Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Dei, Shuntaro; Shibata, Masahito*; Negishi, Kumi*; Sugiura, Yuki; Amano, Yuki; Bateman, K.*; Wilson, J.*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
Results in Earth Sciences (Internet), 3, p.100097_1 - 100097_16, 2025/12
Interactions between cement and host rock in geological repositories for radioactive waste will result in a chemically disturbed zone, which may potentially affect the long-term safety. This paper investigates the chemical evolution at the interface between cement (Ordinary Portland Cement: OPC and Low Alkaline Cement: LAC) and mudstone after 11 years of in situ reactions at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The study combines various analytical techniques to identify the key reactions at the cement-rock interface, including cement dissolution, precipitation of secondary minerals such as calcite and C-(A-)S-H phases, cation exchange in montmorillonite and reduced porosity in mudstone. The study also highlights the effects of cement-mudstone interactions on radionuclide migration, such as reduction of diffusivity due to reduced porosity and enhancement of sorption due to incorporation into secondary minerals in the altered mudstone.
Otsuka, Naohiko*; Devi, V.*; Iwamoto, Osamu
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 225, p.111903_1 - 111903_18, 2025/11
 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Pellegrini, M.*; Yokoyama, Ryo*; Okamoto, Koji*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
 C
CPham, V. H.; Kurata, Masaki; Nagae, Yuji; Ishibashi, Ryo*; Sasaki, Masana*
Corrosion Science, 255, p.113098_1 - 113098_9, 2025/10
Wada, Yuki; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 249, p.127219_1 - 127219_16, 2025/10
Kubo, Kotaro; Mori, Kenji*; Muramatsu, Ken
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114176_1 - 114176_14, 2025/10
Luu, V. N.; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
Soma, Shu; Ishigaki, Masahiro*; Shibamoto, Yasuteru
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 219, p.111455_1 - 111455_12, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Ishii, Katsunori; Morita, Keisuke; Mizuta, Naoki; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Noguchi, Hiroki; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 220, p.111503_1 - 111503_7, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Aiming to establish coupling technologies between a high temperature gas cooled reactor and a hydrogen production plant, JAEA has initiated the HTTR Heat Application Test Project and is conducting the safety design and the safety analysis for the licensing of the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility. The present study proposed a relative evaluation methodology for the demarcation of applicable laws and design standards for the nuclear hydrogen production system and applied it to the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility. The evaluation results showed that a candidate applying the High Pressure Gas Safety Act to the Heat Application Test Facility (hydrogen production plant) and design standards established under the High Pressure Gas Safety Act to the steam reformer did not show the lowest category in any of the metrics, and was proposed as the most superior demarcation option for the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility.
Yildirim, A. C.*; Mei, H.*; Toda, Kanako*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Applied Clay Science, 274, p.107853_1 - 107853_9, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Wang, Z.; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Duan, G.*
Journal of Computational Physics, 537, p.114072_1 - 114072_29, 2025/09
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe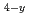 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Cao, T.*; Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; 10 of others*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 940, p.148534_1 - 148534_16, 2025/09
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Miwa, Shuhei
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 218, p.111433_1 - 111433_10, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tamura, Yukiko*; Arakawa, Masato*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Fujinami, So*; Shibata, Motoki*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Yamada, Masako*; Seto, Hideki*; et al.
Polymer, 333, p.128662_1 - 128662_8, 2025/08
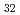 (Al, Zn)
(Al, Zn)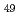 Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorder
Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorderShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Abe, Rion*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Wang, Y.*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 265, p.116730_1 - 116730_7, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0Zheng, R.*; Gong, W.; 6 of others*
Acta Materialia, 293, p.121098_1 - 121098_12, 2025/07
Araki, Shohei; Aizawa, Eiju; Murakami, Takahiko; Arakaki, Yu; Tada, Yuta; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 217, p.111323_1 - 111323_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has modified the STACY from a homogeneous system using solution fuel to a heterogeneous system using fuel rods in order to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris. The modification of the STACY was completed in December 2023. A series of performance inspections were conducted for the start of experimental operations. A new thermal power calibration is required for the performance inspections in order to operate at less than 200 W, which is the permitted thermal power. However, the thermal power measurement method and calibration data used in the former STACY is no longer available due to the modification of the modified STACY. We measured the thermal power of the STACY using the activation method that was improved to adapt to the measurement condition and calibrated the power meter system. Since the positions where activation foils could be installed were very limited, the thermal power was evaluated using numerical calculations supplemented by experimental data. Neutron flux data at the positions of the activation foil was measured by the activation method. Neutron distribution in the core was calculated by the Monte Carlo code MVP. A response function of the activation foil was calculated using the PHITS. The uncertainty of the thermal power measurement was conservatively estimated to be about 15%. Four operations were conducted for the thermal power measurement. The power meter was calibrated by using three operational data and tested with the one operational data. It was found that the indicated value of the meter adjusted by the STACY before the modification work would tend to overestimate the actual output by about 40%. In addition, the current calibration was able to calibrate the meter to within 3% accuracy.
Mochizuki, Akihito; Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Shibata, Masahito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 22, p.e04648_1 - e04648_20, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0The properties of low-pH cement used in the geological disposal of radioactive waste may change through atmospheric carbonation and degradation caused by groundwater during the long-term operation of a repository. In this study, we investigated the effects of atmospheric carbonation and groundwater contact on the chemical, microstructural, and transport properties of shotcrete made from low-pH, high-fly-ash silica-fume cement (HFSC) over a period of 16 years in an underground research laboratory. In both carbonated and degraded zones of the HFSC shotcrete, capillary porosity increased for pores of  300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion Science, 251, p.112897_1 - 112897_15, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Experimental and modeling studies of the oxygen ingression at the crevices of stainless steels were conducted in high-temperature water (288 C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression,
C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression, 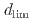 , was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite
, was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite  magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the
magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the 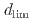 position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell.
position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell. 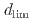 increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.