Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Nakayoshi, Akira; Arai, Yoichi; Sato, Takumi; Ohgi, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Morishita, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-005, 418 Pages, 2023/12
For safe and steady decommissioning of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), information concerning composition and physical/chemical properties of fuel debris generated in the reactors should be estimated and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work including the retrieval of fuel debris and the subsequent storage. For this purpose, in FY2021, samples of contaminants (the wiped smear samples and the deposits) obtained through the internal investigation of the 1F Unit 2 were analyzed to clarify the components and to characterize the micro-particles containing uranium originated from fuel (U-bearing particles) in detail. This report summarized the results of analyses performed in FY2021, including the microscopic analysis by SEM and TEM, radiation analysis, and elemental analysis by ICP-MS, as a database for evaluating the main features of each sample and the probable formation mechanism of the U-bearing particles.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
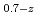 Pu
Pu Am
Am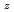 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sugimoto, Masatoshi*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Hino, Tetsushi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101156_1 - 101156_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)In current nuclear fuel cycle systems, to reduce the amount of high-level radioactive waste, minor actinides (MAs) bearing MOX fuel is one option for burning MAs using fast reactor. However, the effects of Am content in fuel on thermal conductivity are unclear because there are no experimental data on thermal conductivity of high Am bearing MOX fuel. In this study, The thermal conductivities of near stoichiometric (U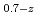 Pu
Pu Am
Am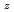 )O
)O solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT)
solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT) ) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U
) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U and Am
and Am . B values were independent of Am content.
. B values were independent of Am content.
Watanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Ueta, Shohei; Yan, X.
Ceramics International, 48(6), p.8706 - 8708, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:75.06(Materials Science, Ceramics)Previous studies have used various methods for sintering of SiC, carbon, and SiC/carbon functionally graded materials (FGM). However, no experimental studies on SiC/graphite FGM manufacturing using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) method have been reported. In this study, a SiC/graphite FGM specimen has been fabricated using SPS. The interface between the adjacent layers of the sintered specimen exhibits no apparent defects such as gaps or delaminations. The SiC and graphite phases in the specimen show no substantial change before and after sintering.
Morishita, Kazuki; Sato, Takumi; Onishi, Takashi; Seki, Takayuki*; Sekine, Shinichi*; Okitsu, Yuichi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-024, 27 Pages, 2021/10
In the case of Plutonium (Pu)-bearing organic materials, organic materials are decomposed by alpha rays emitted mainly from Pu to generate hydrogen gas and other substances. Therefore, to safely store Pu-bearing organic materials for an extended period of time, organic materials must be eliminated. In addition, carbide and nitride fuels must be converted into oxides for safe storage in order to prevent the exothermal reaction of these fuels with oxygen/moisture in air. A survey of the literature on the stabilization treatment of Pu-bearing organic materials confirmed that organic materials can be decomposed and removed by heating at 950  C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950
C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950  C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950
C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950  C was lower than 2.1
C was lower than 2.1 10
10 Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950
Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950  C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.

Watanabe, Masashi; Seki, Takayuki*
Materials Science & Engineering B, 272, p.115369_1 - 115369_6, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effect of oxygen non-stoichiometry on the initial sintering behavior of CeO was investigated. It was found that the initial sintering of the stoichiometric and hypo-stoichiometric composition was controlled by the grain boundary diffusion. The activation energies of cation diffusion were derived from initial sintering data. Moreover, it is suggested that the cation diffusion was caused by a vacancy mechanism.
was investigated. It was found that the initial sintering of the stoichiometric and hypo-stoichiometric composition was controlled by the grain boundary diffusion. The activation energies of cation diffusion were derived from initial sintering data. Moreover, it is suggested that the cation diffusion was caused by a vacancy mechanism.
Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Katsuyama, Kozo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.383 - 398, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Mimura, Hitoshi*
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 31(3), p.43 - 49, 2020/10
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Onishi, Takashi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Katsuyama, Kozo; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 536, p.152119_1 - 152119_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to obtain the release rate coefficients from fuels for fast reactors (FRs), heating tests and the subsequent analyses of the fission products (FPs) and actinides that are released were carried out using samples of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel pellets irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo. Three heating tests targeting temperatures of 2773, 2973 and 3173 K were conducted using an FP release behavior test apparatus equipped with a high-frequency induction furnace and solid FP sampling systems consisting of a thermal gradient tube (TGT) and filters. Irradiated fuel pellets were placed into a tungsten crucible, then loaded into the induction furnace. The temperature was raised continuously at a heating rate of 10 K/s to the targeted temperature and maintained for 500 s in a flowing argon gas atmosphere. The FPs and actinides released from the MOX fuels and deposited in the TGT and filters were quantified by gamma-ray spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis. Based on the analysis, the release rates of radionuclides from MOX fuels for FR were obtained and compared with literature data for light water reactor (LWR) fuels. The release rate coefficients of FPs obtained in this study were found to be similar to or lower than the literature values for LWR fuels. It was also found that the release rate coefficient data for actinides were within the range of variation of literature values for LWR fuels.
Sakamoto, Naoki; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Mizukoshi, Yasutaka
Hozengaku, 19(2), p.125 - 126, 2020/07
The five post-irradiation examination facilities in JAEA's Oarai research and development institute have been operated for over 40 years in order to investigate the irradiation performance of fast reactor fuel materials. The equipment associated with these facilities has been managed to maintain secure from the problems occurred in the process of aging. Therefore, we established a safety assessment method for aging facilities in 2002, and we have been conducting maintenance management of facilities since then. In this study, improvement plans of the safety assessment method are considered in order to solve the issues detected as a result of analysis of past maintenance information.
Onishi, Takashi; Sekioka, Ken*; Suto, Mitsuo*; Tanaka, Kosuke; Koyama, Shinichi; Inaba, Yusuke*; Takahashi, Hideharu*; Harigai, Miki*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Energy Procedia, 131, p.151 - 156, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:98.3(Energy & Fuels)no abstracts in English
Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kosuke; Koyama, Shinichi; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Seki, Takayuki; Katsuyama, Kozo
NEA/NSC/R(2017)3, p.341 - 350, 2017/11
In order to investigate the effect of the addition of americium to MOX fuels on the irradiation behaviour, the "Am-1" program is being conducted at the JAEA. The Am-1 program consists of two short-term irradiation tests of 10-min and 24-h irradiation periods, and a steady-state irradiation test. The short-term irradiation tests and their post irradiation examinations (PIEs) have been successfully completed. To date, the data for PIE of the Am-MOX fuels focused on the microstructural evolution and redistribution behaviour of Am at the initial stage of irradiation have been obtained and reported. In this paper, the results obtained from the Am-1 program are reviewed and detailed descriptions of the fabrication and inspection techniques for the Am-MOX fuels prepared for the program are provided. PIE data for the Am-MOX fuels at the initial stage of irradiation have been accumulated. In this paper, unpublished PIE data for the Am-MOX fuels are also presented.
 inert matrix fuel
inert matrix fuelMiwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 487, p.1 - 4, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxidation and reduction behaviors of prototypic MgO-based inert matrix fuels (IMFs) containing PuO were experimentally investigated by means of thermogravimetry. The oxidation and reduction kinetics of the MgO-PuO
were experimentally investigated by means of thermogravimetry. The oxidation and reduction kinetics of the MgO-PuO specimen were determined. The oxidation and reduction rates of the MgO-PuO
specimen were determined. The oxidation and reduction rates of the MgO-PuO were found to be low compared with those of PuO
were found to be low compared with those of PuO . It is note that the changes in O/Pu ratios of MgO-PuO
. It is note that the changes in O/Pu ratios of MgO-PuO from stoichiometry were smaller than those of PuO
from stoichiometry were smaller than those of PuO at high oxygen partial pressure. From these results, it can be said that MgO matrix lower the oxygen supply and release of PuO
at high oxygen partial pressure. From these results, it can be said that MgO matrix lower the oxygen supply and release of PuO , which is preferable as the minor actinides incineration devices, since the high oxygen potentials of minor actinide oxides can cause certain problems in terms of thermochemical aspects such as enlarged cladding inner-surface corrosion.
, which is preferable as the minor actinides incineration devices, since the high oxygen potentials of minor actinide oxides can cause certain problems in terms of thermochemical aspects such as enlarged cladding inner-surface corrosion.
Ishikawa, Takashi; Onishi, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Katsuyama, Kozo
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2017/00
Tamaoki, Yuichi; Omori, Tsuyoshi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Mizukoshi, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Naoki
Proceedings of 53rd Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling Working Group (HOTLAB 2016) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/11
Post irradiation examinations are conducted in hot laboratories in Oarai Research and Development Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in order to develop fuels and materials for fast reactors. These facilities, the majority of which were constructed in the 1970s, have accumulated operating experience over a period of more than 40 years. Continuous operational safety requires the maintenance of important equipment such as electronic devices, manipulators, in-cell cranes, as well as air conditioning and ventilation systems. A method for the periodic safety review for hot laboratories based on the periodic safety review method employed for preventive maintenance at commercialized power reactors in Japan has been developed. In this paper, the status of implementation of the periodic safety review for hot laboratories using the safety review method are introduced.
Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Nozaki, Takahiro*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 465, p.840 - 842, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential of a prototypic Mo-cermet fuel containing PuO was experimentally determined. It was shown that the oxygen potentials of Mo-cermet fuel containing PuO
was experimentally determined. It was shown that the oxygen potentials of Mo-cermet fuel containing PuO were the same as those of pure PuO
were the same as those of pure PuO . It was also confirmed that the gradual oxidation of the Mo matrix occurred only above the oxygen potential of Mo/MoO
. It was also confirmed that the gradual oxidation of the Mo matrix occurred only above the oxygen potential of Mo/MoO . It is concluded that the oxidation-reduction behavior of the Mo-cermet fuel can be evaluated individually for each phase of actinides oxide and Mo matrix. Better phase structures of the Mo-cermet fuel for taking full advantage of the oxidation-reduction controllability were suggested by the confinement of the actinides oxide phase with Mo.
. It is concluded that the oxidation-reduction behavior of the Mo-cermet fuel can be evaluated individually for each phase of actinides oxide and Mo matrix. Better phase structures of the Mo-cermet fuel for taking full advantage of the oxidation-reduction controllability were suggested by the confinement of the actinides oxide phase with Mo.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu; Hirosawa, Takashi; Kurosaki, Ken*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1285 - 1289, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Polycrystalline specimens of americium-containing barium plutonate have been prepared by mixing the appropriate amounts of (Pu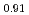 Am
Am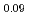 )O
)O and BaCO
and BaCO powders followed by reacting and sintering at 1600 K under the flowing gas atmosphere of dry-air. The sintered specimens had a single phase of orthorhombic perovskite structure and were crack-free. The elastic moduli were determined from the longitudinal and shear sound velocities. The Debye temperature was also determined from the sound velocities and lattice parameter measurements. The thermal conductivity was calculated from the measured density at room temperature, literature values of heat capacity, and thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method in vacuum. The thermal conductivity of americium-containing barium plutonate was roughly independent of the temperature and was almost the same magnitude as that of BaPuO
powders followed by reacting and sintering at 1600 K under the flowing gas atmosphere of dry-air. The sintered specimens had a single phase of orthorhombic perovskite structure and were crack-free. The elastic moduli were determined from the longitudinal and shear sound velocities. The Debye temperature was also determined from the sound velocities and lattice parameter measurements. The thermal conductivity was calculated from the measured density at room temperature, literature values of heat capacity, and thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method in vacuum. The thermal conductivity of americium-containing barium plutonate was roughly independent of the temperature and was almost the same magnitude as that of BaPuO and BaUO
and BaUO .
.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Koyama, Shinichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.619 - 621, 2015/10
In order to evaluate the microstructural change behavior of Am-MOX fuels at the initial stage of irradiation, detailed investigations using image analysis were performed on X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) images and on ceramographs from fuels irradiated in both B11 and B14.
Sato, Isamu; Tanaka, Kosuke; Koyama, Shinichi; Matsushima, Kenichi*; Matsunaga, Junji*; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Endo, Hiroshi*; Haga, Kazuo*
Energy Procedia, 82, p.86 - 91, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experiments simulating overheating conditions of fast reactor severe accidents have been previously carried out with irradiated fuels. For the present study, the chemical forms of the fission products (FPs) included in the irradiated fuels were evaluated by thermochemical equilibrium calculations. At temperatures of 2773 K and 2973 K, the most stable forms of Cs, I, Te, Sb, Pd and Ag are gaseous compounds. Cs and Sb detected in the thermal gradient tube (TGT) in the experiments can take gaseous chemical forms of elemental Cs, CsI, Cs MoO
MoO , CsO and elemental Sb, SbO, SbTe, respectively. By comparing experimental results and the estimations, it is seen CsI thermochemically behaves in a manner that traps it in the TGT, while elemental Cs trends to move as fine particles. The moving behavior of the gaseous FPs will obey not only thermochemical principles, but also those of particle dynamics.
, CsO and elemental Sb, SbO, SbTe, respectively. By comparing experimental results and the estimations, it is seen CsI thermochemically behaves in a manner that traps it in the TGT, while elemental Cs trends to move as fine particles. The moving behavior of the gaseous FPs will obey not only thermochemical principles, but also those of particle dynamics.
Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Mimura, Hitoshi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 82, p.69 - 73, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English