Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.245110_1 - 245110_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a mean-field theory of a novel Kondo effect emerging in systems without a Fermi surface, which instead emerges under strong magnetic fields. We determine the magnitude of the Kondo condensate, which is a particle pairing composed of conducting Dirac fermions and localized impurities. We focus on the competition between the Kondo effect and the energy gap formation that stems from the pairing among the Dirac fermions leading to the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking. We find that this competition induces a quantum critical point. We also investigate finite-temperature effects. This system at vanishing fermion density can be studied with Monte Carlo lattice simulations, which do not suffer from the sign problem.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Ina, Takuya; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Fluid Dynamics Research, 55(6), p.065501_1 - 065501_25, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Mechanics)We investigate the applicability of the data assimilation (DA) to large eddy simulations (LESs) based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). We carry out the observing system simulation experiment of a two-dimensional (2D) forced isotropic turbulence, and examine the DA accuracy of the nudging and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with spatially sparse and noisy observation data of flow fields. The advantage of the LETKF is that it does not require computing spatial interpolation and/or an inverse problem between the macroscopic variables (the density and the pressure) and the velocity distribution function of the LBM, while the nudging introduces additional models for them. The numerical experiments with 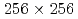 grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with
grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with 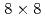 observation points (
observation points (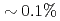 of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
Chiba, Kaori*; Matsui, Takuro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Yutani, Katsuhide*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Protein Science, 32(10), p.e4765_1 - e4765_13, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Wada, Yuki*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Morimoto, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Yoshitaka*; Shinoda, Taro*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 128(15), p.e2023JD038606_1 - e2023JD038606_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.15(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138017_1 - 138017_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The Casimir effect is a quantum phenomenon induced by the zero-point energy of relativistic fields confined in a finite-size system. This effect for photon fields has been studied for a long time, while the realization of counterparts for fermion fields in Dirac/Weyl semimetals is an open question. We theoretically demonstrate the typical properties of the Casimir effect for relativistic electron fields in Dirac/Weyl semimetals and show the results from an effective Hamiltonian for realistic materials such as Cd As
As and Na
and Na Bi. We find an oscillation of the Casimir energy as a function of the thickness of the thin film, which stems from the existence of Dirac/Weyl nodes in momentum space. Experimentally, such an effect can be observed in thin films of semimetals, where the thickness dependence of thermodynamic quantities is affected by the Casimir energy.
Bi. We find an oscillation of the Casimir energy as a function of the thickness of the thin film, which stems from the existence of Dirac/Weyl nodes in momentum space. Experimentally, such an effect can be observed in thin films of semimetals, where the thickness dependence of thermodynamic quantities is affected by the Casimir energy.
Tsurumi, Miwa*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Ikkatai, Yuko*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; Shinoda, Taro*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Tsuji, Naoki*; Diniz, G.*; Kataoka, Jun*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 50(13), p.e2023GL103612_1 - e2023GL103612_9, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Takagi, Hirotaka*; Takagi, Rina*; Minami, Susumu*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Michito*; Yanagi, Yuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Khanh, N.*; Karube, Kosuke*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Tetsuya*; Kato, Takeo*; Oue, Daigo*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 107(8), p.L180406_1 - L180406_6, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yama, Masaki*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kato, Takeo*
Physical Review B, 107(17), p.174414_1 - 174414_15, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.074015_1 - 074015_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.75(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated, which is based on 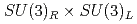 chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the
chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the 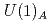 and flavor
and flavor 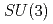 symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons
symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons 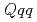 (
(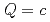 ,
,  and
and 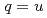 ,
,  ,
,  ), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
Sano, Ryotaro*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review Letters, 130(16), p.166201_1 - 166201_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 276, p.01015_1 - 01015_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We investigate the QCD phase diagram in strong magnetic fields with heavy-quark impurities and determine the ground state within the mean-field analysis. The ground state is characterized by magnitudes of the pairing not only between the light quark and antiquark, i.e., chiral condensate, but also between the light quark and heavy-quark impurity, dubbed the Kondo condensate. We propose signatures of the interplay and/or competition between those two pairing phenomena reflected in the magnitude of the chiral condensate that is saturated with respect to the magnetic-field strength and anomalously increases with increasing temperature.
Ishikawa, Takuto*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kato, Takeo*
Physical Review B, 107(5), p.054426_1 - 054426_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Yan, M.*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Nanomaterials (Internet), 13(1), p.76_1 - 76_9, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:54.89(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)To enhance neutron intensity below cold neutrons, it is proposed that nanosized graphene aggregation could facilitate neutron coherent scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamond. It might also be possible to use it in high neutron radiation conditions due to graphene's strong sp2 bonds. Using the RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source and iMATERIA at J-PARC, we performed neutron measurement experiments, total neutron cross-section, and small-angle neutron scattering on nanosized graphene aggregation. The measured data revealed, for the first time, that nanosized graphene aggregation increased the total cross-sections and small-angle scattering in the cold neutron energy region, most likely due to coherent scattering, resulting in higher neutron intensities, similar to nanodiamond.
 O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Furukawa, Hazuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(9), p.094707_1 - 094707_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)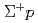 elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/c
elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/cNanamura, Takuya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Naruki, Megumi; Sato, Susumu; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(9), p.093D01_1 - 093D01_35, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:67.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
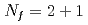 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.050_1 - 050_9, 2022/07
In the early days of QCD, the axial  anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the
anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the 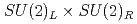 symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial
symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial  breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for
breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for 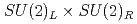 breaking, is actually dominated by the axial
breaking, is actually dominated by the axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 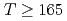 MeV.
MeV.