Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
 -Ti alloy
-Ti alloyZhang, B.*; Xin, S.*; Huang, M.*; Mao, W.; Jia, W.*; Li, Q.*; Li, S.*; Zhang, S.*; Mao, C.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 890, p.145898_1 - 145898_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A significant increase in the recovery strain of a high-Zr  -Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the
-Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the  -grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
-grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences) neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S
SWang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Zhang, K.*; Zhang, Z. D.*; Li, B.*
Applied Physics Letters, 123(1), p.011903_1 - 011903_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.89(Physics, Applied)Jiang, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)As a promising environment-friendly alternative to current vapor-compression refrigeration, solid-state refrigeration based on the barocaloric effect has been attracting world wide attention. Generally, both phases in which a barocaloric effect occurs are present at ambient pressure. Here, instead, we demonstrate that KPF exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
 isomer in
isomer in 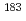 Hg and
Hg and  (
(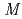 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Liu, B.*; Feng, R.*; Busch, M.*; Wang, S.*; Wu, H.*; Liu, P.*; Gu, J.*; Bahadoran, A.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14121 - 14133, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:98.33(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Q.*; Hu, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, T.*; Ilavsky, J.*; Kuzmenko, I.*; Ma, B.*; Tachi, Yukio
International Journal of Coal Geology, 261, p.104093_1 - 104093_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:69.58(Energy & Fuels) decay of the 8
decay of the 8 isomer in
isomer in 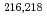 U
UZhang, M. M.*; Tian, Y. L.*; Wang, Y. S.*; Zhang, Z. Y.*; Gan, Z. G.*; Yang, H. B.*; Huang, M. H.*; Ma, L.*; Yang, C. L.*; Wang, J. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024305_1 - 024305_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez-Espinoza, V.*; Groudev, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; Bocanegra, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Berda , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2022) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/05
Gatera, A.*; Belmans, J.*; Boussa, S.*; Davin, F.*; De Cock, W.*; De Florio, V.*; Doucet, F.*; Parez, L.*; Pompon, F.*; Ponton, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 64th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2021), p.186 - 190, 2022/04
Yang, J.*; Ren, W.*; Zhao, X.*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Miao, P.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Zhang, Z.*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 99, p.55 - 60, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-entropy alloys are characteristic of extensive atomic occupational disorder on high-symmetric lattices, differing from traditional alloys. Here, we investigate magnetic and thermal transport properties of the prototype face-centered-cubic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi by combining physical properties measurements and neutron scattering. Direct-current (dc) and alternating-current (ac) magnetizations measurements indicate a mictomagnetic behavior with coexisting antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic interactions in the entire temperature region and three anomalies are found at about 80, 50, and 20 K, which are related to the paramagnetic to antiferromagnetic transition, the antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic transition, and the spin freezing, respectively. The electrical and thermal conductivities are significantly reduced compared to Ni and the temperature dependence of lattice thermal conductivity exhibits a glass-like plateau. Inelastic neutron scattering measurements suggest weak anharmonicity so that the thermal transport is expected to be dominated by the defect scattering.
Unc, A.*; Altdorff, D.*; Abakumov, E.*; Adl, S.*; Baldursson, S.*; Bechtold, M.*; Cattani, D. J.*; Firbank, L. G.*; Grand, S.*; Gudjonsdottir, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems (Internet), 5, p.663448_1 - 663448_11, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:94.29(Food Science & Technology)Agriculture in the boreal and Arctic regions is perceived as marginal, low intensity and inadequate to satisfy the needs of local communities, but another perspective is that northern agriculture has untapped potential to increase the local supply of food and even contribute to the global food system. Policies across northern jurisdictions target the expansion and intensification of agriculture, contextualized for the diverse social settings and market foci in the north. However, the rapid pace of climate change means that traditional methods of adapting cropping systems and developing infrastructure and regulations for this region cannot keep up with climate change impacts. Moreover, the anticipated conversion of northern cold-climate natural lands to agriculture risks a loss of up to 76% of the carbon stored in vegetation and soils, leading to further environmental impacts. The sustainable development of northern agriculture requires local solutions supported by locally relevant policies. There is an obvious need for the rapid development of a transdisciplinary, cross-jurisdictional, long-term knowledge development, and dissemination program to best serve food needs and an agricultural economy in the boreal and Arctic regions while minimizing the risks to global climate, northern ecosystems and communities.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Zhang, B.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(5), p.218 - 223, 2021/05
The oxidation reaction kinetics on Ti(0001) and Ni(111) surfaces were observed by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation to measure the oxidation state and oxide thickness. After the Ti(0001) surface was wholly covered by TiO with a thickness of 1.2 nm, the rapid growth of n-type TiO proceeded through the diffusion of Ti
proceeded through the diffusion of Ti ions to the TiO
ions to the TiO surface at 400
surface at 400 C. A saturation of oxygen uptake on the TiO surface indicates that the O
C. A saturation of oxygen uptake on the TiO surface indicates that the O sticking coefficient on the TiO surface is negligibly small and the segregation of Ti to the TiO surface is a trigger to initiate the TiO
sticking coefficient on the TiO surface is negligibly small and the segregation of Ti to the TiO surface is a trigger to initiate the TiO growth. On the Ni(111) surface at 350
growth. On the Ni(111) surface at 350 C, a thermally stable NiO
C, a thermally stable NiO proceeded preferentially and then the growth of p-type NiO was initiated. The time evolution of NiO thickness was represented by a logarithmic growth model, where the NiO growth is governed by the electron tunneling to the NiO surface.
proceeded preferentially and then the growth of p-type NiO was initiated. The time evolution of NiO thickness was represented by a logarithmic growth model, where the NiO growth is governed by the electron tunneling to the NiO surface.
 -emitting isotope
-emitting isotope  U and abnormal enhancement of
U and abnormal enhancement of  -particle clustering in lightest uranium isotopes
-particle clustering in lightest uranium isotopesZhang, Z. Y.*; Yang, H. B.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, M. L.*; Ma, L.*; 37 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 126(15), p.152502_1 - 152502_6, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:96.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:95.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeakLuo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Leao, J. B.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 12(1), p.392 - 398, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27(Chemistry, Physical)Using neutron spin-echo spectroscopy, we studied the microscopic structural relaxation of a prototypical network ionic liquid ZnCl at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is 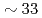 % higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point
% higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point 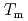 . Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the
. Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the 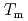 . These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl
. These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
Zhang, D.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, T.*; Abernathy, D. L.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Foley, B. J.*; Yoon, M.*; Choi, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(22), p.224310_1 - 224310_10, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Zhang, F.*; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Lu, Z.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 188, p.21 - 25, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:97.51(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)