Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.73(Microbiology) archaea
archaeaSchoelmerich, M. C.*; Oubouter, H. T.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Penev, P. I.*; Amano, Yuki; West-Roberts, J.*; Welte, C. U.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.7085_1 - 7085_11, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:73.27(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Jaffe, A. L.*; Thomas, A. D.*; He, C.*; Keren, R.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Munk, P.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Farag, I. F.*; Amano, Yuki; Sachdeva, R.*; et al.
mBio, 12(4), p.e00521-21_1 - e00521-21_21, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:89.98(Microbiology)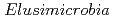 are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome
are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome 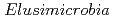 and some have a novel nitrogenase paralog
and some have a novel nitrogenase paralogM heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 14(12), p.2907 - 2922, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:94.42(Ecology)Al-Shayeb, B.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Ward, F.*; Munk, P.*; Devoto, A.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Amano, Yuki; et al.
Nature, 578(7795), p.425 - 431, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:220 Percentile:99.5(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Atz, M.*; Salazar, A.*; Hirano, Fumio; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 124, p.28 - 38, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)The likelihood for criticality in the far field of a repository was evaluated for direct disposal of commercial light water reactor used nuclear fuel. Two models were used in combination for this evaluation: (1) a neutronics model to estimate the minimum critical masses of spherical, water-saturated depositions of fuel material; (2) a transport model to simulate the dissolution of fuel material from multiple canisters and the subsequent transport of the solutes through host rock to a single accumulation location. The results suggest that accumulation of a critical mass is possible under conservative conditions but that these conditions are unlikely to occur, especially in the vicinity of a carefully-arranged repository.
Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Schulz, F.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Kantor, R. S.*; Shih, P.*; Sharon, I.*; Santini, J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Amano, Yuki; Thomas, B. C.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.463_1 - 463_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:86.04(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Okumura, Masahiko; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Lammers, L. N.*; Ikeda, Takashi*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 189, p.135 - 145, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:87.2(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Salazar, A.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.600 - 607, 2017/04
Atz, M.*; Liu, X.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.608 - 614, 2017/04
Liu, X.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.595 - 599, 2017/04
 and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sediments
and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sedimentsHernsdorf, A. W.*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ise, Kotaro; Suzuki, Yohei*; Anantharaman, K.*; Probst, A. J.*; Burstein, David*; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 11, p.1915 - 1929, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:95.92(Ecology)To evaluate the potential for interactions between microbial communities and disposal systems, we explored the structure and metabolic function of a sediment-hosted subsurface ecosystem associated with Horonobe Underground Research Center, Hokkaido, Japan. Overall, the ecosystem is enriched in organisms from diverse lineages and many are from phyla that lack isolated representatives. The majority of organisms can metabolize H , often via oxidative [NiFe] hydrogenases or electron-bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenases that enable ferredoxin-based pathways, including the ion motive Rnf complex. Many organisms implicated in H
, often via oxidative [NiFe] hydrogenases or electron-bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenases that enable ferredoxin-based pathways, including the ion motive Rnf complex. Many organisms implicated in H metabolism are also predicted to catalyze carbon, nitrogen, iron, and sulfur transformations. Notably, iron-based metabolism was predicted in a bacterial lineage where this function has not been predicted previously and in an ANME-2d archaeaon that is implicated in methane oxidation. We infer an ecological model that links microorganisms to sediment-derived resources and predict potential impacts of microbial activity on H
metabolism are also predicted to catalyze carbon, nitrogen, iron, and sulfur transformations. Notably, iron-based metabolism was predicted in a bacterial lineage where this function has not been predicted previously and in an ANME-2d archaeaon that is implicated in methane oxidation. We infer an ecological model that links microorganisms to sediment-derived resources and predict potential impacts of microbial activity on H accumulation and radionuclide migration.
accumulation and radionuclide migration.
Hug, L. A.*; Baker, B. J.*; Anantharaman, K.*; Brown, C. T.*; Probst, A. J.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Butterfield, C. N.*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Amano, Yuki; Ise, Kotaro; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 1(5), p.16048_1 - 16048_6, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:1209 Percentile:99.97(Microbiology)The tree of life is one of the most important organizing principles in biology. Gene surveys suggest the existence of an enormous number of branches, but even an approximation of the full scale of The Tree has remained elusive. Here, we use newly available information from genomes of uncultivated organisms, along with other published sequences, to present a new version of the Tree of life, with Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes included. The depiction is both a global overview and a snapshot of the diversity within each major lineage. The results imply the predominance of bacterial diversification and underline the importance of organisms lacking isolated representatives, with substantial evolution concentrated in a major radiation of such organisms.
Liu, X.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.416 - 425, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Liu, X.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 14th International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWMC 2013) (CD-ROM), p.527 - 534, 2013/04
The present study focuses on the criticality safety of geological disposal of molten fuel. The influences of different geometries in the MCNP models for the simulation of heavy metal precipitates in geological formations are discussed. Bounding calculations for criticality based on the molten fuel in Fukushima Daiichi reactors were made by optimization in a large parameter space. Some critical combinations are observed in the numerical results, and in the iron rich rock, the risk of criticality is significantly reduced.
Murakami, Haruko*; Ahn, J.*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Ikegami, Tetsuo; Ahn, J.*
JAEA-Research 2006-045, 17 Pages, 2006/07
Environmental Impact, which is a newly developed measure in stead of the conventional radio-toxicity, has been evaluated for both the PWR cycle and the FBR cycle in order to clarify what kind of radio-nuclides and how much level of partitioning and transmutation are desirable. Bounding analysis for uncertainty of parameters relevant to radionuclide transport in a repository has also been performed. The evaluated results imply that the targets of partitioning and transmutation can be set; (1)In the case of PWR cycle, the release rate of  Np and
Np and  Am should be controlled under 1 %, in addition to the conventionally assumed release rate of 0.604 % for U and 0.297 % for Pu. (2)In the case of FBR cycle, recovery rate of 99.9 % for all actinide nuclides is appropriate.
Am should be controlled under 1 %, in addition to the conventionally assumed release rate of 0.604 % for U and 0.297 % for Pu. (2)In the case of FBR cycle, recovery rate of 99.9 % for all actinide nuclides is appropriate.
Ahn, J.*; Rob, D. A.*; Kuo, S.*; Cha, P.L.*
PNC TY1952 98-001, 37 Pages, 1998/07
1.INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1.1RESULTS OF PREVIOUS STUDY 1.2OBJECTIVE AND SCOPE OF THIS STUDY 2.REPOSITORY-WIDE TRANSPORT MODEL 2.1ASSUMED HIGH-LEVEL WASTE CHARACTERISTICS 1.2GEOLOGIC FORMATIONS AND REPOSITORY CONFIGURATION 1.3THE MASS TRANSPORT MODEL 1.4MATHEMATICAL FORMULATION 1.4.1MASS TRANSPORT OF RADIONUCLIDES IN REPOSITORY 1.4.2TOTAL MASS EXISTING IN THE FAR FIELD 1.5PARAMETER VALUES 1.6NUMERICAL RESULTS 1.6.1PLUTONIUM 1.6.2URANIUM 1.7SUMMARY 2.UNCERTAINTIES FOR TOTAL URANIUM MASS IN FAR FIELD 2.1INTRODUCTION 2.2LATIN HYPERCUBE SAMPLING 2.3FIXED PARAMETERS 2.4PARAMETERS WITH UNCERTAINTIES 2.4.1WATER VELOCITY IN THE NEAR-FIELD ROCK 2.4.2POROSITY OF THE NEAR-FIELD ROCK 2.4.3POROSITY OF THE BENTONITE BUFFER 2.4.4DIFFUSION COEFFICIENT OF URANIUM IN BUFFER 2.4.5SORPTION DISTRIBUTION COEFFICIENT OF URANIUM IN THE NEAR-FIELD ROCK 2.4.6SORPTION DISTRIBUTION COEFFICIENT OF URANIUM IN BUFFER 2.4.7URANIUM SOLUBILITY 2.5EFFECT OF NUMBER OF REALIZATIONS 2.6EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION FUNCTIONS 2
 and URhGe
and URhGeTateiwa, Naoyuki; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Fisk, Z.
no journal, ,
We study the critical phenomena associated with ferromagnetic transitions in the uranium ferromagnetic superconductors UGe and URhGe. The critical phenomena were found to be of the unconventional type. We will discuss its origin.
and URhGe. The critical phenomena were found to be of the unconventional type. We will discuss its origin.
Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English