Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
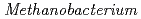 strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe
strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe under a freshwater environment
under a freshwater environmentHirano, Shinichi*; Ihara, Sota*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Dotsuta, Yuma; Otani, Kyohei; Kitagaki, Toru; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Microorganisms (Internet), 10(2), p.270_1 - 270_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:84.82(Microbiology)To understand the role of methanogens in corrosion under anoxic conditions in freshwater, we investigated the corrosion activities of methanogens in samples collected from groundwater and rivers. We enriched microorganisms that can grow with CO /NaHCO
/NaHCO and Fe
and Fe as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that
as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that 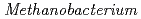 strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe
strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kimura, Junichi*; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Danhara, Toru*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Chang, Q.*; Miyazaki, Takashi*; et al.
Geochemical Journal, 52(6), p.531 - 540, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:65.79(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Okuchi, Takuo*; Tomioka, Naotaka*; Purevjav, N.*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51, p.1564 - 1570, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.9(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)It is demonstrated that quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) is a novel and effective method to analyse atomic scale hydrogen transport processes occurring within a mineral crystal lattice. The method was previously characterized as sensitive for analysing the transport frequency and distance of highly diffusive hydrogen atoms or water molecules in condensed matter. Here are shown the results of its application to analyse the transport of much slower hydrogen atoms which are bonded into a crystal lattice as hydroxyls. Two types of hydrogen transport process were observed in brucite, Mg(OH) : a jump within a single two-dimensional layer of the hydrogen lattice and a jump into the next nearest layer of it. These transport processes observed within the prototypical structure of brucite have direct implications for hydrogen transport phenomena occurring within various types of oxides and minerals having layered structures.
: a jump within a single two-dimensional layer of the hydrogen lattice and a jump into the next nearest layer of it. These transport processes observed within the prototypical structure of brucite have direct implications for hydrogen transport phenomena occurring within various types of oxides and minerals having layered structures.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Nishikawa, Shiro*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Usui, Norihisa*; Kamachi, Masafumi*; Aso, Noriko*; Tanaka, Yusuke*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 18(1), p.81 - 96, 2014/09
A drift simulation of tsunami debris flushed out from the Tohoku district, Japan, into the North Pacific due to the tsunami on March 11, 2011, has been conducted to monitor and forecast the drift path over the North Pacific. Results showed that tsunami debris was first transported eastward by the intense Kuroshio Extension and westerly, spreading in the north and south directions by both an energetic ocean eddy and a storm track over the ocean. Tsunami debris with larger windage was transported over the North Pacific by ocean surface wind rather than ocean current and arrived at the west coast of the North American Continent in the fall of 2011. Tsunami debris located near the North American Continent migrated, associated with the basin-scale seasonal change in the atmospheric pressure pattern. Our forecast run suggested that the tsunami debris belt will be formed from the North American Continent in the east to the Philippines in the west.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Furuno, Akiko; Usui, Norihisa*; Kamachi, Masafumi*; Nishikawa, Shiro*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*
Proceedings of 19th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2014/08
Numerical simulations on oceanic dispersion of the radioactive cesium in the North Pacific from March 2011 to September 2013 were conducted to clarify the concentration of the radioactive cesium released from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. We implemented the oceanic dispersion simulations with two independent ocean reanalysis dataset. It was suggested that the  Cs concentration in the North Pacific was lower than the pre-Fukushima background level about two years after the Fukushima disaster. The intercomparison revealed that meso-scale eddies in the Kuroshio Extension region may have efficiently diluted the radioactive cesium concentration at the sea surface. In addition, it was suggested that the enhanced downward current accompanied by the meso-scale eddies played an important role in transporting the radioactive cesium into the intermediate layer.
Cs concentration in the North Pacific was lower than the pre-Fukushima background level about two years after the Fukushima disaster. The intercomparison revealed that meso-scale eddies in the Kuroshio Extension region may have efficiently diluted the radioactive cesium concentration at the sea surface. In addition, it was suggested that the enhanced downward current accompanied by the meso-scale eddies played an important role in transporting the radioactive cesium into the intermediate layer.
Kumamoto, Yuichiro*; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Watanabe, Shuichi*; Yoneda, Minoru*; Shibata, Yasuyuki*; Togawa, Orihiko; Morita, Masatoshi*; Shitashima, Kiminori*
Journal of Oceanography, 64(3), p.429 - 441, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:25.5(Oceanography)In 1995 and 2000, radiocarbon ratio (
 C) of total dissolved inorganic carbon was measured in the Japan Sea, a semi-closed marginal sea in the western North Pacific, where deep and bottom waters are formed in itself. Compiling them with historical radiocarbon data in the Japan Sea, temporal and spatial variations of the radiocarbon in the bottom water below 2000 m depth were elucidated.
C) of total dissolved inorganic carbon was measured in the Japan Sea, a semi-closed marginal sea in the western North Pacific, where deep and bottom waters are formed in itself. Compiling them with historical radiocarbon data in the Japan Sea, temporal and spatial variations of the radiocarbon in the bottom water below 2000 m depth were elucidated. 
 C in the bottom waters in the western Japan and Yamato Basins increased by about 20 ‰ between 1977/79 and 1995 and did not changed between 1995 and 1999/2000, suggesting penetration of surface bomb-produced radiocarbon into the bottom waters due to bottom ventilation in the earlier period and stagnation of the bottom ventilation in the following period, respectively. In the eastern Japan Basin, the bottom
C in the bottom waters in the western Japan and Yamato Basins increased by about 20 ‰ between 1977/79 and 1995 and did not changed between 1995 and 1999/2000, suggesting penetration of surface bomb-produced radiocarbon into the bottom waters due to bottom ventilation in the earlier period and stagnation of the bottom ventilation in the following period, respectively. In the eastern Japan Basin, the bottom 
 C increased by about 10 ‰ between 1977/79 and 2002, suggesting less ventilation of the bottom water in the basin. The temporal changes of the radiocarbon, tritium, and dissolved oxygen suggest sporadic occurrences of the bottom ventilation between 1979 and 1984 and its stagnation between 1984 and 2004 in the eastern Japan and Yamato Basins. The former is probably due to spreading of a newly ventilated bottom water in the western Japan Basin in the severe winter of 1976-1977 along the abyssal circulation in the Japan Sea. The latter does not conflict with temporal changes of bomb-produced
C increased by about 10 ‰ between 1977/79 and 2002, suggesting less ventilation of the bottom water in the basin. The temporal changes of the radiocarbon, tritium, and dissolved oxygen suggest sporadic occurrences of the bottom ventilation between 1979 and 1984 and its stagnation between 1984 and 2004 in the eastern Japan and Yamato Basins. The former is probably due to spreading of a newly ventilated bottom water in the western Japan Basin in the severe winter of 1976-1977 along the abyssal circulation in the Japan Sea. The latter does not conflict with temporal changes of bomb-produced  Cs and chlorofluorocarbon-11 in the bottom water.
Cs and chlorofluorocarbon-11 in the bottom water.
Aramaki, Takafumi*; Togawa, Orihiko; Watanabe, Shuichi*; Tsunogai, Shizuo*; Taira, Keisuke*
no journal, ,
Radiocarbon data (
 C) were obtained in a wide range of surface and along the 165 degrees East in the western North Pacific between 1991 and 1993. The variability of
C) were obtained in a wide range of surface and along the 165 degrees East in the western North Pacific between 1991 and 1993. The variability of 
 C in surface water at north-south direction was larger than that at east-west direction, and
C in surface water at north-south direction was larger than that at east-west direction, and 
 C markedly decreased northward in the north of 40 degrees North. Comparing
C markedly decreased northward in the north of 40 degrees North. Comparing 
 C data along 165 degrees East with the 1973 GEOSECS, it became clear that the bomb-produced
C data along 165 degrees East with the 1973 GEOSECS, it became clear that the bomb-produced  C was transported from the surface to the intermediate layer in the sub-tropical region during the last 20 years, and not found in deep water in 1993. The distribution of the bomb-produced
C was transported from the surface to the intermediate layer in the sub-tropical region during the last 20 years, and not found in deep water in 1993. The distribution of the bomb-produced  C and age of the deep water suggest that the sub-tropical bomb-
C and age of the deep water suggest that the sub-tropical bomb- C increase is caused from considerably storing in the intermediate layer originated in the sub-arctic region taken by vertical mixing and transported the North Pacific Intermediate Water flowing southward.
C increase is caused from considerably storing in the intermediate layer originated in the sub-arctic region taken by vertical mixing and transported the North Pacific Intermediate Water flowing southward.
Hyakudome, Tadahiro*; Yoshida, Hiroshi*; Tsukioka, Satoshi*; Aoki, Taro*; Iikura, Hiroshi; Nojima, Takehiro; Yasuda, Ryo; Sakai, Takuro; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Maekawa, Yasunari; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya
no journal, ,
A drift simulation on the movement of the tsunami debris was carried out to examine the positions in the North Pacific after the Great East Japan Earthquake occurred on March 11, 2011. We carried out a hindcast experiment from March 2011 to August 2013 using the accurate input data reanalyzed through a three-dimensional variational data assimilation. A forecast experiment from September 2013 to May 2016 followed the hindcast experiment using the input data forecasted by a four-dimensional variational data assimilation system. It is suggested that the tsunami debris was mainly transported eastward by the Kuroshio Extension. The positions and date to wash ashore on the coast of the North American Continent depended on a kind of tsunami debris, because the tsunami debris floating over the sea surface is largely affected by the ocean surface wind. The tsunami debris in the vicinity of the North American Continent inclined to migrate southwestward.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Tanikawa, Wataru*; Hamada, Yohei*; Kameda, Jun*; Yamaguchi, Asuka*; Kimura, Gaku*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Hiroaki; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Chang, Q.*; Kimura, Junichi*
no journal, ,
The chronological information about carbonates is useful for modeling and enables forecast of geological and geochemical environmental changes by simulating. The U-Th-Pb dating method for carbonates which were formed at reducing environment remain to be established. The final goal of our study is to establish in situ U-Th-Pb dating method for carbonates which are filling cracks in pervious rock like fault rocks. In this study, the U-Th-Pb elemental and isotopic two-dimension distribution for an ammonite fossil were visualized by "Imaging" method using Laser-ablation ICP Mass Spectrometry. In U-Pb isotope analysis for carbonates in cracks of granites, we could not obtain significant U-Pb age data by the lack of uranium and influence of non-radiogenic common lead. When the concentration of lead is sufficiently high for the measurement, we obtained reliable isotopic data from carbonates and their lead isotopic composition reflected characteristic composition of their origin water.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Nishikawa, Shiro*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Usui, Norihisa*; Kamachi, Masafumi*
no journal, ,
Tsunami debris was flushed out due to tsunami accompanied by the Great East Japan Earthquake in March 2011. In this study, simulation on distribution of tsunami debris was carried out in cooperation with Japan Agency for JAMSTEC and MRI, JMA. An ocean dispersion model SEA-GEARN developed at JAEA was used in this study. We used the ocean current and sea surface wind data from March 2011 to September 2013 calculated by an ocean data assimilation system MOVE developed at MRI, JMA. On the other hand, we used them from October 2013 to June 2016 calculated by an atmosphere-ocean coupling data assimilation system K7 developed at JAMSTEC. It was suggested that tsunami debris was transported eastward by the Kuroshio Extension and reached the western U.S. coast. In addition, it was forecasted that a large part of tsunami debris would spread in the southern part of the North Pacific.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Takahiro; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Miyazaki, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Chronological and geochemical studies of carbonates, which are commonly found as fracture filling minerals in rocks, can provide information about geochemical conditions present during formation including in deep subsurface environments. A dating technique for the carbonates using laser ablation-multiple collector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICPMS) is still immature partly because of a lack of a consensus international carbonate standard for the in-situ dating technique. In this study, we performed a survey on the carbonate standard materials that may be suitable for high precision U-Th-Pb dating using LA-MC-ICPMS. We examined carbonate standard materials JCp-1 and JCt-1 issued by the Geological Survey of Japan (GSJ). Based on solution-based bulk analysis using MC-ICP-MS, heterogeneities in Pb isotope compositions were confirmed. Nevertheless, the 206Pb-based isotopic compositions were all within 1.2 per mill variations acceptable for a standard used for age determination using LA-MC-ICPMS. Additional tests on the heterogenities in U-Th-Pb compositions of the carbonate standards along with determinations of other trace elements using a 2D imaging LA-ICP-MS are ongoing. Examinations on both natural standards and synthetic standards are ongoing for further efforts in determination of the standard suitable for U-Th-Pb dating of carbonates.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kokubu, Yoko; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Murakami, Hiroaki; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Chang, Q.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Tatsunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kokubu, Yoko; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Murakami, Hiroaki; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Miyazaki, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Chronological and geochemical studies of calcium carbonates can provide precious information for changes in geochemical condition in deep geological environments. Because the carbonate can be found as common filling minerals in rocks, age zoning and spatial distribution of chemical composition in the carbonate could be a wide-use indicator to reconstruct the past environmental changes. Calcite and other carbonate materials have been dated by Isotope Dilution-Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry. On the other hand, a few of U-Pb dating studies in a micro scale area (less than 10 micrometer) such as using laser ablation-multiple collector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICPMS) has been conducted on the carbonate. The U-Pb dating technique for the carbonates using LA-MC-ICPMS is still immature partly because of a lack of consensus international carbonate reference materials for the in-situ dating technique. In order to solve this problem, we performed a survey on the carbonate reference materials that may be suitable for high precision U-Pb dating using LA-MC-ICPMS. Additionally, we conducted experiments to make compositionally homogeneous carbonate (calcite) reference materials.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kokubu, Yoko; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Chang, Q.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirano, Shinichi*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Akihiro*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirano, Shinichi*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English