Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Nakayoshi, Akira; Arai, Yoichi; Sato, Takumi; Ohgi, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Morishita, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-005, 418 Pages, 2023/12
For safe and steady decommissioning of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), information concerning composition and physical/chemical properties of fuel debris generated in the reactors should be estimated and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work including the retrieval of fuel debris and the subsequent storage. For this purpose, in FY2021, samples of contaminants (the wiped smear samples and the deposits) obtained through the internal investigation of the 1F Unit 2 were analyzed to clarify the components and to characterize the micro-particles containing uranium originated from fuel (U-bearing particles) in detail. This report summarized the results of analyses performed in FY2021, including the microscopic analysis by SEM and TEM, radiation analysis, and elemental analysis by ICP-MS, as a database for evaluating the main features of each sample and the probable formation mechanism of the U-bearing particles.
Tsai, T.-H.; Sasaki, Shinji; Maeda, Koji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.715 - 723, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
Nakayoshi, Akira; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Sasaki, Shinji; Maeda, Koji
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-011, 279 Pages, 2022/03
At the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), an investigation inside the reactors has been carried out, and R&D has been made on methods of fuel debris retrieval and storage after retrieval. In order to carry out the decommissioning work safely and steadily, understanding characteristics of fuel debris in the reactors is required. Therefore, in the development of technologies for grasping and analyzing properties of fuel debris project, the characteristics of simulated fuel debris, such as hardness, drying behavior, etc., of fuel debris for design of removal and storage, have been investigated and estimated, and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work. As part of this project, U-containing particles in samples (e.g., deposit on the investigation equipment, sediment in the reactors, etc.) obtained during the internal investigation of the reactors of 1F units 1 to 3 were analyzed. This report summarized the results of FE-SEM/WDX, FE-SEM/EDS, STEM/EDS, and TEM analysis, which were extracted from all analysis results obtained, as a database for the evaluation of the generation mechanism of U-containing particles. The analyses were performed at the JAEA Oarai Research and Development Institute and Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co., LTD.
Sakamoto, Naoki; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Mizukoshi, Yasutaka
Hozengaku, 19(2), p.125 - 126, 2020/07
The five post-irradiation examination facilities in JAEA's Oarai research and development institute have been operated for over 40 years in order to investigate the irradiation performance of fast reactor fuel materials. The equipment associated with these facilities has been managed to maintain secure from the problems occurred in the process of aging. Therefore, we established a safety assessment method for aging facilities in 2002, and we have been conducting maintenance management of facilities since then. In this study, improvement plans of the safety assessment method are considered in order to solve the issues detected as a result of analysis of past maintenance information.
Abe, Yuta; Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 6(2), p.021113_1 - 021113_9, 2020/04
Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Enerugi Rebyu, 39(1), p.44 - 46, 2019/01
For performance improvement of next-generation nuclear system such as fast reactor, it has been expected to develop advanced material resistant to severe in-reactor environment (i.e. high-dose neutron irradiation at high-temperature). Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel for long life fuel cladding tube of fast reactor. Application of ODS ferritic steel to fast reactor fuel can extend the fuel life time twice or more as long as the fuel with conventional cladding tube (i.e. modified SUS316), thus reducing fuel exchange frequency and fuel cost. It can be adaptable to high-temperature plant operation, which is favorable for improvement of power generation efficiency. This paper interprets the development of ODS ferritic steel cladding tube for sodium-cooled fast reactor, which has been led by JAEA for dozens of years.
Abe, Yuta; Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Abe, Yuta; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 4(2), p.020901_1 - 020901_8, 2018/04
A new experimental program using non-transfer type plasma heating is under consideration in JAEA to clarify the uncertainty on core-material relocation (CMR) behavior of BWR. In order to confirm the applicability of this new technology, authors performed preparatory plasma heating tests using small-scale test pieces (107 mm  107 mm
107 mm  222 mm (height)). An excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating to melting high melting-temperature materials such as ZrO
222 mm (height)). An excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating to melting high melting-temperature materials such as ZrO has been obtained. In addition, molten pool was formed at the middle height of the test piece indicating its capability to simulate the initial phase of core degradation behavior consistent with the real UO
has been obtained. In addition, molten pool was formed at the middle height of the test piece indicating its capability to simulate the initial phase of core degradation behavior consistent with the real UO fuel Phebus-FPT tests. Furthermore, application of EPMA, SEM/EDX and X-ray CT led to a conclusion that the pool formed consisted mainly of Zr with some concentration of oxygen which tended to be enhanced at the upper surface region of the pool. Based on these results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the Severe Accident (SA) experimental study was obtained.
fuel Phebus-FPT tests. Furthermore, application of EPMA, SEM/EDX and X-ray CT led to a conclusion that the pool formed consisted mainly of Zr with some concentration of oxygen which tended to be enhanced at the upper surface region of the pool. Based on these results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the Severe Accident (SA) experimental study was obtained.
Sasaki, Shinji; Maeda, Koji; Furuya, Hirotaka*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.276 - 282, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishimi, Akihiro; Katsuyama, Kozo; Maeda, Koji; Furuya, Hirotaka*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(11), p.1274 - 1276, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)Two- and three-dimensional images were obtained in the reaction product between zircaloy and MOX fuel by X-ray CT. In addition, the  -ray intensity distributions of two fission products (Cs-137 and Eu-154) and one neutron-activated nuclide (Co-60) were obtained in this specimen by
-ray intensity distributions of two fission products (Cs-137 and Eu-154) and one neutron-activated nuclide (Co-60) were obtained in this specimen by  -ray measurements. The average values of the fuel density (about 10.5 g/cm
-ray measurements. The average values of the fuel density (about 10.5 g/cm ) and the cladding density (about 6.55 g/cm
) and the cladding density (about 6.55 g/cm ) were obtained in the metallic phase region by evaluation of the density distributions on two-dimensional X-ray CT images. In addition, the distributions of the roughly crushed fuel pellet and the pores in the specimen could be clearly observed on the three-dimensional X-ray CT images. From the
) were obtained in the metallic phase region by evaluation of the density distributions on two-dimensional X-ray CT images. In addition, the distributions of the roughly crushed fuel pellet and the pores in the specimen could be clearly observed on the three-dimensional X-ray CT images. From the  -ray measurement, Cs-137 was observed on the unreacted fuel region and the region where pores exist in the metallic phase, and Eu-154 was widely distributed to all regions. On the other hand, Co-60 was confirmed only in the metallic phase region.
-ray measurement, Cs-137 was observed on the unreacted fuel region and the region where pores exist in the metallic phase, and Eu-154 was widely distributed to all regions. On the other hand, Co-60 was confirmed only in the metallic phase region.

Kato, Masato; Nakamura, Hiroki; Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Machida, Masahiko
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 375, p.57 - 70, 2017/05
The basic properties of PuO were reviewed, and the equilibrium defects in PuO
were reviewed, and the equilibrium defects in PuO were evaluated from the experimental data of the oxygen potential and electrical conductivity as well as the Ab-initio calculation results. Consistency among various properties was confirmed, and the mechanistic models for thermal property representations were derived.
were evaluated from the experimental data of the oxygen potential and electrical conductivity as well as the Ab-initio calculation results. Consistency among various properties was confirmed, and the mechanistic models for thermal property representations were derived.
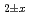
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 487, p.424 - 432, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:75.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential of (U,Pu)O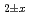 was evaluated based on defect chemistry using an updated experimental data set. The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation
was evaluated based on defect chemistry using an updated experimental data set. The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation  in (U,Pu)O
in (U,Pu)O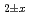 was analyzed, and equilibrium constants of defect formation were determined as functions of Pu content and temperature. Brouwer's diagrams were constructed using the determined equilibrium constants, and a relational equation to determine O/M ratio was derived as functions of O/M ratio, Pu content and temperature. In addition, relationship between oxygen potential and oxygen diffusion coefficients were described.
was analyzed, and equilibrium constants of defect formation were determined as functions of Pu content and temperature. Brouwer's diagrams were constructed using the determined equilibrium constants, and a relational equation to determine O/M ratio was derived as functions of O/M ratio, Pu content and temperature. In addition, relationship between oxygen potential and oxygen diffusion coefficients were described.
Abe, Yuta; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/04
Sasaki, Shinji; Tanno, Takashi; Maeda, Koji
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2017/00
During irradiation in a fast reactor, the microstructure change of the mixed oxide fuels and the changes of element distributions occur because of a radial temperature gradient. Therefore, it is important to study the irradiation behavior of MA-MOX for advancement of fast reactor fuels. In order to make detailed observations of microstructure and elemental analyses of MA-MOX, irradiated MA-MOX specimens were carried out PIE by using a FE-SEM equipped with WDX. Because fuel samples have high radio activities and emit alpha-particles, the instrument was modified. the instrument was installed in a lead shield box and the control unit was separately located outside the box. The microstructure changes were observed in irradiated MA-MOX specimen. The characteristic X-rays peaks were detected successfully. By measuring the intensities of characteristic X-rays, it was tried quantitative analysis of U, Pu, Am along radial direction of irradiated specimen.
Katsuyama, Kozo; Ishimi, Akihiro; Tanaka, Kosuke; Kihara, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 53rd Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling Working Group (HOTLAB 2016) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2016/11
Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, a feasibility study on the application of X-ray CT technique for observation of the inner condition of the fuel debris was initiated. First, a preliminary test was performed using a dummy specimen of irradiated fuel pellets, which was heated to 2373 K. As a result, we obtained high resolution X-ray CT images in which the small pieces of fuel pellets could be clearly distinguished from one another. Analyzing these X-ray CT images enables us to know the density distribution of the fuel debris.
Ishimi, Akihiro; Katsuyama, Kozo; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; *
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(7), p.951 - 956, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)Three fuel rods containing hollow MOX pellets of uranium and plutonium oxides were fabricated and irradiated at a high linear heat rate to burn-up of nearly 30,000 MWd/t in the experimental fast reactor, JOYO MK-II. After irradiation, one of the fuel rods pellets was examined by X-ray CT and conventional nondestructive and destructive methods. Swelling rate was evaluated by both dimensional change and radial density distribution. There were no differences between both types of results and it was concluded that swelling rate can be examined in detail by the X-ray CT technique by dismantling the assembly. In addition, the swelling rate of hollow pellets was nearly the same as values reported for the fuel rods containing solid pellets. LHR was higher in the examined fuel rod containing hollow pellets than in the conventional fuel rod containing solid pellets, but fission gas release rates for both fuel rods were nearly the same. Since it is possible to decrease the maximum temperature in the radial center of the hollow fuel pellets, they can be effectively utilized in reactor operation at higher LHR.
Abe, Yuta; Sato, Ikken; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nakagiri, Toshio; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2016/06
A new experimental program using non-transfer type plasma heating is under consideration in JAEA to clarify the uncertainty on core-material relocation (CMR) behavior of BWR. In order to confirm the applicability of this new technology, authors performed preparatory plasma heating tests using small-scale test pieces (107 mm  107 mm
107 mm  222 mmh). Based on these preliminary results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the SA (Severe Accident) experimental study was obtained. Furthermore, JAEA is preparing for the next step intermediate-scale preparatory tests in 2016 using ca. 50 rods and a control blade that would not only confirm its technical applicability, but also some insights relevant to the issue on CMR itself.
222 mmh). Based on these preliminary results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the SA (Severe Accident) experimental study was obtained. Furthermore, JAEA is preparing for the next step intermediate-scale preparatory tests in 2016 using ca. 50 rods and a control blade that would not only confirm its technical applicability, but also some insights relevant to the issue on CMR itself.
Kato, Masato
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 114, p.987 - 988, 2016/06
In Japan, uranium and plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) has been developed as fuels of sodium-cooled fast reactors. The developing MOX fuels come in variety of O/M ratio, Pu content, minor actinide (MA) content and density. We have studied a science based fuel technology to evaluate fuel behaviors in fabrication process and irradiation condition of such various fuels. The technologies which are constructed based on experimental database can apply to mechanistic evaluation of fuel behaviors. To develop the science based fuel technology, many different varieties of basic properties have been investigated, and experimental database was constructed. And a mechanistic physical property model has been studied. The models contribute to describe various behaviors in fuel fabrication process and irradiation condition.