Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okada, Yuji; Magome, Hirokatsu; Matsui, Yoshinori
JAEA-Technology 2022-014, 113 Pages, 2022/09
Material irradiation test system had been newly installed in JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) with taking 5 years which was from 2008 through 2013. The aim of material irradiation test system is to conduct IASCC (Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking) evaluation study. This system is mainly consist of water control unit, which can simulate elevated temperature and pressure of the light water reactor environment in the reactor, and load control unit, which can perform the crack propagation examination under irradiation. This load control unit gives a load to CT (Compact Tension) specimen, and perform the crack propagation examination. The principle of loading to CT specimen is using pressure difference between pressure generated by high temperature and high pressure water by water control unit in capsule and pressure generated by load gas pressure supplied by helium gas cylinder in bellows installed in load control unit. In 2013, the commissioning of material irradiation test system was carried out for adjustment. During this commissioning, the correlation between the differential pressure in load control unit and the load was confirmed by using the test container connected to load control unit with load cell. From the results of commissioning, the problem, which the load change speeds at loading and unloading were different due to different pressure change speeds by the piping resistance performance in the periodic loading test in which load from minimum to maximum repeatedly applied, was confirmed. This report summarizes the problem of load change speed due to the piping resistance performance, which was confirmed in 2013, the improvement and performance test of load control unit for solving the problem described above, which were carried out from 2014 to 2015, and operating procedure.
Shimada, Taro; Sukegawa, Takenori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.396 - 415, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation source models in DecDose code for assessing public and worker exposure doses during the decommissioning of nuclear facilities were improved in this study. A segmentation model evaluating the length, volume, and surface area of kerfs in the object to be dismantled was improved to deal with seven shapes of objects simulating most of the components and the structures in nuclear facilities. Models for the evaluation of the external dose by direct and skyshine radiation were also improved to deal with the distribution of waste containers temporarily placed in the building and the quantity of radionuclides stored in the individual container. Good agreement was observed between actual and calculated kerf volumes in cutting some components such as the reactor pressure vessel of the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor. It is an indication of the validity of the model improved in this study. On the other hand, some discrepancies were observed between actual and calculated quantities of radionuclides discharged into the ocean, indicating the necessity of further validation of the model.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 135(6), p.061403_1 - 061403_8, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Mechanical)When weld defects are observed during an inspection after welding, repair welding is performed after removing the defects. However, partial repair welding can potentially complicate the weld residual stress distribution. In this study, we performed thermal-elastic-plastic analyses to evaluate the weld residual stress produced by repair welding after pipe butt-welding. In addition, based on the analysis results for varying repair-welding conditions, we also performed structural integrity assessments related to stress corrosion cracking using the probabilistic fracture mechanics analysis code PASCAL-SP. It was clearly observed that the tensile stress in the repair-welded region increased and that compressive stresses occurred outside the repair-welded region. A deeper mechanical cutting depth caused larger increases in the tensile residual stress of the repair-welded region. It was also clarified that partial repair welding may favorably affect the break probability of piping welds.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Udagawa, Makoto; Nakamura, Mitsuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 135(5), p.051402_1 - 051402_9, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:72.37(Engineering, Mechanical)The residual stresses generated within the weld-overlay cladding and base material of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steel was evaluated for as-welded and post-welded heat-treated conditions using thermo-elastic plastic creep analyses considering phase transformation. By comparing the analytical results with the experimentally determined values, we found a good agreement for the residual stress distribution within the cladding and the base material. It was shown that considering phase transformation during welding was important for improving the accuracy of residual stress analysis. Using the calculated residual stress distribution, we performed fracture mechanics analyses for an RPV during pressurized thermal shock events. We evaluated the effect of the weld residual stress on the structural integrity of an RPV. The results indicated that consideration of residual stress produced by weld-overlay cladding and PWHT is important for assessing the structural integrity of RPV.
Takeda, Seiji; Inoue, Yoshihisa; Kimura, Hideo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.237 - 242, 2013/10
The sensitive analysis of radionuclide migration for the scenarios on deterioration or loss of safety functions expected in HLW disposal system due to the human error (initial defective scenarios) is performed in this study. Release rates for Cs-135 and Se-79 are estimated from Monte Carlo-based analysis. Maximum release rates of radionuclides for initial defective scenarios, buffer (colloidal transport case) and sealing plugs (pathway of short-circuit), are about one or two order magnitude higher than that normal scenario. From a viewpoint of future safety review, these results especially indicate the need to understand the feasibility on two types of initial defective scenario for the buffer and sealing plugs, leading to the loss of restraint of colloidal migration in the buffer and the loss of restraint with the plugs from migration through dominant pathway in tunnels and their vicinity.
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Masaki, Koichi*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 12(3), p.211 - 221, 2013/09
Probabilistic fracture mechanics analysis code PASCAL3 has been developed at JAEA to support the validation of the codes and standards which provide the structural integrity assessment method of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) during pressurized thermal shock. Previous version of PASCAL2 has many functions including the evaluation method for an embedded crack, PTS transient database, non-destructive inspection models. This code has been improved mainly focusing on cladding on the inner surface of RPV. Using the PASCAL3 code, effects of the initiation and growth model for a surface flaw have been analyzed to determine the standard condition of PASCAL3. Deterministic and probabilistic evaluation using PASCAL3 for current structural integrity assessment method for RPV has also been conducted. The results show that the consideration of warm pre-stress effect decreases the conditional probability
Masaki, Koichi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance (Internet), 5(2), p.85 - 92, 2013/08
In order to obtain the technical basis to judge the needs of surveillance test specimens from HAZ materials, the features of inhomogeneity of HAZ in RPV steels were investigated. Concerning on the fracture toughness in HAZ, HAZ materials close to weld metal indicated higher toughness than that of base metal due to high-toughness phase, while HAZ materials close to base metal were equivalent or slightly lower toughness than that of base metal due to the same phase as base metal. A structural integrity assessment method concerning such inhomogeneous distribution of fracture toughness for HAZ materials was developed and incorporated into PFM analysis code PASCAL3. Case studies on postulated flaws distribution and chemical composition were performed by using PASCAL3. It was shown that in highly irradiated conditions, CPI and CPF in HAZ close to weld metal are lower than base metal, while those in HAZ close to base metal were almost equivalent to base metal.
 C
CMaeda, Toshikatsu; Chiba, Noriaki; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 12(2), p.158 - 164, 2013/06
no abstracts in English
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Kitagawa, Isamu
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.411 - 422, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.52(Chemistry, Physical)Diffusive transport of Cs in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures was studied by a through diffusion method. Experiments were performed under variable aqueous compositions. Effective diffusivity (
in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures was studied by a through diffusion method. Experiments were performed under variable aqueous compositions. Effective diffusivity (
 ) values of 5.2E-10
) values of 5.2E-10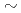 5.9E-9 m
5.9E-9 m s
s were obtained. The variation was somewhat large in the
were obtained. The variation was somewhat large in the 
 values. Apparent diffusivity (
values. Apparent diffusivity (
 ) values, on the other hand, were 2.0E-12
) values, on the other hand, were 2.0E-12  6.2E-12 m
6.2E-12 m s
s , which shows small variation. The results indicate that, in applying Fick's 1st law of diffusion, diffusive flux is proportional to the apparent concentration gradient of Cs in the sand-bentonite mixture rather than the gradient of Cs concentration in pore water. Since the apparent concentration gradient in sand-bentonite mixtures is nearly equal to the gradient of adsorbed Cs, diffusion of Cs under adsorbed state would be the main mechanism of diffusion of Cs in sand-bentonite mixtures.
, which shows small variation. The results indicate that, in applying Fick's 1st law of diffusion, diffusive flux is proportional to the apparent concentration gradient of Cs in the sand-bentonite mixture rather than the gradient of Cs concentration in pore water. Since the apparent concentration gradient in sand-bentonite mixtures is nearly equal to the gradient of adsorbed Cs, diffusion of Cs under adsorbed state would be the main mechanism of diffusion of Cs in sand-bentonite mixtures.
 concrete/clay interactions at the Tournemire URL
concrete/clay interactions at the Tournemire URLYamaguchi, Tetsuji; Kataoka, Masaharu; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Mukai, Masayuki; Hoshino, Seiichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Marsal, F.*; Pellegrini, D.*
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.185 - 197, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.54(Chemistry, Physical)Highly alkaline environments induced by cement based materials are likely to deteriorate the physical and/or chemical properties of the bentonite buffer materials in radioactive waste repositories. Predicting long-term alteration of concrete/clay systems requires physico-chemical models and a number of input parameters. In order to provide reliability to the long-term prediction of bentonite buffer performance under disposal conditions, it is necessary to develop and verify reactive transport codes for concrete/clay systems. In this study, a PHREEQC-based, reactive transport analysis code (MC-CEMENT ver.2) was developed and was verified by comparing results of the calculations with  observations of the mineralogical evolution at the concrete/argillite interface. The calculation reproduced the observations such as the mineralogical changes limited within one cm in thickness, formation of CaCO
observations of the mineralogical evolution at the concrete/argillite interface. The calculation reproduced the observations such as the mineralogical changes limited within one cm in thickness, formation of CaCO and CSH, dissolution of quartz, decrease of porosity in argillite and increase in concrete. These agreements indicate possibility that the models based on lab-scale (
and CSH, dissolution of quartz, decrease of porosity in argillite and increase in concrete. These agreements indicate possibility that the models based on lab-scale ( 1 y) experiments can be applied to longer time scale. The fact that the calculation did not reproduce the dissolution of clays and the formation of gypsum indicates that there is still room for improvement in our model.
1 y) experiments can be applied to longer time scale. The fact that the calculation did not reproduce the dissolution of clays and the formation of gypsum indicates that there is still room for improvement in our model.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Kadowaki, Mitsushi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.403 - 410, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:23.68(Chemistry, Physical)Montmorillonite is the main constituent of bentonite clay buffer materials in radioactive waste repositories. Highly alkaline environments induced by cement based materials are likely to alter montmorillonite, and to deteriorate the physical and/or chemical properties of the buffer materials. The deterioration may cause variation in hydraulic conductivity of the buffer and induce major uncertainties in the radionuclide migration analysis. Empirical data on the variation of hydraulic conductivity are, however, scarce mainly because the alteration of compacted buffer materials, sand-bentonite mixture specimen, is extremely slow. In this study, laboratory experiments were performed to observe changes in hydraulic conductivity of sand-bentonite mixtures accompanied with their alkaline alteration using NaOH based solutions at 80-90  C. Three types of experiments proved that the alkaline alteration of bentonite buffer can increase the hydraulic conductivity. The data obtained in this study are useful for verification of the code that will be used for assessing the alteration.
C. Three types of experiments proved that the alkaline alteration of bentonite buffer can increase the hydraulic conductivity. The data obtained in this study are useful for verification of the code that will be used for assessing the alteration.
Shibata, Toshio*; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Taniguchi, Naoki; Shimizu, Akihiko*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 62(2), p.70 - 77, 2013/02
In the oxygen depleted underground environment, carbon steel reacts with H O, producing H
O, producing H gas and forming corrosion film on the steel surface. Corrosion rate is controlled by diffusion of reaction species through corrosion film. Diffusion constants of some species working in the corrosion process were obtained from literatures. However, no data were found on the diffusion constant of H
gas and forming corrosion film on the steel surface. Corrosion rate is controlled by diffusion of reaction species through corrosion film. Diffusion constants of some species working in the corrosion process were obtained from literatures. However, no data were found on the diffusion constant of H O in iron oxides based on an appropriate assumption. Mass transfer model for the corrosion rate was used to simulate the corrosion rate of carbon steel. Liquid phase diffusion model of Fe
O in iron oxides based on an appropriate assumption. Mass transfer model for the corrosion rate was used to simulate the corrosion rate of carbon steel. Liquid phase diffusion model of Fe or H
or H O through pores in the corrosion film and solid phase diffusion model of H
O through pores in the corrosion film and solid phase diffusion model of H O through corrosion film itself were examined by Excel simulation. Change in corrosion current density and corrosion loss with time and pH and temperature dependence of corrosion current density were examined. By comparing the results, it is suggested that the solid phase diffusion of H
O through corrosion film itself were examined by Excel simulation. Change in corrosion current density and corrosion loss with time and pH and temperature dependence of corrosion current density were examined. By comparing the results, it is suggested that the solid phase diffusion of H O in the corrosion film controls the corrosion rate of carbon steel in oxygen depleted environment.
O in the corrosion film controls the corrosion rate of carbon steel in oxygen depleted environment.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Seguchi, Tadao*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 82, p.69 - 73, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:97.76(Chemistry, Physical)The oxidation products formed by thermal and radiation ageing of crosslinked polyethylene for cable insulation were analyzed by FTIR-ATR spectrometry. The most of products were composed of carboxylic acid, carboxylic ester, and carboxylic anhydride. The carboxylic acid was the primal product, and the others were the secondary products by the thermal reaction of carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid as the primal oxidation product supports the proposed new oxidation mechanisms that the main chain scission should occur directly by oxidation of polyethylene radicals.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Watashi, Katsumi; Suzuki, Masahide; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Oshima, Takeshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*
JAEA-Research 2012-029, 158 Pages, 2012/12
The degradation mechanisms of ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR), crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE), polyvinylchloride (PVC), and silicone rubber (SiR) as the cable insulation materials were investigated for the cable ageing research of the nuclear power plant. The materials as same insulations for the practical cable (practical formulation) and as the model formulation containing specific additive were selected. They were exposed to the accelerated radiation and thermal environments. The mechanical properties, the crosslinking and chain scission, and the distribution of antioxidant and of oxidative products were measured and analyzed.
Toyokawa, Takuya; Usami, Koji; Shiina, Hidenori; Onozawa, Atsushi
Proceedings of 49th Conference on Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2012) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2012/09
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Oshima, Takeshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2012-027, 46 Pages, 2012/08
The research on cable degradation mechanisms was conducted for 5 years in 2006 - 2010 as the project research of plant life management for nuclear power plant by NISA (Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency) of METI (Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry). At the finish of above research, the degradation mechanisms were reviewed on the analysis of many reports on cable degradation. The reports published after 1970 were mainly surveyed and the facts or data containing the experimental accuracy were selected. The verified facts, the reasonable interpretation of the facts, unresolved aspects were checked on the view points of recent techniques or analysis, and proposed the new model of degradation mechanisms was proposed.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2012 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2012) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2012/07
When weld defects are found by inspection after welding, partial repair welding need to be performed after removing the defects. The partial repair welding has a possibility to produce locally high tensile stress. In this study, we have performed thermal-elastic-plastic analyses to evaluate the weld residual stress produced by repair welding after piping butt-welding. The analysis results were validated through the comparison with experimental measurements. From the analysis results with varying the repair welding conditions, it was found that deeper cutting depth causes higher tensile residual stress at the partial welded region. We also performed structural integrity assessments related to SCC using the weld residual stress distribution calculated and probabilistic fracture mechanics analysis code PASCAL-SP. It was clarified that partial repair welding might have an effect to decrease the break probability of piping welds.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 134(3), p.031402_1 - 031402_7, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.74(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to provide the technical basis for the needs of surveillance specimens from heat-affected zone (HAZ) in reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels, we performed a research on the characterization of metallurgical and mechanical properties of HAZ in RPV steels. The distributions of grain size and phases were drawn as a map based on temperature histories obtained from welding simulation. Referring to the HAZ map, typical HAZ materials were made by simulating temperature histories including PWHT. Metallurgical and mechanical characteristics for the HAZ materials were compared with those of base metal. From the results, it was clarified that mechanical properties of HAZ materials depended not on the grain size, but mostly on the phases. HAZ materials close to weld metal indicated higher toughness due to mixed structure of martensite and lower bainite, while HAZ materials close to base metal were equivalent or slightly lower toughness due to the same phase as base metal of upper bainite.
Otsuka, Ichiro*; Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Kato, Osamu*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1475, p.507 - 512, 2012/06
We conducted corrosion experiments of carbon wires to identify the cathode reaction with overpack corrosion. Carbon steel wires were immersed in selected aqueous solutions of distilled water, sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and sodium sulfate solution sealed in glass ampoules. The ampoules were kept at 60  C for 150 days. Corrosion products, liquid phase and gas phases were analyzed. The results showed that hydrogen gas generation by reduction of hydrogen ions was dominant cathode reaction. Reduction of sulfate and carbonate anions was not observed. Amorphous ferrous hydroxide and/or iron oxides were identified in all the experiments as the corrosion products. Iron carbonate was also identified in the sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. This result indicates that the hydrogen generation reaction might be the dominant cathode reaction under geological disposal environment and that the Eh of the pore water would reach the equilibrium potential of the hydrogen generation reaction.
C for 150 days. Corrosion products, liquid phase and gas phases were analyzed. The results showed that hydrogen gas generation by reduction of hydrogen ions was dominant cathode reaction. Reduction of sulfate and carbonate anions was not observed. Amorphous ferrous hydroxide and/or iron oxides were identified in all the experiments as the corrosion products. Iron carbonate was also identified in the sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. This result indicates that the hydrogen generation reaction might be the dominant cathode reaction under geological disposal environment and that the Eh of the pore water would reach the equilibrium potential of the hydrogen generation reaction.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Tobita, Toru; Ito, Hiroto*; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 134(2), p.021403_1 - 021403_9, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.01(Engineering, Mechanical)Stress corrosion crackings (SCCs) in recirculation pipes of Type 316L stainless steel (SS) have been observed near butt-welding joints. These SCCs in Type 316L SS grow near the welding zone mainly due to high tensile residual stress by welding. In present work, scatters of welding conditions such as heat input and welding speed were measured experimentally by fabricating a series of butt-welded pipes. Residual stress distributions were measured by stress relief and X-ray diffraction methods. The effects of welding conditions on residual stress have been evaluated by parametric FEM analyses considering the variation of some welding parameters based on the experiments. The effects of welding conditions on crack growth behavior have been also evaluated by using calculated residual stress distributions. It was clearly shown that the uncertainties on welding heat input and speed have strong influences on SCC growth behavior.