Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Ozaki, Toshinori*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(2), p.023001_1 - 023001_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.95(Physics, Applied)We show that Xe ion irradiation with 80 MeV to GdBa Cu
Cu Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at
Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at 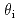 = 45
= 45 , whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (
, whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (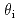 = 0
= 0 ) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density
) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density  .
.
 baking method for degassing of a kicker magnet in accelerator beam line
baking method for degassing of a kicker magnet in accelerator beam lineKamiya, Junichiro; Ogiwara, Norio; Yanagibashi, Toru*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yasuda, Yuichi*
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 34(2), p.021604_1 - 021604_10, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.94(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)In this study, we propose a new  degassing method by which only kicker magnets in the accelerator beam line are baked out without raising the temperature of the vacuum chamber to prevent unwanted heat expansion of the chamber. The bake-out system comprises the heater and thermal radiation shield plates, which are installed between the kicker magnet and the chamber wall. The result of the verification test showed that each part of the kicker magnet was heated to above the target temperature with a small rise in the vacuum chamber temperature. A graphite heater was selected in this application to bake-out the kicker magnet in the beam line to ensure reliability and easy maintainability of the heater. The vacuum characteristics of graphite were suitable for heater operation in the beam line. A preliminary heat-up test conducted in the accelerator beam line also showed that each part of the kicker magnet was successfully heated and that heat expansion of the chamber was negligibly small.
degassing method by which only kicker magnets in the accelerator beam line are baked out without raising the temperature of the vacuum chamber to prevent unwanted heat expansion of the chamber. The bake-out system comprises the heater and thermal radiation shield plates, which are installed between the kicker magnet and the chamber wall. The result of the verification test showed that each part of the kicker magnet was heated to above the target temperature with a small rise in the vacuum chamber temperature. A graphite heater was selected in this application to bake-out the kicker magnet in the beam line to ensure reliability and easy maintainability of the heater. The vacuum characteristics of graphite were suitable for heater operation in the beam line. A preliminary heat-up test conducted in the accelerator beam line also showed that each part of the kicker magnet was successfully heated and that heat expansion of the chamber was negligibly small.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Uraguchi, Yusei*; Kai, Takashi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.6603004_1 - 6603004_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.61(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To investigate the effect of discontinuity of 1-D pinning centers on the flux pinning in a wide range of magnetic field directions, discontinuous columnar defects (CDs) and continuous CDs were formed in GdBCO coated conductors using Xe-ion irradiations with 80 and 270 MeV, respectively. An overall shift upward in Jc, for the 80-MeV-irradiated sample compared to the 270-MeV-irradiated one, can be observed in every direction of magnetic field, which is more remarkable as temperature decreases. This implies a synergetic effect of the pinning interaction between the linearity and the discontinuity for the discontinuous CDs.
Yasuda, Takako*; Oda, Shoji*; Asaka, Tomomi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Mitani, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 85, 2015/03
In this present study, we examined the effects of heavy carbon-ions on development in pre-implantation period utilizing medaka blastula stage embryos (st. 11: blastderm diameter is about 500  m). We performed targeted irradiation by carbon-ion micro-beam (diameters of 120, 180
m). We performed targeted irradiation by carbon-ion micro-beam (diameters of 120, 180  m) to a central parts of blastoderm and observed the abnormalities during development compared with whole-body irradiated embryos. As a results, retardation and characteristic malformed eyes were observed during development when blastoderm cells were partially irradiated, However, more than half of 50 Gy-irradiated embryos (area size=120
m) to a central parts of blastoderm and observed the abnormalities during development compared with whole-body irradiated embryos. As a results, retardation and characteristic malformed eyes were observed during development when blastoderm cells were partially irradiated, However, more than half of 50 Gy-irradiated embryos (area size=120  m diameter) could hatch normally in contrast to all embryos with 2 Gy of whole-body irradiation being lethal before hutching.
m diameter) could hatch normally in contrast to all embryos with 2 Gy of whole-body irradiation being lethal before hutching.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.301 - 307, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:81.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the severe accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant, large amounts of contaminated stagnant water have accumulated in turbine buildings and their surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of the radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. This evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011. The release ratios of tritium, iodine, and cesium were several tens of percent, whereas those of strontium and barium were smaller by one or two orders of magnitude. The release ratios in the Fukushima accident were equivalent to those in the TMI-2 accident.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(1), p.13 - 19, 2012/03
After the severe accident in the Fukushima-1 Nuclear Power Plant, large amount of contaminated stagnant water has been produced in turbine buildings and those surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. The present evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011.
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Akiyama, Kazuhiko*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 97(2), p.83 - 89, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:77.78(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Anion-exchange chromatography of element 105, dubnium (Db), produced in the  Cm(
Cm( F, 5n)
F, 5n) Db reaction is investigated together with the homologues Nb and Ta, and the pseudo-homologue Pa in 13.9 M hydrofluoric acid (HF) solution. The distribution coefficient (K
Db reaction is investigated together with the homologues Nb and Ta, and the pseudo-homologue Pa in 13.9 M hydrofluoric acid (HF) solution. The distribution coefficient (K ) of Db on an anion-exchange resin is successfully determined by running cycles of the 1702 chromatographic column separations. The result clearly indicates that the adsorption of Db on the resin is significantly different from that of the homologues and that the adsorption of anionic fluoro complexes of these elements decreases in the sequence of Ta
) of Db on an anion-exchange resin is successfully determined by running cycles of the 1702 chromatographic column separations. The result clearly indicates that the adsorption of Db on the resin is significantly different from that of the homologues and that the adsorption of anionic fluoro complexes of these elements decreases in the sequence of Ta  Nb
Nb  Db
Db  Pa.
Pa.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Hirata, Masaru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126(16), p.5219 - 5224, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:72.51(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Fluoride complexation of element 104, rutherfordium (Rf), produced in the  Cm(
Cm( O,5n)
O,5n) Rf reaction has been studied by anion-exchange chromatography on an atom-at-a-time scale. The anion-exchangechromatographic behavior of Rf was investigated in 1.9-13.9 M hydrofluoric acid together with those of the group-4 elements Zr and Hf produced in the
Rf reaction has been studied by anion-exchange chromatography on an atom-at-a-time scale. The anion-exchangechromatographic behavior of Rf was investigated in 1.9-13.9 M hydrofluoric acid together with those of the group-4 elements Zr and Hf produced in the  O-induced reactions on Ge and Gd targets, respectively. It was found that the adsorption behavior of Rf on anion-exchange resin is quite different from those of Zr and Hf, suggesting the influence of relativistic effect on the fluoride complexation of Rf.
O-induced reactions on Ge and Gd targets, respectively. It was found that the adsorption behavior of Rf on anion-exchange resin is quite different from those of Zr and Hf, suggesting the influence of relativistic effect on the fluoride complexation of Rf.
Yasuda, Ryo; Nakata, Masahito; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Harada, Katsuya; Hatakeyama, Yuichi; Amano, Hidetoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 320(3), p.223 - 230, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron radiography is one of effective tools to determine hydrided region in Zircaloy cladding tubes. In this work, the practicability of the neutron radiography for hydrogen analysis is further investigated by using standard samples with known hydrogen concentration. Local hydrogen concentration in hydrided Zircaloy tube is quantitatively estimated using the standard samples by neutron imaging plate (NIP) method. The local area is equivalent to a picture element in the image; e.g., 0.1mm 0.1mm. In addition, contribution of an oxide film in the tubes to the images is investigated using oxidized samples with hydrides or no hydride. In NIP images of oxidized tube no oxide film was recognized. Numerical image analysis also shows no effect of the oxide film on the image. These results show that the influence of oxygen on image contrast can be neglected when hydrogen analysis is performed on the Zircaloy tube with oxide film and hydrides by NIP method.
0.1mm. In addition, contribution of an oxide film in the tubes to the images is investigated using oxidized samples with hydrides or no hydride. In NIP images of oxidized tube no oxide film was recognized. Numerical image analysis also shows no effect of the oxide film on the image. These results show that the influence of oxygen on image contrast can be neglected when hydrogen analysis is performed on the Zircaloy tube with oxide film and hydrides by NIP method.
Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Nozomi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
We have measured radioactivities in soils contaminated by the severe accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The soil samples were taken at the 83 points distributed around the north area of Ibaraki prefecture. Radioactivities in the soils were measured by  -ray spectrometry, and distributions of
-ray spectrometry, and distributions of 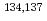 Cs in this area were clarified. The highest radioactivity of 130 kBq/m
Cs in this area were clarified. The highest radioactivity of 130 kBq/m of
of  Cs was observed at the boundary among Tochigi, Fukushima, and Ibaraki prefecture, while it was about 3 kBq/m
Cs was observed at the boundary among Tochigi, Fukushima, and Ibaraki prefecture, while it was about 3 kBq/m at the center of Ibaraki.
at the center of Ibaraki.
Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Nozomi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
The massive earthquakes and the following tsunami that struck the Tohoku and north Kanto regions of Japan on 11 March 2011 caused severe damage of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. In consequence, a large amount of radio isotopes accumulated in the nuclear reactor was discharged to environment of Tohoku and Kanto region. Assessment of individual radionuclide distributions on soil in the area is required because of estimation of radiation dose rate for people in the area from the contaminated surface, planning for cultivation, and establishment of regional land utilization. We performed to collect soil samples around north part of Ibaraki prefecture, and measured  -ray of soil samples by using high pure Ge detectors, and assessed the individual distribution of radio isotopes.
-ray of soil samples by using high pure Ge detectors, and assessed the individual distribution of radio isotopes.
 ), a vertebrate model
), a vertebrate modelYasuda, Takako*; Oda, Shoji*; Hibi, Yusuke*; Urushihara, Yusuke*; Mitani, Hiroshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Using heavy-ion microbeam system of JAEA-Takasaki, we irradiated brain of the embryos of the Medaka with carbon ion microbeam. After irradiation, inductions of apoptosis were observed using whole-mount staining of acridine orange. In targeted position of the brain, we observed the induction of radiation induced apoptosis, indicating that the system can irradiate specific region of the brain of the Medaka embryo.
Oda, Shoji*; Yasuda, Takako*; Asaka, Tomomi*; Mitani, Hiroshi*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Muto, Yasuko*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
The method for targeting and irradiating the testis of fry and adult of Medaka fish using carbon-ion microbeam was established. To irradiate the testis of the fry, a transgenic Medaka that expresses GFP protein specifically in its testis was used. The position of the testis was observed under fluorescent microscopy and then the testis was targeted and irradiated with carbon ion microbeam. To irradiate the testis of the adult Medaka, a adult male of p53 knock out transgenic fish was used. The microbeam was irradiated on the estimated testis position; thereafter the success of irradiation was confirmed by the induction of testis-ova, which is known as induced by the radiation of testis in p53 knock out fish.
Oda, Shoji*; Yasuda, Takako*; Hibi, Yusuke*; Asaka, Tomomi*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Muto, Yasuko*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a new irradiation protocol for tissue specific irradiation to living embryo and adult medaka,  . In the study, a testis of p53 knockout fish were irradiated with multi-shots of microbeam. Less numbers of testis-ova were induced in the in p53- lacking testis 1 week after the irradiation compared to whole body irradiated testis. Specific irradiation of microbeam onto the right (or left) lobe of the optic tectum in medaka embryos of 2 days post fertilization ectopically induced apoptotic cells in the body trunk and the tail in addition to the irradiated position. The systemic effects as endocrine system, autonomic nervous system and immunity reactions occur in adult medaka and these results suggested that the systemic effects might be functional even in developing embryos.
. In the study, a testis of p53 knockout fish were irradiated with multi-shots of microbeam. Less numbers of testis-ova were induced in the in p53- lacking testis 1 week after the irradiation compared to whole body irradiated testis. Specific irradiation of microbeam onto the right (or left) lobe of the optic tectum in medaka embryos of 2 days post fertilization ectopically induced apoptotic cells in the body trunk and the tail in addition to the irradiated position. The systemic effects as endocrine system, autonomic nervous system and immunity reactions occur in adult medaka and these results suggested that the systemic effects might be functional even in developing embryos.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we used PHITS code to simulate the behavior of the low-energy muon in a thin layer of the solid hydrogen.
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we used PHITS code to simulate the behavior of the low-energy muon in a thin layer of the solid hydrogen.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
When muons are injected into a deuterium thin film target, muon molecules are formed. The muons released after intramolecular fusion (recycling muons) are important for the development of slow muon beams. In this study, corresponding to an experiment in which recycling muons are transported using a coaxial transport tube, the energy distribution of scattered muons, muons after deceleration, and background radiation due to bremsstrahlung by decay electrons and neutrons are analyzed by numerical simulations.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
We are attempting to observe regenerative muons emitted from the surface of a solid hydrogen thin film by muon-catalyzed fusion by irradiating the film with muons that have the same charge as electrons and 207 times the mass of electrons. The main background factors in detecting regenerative muons are scattered muons from the accelerator, which are slowed down to the same level as regenerative muons by the target, and bremsstrahlung generated by the components of the device. The results show that there is little scattering within the solid hydrogen, and that the dominant slowing down process is at the Al foil upstream of the solid hydrogen target. The energy distribution of Bremsstrahlung at the X-ray detection position will be reported.