Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aghamiri, S. M. S.*; Sugawara, Naoya*; Ukai, Shigeharu; Ono, Naoko*; Sakamoto, Kan*; Yamashita, Shinichiro
Materials Characterization, 176, p.111043_1 - 111043_6, 2021/06
Advanced oxidation-resistant FeCrAl ODS alloys were developed via the control of composition-processing conditions for the accident tolerant fuel (ATF) cladding. For the first time, a single-crystal like recrystallized FeCrAl ODS alloy was achieved with a unique crystallographic texture of 110-plane and 211-direction and a high number density of fine nanoscale oxide particles. Evaluation of yield strengths at different temperatures showed higher values in transverse (T) direction than longitudinal (L) direction. The crystal orientation dependence of the yield strength up to 800 C was attributed to lower value of Schmid factor in transverse direction. Accordingly, the critical resolved shear stress of this practical class of advanced materials was calculated in various temperatures.
C was attributed to lower value of Schmid factor in transverse direction. Accordingly, the critical resolved shear stress of this practical class of advanced materials was calculated in various temperatures.

Kitagaki, Toru; Hoshino, Takanori; Yano, Kimihiko; Okamura, Nobuo; Ohara, Hiroshi*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Koizumi, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 4(3), p.031011_1 - 031011_7, 2018/07
Nagase, Fumihisa; Sakamoto, Kan*; Yamashita, Shinichiro
Corrosion Reviews, 35(3), p.129 - 140, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.97(Electrochemistry)As the lessons learnt from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, advanced cladding materials are being developed to enhance accident tolerance comparing with conventional zirconium alloys. The present paper reviews the progress of the development and summarizes subjects to be solved for the enhanced accident-tolerance fuel cladding, focusing on performance degradation under various corrosive environmental conditions that should be considered in designing the LWR fuel.
Sato, Isamu; Tanaka, Kosuke; Koyama, Shinichi; Matsushima, Kenichi*; Matsunaga, Junji*; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Endo, Hiroshi*; Haga, Kazuo*
Energy Procedia, 82, p.86 - 91, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experiments simulating overheating conditions of fast reactor severe accidents have been previously carried out with irradiated fuels. For the present study, the chemical forms of the fission products (FPs) included in the irradiated fuels were evaluated by thermochemical equilibrium calculations. At temperatures of 2773 K and 2973 K, the most stable forms of Cs, I, Te, Sb, Pd and Ag are gaseous compounds. Cs and Sb detected in the thermal gradient tube (TGT) in the experiments can take gaseous chemical forms of elemental Cs, CsI, Cs MoO
MoO , CsO and elemental Sb, SbO, SbTe, respectively. By comparing experimental results and the estimations, it is seen CsI thermochemically behaves in a manner that traps it in the TGT, while elemental Cs trends to move as fine particles. The moving behavior of the gaseous FPs will obey not only thermochemical principles, but also those of particle dynamics.
, CsO and elemental Sb, SbO, SbTe, respectively. By comparing experimental results and the estimations, it is seen CsI thermochemically behaves in a manner that traps it in the TGT, while elemental Cs trends to move as fine particles. The moving behavior of the gaseous FPs will obey not only thermochemical principles, but also those of particle dynamics.
Sakamoto, Kan*; Shibata, Hiroki; Une, Katsumi*; Ouchi, Atsushi*; Aomi, Masaki*; Kurata, Masaki
Proceedings of 2014 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting/ Top Fuel / LWR Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2014/09
The depth profiles of hydrogen were measured at outer surface of fuel claddings corroded in high temperature steams at 1073-1473 K to examine the barrierness of surface oxide layer against the hydrogen absorption/desorption. The results indicated that the oxide layer would be no longer the barrier against the hydrogen under some conditions although it remained as the barrier against the oxidation.
 powder induced by helium precipitation
powder induced by helium precipitationSerizawa, Hiroyuki; Matsunaga, Junji*; Shirasu, Noriko; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kashibe, Shinji*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies (Internet), 1(3), p.289 - 295, 2013/09
This report addresses the precipitation of helium in polycrystalline UO , which deforms the morphology of the grains and their surfaces Helium was injected into pulverized UO
, which deforms the morphology of the grains and their surfaces Helium was injected into pulverized UO particles at 1473 K by hot isostatic pressing (HIP). The specific surface area measured by volumetric gas adsorption instrument implied that small pores should exist on the as-helium-treated sample surface. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy observations showed that numerous shallow basins (approximately 500 nm in radius) with hexagonal fringe were formed on the surface. The basin resembles a ruptured blister whose lid has been forced open. SEM observations showed a uniform polygonal-shaped section of the gas bubble on the fracture surface; this implies that precipitated helium forms a negative crystal in the grain.
particles at 1473 K by hot isostatic pressing (HIP). The specific surface area measured by volumetric gas adsorption instrument implied that small pores should exist on the as-helium-treated sample surface. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy observations showed that numerous shallow basins (approximately 500 nm in radius) with hexagonal fringe were formed on the surface. The basin resembles a ruptured blister whose lid has been forced open. SEM observations showed a uniform polygonal-shaped section of the gas bubble on the fracture surface; this implies that precipitated helium forms a negative crystal in the grain.
Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Matsunaga, Junji*; Haga, Yoshinori; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Akabori, Mitsuo; Tsuru, Tomohito; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Kashibe, Shinji*; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
Crystal Growth & Design, 13(7), p.2815 - 2823, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.72(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Since the shape of the negative crystal closely relates to the morphology of the crystal habits, the formation and the growth mechanism is important subject in a field of the physical science. Whereas, the negative crystal formed in a large single crystal mass has been arousing interest as an expensive jewelry because of its mysterious appearance and rarity. However, it is difficult to control the shape of this polyhedral cavity embedded in a solid medium arbitrary. Here we report the recent discovery on the growth process of the negative crystal. We found that precipitated helium forms the negative crystal in UO ; the shape changes drastically with the condition of the helium precipitation. The transformation mechanism was discussed in this article. Our investigation implies that the shape of the negative crystal can be arbitrary controlled by controlling the precipitation condition.
; the shape changes drastically with the condition of the helium precipitation. The transformation mechanism was discussed in this article. Our investigation implies that the shape of the negative crystal can be arbitrary controlled by controlling the precipitation condition.
Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Matsunaga, Junji*; Haga, Yoshinori; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kashibe, Shinji*; Iwai, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2011-025, 32 Pages, 2011/11
This report deals with the precipitation of helium in UO matrix to deform the microstructure. The examination was performed using single and polycrystalline UO
matrix to deform the microstructure. The examination was performed using single and polycrystalline UO sample. The helium-treated samples under 900 atm at 1473 K were reheat-treated at much more high temperature, 1573 K or 1973 K to release the infused helium. The microstructure of the sample was examined by FIB, FE-STEM and FE-TEM. It was confirmed that precipitated helium atoms form a negative crystal in the grain or the matrix of the single crystal. At 1573 K, helium can be released without formation of intergranular tunnel since the surface diffusion coefficient of helium is large. However, some open grain boundaries were observed in the sample heat-treated at 1973 K. This might be related to the activity of helium in the grain boundary region. The structure of the negative crystal was analyzed from the view point of the thermodynamics of the surface growth.
sample. The helium-treated samples under 900 atm at 1473 K were reheat-treated at much more high temperature, 1573 K or 1973 K to release the infused helium. The microstructure of the sample was examined by FIB, FE-STEM and FE-TEM. It was confirmed that precipitated helium atoms form a negative crystal in the grain or the matrix of the single crystal. At 1573 K, helium can be released without formation of intergranular tunnel since the surface diffusion coefficient of helium is large. However, some open grain boundaries were observed in the sample heat-treated at 1973 K. This might be related to the activity of helium in the grain boundary region. The structure of the negative crystal was analyzed from the view point of the thermodynamics of the surface growth.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi; Kikuchi, Masahiko; Kita, Satoshi; Yonekawa, Minoru; Nakano, Junichi; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Nakajima, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part1), p.331 - 334, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) caused by simultaneous effects of neutron irradiation and high temperature water environments has been pointed out as one of the major concerns of in-core structural materials not only for the light water reactors (LWRs) but also for the water-cooled fusion reactor. It is necessary to evaluate precisely stress condition under irradiation environment, because stress is one of key factors on IASCC. Stress relaxation of tensile type specimens under fast neutron irradiation at 288 C has been studied for type 316L stainless steel in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). This paper describes the in-pile and out-of-pile stress-relaxation test results of tensile type specimens for type 316L stainless steel as compared with the literature data by Foster, which were mainly obtained by bent beam specimens. Moreover these experimental results were compared with the analytical ones by using Nakagawa's model.
C has been studied for type 316L stainless steel in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). This paper describes the in-pile and out-of-pile stress-relaxation test results of tensile type specimens for type 316L stainless steel as compared with the literature data by Foster, which were mainly obtained by bent beam specimens. Moreover these experimental results were compared with the analytical ones by using Nakagawa's model.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Matsui, Yoshinori; Kita, Satoshi; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsukada, Takashi; Tsuji, Hirokazu
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 217(3), p.283 - 288, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), in-pile strain measurement techniques have been developed using the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In order to evaluate the performance of fiber optic grating sensors under irradiation environment, heat-up and performance tests at elevated temperatures before irradiation and in-pile tests were performed in JMTR. It was determined that it is possible to measure strain under irradiation environment below 1 1023n/m
1023n/m (E
(E 1MeV) by a fiber optic grating sensor, because in-pile temperature characteristics were in good agreement with out-of-pile test results.
1MeV) by a fiber optic grating sensor, because in-pile temperature characteristics were in good agreement with out-of-pile test results.
Morihira, Masayuki; Segawa, Tomoomi; Namekawa, Takashi; Matsuyama, Shinichiro*; Yuda, Ryoichi*; Mizusako, Fumiki*
no journal, ,
Investigation of oxygen getter option is in progress for FBR MOX fuel to restrain the cladding inner surface corrosion at the high burn-up of 150 GWd/t. Evaluation of the requirement for the oxygen getter materials showed that Zr and Ti were promising candidate materials. Method of loading getter materials into a fuel element was also investigated. Their oxygen uptake ability and restructuring behavior during the oxidation were evaluated by the heating at 1573 K for 10 h under the controlled oxygen potential. As a result, it was shown that both Zr and Ti were available as an oxygen absorber but Ti was superior from the geometrical stability.
 and FMS
and FMSSegawa, Tomoomi; Morihira, Masayuki; Namekawa, Takashi; Matsuyama, Shinichiro*; Yuda, Ryoichi*; Mizusako, Fumiki*
no journal, ,
Heating tests were carried out for the disc pares of Zr-FMS, Ti-FMS, Zr-UO and Ti-UO
and Ti-UO to evaluate the compatibility of the candidate materials of oxygen getter with UO
to evaluate the compatibility of the candidate materials of oxygen getter with UO and FMS, and the interfaces of each disc were investigated. No reaction was observed between Zr and UO
and FMS, and the interfaces of each disc were investigated. No reaction was observed between Zr and UO also FMS in the test conditions. For Ti and FMS, Ti-Fe-O phase with the maximum thickness of 14
also FMS in the test conditions. For Ti and FMS, Ti-Fe-O phase with the maximum thickness of 14  m was formed in the Ti disc at 700
m was formed in the Ti disc at 700 C for 100 h but no penetration of Ti into FMS disc was observed. For Ti and UO
C for 100 h but no penetration of Ti into FMS disc was observed. For Ti and UO , Ti-U or Ti-U-O phase were formed near the surface of the Ti disc but these were limited in Ti disc side. No penetration of Ti into UO
, Ti-U or Ti-U-O phase were formed near the surface of the Ti disc but these were limited in Ti disc side. No penetration of Ti into UO disc was observed. As a result, it is considered that no harmful influence is expected for Zr and Ti on the integrity of UO
disc was observed. As a result, it is considered that no harmful influence is expected for Zr and Ti on the integrity of UO and FMS cladding.
and FMS cladding.
Matsunaga, Junji*; Une, Katsumi*; Kusagaya, Kazuyuki*; Hirosawa, Takashi; Sato, Isamu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 by helium release
by helium releaseMatsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Iwai, Takashi
no journal, ,
Variation of microstructure of UO by precipitation of helium was examined using FIB and FE-TEM. The swelling accompanied by the formation of a gas bubble was evaluated. The number of helium gas bubble increased remarkably at the temperature more than 1300
by precipitation of helium was examined using FIB and FE-TEM. The swelling accompanied by the formation of a gas bubble was evaluated. The number of helium gas bubble increased remarkably at the temperature more than 1300  C. The formation of a tunnel was observed in the grain boundary after the heat treatment at 1700
C. The formation of a tunnel was observed in the grain boundary after the heat treatment at 1700  C.
C.
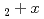
Matsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Iwai, Takashi; Haga, Yoshinori; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
The aim of this study is to clarify the behavior of helium precipitated in UO . The micro-structure of UO
. The micro-structure of UO matrix deformed by helium infusion was examined by FE-SEM and FE-TEM. It was deduced that the shape of the negative crystal is determined by the balance between the surface energy of the lattice plane and the inner pressure of helium.
matrix deformed by helium infusion was examined by FE-SEM and FE-TEM. It was deduced that the shape of the negative crystal is determined by the balance between the surface energy of the lattice plane and the inner pressure of helium.

Matsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Iwai, Takashi; Haga, Yoshinori; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
Helium generated in MOX fuel increases inner pressure of fuel rod and helium could also form additional bubbles in fuel pellet by the combination of radiation defects and high temperature. Therefore it is important to understand the behavior of helium in oxide fuel for reliable operation of MOX fuels. In the present study, the helium infusion treatments in high temperature and high pressure of helium were performed for both sintered polycrystalline UO fragments and hyperstoichiometric monograin UO
fragments and hyperstoichiometric monograin UO particles fabricated by the transportation method. It was suggested that the difference in the composition of UO
particles fabricated by the transportation method. It was suggested that the difference in the composition of UO is closely related with the condition of the formation of the negative crystal.
is closely related with the condition of the formation of the negative crystal.
 and its inner pressure
and its inner pressureMatsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Iwai, Takashi; Haga, Yoshinori; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
In the present study, the helium infusion were conducted at high temperature with highly pressurized helium for both UO . Following a high temperature treatment, the negative crystal formed in the sample was examined by FE-SEM. The SEM image was analyzed to measure the area of the surface on the negative crystal which is composed of facetted lattice planes. It was confirmed that the shape of the negative crystal formed in this method is deviated from the equilibrium shape reported previously, which means that the higher inner pressure produced by the helium precipitated in the cavity relate to the shape of the negative crystal.
. Following a high temperature treatment, the negative crystal formed in the sample was examined by FE-SEM. The SEM image was analyzed to measure the area of the surface on the negative crystal which is composed of facetted lattice planes. It was confirmed that the shape of the negative crystal formed in this method is deviated from the equilibrium shape reported previously, which means that the higher inner pressure produced by the helium precipitated in the cavity relate to the shape of the negative crystal.

Matsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
We applied the helium infusion technique by a hot isothermal pressing (HIP) method and CeO was used for helium infusion. A sintered CeO
was used for helium infusion. A sintered CeO pellet was reduced in hydrogen atmosphere at 1073 K for 1 hour. O/Ce ratio of as-sintered CeO
pellet was reduced in hydrogen atmosphere at 1073 K for 1 hour. O/Ce ratio of as-sintered CeO and reduced CeO
and reduced CeO was evaluated by XRD as 2.00 and 1.99, respectively. The helium infusion was conducted under the experimental condition at 1473 K and 50 MPa of helium for CeO
was evaluated by XRD as 2.00 and 1.99, respectively. The helium infusion was conducted under the experimental condition at 1473 K and 50 MPa of helium for CeO and CeO
and CeO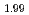 . As helium treated samples were annealed at 1773 K under atmospheric pressure in argon. By the heat treatment, additional intra- and intergranular bubbles were formed in CeO
. As helium treated samples were annealed at 1773 K under atmospheric pressure in argon. By the heat treatment, additional intra- and intergranular bubbles were formed in CeO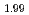 . However, such kind of bubble was not found in the stoichiometric CeO
. However, such kind of bubble was not found in the stoichiometric CeO . The sizes of intragranular bubbles in CeO
. The sizes of intragranular bubbles in CeO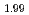 were about less than 100 nm, and intergranular bubbles were larger than those in grain. We at this consider that helium can dissolve into CeO
were about less than 100 nm, and intergranular bubbles were larger than those in grain. We at this consider that helium can dissolve into CeO matrix and oxygen vacancy would increase solubility of helium.
matrix and oxygen vacancy would increase solubility of helium.
Matsunaga, Junji*; Kashibe, Shinji*; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Oishi, Yuji*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
In the developing MA-MOX fuel, the accumulation of helium should be serious problem since minor actinides are  -emitter. In this paper, we will discuss a mechanism of inter-granular gas bubble produced by the helium injected into UO
-emitter. In this paper, we will discuss a mechanism of inter-granular gas bubble produced by the helium injected into UO using HIP.
using HIP.
Sato, Isamu; Tanaka, Kosuke; Koyama, Shinichi; Matsushima, Kenichi*; Matsunaga, Junji*; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Endo, Hiroshi*; Haga, Kazuo*
no journal, ,
Thermochemical equilibrium calculations of gaseous chemical forms and adhering chemical forms of fission products and fuel elements were performed simulating the heating test condition done for irradiated fuels to discuss the release behavior of fission products from overheated fuels.