Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
 -Fe
-FeSuzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(7), p.075102_1 - 075102_7, 2024/02
Fracture of body centred cubic (bcc) metals and alloys below the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is brittle. This is theoretically explained by the notion that the critical stress intensity factor of a given crack front for brittle fracture is smaller than that for plasticdeformation; hence, brittle fracture is chosen over plastic deformation. Although this view is true from a macroscopic point of view, such brittle fracture is always accompanied by small-scale plastic deformation in the vicinity of the crack tip, i.e. crack tip plasticity. This short paper investigates the origin of this plasticity using atomistic modeling with a recently developed machine-learning interatomic potential of  -Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
-Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
Kawamura, Takuma; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Journal of Visualization, 27(1), p.89 - 107, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Interactive in-situ steering is an effective tool for debugging, searching for optimal solutions, and analyzing inverse problems in fast and large-scale computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. We propose an interactive in-situ steering framework for large-scale CFD simulations on GPU supercomputers. This framework employs in-situ particle-based volume rendering (PBVR), in-situ data sampling, and a file-based control that enables interactive communication of steering parameters, compressed particle data, and sampled monitoring data between supercomputers and user PCs. The parallelized PBVR is processed on the host CPU to avoid interference with CFD simulations on the GPU. We apply the proposed framework to a real-time plume dispersion analysis code CityLBM on GPU supercomputers. In the numerical experiment, we address an inverse problem to find a pollutant source from the monitoring data, and demonstrate the effectiveness of the human-in-the-loop approach.
Shiga, Motoyuki; Thomsen, B.; Kimizuka, Hajime*
Physical Review B, 109(5), p.054303_1 - 054303_12, 2024/02
Inelastic neutron scattering spectra of hydrogen in palladium were calculated considering nuclear quantum effects at finite temperatures. A computational method combining semiclassical molecular dynamics based on path integrals and machine learning potentials was used. The calculated spectra agree well with the experimental spectra with respect to the positions and intensities of the peaks corresponding to the fundamental and first harmonic of the vibrational excitation of hydrogen atoms. Comparison with classical molecular dynamics shows that nuclear quantum effects play an essential role in the inelastic neutron scattering spectra.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Zairyo, 73(2), p.129 - 135, 2024/02
Body-centered-cubic transition metals, such as Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane. To find out the mechanism of this response, atomistic simulations of curved crack-fronts of bcc Fe were conducted at 0 K using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network (ANN) technique. We discovered that dislocations can be emitted from the curved crack fronts along the {110} crack plane, and this phenomenon explains why the cleavage is observed only along the {100} plane. In addition, the cleavage simulations along {100} at the elevated temperature were found to be accompanied by plasticity; namely, they represented more realistic fracture.
HPC Technology Promotion Office
JAEA-Review 2023-018, 159 Pages, 2023/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducts research and development (R&D) in various fields related to nuclear power as a comprehensive institution of nuclear energy R&Ds, and utilizes computational science and technology in many activities. Over the past 10 years or so, the publication of papers utilizing computational science and technology at JAEA has accounted for about 20 percent of the total publications each fiscal year. The supercomputer system of JAEA has become an important infrastructure to support computational science and technology. In FY2022, the system was used for R&D of light water reactors, high-temperature gas reactors, and fast reactors to contribute to carbon neutrality as a priority issue, as well as for JAEA's major projects such as Various R&D related to nuclear science and technology, R&D related to the response to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Development of technology for treatment and disposal of high-level radioactive waste, Support of nuclear safety regulation and nuclear disaster prevention, and safety research for this purpose. This report presents a great number of R&D results accomplished by using the system in FY2022, as well as user support, operational records and overviews of the system, and so on.
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Ina, Takuya; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Fluid Dynamics Research, 55(6), p.065501_1 - 065501_25, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Mechanics)We investigate the applicability of the data assimilation (DA) to large eddy simulations (LESs) based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). We carry out the observing system simulation experiment of a two-dimensional (2D) forced isotropic turbulence, and examine the DA accuracy of the nudging and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with spatially sparse and noisy observation data of flow fields. The advantage of the LETKF is that it does not require computing spatial interpolation and/or an inverse problem between the macroscopic variables (the density and the pressure) and the velocity distribution function of the LBM, while the nudging introduces additional models for them. The numerical experiments with 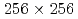 grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with
grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with 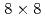 observation points (
observation points (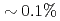 of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
JAEA-Research 2023-006, 47 Pages, 2023/10
This report presents a new surface capturing method based on the phase field model for gas-liquid two-phase flows simulation. In the conventional phase field model, the interface correction strength parameter was determined from the maximum flow velocity in the computational domain, but because the interface correction was applied uniformly to the entire space, it was also applied to locations that did not require correction. In the new method, the phase field parameter or the intensity of the phase field model is extended to have a spatial distribution, allowing us to set the optimal parameters depending on the local flow velocity fields. We also propose a method to derive the optimal phase field parameter based on systematic parameter scans using error analysis of the interface advection test and bubble rising calculations. Through benchmark tests of gas-liquid two-phase flows, the proposed model is verified, and it is shown that the proposed model has higher accuracy than the conventional phase field model.
Shiga, Motoyuki; Thomsen, B.; Nagai, Yuki
Ansanburu, 25(4), p.303 - 310, 2023/10
The parallel molecular simulation software "PIMD" will be presented. The use of PIMD will be explained through specific examples such as water structure by ab initio path integral molecular dynamics, quantum diffusion of hydrogen in metal by ring polymer molecular dynamics, machine learning potential generation and phonon properties of superconductors, and polyalcohol dehydration reaction by metadynamics.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Isotope News, (789), p.20 - 23, 2023/10
Radium is a radioactive element produced from uranium and thorium and is important for environmental contamination issues around uranium mines and for geological disposal. In addition, radium is used in radiometric dating and cancer therapy, making it important not only in environmental chemistry but also in many other fields, including geochemistry and nuclear medicine. However, because radium is a radioactive element with no stable isotopes, spectroscopic measurement of radium is difficult, and little information at the molecular level has been obtained so far. In this study, we have clarified the molecular-level information of hydrated radium for the first time in the world by combining extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements and first-principles molecular dynamics simulations.
Yamaguchi, Masatake
Materia, 62(10), p.646 - 651, 2023/10
The tendency of solid metal in contact with a liquid metal to undergo brittle fracture is called liquid metal embrittlement. The degree of embrittlement varies depending on the liquid-solid metal combination, called the element selectivity (specificity) of liquid metal embrittlement. We have added further explanations to a published paper that discusses the energetics of embrittlement-prone combinations and possible embrittling mechanisms based on energetic considerations from first-principles calculations.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 237(5), p.947 - 957, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.72(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. However, the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components are damaged is difficult to estimate if the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA based on event trees and fault trees. A methodology coupling thermal-hydraulic analysis with external event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID) is therefore proposed to overcome this limitation. A flood propagation model based on Bernoulli's theorem was applied to represent internal flooding in the turbine building of the pressurized water reactor. Uncertainties were also taken into account, including the flow rate of the floodwater source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. The simulated recovery actions included the operator isolating the floodwater source and using a drainage pump; these actions were modeled using several simplifications. Overall, the results indicate that combining isolation and drainage can reduce the conditional core damage probability upon the occurrence of flooding by approximately 90%.
Yamaguchi, Akiko
Hosha Kagaku, (48), p.56 - 59, 2023/09
The adsorption reaction on clay minerals is an important chemical reaction that controls the environmental behaviors of various ions at the Earth's surface, but the details are unknown due to the complexity of the reaction, such as the diversity of clay mineral compositions and the existence of multiple adsorption sites. In this study, we focused on the adsorption structure on clay minerals at the atomic level, and clarified it in detail by combining X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) methods and first-principles calculations. In particular, XAFS measurements of radium, which has the largest ionic radius among alkaline earth metals and has been difficult to measure at the atomic level, were successfully performed, and new knowledge was obtained by comparing the results with those of other elements.
Yamashita, Susumu; Sato, Takumi; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1029 - 1045, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology) =1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl
=1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurements
in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurementsKimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okunishi, Koichi*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kikuchi, Hikomitsu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(9), p.094701_1 - 094701_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Yamashita, Susumu; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00485_1 - 22-00485_25, 2023/08
A detailed evaluation for air cooling of fuel debris in actual reactors will be essential in fuel debris retrieval under dry conditions. To understand the heat transfer in and around fuel debris, which is assumed as a porous medium in the primary containment vessel (PCV) mechanistically, we newly applied the porous medium model to the multiphase and multicomponent computational fluid dynamics code named JUPITER (JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research). We applied the Darcy-Brinkman model as for the porous medium model. This model has high compatibility with JUPITER because it can treat both a pure fluid and a porous medium phase simultaneously in the same manner as the one-fluid model in multiphase flow simulation. We addressed the case of natural convection with a high-velocity flow standing out nonlinear effects by implementing the Forchheimer model, including the term of the square of the velocity as a nonlinear effect to the momentum transport equation of JUPITER. We performed some simple verification and validation simulations, such as the natural convection simulation in a square cavity and the natural convective heat transfer experiment with the porous medium, to confirm the validity of the implemented model. We confirmed that the result of JUPITER agreed well with these simulations and experiments. In addition, as an application of the updated JUPITER, we performed the preliminary simulation of air cooling of fuel debris in the condition of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station unit 2 including the actual core materials. As a result, JUPITER calculated the temperature and velocity field stably in and around the fuel debris inside the PCV. Therefore, JUPITER has the potential to estimate the detailed and accurate thermal-hydraulics behaviors of fuel debris.