Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Higuchi, Yuki*; Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kato, Satoru*; Hibi, Shogo*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Harada, Masashi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.33_1 - 33_7, 2024/02
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Kudo, Takuto*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Sentoku, Sawako*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.1797_1 - 1797_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0The amount of C in steel, which is critical in determining its properties, is strongly influenced by steel production technology. We propose a novel method of quantifying the bulk C content in steel non-destructively using muons. This revolutionary method may be used not only in the quality control of steel in production, but also in analyzing precious steel archaeological artifacts. A negatively charged muon forms an atomic system owing to its negative charge, and is finally absorbed into the nucleus or decays to an electron. The lifetimes of muons differ significantly, depending on whether they are trapped by Fe or C atoms, and identifying the elemental content at the muon stoppage position is possible via muon lifetime measurements. The relationship between the muon capture probabilities of C/Fe and the elemental content of C exhibits a good linearity, and the C content in the steel may be quantitatively determined via muon lifetime measurements. Furthermore, by controlling the incident energies of the muons, they may be stopped in each layer of a stacked sample consisting of three types of steel plates with thicknesses of 0.5 mm, and we successfully determined the C contents in the range 0.20 - 1.03 wt% depth-selectively, without sample destruction.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2023-020, 90 Pages, 2023/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Technology development of diamond-base neutron sensors and radiation-resistive integrated-circuits for shielding-free criticality approach monitoring system" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to develop key components of neutron detection system without a radiation shield for a criticality approach monitoring system with high neutron detection efficiency (a few count/nv) under high gamma ray background (1kGy/h). Developed components are neutron detection devices based on diamond sensors and a high radiation resistive signal-processing data-transfer system based on radiation resistive integrated circuit technologies.
Tsuji, Hayato*; Nakahata, Masaki*; Hishida, Mafumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Inoue, Takeru*; Egawa, Yasunobu*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(49), p.11235 - 11241, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Hiroki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Setoyama, Daigo*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Sasaki, Tsuyoshi*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.22082_1 - 22082_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)

 Sn
Sn (
( = Rh and Ir)
= Rh and Ir)Shimoda, Ami*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Hironori*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 38, p.011091_1 - 011091_6, 2023/05
 laser stripping at J-PARC RCS
laser stripping at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.272 - 276, 2023/01
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2022-031, 89 Pages, 2022/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Technology development of diamond-base neutron sensors and radiation-resistive integrated-circuits for shielding-free criticality approach monitoring system" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop key components of neutron detection system without a radiation shield for a criticality approach monitoring system. It is required high neutron detection efficiency for a few cps/nv under 1 kGy/h and compact-light-weight to fit constraints of the penetration size and the payload. The project aims to design and evaluate neutron detection devices based on diamond sensors and a high radiation resistive signal-processing data-transfer system based on radiation resistive integrated circuit technologies …
 Mn
Mn Te studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
Te studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroismVerma, V.*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Ishikawa, Koichiro*; Singh, V. R.*; Ishigami, Keisuke*; Shibata, Goro; Kadono, Toshiharu*; Koide, Tsuneharu*; Kuroda, Shinji*; Fujimori, Atsushi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 642, p.414129_1 - 414129_5, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.42(Physics, Condensed Matter)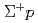 elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/c
elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/cNanamura, Takuya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Naruki, Megumi; Sato, Susumu; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(9), p.093D01_1 - 093D01_35, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:67.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)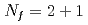 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.050_1 - 050_9, 2022/07
In the early days of QCD, the axial  anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the
anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the 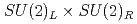 symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial
symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial  breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for
breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for 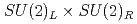 breaking, is actually dominated by the axial
breaking, is actually dominated by the axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 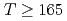 MeV.
MeV.
 anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperature
anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperatureAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(2), p.023B05_1 - 023B05_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:81.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The chiral susceptibility, or the first derivative of the chiral condensate with respect to the quark mass, is often used as a probe for the QCD phase transition since the chiral condensate is an order parameter of 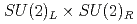 symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial
symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial  symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial
symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial  breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial
breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial  breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial
breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 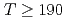 MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2021-042, 115 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and development of radiation-resistant sensor for fuel debris by integrating advanced measurement technologies" conducted from FY2018 to FY2020. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2020, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to in-situ measure and analyze the distribution status and criticality of flooded fuel debris. For this purpose, we construct a neutron measurement system by developing compact diamond neutron sensor and integrated circuit whose radiation resistance was improved by circuit design.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2021-038, 65 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Technology development of diamond-base neutron sensors and radiation-resistive integrated-circuits for shielding-free criticality approach monitoring system" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to develop key components of neutron detection system without a radiation shield for a criticality approach monitoring system. It is required high neutron detection efficiency for a few cps/nv under high gamma ray radiation environment (i.e. 1 kGy/h maximum) and compact-light-weight to fit constraints of the penetration size and the payload.
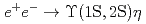 and
and 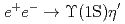 at
at 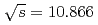 GeV with the Belle detector
GeV with the Belle detectorKovalenko, E.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 181 of others*
Physical Review D, 104(11), p.112006_1 - 112006_12, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Astronomy & Astrophysics)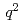 moments of inclusive
moments of inclusive 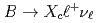 decays with hadronic tagging
decays with hadronic taggingvan Tonder, R.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 202 of others*
Physical Review D, 104(11), p.112011_1 - 112011_32, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:65.5(Astronomy & Astrophysics)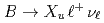 decays
decaysCao, L.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 199 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 127(26), p.261801_1 - 261801_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:49.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)