Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Yuki*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Kubo, Mamoru*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Shinoda, Taro*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Ushio, Tomoo*; Sato, Yosuke*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 48(7), 11 Pages, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:90.11(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)During three winter seasons from November 2016 to March 2019, 11 gamma-ray glows were detected at a single observation site of our ground-based gamma-ray monitoring network in Kanazawa, Japan. These events are analyzed with observations of an X-band radar network, a ceilometer, a disdrometer, and a weather monitor. All the detected glows were connected to convective high-reflectivity regions of more than 35 dBZ, developed up to an altitude of  2 km. They were also accompanied by heavy precipitation of graupels. Therefore, graupels in the lower layer of thunderclouds that correspond to high-reflectivity regions can form strong electric fields producing gamma-ray glows. Also, these events are compared with a limited sample of nondetection cases, but no significant differences in meteorological conditions were found between detection and nondetection cases in the present study.
2 km. They were also accompanied by heavy precipitation of graupels. Therefore, graupels in the lower layer of thunderclouds that correspond to high-reflectivity regions can form strong electric fields producing gamma-ray glows. Also, these events are compared with a limited sample of nondetection cases, but no significant differences in meteorological conditions were found between detection and nondetection cases in the present study.
Wada, Yuki*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Nakamura, Yoshitaka*; Morimoto, Takeshi*; Sato, Mitsuteru*; Ushio, Tomoo*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 125(4), p.e2019JD031730_1 - e2019JD031730_11, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:80.58(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)Wada, Yuki*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Nakamura, Yoshitaka*; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Morimoto, Takeshi*; Sato, Mitsuteru*; Matsumoto, Takahiro*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.67_1 - 67_9, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:93.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Ishii, Katsunori; Suzuki, Masahiro; Fujita, Shunya*; Kobayashi, Shohei*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/05
A solution of plutonium nitrate and uranyl nitrate is converted into a mixed oxide by microwave heating denitration method. In the present study, for improving the efficiency of microwave heating and achieving high-temperature uniformity to produce homogeneous UO powder, the microwave heating test of potassium chloride and uranyl nitrate solution, and numerical simulation analysis were conducted. The potassium chloride agar was adjusted to the dielectric loss, which is close to that of the uranyl nitrate solution and the optimum support table height was estimated to be 50 mm for denitration of the uranyl nitrate solution by microwave heating. The adiabator improved the efficiency of microwave heating denitration. Moreover, the powder yield was improved by using the adiabator owing to ease of scraping of the denitration product from the bottom of the denitration vessel.
powder, the microwave heating test of potassium chloride and uranyl nitrate solution, and numerical simulation analysis were conducted. The potassium chloride agar was adjusted to the dielectric loss, which is close to that of the uranyl nitrate solution and the optimum support table height was estimated to be 50 mm for denitration of the uranyl nitrate solution by microwave heating. The adiabator improved the efficiency of microwave heating denitration. Moreover, the powder yield was improved by using the adiabator owing to ease of scraping of the denitration product from the bottom of the denitration vessel.
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori
Proceedings of 11th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-11) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2018/11
Mixed uranium oxide and plutonium oxide powder is produced from uranyl nitrate and plutonium nitrate mixed solution by the microwave heating denitration method in the spent fuel reprocessing process. Since the microwave heating method is accompanied by a boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to fully grasp the operating conditions in order to avoid flashing and spilling in the mass production of denitrification technology for the future. In this research, it was clarified that the heat transfer coefficient became lower as the dielectric constant increased. The dominant factor of the blowing up phenomena is supposed to be generation of the innumerable bubble rather than bubble's growth.
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Ishii, Katsunori
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/07
Mixed uranium oxide and plutonium oxide powder is produced from uranyl nitrate and plutonium nitrate mixed solution by the microwave heating denitration method in the spent fuel reprocessing process. Since the microwave heating method is accompanied by a boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to fully grasp the operating conditions in order to avoid flashing and spilling in the mass production of denitrification technology for the future. In this research, it was confirmed that a potassium chloride aqueous solution as a simulant of uranyl nitrate aqueous solution with high dielectric loss cause loss of microwave at the solution surface as the dielectric loss increased with the increase of KCl concentration by experimental and electromagnetic field analysis, and revealed that the change in the heating condition affects the generation of flushing.
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Chonan, Fuminori*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Yamaki, Tatsunori*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/07
From the observation results, in the process of flushing, the behaviors leading to flushing were classified divided into three types. First type is that first generation bubble from heating leads to flushing. Second type is that nucleate boiling continues during heating and stop, finally single bubble generates and leads to flushing. Third type is defined that gradual evaporation occurs without bubbles. It was revealed that the total quantities of heat released by flushing are approximately equal when assuming the flushing mechanism, it can be triggered that a large amount of micro bubbles are instantaneously generated and grew.
Kono, Hidetoshi; Yuasa, Tomo*; Nishiue, Shinya*; Yura, Kei
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D409 - D413, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:34.85(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have developed coliSNP, a database server (http://yayoi.kansai.jaea.go.jp/colisnp) that maps non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) on the three-dimensional (3D) structure of proteins. Once a week, the SNP data from the dbSNP database and the protein structure data from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) are downloaded, and the correspondence of the two data sets is automatically tabulated in the coliSNP database. Given an amino acid sequence, protein name or PDB ID, the server will immediately provide known nsSNP information, including the amino acid mutation caused by the nsSNP, the solvent accessibility, the secondary structure and the flanking residues of the mutated residue in a single page. The position of the nsSNP within the amino acid sequence and on the 3D structure of the protein can also be observed. The database provides key information with which to judge whether an observed nsSNP critically affects protein function and/or stability. As far as we know, this is the only web-based nsSNP database that automatically compiles SNP and protein information in a concise manner.
 Co
Co thin film
thin filmDoi, Masaaki*; Mano, Tomonori*; Shiota, Megumi*; Yuasa, Hiromi*; Takeda, Masayasu; Sahashi, Masashi*
no journal, ,
We have reported the high bulk scattering spin-asymmetry coefficient, 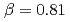 , of an alternate monatomic layered epitaxial film (AML) [Fe/Co]
, of an alternate monatomic layered epitaxial film (AML) [Fe/Co] . This high value of
. This high value of  and the long-range order parameter of B
and the long-range order parameter of B structure in Fe
structure in Fe Co
Co seem to be correlated. The neutron diffraction measurements of the AML [Fe/Co]
seem to be correlated. The neutron diffraction measurements of the AML [Fe/Co] were performed to determine the order parameter, and the value of about 0.7 was obtained. This value is consistent with a theoretical calculation. We discuss the correlation between the
were performed to determine the order parameter, and the value of about 0.7 was obtained. This value is consistent with a theoretical calculation. We discuss the correlation between the  and the order parameter together with the results of [Fe
and the order parameter together with the results of [Fe Co
Co /Cu]
/Cu] and a thin film of the Fe
and a thin film of the Fe Co
Co alloy.
alloy.
Chonan, Fuminori*; Abe, Yutaka*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu
no journal, ,
In a reprocessing process of nuclear fuel cycle, an uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) raw powder is converted from a mixture solution of uranyl nitrate and plutonium nitrate by the microwave heating denitration method (MH method). The MH method is applied to remove water and nitric acid from a metallic nitrate solution, and a metallic oxide is obtained. In order to improve the efficiency of MH method, optimizing the equipment and conditions is needed to prevent flushing of a mixture solution during microwave heating. In our group, we have been studied that the influence of height of supporter which placed under the mixture solution in the vessel on its heating phenomena. Also we have been analyzed simulation of electromagnetic field during microwave heating in microwave oven. From those results, we considered the appropriate height of supporter in the oven. It was clarified that height of supporter was one of the important parameter for the efficiency of microwave heating.
Chonan, Fuminori*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Kanagawa, Tetsuya*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Chonan, Fuminori*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Yamaki, Tatsunori*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Chonan, Fuminori*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Kanagawa, Tetsuya*; Fujita, Shunya*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu
no journal, ,
A mixed solution of uranyl nitrate and plutonium nitrate is converted to MOX raw powder by the microwave heating de-nitration method in nuclear fuel reprocessing. Since the microwave heating causes a boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to sufficiently confirm operating conditions to prevent flushing and overflow phenomena of solution. In this study, visualization observation of the microbubble generation and growth behavior near the liquid surface, measuring of bubble diameters, calculating the frequency of nucleation and estimating the quantity of heat of required for generation and growth of microbubbles were performed for the purpose of clarifying the generation mechanism of the flushing phenomena caused by microwave heating. As a result of comparative study with the amount of heat of released by flushing, it was confirmed that the quantities of the heat of released by flushing and the heat of required for generation and growth of microbubbles agree on the order.
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Yamada, Yoshikazu
no journal, ,
A mixed solution of uranyl nitrate and plutonium nitrate is converted to MOX raw powder by the microwave heating de-nitration method in nuclear fuel reprocessing. Since the microwave heating causes a boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to sufficiently confirm operating conditions to prevent flushing and overflow phenomena of solution, and it is necessary to evaluate the influence of the dielectric property of the object on the microwave heating characteristics and to optimize the equipment and operating conditions. In this study, the visualization observation using a potassium chloride aqueous solution and agar as a high dielectric constant solution and evaluation of a heating portion, and the electromagnetic field analysis are performed for the purpose of evaluating the influence of the dielectric constant of the material and the installation position on microwave heating characteristics.
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamada, Yoshikazu; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Ishii, Katsunori
no journal, ,
Mixed uranium oxide and plutonium oxide (MOX) powder is produced from uranyl nitrate and plutonium nitrate mixed solution by the microwave heating denitration method in the spent fuel reprocessing process. Since the MH method is accompanied by a boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to fully grasp the operating conditions in order to avoid flashing and spilling in the mass production of denitrification technology for the future. In this research, for the purpose of clarifying the mechanism of flashing phenomenon during microwave heating, the generation mechanism of bubbles that innumerably occur at the time of flashing is considered. When the contact angle at the heterogeneous nucleation of bubbles was 177  C, the theoretical value of the heterogeneous nucleation approximately agreed with the experimental value at the time the superheat degree was found to be close to 35
C, the theoretical value of the heterogeneous nucleation approximately agreed with the experimental value at the time the superheat degree was found to be close to 35  C.
C.
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori
no journal, ,
The microwave heating denitration method is used in the spent fuel reprocessing process of the nuclear fuel cycle. Since the microwave heating method is accompanied by a transient boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to grasp the operating conditions and to clarify the mechanism of flashing and spilling in order to avoid it. In this study, by assuming the flashing model for the purpose of the clarification of the flashing mechanism by microwave heating, the flashing mechanism of instantaneous generation and growth is considered by calculating the generation frequency and volume of bubble from the visualization result at flushing. The mechanism of flashing phenomenon during microwave heating is thought that the significant flushing phenomenon occurs by the process that a large amount of nanobubbles are generated at a solid-fluid interface in a overheated liquid phase, the bubble group grows exponentially and collapses, and its internal pressure releases.
Kobayashi, Shohei*; Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori
no journal, ,
The microwave heating denitration method is used in the spent fuel reprocessing process. In order to develop the mass production of denitrification technology for the future, it is necessary to fully grasp the operating conditions to avoid flashing and overflow phenomena of solution. In this research, the conditions of the generation of flashing are evaluated using the potassium chloride aqueous solution as the simulated solution, and the concentration of potassium chloride and the microwave output as parameters. It is found that it is difficult to occur the flashing phenomenon as the concentration of potassium chloride increases.