowiez, D.*; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichi; Funtowiez, D.*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke; et al.
no journal, ,
Product yields of water radiolysis are inevitably important in understanding detailed mechanism of indirect action of ionizing radiations. We have conducted yield measurement of main products such as hydrated electron, hydroxyl radical ( OH) and hydrogen peroxide. We have also developed a sensitive method to determine
OH) and hydrogen peroxide. We have also developed a sensitive method to determine  OH yield with a fluorescent probe. In the method, aqueous solution of coumarin-3-carboxylic acid (CCA) is irradiated and
OH yield with a fluorescent probe. In the method, aqueous solution of coumarin-3-carboxylic acid (CCA) is irradiated and  OH is scavenged by CCA, resulting in production of fluorescent product 7OH-CCA. Applying this method,
OH is scavenged by CCA, resulting in production of fluorescent product 7OH-CCA. Applying this method,  OH yield near the Bragg peak has been measured in this study because the Bragg peak is overlapped cancer position in actual therapy. Beams of C 290 and 135 MeV/u and so on were taken for irradiation at the biological irradiation port at HIMAC facility of NIRS. It was found that
OH yield near the Bragg peak has been measured in this study because the Bragg peak is overlapped cancer position in actual therapy. Beams of C 290 and 135 MeV/u and so on were taken for irradiation at the biological irradiation port at HIMAC facility of NIRS. It was found that  OH yield show minimal value around the Bragg peak for every ion beam and it drastically jumps up several times at just downstream of the Bragg peak. It is already well known that contributions of fragmentation particles become non-negligible for high-energy heavy ions. Thus, further consideration including fragmentations is necessary to separate contributions of different fragmentation particles. Such consideration is being attempted by using simulations with HIBRAC and PHITS.
OH yield show minimal value around the Bragg peak for every ion beam and it drastically jumps up several times at just downstream of the Bragg peak. It is already well known that contributions of fragmentation particles become non-negligible for high-energy heavy ions. Thus, further consideration including fragmentations is necessary to separate contributions of different fragmentation particles. Such consideration is being attempted by using simulations with HIBRAC and PHITS.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Maeyama, Takuya*; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Recently, cancer therapy with high-energy heavy ions has been utilized, showing high efficiency in actual treatment. While its effectiveness has already been certificated phenomenologically, detailed mechanism through which such a feature appears has not been clarified yet. Water is a main component of human body, and then, it is inevitably important to comprehend water radiolysis. In this study, water radiolysis near the Bragg peak was focused on because the peak is overlapped to cancer in actual treatment, and yield of hydroxyl radical ( OH) has been determined because
OH) has been determined because  OH is assumed as a species most responsible to indirect action. In addition, contribution of fragmentation reactions which is significant for high-energy heavy ions were discussed from the viewpoint of
OH is assumed as a species most responsible to indirect action. In addition, contribution of fragmentation reactions which is significant for high-energy heavy ions were discussed from the viewpoint of  OH yield.
OH yield.
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Saiki, Seiichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Detection and quantification of the oxidative radicals such as hydroxyl radical or superoxide anion radical are very important to clarify the biological oxidative damages. These oxidative radicals, produced by water decomposition with  -ray irradiation, were detected as spin adducts of CYPMPO and themselves. In this work, reactivity CYPMPO and behavior of spin adducts were investigated.
-ray irradiation, were detected as spin adducts of CYPMPO and themselves. In this work, reactivity CYPMPO and behavior of spin adducts were investigated.
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Saiki, Seiichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
The oxygen radicals play a crucial role in biological oxidative damage. It is important to clarify behavior of hydroxyl and superoxide radicals, detection and quantification of these radicals are required. In present work, the reactivities of CYPMPO toward a hydrated electron and a hydroxyl radical utilizing a pulse radiolysis system are investigated, and compared with DMPO (5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide) results. The oxygen radicals produced by  -ray irradiation are also discussed.
-ray irradiation are also discussed.
Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
5-(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propoxy cyclophosphoryl)-5-methyl-1pyrroline N-oxide (CYPMPO) is a recently developed spin-trapping agent, which is expected to distinguish O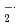 from
from 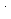 OH. We have determined its reactivity with water decomposed radicals, especially with
OH. We have determined its reactivity with water decomposed radicals, especially with  OH and with e
OH and with e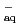 by pulse radiolysis, and compared results with commonly-used spin trapping agent, 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO). Furthermore, the reactions with oxidative radicals such as
by pulse radiolysis, and compared results with commonly-used spin trapping agent, 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO). Furthermore, the reactions with oxidative radicals such as  COO
COO , NO
, NO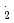 and Br
and Br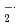 have also been investigated.
have also been investigated.
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Itahashi, Shiho*; Fujisaki, Kenta*; Fushimi, Hidehiko*; Hasegawa, Sunao*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Fushimi, Hidehiko*; Narumi, Issei; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; Kawai, Hideyuki*; Kobayashi, Kensei*; et al.
no journal, ,
Delamea, N.*; Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Saiki, Seiichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*
no journal, ,
In order to measure the transient radicals quantitatively, the spin trapping technique with a newly developed CYPMPO in 2006 has been applied to detect the water decomposition and secondary radicals using by ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) spectroscopy. We have succeeded to identify five radicals assigned to the spin adducts of  OH, O
OH, O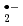 , HO
, HO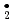 ,
,  COO
COO and H
and H .
.
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Saiki, Seiichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Delamea, N.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*
no journal, ,
A novel spin-trap CYPMPO (5-(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propoxy cyclophos-phoryl)-5-methyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide) was applied to detect the water decomposed radicals using by ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) spectroscopy, and their lifetimes were estimated.
Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Yang, Y.*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Yoshimura, Yoshitaka*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Kensei*; Tabata, Makoto*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Narumi, Issei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Narumi, Issei; Takahashi, Yuichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; Yoshimura, Yoshitaka*; Tabata, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sugino, Tomohiro*; Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Hasegawa, Sunao*; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Imai, Eiichi*; Okudaira, Kyoko*; Kawai, Hideyuki*; Tabata, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Narumi, Issei; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; Imai, Eiichi*; Kawai, Hideyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Yang, Y.*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Narumi, Issei; Nakagawa, Kazumichi*; Tabata, Makoto*; Kobayashi, Kensei*; Marumo, Katsumi*; et al.
no journal, ,