Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Noda, Masaru*; Ando, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*
JNC TJ7420 2005-023, 116 Pages, 2004/03
The Objectives of this study is to develop the modeling strategy for high permeable fracture zone around active fault and influence of tectonically movement. Hydrogeological model of Atotsugawa-fault and Tsukiyoshi fault is developed for groundwater flow analysis. Last year, literature survey for hydrogeological modeling and groundwater flow analysis was performed, and hydrogeological model of Mozumisukenobu-fault was initiated based on JNC research. This year, the strategy for hydrogeological model of Mozumisukenobu-fault, Tsukiyoshi fault and active fault of Tottori-ken Seibu Earthquake is developed. The quality and quantity of hydrogeological information are different among the above three areas, therefore well developed strategy for the adequate modeling and analyzing is required. Finally local scale model of Mozumisukenobu-fault (2kmx2kmx500m) and Tsukyoshi-fault(4kmx6km3km), and regional scale model of active fault of Tottori-ken Seibu Earthquake(30kmx30kmx5km) are created and analyzed as an initial model.
Noda, Masaru*; Ando, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*
JNC TJ7400 2005-068, 133 Pages, 2004/03
The objectives of this study is to evaluate the applicability of several well test simulators using field data. Single hole well test is effective method to evaluate hydraulic conductivity using a borehole. Recently comprehensive well test and interactive software for computer-aided interpretation of well test have been developed. Especially deep geological condition with low permeability domain requires more effective method. This study motivates for selecting different interpretation codes like AQTESOLV as a semi-analytical codes, nSights and MULTISIM as a historical matching type graphical inverse code, and TOUGH2/ITOUGH2 as a FDM inverse code. Then all codes apply to three categorized data, that one is theoretical data as a code evaluation, then two data are from real field to demonstrate that not only codes but also processes may affect the result. Finally evaluation of codes, fluctuation of hydraulic property, and code specific handling are studied and the basis for well test strategy is obtained.
Toriihara, Makoto*; Maruyama, Makoto*; Suzuki, Kenichiro*; Namiki, Kazuto*
JNC TJ7400 2005-034, 179 Pages, 2004/02
Elucidation of the physichal process leading to brittle failure in crystalline rocks and modeling its mechanism is of fundamental importance in evaluating the mechanical and hydraulic properties of EDZ. In this study, Granitic rock columns and plates with circular opening were subjected to triaxial compression and tension tests and measured elastic wave velocity and resisitivity to analyze nucleation and growth of microcracks. The following conclusions were important to note that: (1)During 90% to 100% stress levels to failure stress, it appear that cracks grew on their size but no cracks were nucleated. (2)It was demonstrated that crack tensor F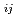 was closely related the second rank tensor V
was closely related the second rank tensor V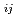 which was determined by measuring elastic wave velocity on at least six direction. (3)The applicability of numerical analysis model based on the micromechanics was introduced. This could be considered the mechanism of the damage growth (microcrack growth) and the interaction among microcracks. (4)On the experiment of Granitic rock plates with circular opening, the process leading to brittle failure and damage growth of the rock around the opening were observed with AE monitoring and so on. (5)In order to evaluate the variety of permeability with the damage growth, it was showed that permeability tensor in terms of crack tensor gave the permeability change in stress history.
which was determined by measuring elastic wave velocity on at least six direction. (3)The applicability of numerical analysis model based on the micromechanics was introduced. This could be considered the mechanism of the damage growth (microcrack growth) and the interaction among microcracks. (4)On the experiment of Granitic rock plates with circular opening, the process leading to brittle failure and damage growth of the rock around the opening were observed with AE monitoring and so on. (5)In order to evaluate the variety of permeability with the damage growth, it was showed that permeability tensor in terms of crack tensor gave the permeability change in stress history.
Noda, Masaru*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*
JNC TJ7420 2005-028, 247 Pages, 2003/03
The Objectives of this study is to develop the modeling strategy for high permeable fracture zone around active fault and influence of tectonically movement. Hydrogeological model of Mozumisukenobu-fault is developed for groundwater flow analysis. The literature survey for hydrogeological modeling and groundwater flow analysis was performed. Information of the characterization methods of faults, hydrogeological modeling of faults and the correlation anisotropy and the stress satate in 20 documents was arranged.Data concerning the fault rock and the fracture geometry needed to hydrogeological modeling and groundwater anaysis was extracted, interpreted and digitalized based on JNC existing research. Hydrogeological model of Mozumisukenobu-fault was initiated based on JNC research. Finally local scale model of Mozumisukenobu-fault (2kmx2kmx500m) is created and analyzed as an initial model.
Somaki, Takahiro*; Miyamoto, Akinori*
JNC TJ9420 2003-005, 129 Pages, 2003/02
In order to realize the concept of a vertical isolation system called common deck system, research and development on the vertical isolation structure is now underway. In its first step, structure plans of each of the isolation element and the damper element will be drawn up, and in the next step, tests on these elements will be planed, executed, analyzed, and evaluated, to be reflected to the structure plan. In this report, the study of analysis, the structure plan and test plan of vertical isolation devices is reported. /The appropriateness of analysis was confirmed by comparison between test results and analysis results. And the loading mechanism and the stress condition of dish spring as piling five lines were analyzed./The formula of Creep was examined on creep test results. And the influence of amount of deformation by creep behavior was made clear on the life of building./The characteristic of loading in actual typical model was presumed by test results, design formula and FEM analysis. These results were mostly coincided and the appropriateness of design method was confirmed./Response displacement of a vertical isolation and response acceleration of primary instruments were analyzed and confirmed beyond restriction values by dynamic analysis./The total fabrication of isolation device and each component were drowned on the result of these studies./The scale of test model was estimated and the map of test model was drowned. And several test plans reflects design guideline were made.
Toriihara, Makoto*; Maruyama, Makoto*; Kuwahara, T.*; Suzuki, Kenichiro*
JNC TJ7400 2005-032, 206 Pages, 2003/02
Elucidation of the physical process leading to brittle failure in crystalline rocks and modeling its mechanism is of fundamental importance in evaluating the mechanical and hydraulic properties of EDZ. In this study, Granitic rock columns and plates with circular opening were subjected to triaxial compression and tension tests and measured elastic wave velocity and resisitivity to analyze nucleation and growth of microcracks. The following conclusions were important to note that: (1)During 90% to 100% stress levels to failure stress, it appear that cracks grew on their size but no cracks were nucleated. (2)It was demonstrated that crack tensor F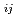 was closely related the second rank tensor V
was closely related the second rank tensor V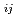 which was determined by measuring elastic wave velocity on at least six direction. (3)The applicability of numerical analysis model based on the micromechanics was introduced. This could be considered the mechanism of the damage growth (microcrack growth) and the interaction among microcracks. (4)On the experiment of Granitic rock plates with circular opening, the process leading to brittle failure and damage growth of the rock around the opening were observed with AE monitoring and so on. (5)In order to evaluate the variety of permeability with the damage growth, it was showed that permeability tensor in terms of crack tensor gave the permeability change in stress history.
which was determined by measuring elastic wave velocity on at least six direction. (3)The applicability of numerical analysis model based on the micromechanics was introduced. This could be considered the mechanism of the damage growth (microcrack growth) and the interaction among microcracks. (4)On the experiment of Granitic rock plates with circular opening, the process leading to brittle failure and damage growth of the rock around the opening were observed with AE monitoring and so on. (5)In order to evaluate the variety of permeability with the damage growth, it was showed that permeability tensor in terms of crack tensor gave the permeability change in stress history.
Maruyama, Makoto*; Toriihara, Makoto*; Mikami, Tetsuji*; Hata, Koji*
JNC TJ7400 2005-030, 106 Pages, 2003/02
no abstracts in English