Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Sekiya, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara
Applied Physics A, 131, p.165_1 - 165_8, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Among various analytical methods for liquid samples, time-resolved laser-induced luminescence spectroscopy enables real-time measurements of Gd ion concentrations in aqueous solution without sample introduction into the spectrometer. In this work, we have developed a real-time monitoring method for Gd concentration in water. The detection limit was determined to be  60 ppb for Gd sulfate in ultrapure water. This value is about two orders of magnitude better than the reported value using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and is close to that using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry which requires sample introduction into the spectrometer.
60 ppb for Gd sulfate in ultrapure water. This value is about two orders of magnitude better than the reported value using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and is close to that using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry which requires sample introduction into the spectrometer.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wells, S. R.*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In this study, triple and double resonance ionization schemes of atomic Ca were developed, aiming for the separation of odd isotopes by (i) laser polarization-dependent selection rules, and (ii) large isotope shifts of odd Ca isotopes in the Rydberg levels. Separation of odd isotopes was confirmed under the orthogonal condition. Suppression of non-resonant ionization of  Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of
Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of  Ca.
Ca.
Takasaki, Koji
Hokeikyo Nyusu, (73), p.2 - 5, 2024/04
The development of radiation measurement and digital technology for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, which is being conducted by the Remote System and Sensing Technology Division of CLADS, will be presented.
Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo; Taira, Takunori*
Sumato Purosesu Gakkai-Shi, 13(2), p.51 - 58, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 41(1), p.119 - 126, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:42.60(Optics)Calcium Rydberg levels are of significant interest for efficient and isotope-selective resonance ionization of trace radionuclides such as calcium-41 ( Ca). In this study, we report novel measurement data on the energy level shifts of calcium-43 (
Ca). In this study, we report novel measurement data on the energy level shifts of calcium-43 (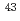 Ca) for 4sns
Ca) for 4sns  S
S and 4s(n-1)d
and 4s(n-1)d  D
D (n=40, 45, 50, 55, 60) Rydberg levels due to hyperfine-induced singlet-triplet mixing specific to isotopes with an odd mass number.
(n=40, 45, 50, 55, 60) Rydberg levels due to hyperfine-induced singlet-triplet mixing specific to isotopes with an odd mass number.
Ikeda, Yuji*; Soriano, J. K.*; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.4828_1 - 4828_9, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(2), p.347 - 358, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:49.56(Chemistry, Analytical)To develop remote isotopic analysis for the nuclids with small isotope shifts, Doppler-free fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca was performed using laser ablation plume. Counter-propagating laser beams from two external cavity diode lasers were used to irradiate the plume in order to excite the ground-state Ca atoms to the  D
D state through a double resonance scheme of
state through a double resonance scheme of  S
S

 P
P

 D
D . Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the
. Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the  D
D to
to  P
P states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step
states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step  P
P

 D
D transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,
transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,  Ca,
Ca, 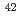 Ca, and
Ca, and 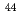 Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Saruta, Koichi; Miyabe, Masabumi; Ito, Chikara; Shibata, Takuya; Inoue, Kaoru*; Terabayashi, Ryohei*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Physica Scripta, 98(3), p.035112_1 - 035112_22, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of kW class quasi-continuous wave (a pulse duration of 10 ms) laser interaction with metal targets and those with metal oxide targets are presented in respect to the laser induced breakdown and the successive laser induced melting and evaporation coupled with a mechanical response followed by ejection of various kinds of particles and fragments. An experiment was performed using fiber lasers coupled with a high-speed camera to observe dynamics of the interaction. Ejected fine particles were collected using a cascade impactor and a home-made collector and were observed with electron microscopes. Shapes of irradiation marks were observed with a digital optical microscope. We also measured total ejected mass from a target. The experimental results reveal that firstly the laser threshold intensity of the interaction with the metal target was lower and more stable than those with the metal oxide targets. Secondly, in the stainless steel targets, the dynamics of molten layer created by thermal conduction from the laser heated thin layer and successive particle ejection with less mechanical response by the adjacent solid layer are dominant processes, while in the metal oxide targets, the fracturing in the relatively deeper interaction region coupled with brittle material response having relatively large laser shot to shot fluctuation appears to play a significant role in addition to the laser induced melting.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Sekiya, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(12), p.123H01_1 - 123H01_12, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In this work, we constructed an experimental setup based on time-resolved laser-induced luminescence spectroscopy to investigate the emission characteristics of Gd ions in water. The excitation laser wavelength was tuned in the range of 245-255 nm, and large resonant peaks were observed at 246.2 nm and 252.3 nm with measured emission lifetimes of around 3 ms. Good linearity was observed between Gd concentration and emission intensity for these two wavelengths, indicating that our setup is useful for remote monitoring of Gd concentration.
ions in water. The excitation laser wavelength was tuned in the range of 245-255 nm, and large resonant peaks were observed at 246.2 nm and 252.3 nm with measured emission lifetimes of around 3 ms. Good linearity was observed between Gd concentration and emission intensity for these two wavelengths, indicating that our setup is useful for remote monitoring of Gd concentration.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 275, p.107882_1 - 107882_9, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.53(Optics)Following the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, an isotope-selective analysis method using laser resonance ionization has been developed for strontium-90. In this study, the isotope shifts and hyperfine structure constants of stable isotopes were measured for two schemes expected to have high isotopic selectivity, and the isotope shifts of strontium-90 were evaluated using the King plot analysis. The measured strontium-90 optical isotopic selectivities ranged from 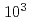 to
to 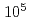 , which are sufficient for analysis of real samples.
, which are sufficient for analysis of real samples.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Satou, Yukihiko; Wakaida, Ikuo; Terabayashi, Ryohei*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Tomita, Hideki*; Zhao, Y.*; Sakamoto, Tetsuo*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 54(14), p.145003_1 - 145003_8, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.66(Optics)Two-color two-step photoionization optogalvanic spectroscopy was performed using high-repetition-rate titanium sapphire lasers and a uranium hollow cathode lamp to find the two-step resonance ionization schemes of uranium. Many ionization transitions were observed by exciting uranium atoms in a ground state into five, even parity, excited levels with the first-step laser and by scanning the second-step laser wavelengths. By blocking the first-step laser, single-color, two-photon ionization transitions were also identified. From these results, we have found more than 50 odd-parity autoionizing levels of uranium in the energy, ranging from the ionization potential (49958.4 cm ) to 51150 cm
) to 51150 cm . The determined energy levels are within 1 cm
. The determined energy levels are within 1 cm of previously reported values.
of previously reported values.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 265, p.107549_1 - 107549_7, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.34(Optics)Following the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, an isotope-selective analysis method using laser resonance ionization has been developed for strontium-90. In this study, we focused on ionization via autoionization states in terms of high isotopic selectivity and ionization efficiency, and the DC Stark shifts caused by the external electric field were measured for these states. It was found that the external electric field in the ionization region has to be of the order of 0.1 V/cm or less to suppress its effect on the observed spectra.
Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo; Tanabe, Rie*; Ito, Yoshiro*
Optics Express (Internet), 29(4), p.5205 - 5212, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:87.64(Optics)Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) combined with liquid jets was applied to the detection of trace sodium (Na) in aqueous solutions. The sensitivities of two types of liquid jets were compared: a liquid cylindrical jet with a diameter of 500  m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20
m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20  m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57
m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57  g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5
g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5  g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 126(3), p.213_1 - 213_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in low pressure rare gas ambient was investigated with laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy for three refractory metals, i.e. titanium, zirconium and hafnium. A comparison of the plume expansion behaviors for the species of these elements revealed an atomic weight effect on the plume structure formation. A hemispherical thin layer and cavity structure reported previously for gadolinium were observed also for these elements. It was found that the plume size increases as well as the layer thickness decreases with increasing atomic weight. For ground state atoms of Ti, substantial amount of atoms were observed even at the center of the plume. Also, the persistence of the Ti atomic plume was as long as 300  s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(2), p.022401_1 - 022401_4, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.39(Physics, Applied)We used laser-induced fluorescence imaging with a varying beam focal point to observe ablation plumes from metal and oxide samples of gadolinium. The plumes expand vertically when the focal point is far from the sample surface. In contrast, the plume becomes hemispherical when the focal point is on the sample surface. In addition, the internal plume structure and the composition of the ablated atomic and ionic particles also vary significantly. The fluorescence intensity of a plume from a metal sample is greater than that from an oxide sample, which suggests that the number of monatomic species produced in each plume differs. For both the metal and oxide samples, the most intense fluorescence from atomic (ionic) species is observed with the beam focal point at 3-4 mm (2 mm) from the sample surface.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Khumaeni, A.*; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 110, p.101 - 117, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:81.14(Spectroscopy)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in ambient gas has been investigated by laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. The second harmonic beam from an Nd:YAG laser (0.5-6J/cm ) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
Ozu, Akira; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 60(1), p.75 - 80, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Microscopic studies on laser-induced fluorescence emitted from asbestos (chrysotile) and a building material (glass-wool: a substitute material for asbestos) fibrous particle excited by a ultra-violet (266 nm) laser, have been conducted by visualizing those particles with the fluorescence. The fluorescence characteristics observed under the microscope agreed approximately with those observed in the determination using bulk samples. The decay ratio of the fluorescence intensity at 540 nm and other wavelength was in good agreement with that with bulk sample. The total amount of the intensity of glass-wool per unit area at  350 nm was 23 times larger than that of chrysotile, corresponding to that with bulk sample. A practical microscopic method used to discriminate asbestos by combining the decay ratio and total amount of the intensity are proposed.
350 nm was 23 times larger than that of chrysotile, corresponding to that with bulk sample. A practical microscopic method used to discriminate asbestos by combining the decay ratio and total amount of the intensity are proposed.
Ozu, Akira; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 58(6), p.569 - 576, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Laser-induced fluorescence of asbestos and several kinds of building materials such as glass-wools and talc, etc., have been studied for discriminating asbestos from the other materials. The fluorescence spectrums excited by ultra-violet (266 nm) laser pulse were observed over the wavelength range 350 to 700 nm, and the difference of the spectrum in shape between asbestos and the other materials was identified. The lifetime and relative intensity of the fluorescence emitted from those materials were also investigated and evaluated for the numerical discrimination of asbestos. Novel methods are presented for discriminating asbestos by comparing the relative ratio of the fluorescence intensity between two different ranges (430 and 575 nm) of the wavelength, and/or the lifetime and the total amount of the fluorescence. Applications of the method to conventional particle measurement systems, as examples, a microscopic method and an optical particle counter, are discussed.
Ozu, Akira; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 48(4), p.042303_1 - 042303_5, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.96(Physics, Applied)Nanosecond time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy was performed on five kinds of asbestos materials (chrysotile, crocidolite, amosite, tremolite and anthophyllite) using a ultra-violet laser pulse of 266 nm. Most of the fluorescence spectra had a broad wavelength band of 350-700 nm and a maximum near around 450 nm in the visible region. The spectra also varied in shape over time. Although all the spectra were similar in shape, a significant difference in the relative ratio of fluorescence intensity between the two different wavelength regions was identified. The lifetime and total amount of fluorescence intensity were also investigated and the differences were observed for the different kinds of asbestos. Several methods potentially useful for discriminating asbestos from other materials through use of their fluorescence characteristics are discussed.