Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Secretariat of Symposium on Advanced Photon Research
JAEA-Conf 2016-001, 53 Pages, 2016/03
The 16th Symposium on Advanced Photon Research was held at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA-KPSI) in Kizugawa city, Kyoto on October 15 - 16, 2015. This report consists of invited and contributed papers presented at the oral and poster sessions in the Symposium.
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Fukuda, Yuji
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 58(3), p.034013_1 - 034013_6, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:77.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to understand the synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas dynamics, we have conducted ion acceleration experiments using CO clusters (250 nm in dia.) embedded in background H
clusters (250 nm in dia.) embedded in background H gas with the J-KAREN laser (1 J, 40 fs, 10
gas with the J-KAREN laser (1 J, 40 fs, 10 contrast) at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of etch pit positions on CR-39 and their structures including the etch pit growth behavior analysis with the multi-step etching technique, energy spectra for protons from the background gas and carbon/oxygen ions from the clusters are obtained separately. The maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are determined as 1.6 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles.
contrast) at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of etch pit positions on CR-39 and their structures including the etch pit growth behavior analysis with the multi-step etching technique, energy spectra for protons from the background gas and carbon/oxygen ions from the clusters are obtained separately. The maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are determined as 1.6 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles.
Oks, E.*; Dalimier, E.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Andreev, A.*; Koga, J. K.; Sakaki, Hironao; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 23(25), p.31991 - 32005, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.91(Optics)We present experiments dealing with a femtosecond laser-driven cluster-based plasma, where by analyzing the nonlinear phenomenon of satellites of spectral lines of Ar XVII, we revealed the nonlinear phenomenon of the generation of the second harmonic of the laser frequency. For performing this analysis we developed new results in the theory of satellites of spectral lines. From such lineshape analysis we found, in particular, that the efficiency of converting the short (40 fs) intense (3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm ) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
Okada, Hajime; Maruyama, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Nagashima, Keisuke
JAEA-Technology 2015-029, 29 Pages, 2015/11
We develop high repetitive and short pulse laser system using Yb doped laser ceramics for future laser application of generating high power tera-hertz wave for experimental proof of isotope separation and generating a Laser-Compton Scattering  -ray source for precise specific isotopes analysis. As these future laser applications needs very stable and high average power laser system, we develop thin disk laser system using Yb:YAG ceramics because of its large stored energy property and large thermal conductivity, which could avoid thermal induced effects and thermal fracture limitation due to large pumping power. A few hundred
-ray source for precise specific isotopes analysis. As these future laser applications needs very stable and high average power laser system, we develop thin disk laser system using Yb:YAG ceramics because of its large stored energy property and large thermal conductivity, which could avoid thermal induced effects and thermal fracture limitation due to large pumping power. A few hundred  m thickness of thin disk laser material in laser amplifier needs multi pass optical components for enough absorption of pump power, the pumping profile and spot size on laser disk should be variable for required laser performance. We design multi pass pumping module for thin disk laser material which consists of commercial optical components and precise stages and also design doublet and triplet for various pumping profile and spot size, the laser oscillation power is evaluated with this pumping module.
m thickness of thin disk laser material in laser amplifier needs multi pass optical components for enough absorption of pump power, the pumping profile and spot size on laser disk should be variable for required laser performance. We design multi pass pumping module for thin disk laser material which consists of commercial optical components and precise stages and also design doublet and triplet for various pumping profile and spot size, the laser oscillation power is evaluated with this pumping module.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao
Isotope News, (739), p.15 - 20, 2015/11
We introduce the multi-charged heavy-ion acceleration mechanisms and the recent results obtained at the KPSI JAEA. We also propose the novel application of the laser-driven multi-charged heavy ion beam.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ragozin, E. N.*
Physics-Uspekhi, 58(11), p.1095 - 1105, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:56.75(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Murakami, Hiroshi
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 210, Part A, p.37 - 43, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.6(Chemistry, Physical)Picosecond relaxation dynamics of water before and after water shedding from reverse micelles are studied using temperature-dependent terahertz time-domain spectroscopy measurements to clarify the confinement effect of the reverse micelle on the dynamics of water. Before water shedding, the relaxation process due to the collective motion of bulk-like water in the core of the reverse micelle exhibits a considerable slowing down in comparison with that in liquid water as the temperature decreases. This is attributed to the confinement effect of reverse micelles. Moreover, the time constant abruptly drops at the water shedding, and its temperature behavior is similar to that of liquid water afterwards. These results demonstrate that the water extracted from the reverse micelle attains the property of liquid water by reduction in the confinement imposed on the motion of the water.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(10), p.677 - 681, 2015/10
, 57(10), p.677 - 681, 2015/10
Light, such as, High intensity short pulse laser interacting with the thin-foil target, accelerates the almost fully stripped Iron ions towards the energy of 0.9 GeV. It is quite difficult for the conventional ion sources to make the highly charged heavy ions within few tens of femtoseconds and at the same time accelerates them towards higher energies. The achievement explained here is one new step towards the novel type compact ion sources.
Kim, C. M.*; Steil, H.*; Matou , B.*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Tran, K. A.*; Janulewicz, K. A.*
, B.*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Tran, K. A.*; Janulewicz, K. A.*
Physical Review A, 92(4), p.043807_1 - 043807_7, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19(Optics)We present polarization measurement of a Ni-like Ag X-ray laser working in the transient collisional excitation scheme. A calibrated membrane multilayer beam splitter was used to determine the energies of two mutually perpendicular polarization components (s and p components). As a result, we observed a high degree of polarization that fluctuated from shot to shot. The dominant polarization component switched from s to p when pumping was made stronger. The measurement results are discussed from the point of view of the general polarization theory and supported by a numerical simulation based on Maxwell-Bloch equations.
Secretariat of Symposium on Advanced Photon Research
JAEA-Conf 2015-001, 93 Pages, 2015/07
The 15th Symposium on Advanced Photon Research was held at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA-KPSI) in Kizugawa city, Kyoto on November 13 - 14, 2014. This report consists of invited and contributed papers presented at the oral and poster sessions in the Symposium.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kawase, Keigo*; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; Kando, Masaki; Koga, J. K.; Bulanov, S. V.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(7), p.074501_1 - 074501_5, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Kanasaki, Masato; et al.
Research Using Extreme Light; Entering New Frontiers with Petawatt-Class Lasers II (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9515), p.95151D_1 - 95151D_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Experimental demonstration of multi-charged heavy ion acceleration from the interaction between the ultra-intense short pulse laser system and the metal target is presented. The laser pulse of  10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of
10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of  10
10 from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of
from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of  10
10 Wcm
Wcm interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
Fukuda, Yuji
Kyo Koshiba Kagaku No Tenkai CSJ Karento Rebyu, p.116 - 122, 2015/03
We review research activities concerning laser-cluster interactions and introduce laser-driven ion acceleration studies mainly focusing on that using relativistic plasmas produced from cluster targets, which are now intensively carrying out at JAEA-KPSI.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T.*; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 22(3), p.033107_1 - 033107_8, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:96.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic low-emittance high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a compact radio isotope source in combination with conventional technology.
Awual, M. R.; Hasan, M. M.*; Khaleque, M. A.*
Sensors and Actuators B; Chemical, 209, p.194 - 202, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:218 Percentile:99.69(Chemistry, Analytical)Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Choi, I. W.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Tatsufumi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Daito, Izuru*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_9, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.75(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Projection images of a metal mesh produced by directional MeV electron beam together with directional proton beam, emitted simultaneously from a thin foil target irradiated by an ultrashort intense laser. The mesh patterns are projected to each detector by the electron beam and the proton beam originated from tiny virtual sources of  20 micron meter and
20 micron meter and  10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Kon, Akira; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kanasaki, Masato*; et al.
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 21(1), p.1601118_1 - 1601118_18, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:95.3(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)This paper reviews the development of a high-contrast high-intensity petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser for research on high field science. We discuss in detail the design, performance and characterization of the laser. We also describe the on-going upgrade of the laser system and some applications for the laser in relativistic dominated laser-matter interactions.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Y.; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science XI; Springer Series in Chemical Physics, Vol.109, p.215 - 233, 2015/00
Clusters formed in supersonic gas expansion through a three-staged conical nozzle have been verified by measuring the angular distribution of the light scattered from cluster target. The size distirbutions of the clusters are calculated based on the Mie theory. The reliability of the size measurement is verified to be an experimental error of 10% using standard particles. The mean sizes of CO clusters for the cases of CO
clusters for the cases of CO /H
/H and CO
and CO /He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26
/He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26  m and 0.22
m and 0.22  m, respectively. For the CO
m, respectively. For the CO /H
/H , the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5
, the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5 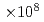 clusters/cm
clusters/cm by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Koga, J. K.; Mori, Michiaki; Kawase, Keigo*; et al.
RAL-TR-2015-025, P. 22, 2015/00
Nishimura, Akihiko; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Takehiro*; Shimomura, Takuya; Terada, Takaya; Daido, Hiroyuki
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 9(3), p.221 - 224, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heat resistant FBG sensors were developed by femtosecond laser processing to apply them to high temperature operated piping system of nuclear power plants. The FBG sensor was installed on the surface of a steel blade and a vibration test was conducted to detect the resonant vibration frequency of the vibrating blade. The FBG sensor had the heatproof performance at 600 C. A frequency stabilized sensing system using a tunable laser was tested for structural health monitoring in daily operation of nuclear power plants. The FBG sensor was installed on the surface of a steel blade for vibration induced strain measurements. Welding, brazing, soldering and noble metal powder adhesive were discussed for molding the FBG sensors.
C. A frequency stabilized sensing system using a tunable laser was tested for structural health monitoring in daily operation of nuclear power plants. The FBG sensor was installed on the surface of a steel blade for vibration induced strain measurements. Welding, brazing, soldering and noble metal powder adhesive were discussed for molding the FBG sensors.