Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary) SnSe
SnSe
Ren, Q.*; Gupta, M. K.*; Jin, M.*; Ding, J.*; Wu, J.*; Chen, Z.*; Lin, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J. A.*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Materials, 22, p.999 - 1006, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:99.21(Chemistry, Physical)Sano, Ryotaro*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review Letters, 130(16), p.166201_1 - 166201_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary) BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:56.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences) K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Funato, Takumi*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 540, p.168436_1 - 168436_7, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi*; Kato, Takeo*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 104(12), p.L121401_1 - L121401_5, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yama, Masaki*; Tatsuno, Masahiro*; Kato, Takeo*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 104(5), p.054410_1 - 054410_9, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Funato, Takumi*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 104(6), p.L060412_1 - L060412_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakata, Koki; Onuma, Yuichi*; Matsuo, Mamoru*
Physical Review B, 99(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_7, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.61(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study a frequency-dependent noise-to-current ratio for asymmetric, symmetric, and noncommutative current noise in a ferromagnetic insulating junction, and extract quantum-mechanical properties of magnon transport at low temperatures. We demonstrate that the noncommutative noise, which vanishes in the dc limit (i.e., a classical regime), increases monotonically as a function of frequency, and show that the noncommutative noise associated directly with quantum fluctuations of magnon currents breaks through the classical upper limit determined by the symmetric noise and realizes asymmetric quantum shot noise. Finally, we show that our theoretical predictions are within experimental reach with current device and measurement schemes while exploiting low temperatures. Our work provides a platform toward experimental access to quantum fluctuations of magnon currents.
Nakata, Koki; Onuma, Yuichi*; Matsuo, Mamoru*
Physical Review B, 98(9), p.094430_1 - 094430_8, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:48.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically establish mutual relations among magnetic momentum, heat, and fluctuations of propagating magnons in a ferromagnetic insulating junction in terms of noise and the bosonic Wiedemann-Franz (WF) law. Using the Schwinger-Keldysh formalism, we calculate all transport coefficients of a noise spectrum for both magnonic spin and heat currents, and establish Onsager relations between the thermomagnetic currents and the zero-frequency noise. Making use of the magnonic WF law and the Seebeck coefficient in the low-temperature limit, we theoretically discover universal relations, i.e. being independent of material parameters, for both the nonequilibrium and equilibrium noise, and show that each noise is described solely in terms of thermal conductance.
Maekawa, Sadamichi
Seramikkusu, 46, P. 1072, 2011/12
no abstracts in English
Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Hata, Kuniki; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari; Hatano, Yoshihiko
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1192 - 1197, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:87.25(Chemistry, Physical) source from high contrast fs laser plasmas in regime of Relativistic Engineering
source from high contrast fs laser plasmas in regime of Relativistic EngineeringChen, L.-M.; Koga, J. K.; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Xu, M. H.*; Li, Y.-T.*; Dong, Q. L.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Interaction of intense Ti: Sapphire laser with Cu foil targets has been studied by measuring hard X-ray generation. Hard X-ray spectroscopy and K X-ray conversion efficiency (
X-ray conversion efficiency (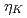 ) from Cu plasma have been studied as a function of laser intensity via pulse duration scan (60 fs
) from Cu plasma have been studied as a function of laser intensity via pulse duration scan (60 fs  600 fs), laser pulse energy scan (60 mJ
600 fs), laser pulse energy scan (60 mJ  600 mJ) and target displacement scan from best focus. For intensity I
600 mJ) and target displacement scan from best focus. For intensity I 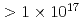 W/cm
W/cm , the Cu
, the Cu 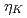 keep on increasing to reach a maximum value of
keep on increasing to reach a maximum value of 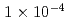 at an intensity
at an intensity 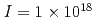 W/cm
W/cm . The focusing is varied widely to give a range of intensities from 10
. The focusing is varied widely to give a range of intensities from 10 W/cm
W/cm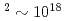 W/cm
W/cm . Comparing to a recent publication, two individual emission peaks are obtained, one is at best focal spot and the other is at larger target offset corresponding to
. Comparing to a recent publication, two individual emission peaks are obtained, one is at best focal spot and the other is at larger target offset corresponding to 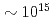 W/cm
W/cm . Each peak is corresponding to different energy absorption mechanism. In addition, when we introduce slightly detuning of compressor gratings at the best focal condition, it shows
. Each peak is corresponding to different energy absorption mechanism. In addition, when we introduce slightly detuning of compressor gratings at the best focal condition, it shows 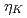 generated by negatively skewed 100 fs pulse width laser irradiation reach
generated by negatively skewed 100 fs pulse width laser irradiation reach 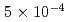 and almost 7 times greater than the case of positively skewed pulse. Vacuum Heating is greatly stimulated in this case and preciously control of pre-plasma is the key factor in tuning control of X-ray emission in relativistic fs regime.
and almost 7 times greater than the case of positively skewed pulse. Vacuum Heating is greatly stimulated in this case and preciously control of pre-plasma is the key factor in tuning control of X-ray emission in relativistic fs regime.
Koga, J. K.; Chen, L.-M.; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Gu, Y. Q.*; Peng, H. S.*; Hua, J. F.*; An, W. M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
First experiments for electron acceleration with the laser-gas plasma interaction have been carried out with 30 fs, 100 TW relativistic Ti:Sapphier laser pulse into a long slit (1.2  10 mm
10 mm ) gas plasma. The 10 mm length plasma channel formed that was longer than 20 times the Rayleigh length. Plasma density was the key factor for this long channel stimulation under 100 TW laser pulse irradiation that was much higher than critical power for relativistic self-focusing. For the first time, channel characteristics such as laser bending, hosing and cavity formation were demonstrated experimentally. In case of long channel guiding, accelerated electron bunch was tightly collimated with low emmitance
) gas plasma. The 10 mm length plasma channel formed that was longer than 20 times the Rayleigh length. Plasma density was the key factor for this long channel stimulation under 100 TW laser pulse irradiation that was much higher than critical power for relativistic self-focusing. For the first time, channel characteristics such as laser bending, hosing and cavity formation were demonstrated experimentally. In case of long channel guiding, accelerated electron bunch was tightly collimated with low emmitance 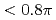 mm mrad and quasi-monoenergetic electron bunch (
mm mrad and quasi-monoenergetic electron bunch ( 70 MeV) was obtained as well. Accelerated electron charge current with electron energy
70 MeV) was obtained as well. Accelerated electron charge current with electron energy  1 MeV was
1 MeV was  10 nC/shot which was highest value in laser accelerator, to our knowledge, and ascribed to the contribution of long plasma channel. These well controlled laser-driven acceleration is an important cornerstone of relativistic engineering.
10 nC/shot which was highest value in laser accelerator, to our knowledge, and ascribed to the contribution of long plasma channel. These well controlled laser-driven acceleration is an important cornerstone of relativistic engineering.
Nakata, Koki; Onuma, Yuichi*; Matsuo, Mamoru*
no journal, ,
Extending a Boltzmann-Langevin theory to magnons, we show a universality of current-noise suppression in diffusive systems against the difference of quantum-statistical properties of bosons and fermions. We theoretically discover that compared with a Poissonian shot noise of magnons in an insulating ferromagnetic junction, the magnonic shot noise is suppressed in the diffusive insulating bulk magnet and noise-to-current ratio (Fano factor) at low temperatures exhibits a universal behavior, i.e., the same suppression 1/3 as the one for electron transport in diffusive conductors, despite the difference of quantum-statistical properties.
Nakata, Koki; Onuma, Yuichi*; Matsuo, Mamoru*
no journal, ,
Using the Keldysh formalism, we calculate a magnonic current-noise and compare it with the current-noise of electrically charged electrons. We thus discuss the universality of current-noise against the difference of quantum-statistical properties of bosons and fermions.