Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara; Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Chiba, Go*; Ono, Michitaka*; Tojo, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.830 - 839, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:88.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear data processing code is important to connect evaluated nuclear data libraries and radiation transport codes. The nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 1 was released in 2019 to generate ACE formatted cross section files with simple input data. After we released FRENDY version 1, many functions were developed, e.g., neutron multi-group cross section generation, explicit consideration of the resonance interference effect among different nuclides in a material, consideration of the resonance upscattering, ACE file perturbation, and modification of ENDF-6 formatted file. FRENDY version 2 was released including these new functions. It generates GENDF and MATXS formatted neutron multi-group cross section files from an ACE formatted cross section file or an evaluated nuclear data file. This paper explains the features of the new functions implemented in FRENDY version 2 and the verification of the neutron multigroup cross section generation function of this code.
 U
UKunieda, Satoshi
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.138 - 142, 2024/02
The AMUR code was updated for analysis of neutron cross-sections on the heavier nuclei by introducing approximated R-matrix formulae defined in the ENDF-6 format. In this work, with the updated version of AMUR, let me demonstrate a feasibility analysis to experimental cross-sections on  U which are stored in the EXFOR database. It was confirmed that the values of the resonance parameters were successfully obtained through the fitting procedure, together with their covariance data. In this presentation, I will focus on discussions on the resulting correlation matrices of cross-sections, where the present results certainly show traces of constraints from the R-matrix theory.
U which are stored in the EXFOR database. It was confirmed that the values of the resonance parameters were successfully obtained through the fitting procedure, together with their covariance data. In this presentation, I will focus on discussions on the resulting correlation matrices of cross-sections, where the present results certainly show traces of constraints from the R-matrix theory.
Schnabel, G.*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara; Nakayama, Shinsuke; 27 of others*
Nuclear Data Sheets, 193, p.1 - 78, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:99.11(Physics, Nuclear)Fusion Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (FENDL), which has been coordinated by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), was updated for the neutronics analysis on the fusion reactors and related applications. The main sources of data files are the national nuclear data libraries such as ENDF, JEFF and JENDL, where the best data was selected for each isotope through comparisons of the evaluated cross-sections and a number of benchmark analyses. Large differences from the previous library (FENDL-2.1) are extension of the upper energy limit from 20 MeV to 200 MeV and inclusion of the charged-particle reaction data, which had been requested by accelerator-based studies on structural materials for the fusion reactors. This paper gives a comprehensive description on the latest version FENDL-3.2b. A number of validations on the neutronics analysis show that the performance of FENDL-3.2b is better than FENDL-2.1.
Sugawara, Takanori; Kunieda, Satoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/08
This study investigates the impact of the change from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5 on neutronics analysis of transmutation systems. As the transmutation systems, the following two systems are targeted: JAEA-ADS, a lead-bismuth cooled accelerator-driven system, and MARDS, a molten salt chloride accelerator-driven system. For the JAEA-ADS, the k-eff value increased 189 pcm from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5. It was found that the revisions of various nuclides affected to this difference. For example, the revision of  N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of
N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of  Cl and
Cl and  Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Dimitriou, P.*; Chen, Z.*; deBoer, R. J.*; Hale, G.*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Leeb, H.*; Paris, M.*; Pigni, M. T.*; Srdinko, Th.*; Tamagno, P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.03002_1 - 03002_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Charged-particle-induced reactions at low energies in the resolved resonance region are important for applications such as ion beam analysis of materials and management of the nuclear fuels. However, the evaluated nuclear data libraries maintained by national or international coordinated efforts (ENDF, JEFF, JENDL, CENDL) are to date, incomplete as far as charged-particle- induced reactions in the resolved resonance region are concerned. The IAEA Nuclear Data Section is coordinating an international effort to (i) verify that the existing R-matrix codes are consistent, (ii) evaluate charged-particle cross sections in the resolved resonance region, (iii) produce evaluated nuclear data files for further processing and finally (iv) disseminate the evaluated data through general purpose evaluated nuclear data libraries. We present the results of the effort made thus far on (1) verification of the available R-matrix codes, minimization methods and calculation of covariances, (2) the evaluation of the compound system  Be*, and (3) improving
Be*, and (3) improving 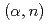 reaction data for the applications.
reaction data for the applications.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Tada, Kenichi; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.14001_1 - 14001_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kunieda, Satoshi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.03014_1 - 03014_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)For thorough understanding resonant theories and cause of discrepancies among different cross-section measurements, development of an R-matrix analysis code AMUR is being progressed. The code is organized by "theoretical" and "experimental" classes based on the object-oriented framework. In the theoretical class, with sharing the same compound nucleus, the independent distant poles can optionally be assumed for the simultaneous analysis of different projectile + nucleus pairs to see the relation between the channel radius and the theoretical background. In the experimental class, to simulate experimental conditions, calculated cross-sections can be corrected by the Doppler broadening, resolution functions, re-normalization, adding contaminant elements. I demonstrate some example analyses of measured cross-sections with AMUR both for the light and heavier nuclei to show effects of those new options. Also, preliminary results will be shown from analyses for experimental data of J-PARC/ANNRI.
Kunieda, Satoshi; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00017_1 - 00017_6, 2023/03
The AMUR code, which is based on the multi-channel/multi-level R-matrix theory, is under development for the cross-section evaluation with the covariance data in the resolved resonance energy region. Although, the code was initially designed for the analysis of the light-nuclei, the authors extended its capability toward the analysis of heavier nuclei by introducing the Reich-Moore approximation and the free-gas approximation for the Doppler broadening. In this work, we challenge a resonance analysis of neutron cross-section data measured in J-PARC/ANNRI with AMUR, in which the resolution functions and the double-bunching effects were taken into account inside the code. In this presentation, let us show results of resonance analysis on some of the J-PARC/ANNRI measurements together with covariance of the resonance parameters and cross-sections, for the first time. We also plan to discuss differences of correlation matrices among approximations of the R-matrix theory to understand physics underlying on the resonant reaction.
Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nagaya, Yasunobu
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-009, 208 Pages, 2023/02
The nuclear data processing code has an important role to connect evaluated nuclear data libraries and neutronics calculation codes. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed the nuclear data processing code FRENDY since 2013 to generate cross section files from evaluated nuclear data libraries, such as JENDL, ENDF/B, JEFF, and TENDL. The first version of FRENDY was released in 2019. FRENDY version 1 generates ACE files which are used for continuous energy Monte Carlo codes such as PHITS, Serpent, and MCNP. FRENDY version 2 generates multi-group neutron cross-section files from ACE files. The other major improvements are as follows: (1) uncertainty quantification for the probability tables of the unresolved resonance cross-section; (2) perturbation of the ACE file for the uncertainty quantification using a continuous Monte Carlo code; (3) modification of the ENDF-6 formatted nuclear data file. This report describes an overview of the nuclear data processing methods and input instructions for FRENDY.
Kunieda, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Fukahori, Tokio; Chiba, Satoshi*
European Physical Journal A, 59(1), p.2_1 - 2_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.87(Physics, Nuclear)Optical model or coupled-channels calculation serves as an entrance to sophisticated calculation of nuclear data. It was a great contribution of Dr. Efrem Sh. Soukhovitsukii who has developed an excellent computation scheme which takes account of the low-lying collective nuclear structure in terms of the soft-rotator + vibrational model, and integrated it into the coupled-channels calculation. In Japan, we had a fortuitous experience with him in parametrization of the optical model potential (OMP) and to employ this methodology in nuclear data evaluation for JENDL. Firstly, we summarize our collaborative works with him in this paper. Secondly, let us have a discussion on a new parameterization of OMP which we obtained for light nuclei within his framework, quite recently. It was found that values of the potential parameters themselves are rather similar among different nuclei while the nuclear deformation describes one of the main characteristics of each isotopes.
 Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5
Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5Kunieda, Satoshi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Konno, Chikara; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Ikeda, Yujiro*
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.329 - 335, 2023/01
We have evaluated double-differential cross-sections (DDX) of the  Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:213 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kunieda, Satoshi; Furutachi, Naoya*; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu
NEA/NSC/R(2020)4 (Internet), p.329 - 331, 2022/10
A new nuclear data library, ImPACT/LLFP-2018, is developed for an innovative study on the transmutation of long-lived fission products. In this work, we estimated cross-sections based on a nuclear model code CCONE, reflecting new knowledge on the nuclear structure theory and cross-section measurement. For instance, we used microscopic nuclear model to improve a phenomenological level density model. The pre-equilibrium model parameters are also optimized based on new experimental data of RIKEN/RIBF. Present library stores neutron and proton-induced cross-sections up to 200 MeV for 160 stable/unstable nuclei covering the long-lived fission products such as  Se,
Se,  Zr,
Zr,  Pd and
Pd and  Cs. Through a comparison with available experimental data on the stable isotopes, it is found that the present data gives predictions of cross-sections better than those from JENDL-4.0/HE, TENDL-2017 and the INCL model.
Cs. Through a comparison with available experimental data on the stable isotopes, it is found that the present data gives predictions of cross-sections better than those from JENDL-4.0/HE, TENDL-2017 and the INCL model.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kunieda, Satoshi; 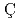 elik, Y.*; Furutachi, Naoya*; Niita, Koji*
elik, Y.*; Furutachi, Naoya*; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.665 - 675, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:93.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)A benchmark study of PHITS3.24 has been conducted using neutron-shielding experiments listed in the Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database. Five neutron sources were selected, which are generated from (1) 43- and 68-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thin lithium target, (2) 52-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick graphite target, (3) 590-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick lead target, (4) 500-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick tungsten target, and (5) 800-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick tantalum target. For all cases, overall agreements in the results are satisfactory when using the JENDL-4.0/HE to simulate neutron- and proton-induced reactions up to 200 MeV. However, discrepancies using PHITS default settings are observed in the results. For an accurate neutron-shielding design for accelerator facilities, using JENDL-4.0/HE in the particle and heavy-ion transport code system calculation is favorable.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kunieda, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.334 - 344, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)A hybrid nuclear data estimator (G-HyND) based on a machine learning technique with Gaussian processes (GP) was developed. G-HyND estimates cross-sections from a hybrid training dataset composed of an experimental dataset and an analytical dataset based on a nuclear physics model, and generates the cross-section datasets including the dataset's uncertainty information. It was demonstrated that an experimental dataset and a physics model-based analytical dataset perform a complementary role in nuclear data generation, and that the generated nuclear data from the hybrid training dataset are more reasonable than only those from the experimental dataset. Furthermore, solutions for two inherent GP problems, i.e., overfitting and computational cost, are presented within the G-HyND framework.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Shibata, Keiichi; Ichihara, Akira; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.09002_1 - 09002_6, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:99.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tada, Kenichi; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.48 - 49, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear data processing is an important interface between evaluated nuclear data library and neutronics transport codes. JAEA developed a new nuclear data processing code FRENDY in order to process the evaluated nuclear data library JEND. JAEA released FRENDY version 1 as an open source software under the 2-clause BSD license. The current version of FRENDY can generate ACE formatted files for continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation codes such as MCNP and PHITS. It uses the same processing method as NJOY because the implementation of the conventional method is an important step to develop the new code. For verification, we compared the processing results of FRENDY with those of NJOY and confirmed FRENDY provided us with almost the same outputs as NJOY. In this presentation, we explains the overview and a future plan of FRENDY.
Kunieda, Satoshi; Furutachi, Naoya; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Ebata, Shuichiro*; Yoshida, Toru*; Nishihara, Kenji; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(12), p.1073 - 1091, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:66.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new nuclear data library, JENDL/ImPACT-2018, is developed for an innovative study on the transmutation of long-lived fission products. Nuclear reaction cross- sections are newly evaluated for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV for 163 nuclides including long-lived nuclei such as  Se,
Se,  Zr,
Zr,  Pd and
Pd and  Cs. Our challenge is an evaluation of cross-sections for a number of unstable nuclei over a wide energy range where the experimental data are very scarce. We estimated cross- sections based on a nuclear model code CCONE that incorporates an advanced knowledge on the nuclear structure theory and a model-parameterization based on a new experimental cross-sections measured by the inverse kinematics. Through comparisons with available experimental data on the stable isotopes, it is found that the present data give predictions of cross-sections better than those in the existing libraries.
Cs. Our challenge is an evaluation of cross-sections for a number of unstable nuclei over a wide energy range where the experimental data are very scarce. We estimated cross- sections based on a nuclear model code CCONE that incorporates an advanced knowledge on the nuclear structure theory and a model-parameterization based on a new experimental cross-sections measured by the inverse kinematics. Through comparisons with available experimental data on the stable isotopes, it is found that the present data give predictions of cross-sections better than those in the existing libraries.
Tada, Kenichi; Kunieda, Satoshi
KURNS-EKR-5, p.229 - 232, 2019/12
The R-matrix limited formula is formatted by the current nuclear data format and it is adopted some nuclei in the latest evaluated nuclear data library. Since the processing of the R-matrix limited formula is significantly different to the other resonance formulae, it is difficult to treat this formula without large modification of the nuclear data processing code. In this study, we implemented one of the Rmatrix code AMUR to treat this formula in FRENDY. The processing results of FRENDY are compared to those of NJOY2016 to verify FRENDY. The comparison results indicate that FRENDY appropriately treat the R-matrix limited formula with similar computational time.
 Be system
Be systemThompson, I. J.*; deBoer, R. J.*; Dimitriou, P.*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Pigni, M. T.*; Arbanas, G.*; Leeb, H.*; Srdinko, Th.*; Hale, G.*; Tamagno, P.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 55(6), p.92_1 - 92_16, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:74.41(Physics, Nuclear)In this paper we present, for the first time, the results of a comprehensive effort to verify the most widely used R-matrix codes in the various fields of nuclear science and applications: AMUR, AZURE2, CONRAD, EDA, FRESCO, GECCCOS, and SAMMY. In addition to the description of the capabilities of the codes and their specifications, we discuss the results of a joint exercise which was coordinated by the International Atomic Energy Agency. The aim of the exercise was to compare calculations of charged-particle reaction cross sections for the light composite system  Be. The calculations were performed by the codes using identical input R-matrix parameters and other specifications and were limited to charged-particle channels.
Be. The calculations were performed by the codes using identical input R-matrix parameters and other specifications and were limited to charged-particle channels.