Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ssbauer spectra of
ssbauer spectra of 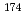 Yb measured with internal conversion electrons
Yb measured with internal conversion electronsMasuda, Ryo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Kitao, Shinji*; Kurokuzu, Masayuki*; Saito, Makina*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Mitsui, Takaya; Iga, Fumitoshi*; Seto, Makoto
Applied Physics Letters, 104(8), p.082411_1 - 082411_5, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:65.2(Physics, Applied)A detection system for synchrotron-radiation (SR)-based M ssbauer spectroscopy was developed to enhance the nuclear resonant scattering counting rate and thus increase the available nuclides. In the system, a windowless avalanche photodiode (APD) detector was combined with a vacuum cryostat to detect the internal conversion (IC) electrons and fluorescent X-rays accompanied by nuclear de-excitation. As a feasibility study, the SR-based M
ssbauer spectroscopy was developed to enhance the nuclear resonant scattering counting rate and thus increase the available nuclides. In the system, a windowless avalanche photodiode (APD) detector was combined with a vacuum cryostat to detect the internal conversion (IC) electrons and fluorescent X-rays accompanied by nuclear de-excitation. As a feasibility study, the SR-based M ssbauer spectrum using the 76.5 keV level of
ssbauer spectrum using the 76.5 keV level of 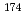 Yb was observed without
Yb was observed without 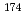 Yb enrichment of the samples. The counting rate was five times higher than that of our previous system, and the spectrum was obtained within 10 h. This result shows that nuclear resonance events can be more efficiently detected by counting IC electrons for nuclides with high IC coefficients. Furthermore, the windowless detection system enables us to place the sample closer to the APD elements and is advantageous for nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements. Therefore, this detection system can not only increase the number of nuclides accessible in SR-based M
Yb enrichment of the samples. The counting rate was five times higher than that of our previous system, and the spectrum was obtained within 10 h. This result shows that nuclear resonance events can be more efficiently detected by counting IC electrons for nuclides with high IC coefficients. Furthermore, the windowless detection system enables us to place the sample closer to the APD elements and is advantageous for nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements. Therefore, this detection system can not only increase the number of nuclides accessible in SR-based M ssbauer spectroscopy but also allows the nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements of small single crystals or enzymes with dilute probe nuclides that are difficult to measure with the previous detection system.
ssbauer spectroscopy but also allows the nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements of small single crystals or enzymes with dilute probe nuclides that are difficult to measure with the previous detection system.