Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
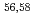 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 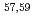 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 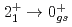 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 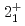 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 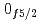 and
and 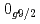 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,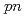 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 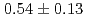 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Otani, Masashi*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.37 - 40, 2019/06
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 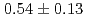 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Uraguchi, Yusei*; Kai, Takashi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.6603004_1 - 6603004_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.61(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To investigate the effect of discontinuity of 1-D pinning centers on the flux pinning in a wide range of magnetic field directions, discontinuous columnar defects (CDs) and continuous CDs were formed in GdBCO coated conductors using Xe-ion irradiations with 80 and 270 MeV, respectively. An overall shift upward in Jc, for the 80-MeV-irradiated sample compared to the 270-MeV-irradiated one, can be observed in every direction of magnetic field, which is more remarkable as temperature decreases. This implies a synergetic effect of the pinning interaction between the linearity and the discontinuity for the discontinuous CDs.
Li, T.*; Garg, U.*; Liu, Y.*; Marks, R.*; Nayak, B. K.*; Madhusudhana Rao, P. V.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru*; Hashimoto, Hisanobu*; Nakanishi, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 81(3), p.034309_1 - 034309_11, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:97.48(Physics, Nuclear) O(
O(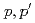 ) reaction at forward angles and structure of the spin-dipole resonances
) reaction at forward angles and structure of the spin-dipole resonancesKawabata, Takahiro*; Ishikawa, Takatsugu*; Ito, M.*; Nakamura, M.*; Sakaguchi, Harutaka*; Takeda, H.*; Taki, T.*; Uchida, Makoto*; Yasuda, Yusuke*; Yosoi, Masaru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 65(6), p.064316_1 - 064316_12, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:70.12(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Ito, M.*; Sakaguchi, Harutaka*; Ishikawa, Takatsugu*; Kawabata, Takahiro*; Murakami, Tetsuya*; Takeda, H.*; Taki, T.*; Tsukahara, N.*; Uchida, Makoto*; Yasuda, Yusuke*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 687(1-2), p.52c - 57c, 2001/04
no abstracts in English
 O (p,p') experiment
O (p,p') experimentKawabata, Takahiro*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujita, Hirohiko*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Hara, Keigo*; Hatanaka, Kichiji*; Hosono, K.*; Ishikawa, Takatsugu*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 459(1-2), p.171 - 176, 2001/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Chiba, Satoshi; Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Nozomi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
We have measured radioactivities in soils contaminated by the severe accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The soil samples were taken at the 83 points distributed around the north area of Ibaraki prefecture. Radioactivities in the soils were measured by  -ray spectrometry, and distributions of
-ray spectrometry, and distributions of 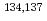 Cs in this area were clarified. The highest radioactivity of 130 kBq/m
Cs in this area were clarified. The highest radioactivity of 130 kBq/m of
of  Cs was observed at the boundary among Tochigi, Fukushima, and Ibaraki prefecture, while it was about 3 kBq/m
Cs was observed at the boundary among Tochigi, Fukushima, and Ibaraki prefecture, while it was about 3 kBq/m at the center of Ibaraki.
at the center of Ibaraki.
Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Projectile charge-changing cross sections for nuclei in galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) on hydrogen play essentially important roles for the study of origin and source composition of GCRs. Previous experimental and theoretical works done so far made much progress on those cross sections. However, there are still uncertainties in much of the cross section data, and therefore the present knowledge of cross sections has not led to successful determination of the GCR source composition. To improve the uncertainties, a novel measurement system of projectile charge-changing cross section using CR-39 plastic nuclear track detectors with excellent position and nuclear charge resolutions has been developed. We carried out measurements of total and partial charge-changing cross sections for Fe and Mg on 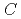 and
and 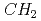 targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Nozomi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
The massive earthquakes and the following tsunami that struck the Tohoku and north Kanto regions of Japan on 11 March 2011 caused severe damage of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. In consequence, a large amount of radio isotopes accumulated in the nuclear reactor was discharged to environment of Tohoku and Kanto region. Assessment of individual radionuclide distributions on soil in the area is required because of estimation of radiation dose rate for people in the area from the contaminated surface, planning for cultivation, and establishment of regional land utilization. We performed to collect soil samples around north part of Ibaraki prefecture, and measured  -ray of soil samples by using high pure Ge detectors, and assessed the individual distribution of radio isotopes.
-ray of soil samples by using high pure Ge detectors, and assessed the individual distribution of radio isotopes.
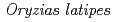 ), a vertebrate model
), a vertebrate modelYasuda, Takako*; Oda, Shoji*; Hibi, Yusuke*; Urushihara, Yusuke*; Mitani, Hiroshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Using heavy-ion microbeam system of JAEA-Takasaki, we irradiated brain of the embryos of the Medaka with carbon ion microbeam. After irradiation, inductions of apoptosis were observed using whole-mount staining of acridine orange. In targeted position of the brain, we observed the induction of radiation induced apoptosis, indicating that the system can irradiate specific region of the brain of the Medaka embryo.
Oda, Shoji*; Yasuda, Takako*; Hibi, Yusuke*; Asaka, Tomomi*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Muto, Yasuko*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a new irradiation protocol for tissue specific irradiation to living embryo and adult medaka, 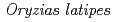 . In the study, a testis of p53 knockout fish were irradiated with multi-shots of microbeam. Less numbers of testis-ova were induced in the in p53- lacking testis 1 week after the irradiation compared to whole body irradiated testis. Specific irradiation of microbeam onto the right (or left) lobe of the optic tectum in medaka embryos of 2 days post fertilization ectopically induced apoptotic cells in the body trunk and the tail in addition to the irradiated position. The systemic effects as endocrine system, autonomic nervous system and immunity reactions occur in adult medaka and these results suggested that the systemic effects might be functional even in developing embryos.
. In the study, a testis of p53 knockout fish were irradiated with multi-shots of microbeam. Less numbers of testis-ova were induced in the in p53- lacking testis 1 week after the irradiation compared to whole body irradiated testis. Specific irradiation of microbeam onto the right (or left) lobe of the optic tectum in medaka embryos of 2 days post fertilization ectopically induced apoptotic cells in the body trunk and the tail in addition to the irradiated position. The systemic effects as endocrine system, autonomic nervous system and immunity reactions occur in adult medaka and these results suggested that the systemic effects might be functional even in developing embryos.
Goke, Mitsuo*; Okihara, Mitsunobu*; Maemura, Tsuneyuki*; Yasuda, Ryo*; Matsui, Hiroya; Ozaki, Yusuke; Mochizuki, Akihito
no journal, ,
We performed the numerical simulation to simulate the long term change in geological environment under open drift condition. We developed the conceptual model for the purpose and performed the geomechanical and hydrological simulation with the models considering the existence of excavation damaged zone and tunnel support. The geomechanical simulation results suggested that the deformation for long term is so slight that the excavation damaged zone does not enlarge. The hydrological simulation considering the degassing predicted the expansion of the unsaturated zone in the high pore pressure domain.