Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-001, 110 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2006 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-002, 88 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2007 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site and the Shobasama Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Hazama, Taira; Chiba, Go; Sato, Wakaei; Numata, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Review 2009-003, 59 Pages, 2009/05
SLAROM-UF is a cell calculation code for fast reactors to produce effective cross sections with high accuracy in practical computing time, taking full advantage of fine and ultra-fine group calculation schemes. The fine group calculation scheme covers the whole energy range in a maximum of 900-group structure. Its group structure is finer above 52.5 keV with a minimum lethargy width of 0.008. Effective cross sections are evaluated based on the Bondarenko method. The ultra-fine group calculation scheme covers the energy range below about 52.5 keV. Its group structure is so fine ( 100,000 groups) as to treat resonance peaks as they are. Effective cross sections are calculated by solving an integral slowing down equation effectively, focusing only on elastic scattering and absorption reactions. Temperature can be specified freely by a user in the input data. The effective cross sections thus obtained are combined to calculate cell averaged cross sections.
100,000 groups) as to treat resonance peaks as they are. Effective cross sections are calculated by solving an integral slowing down equation effectively, focusing only on elastic scattering and absorption reactions. Temperature can be specified freely by a user in the input data. The effective cross sections thus obtained are combined to calculate cell averaged cross sections.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Iyatomi, Yosuke; Shimada, Akiomi; Ogata, Nobuhisa
JAEA-Review 2009-004, 123 Pages, 2009/05
The Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a geoscientific studies in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. Information and Opinion Exchange Conference on Geoscientific Study has been held by TGC annually. The conference provides technical information and an opportunity for peer review and exchange of opinions on the geoscientific studies conducted at TGC. Research specialists and engineers from Japanese universities, research organizations and private companies usually participate the conference. This document compiles research presentations, posters of the conference on October 16th, 2008 at Mizunami.
Endo, Hidetoshi
JAEA-Review 2009-005, 30 Pages, 2009/05
IAEA stands out the activity of the knowledge management of nuclear safety and the movement to introduce the idea of the life cycle management into the quality control of maintenance of the nuclear power generation facilities to assure the knowledge preservation and to succeed the technology of facilities. JAEA also has such activities as the knowledge preservation of research and development, and related information. The facilities' performance and reliability can be easily checked with the technology of data processing in the general industry and the results of the knowledge repository, transmitting technology and knowledge management by referring to the information and knowledge if the information and knowledge at each step of the life-cycle of facilities can be built. This report shows the strategy of the construction of the engineering database to support the life cycle of facilities and the basic function of the management system.
Ishii, Tetsuro; Osa, Akihiko; Okayasu, Satoru; Ishikawa, Norito; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Ishiyama, Hironobu*
JAEA-Review 2009-006, 286 Pages, 2009/04
Workshop of the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator was held every two years. As a memorial of 100,000-hour operation of the tandem accelerator, we reviewed developments and experiments carried out so far, together with discussion of experiments in progress and in future. As previous series of workshops, we offered an opportunity to have active discussion among scientists of different fields including accelerator, nuclear physics, nuclear chemistry, radiation effects, atomic physics and so on, aiming at extending facility and research interactively. As a memorial lecture, Dr. Akira Tonomura, fellow of Hitachi, Ltd., delivered a lecture titled "Structure of magnetic flux observed by electron beam". Prof. Shigeru Kubono of University of Tokyo encouraged us through a talk of "Expectations for the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator". This workshop was held at Nuclear Science Research Institute on January 6-7th in 2009, having 24 oral presentations and 48 posters, as many as 120 participants.
Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management
JAEA-Review 2009-007, 99 Pages, 2009/06
This reports described the activities of Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management (DDWM) in the period from April 1, 2007 to March 31, 2008. In FY2007 radioactive wastes generated from R&D activities were about 371 m of combustible solid wastes, 152 m
of combustible solid wastes, 152 m of noncombustible solid wastes and 510 m
of noncombustible solid wastes and 510 m of liquid wastes. After adequate treatment 2,111 waste packages were generated. Two new approaches were conducted for radioactive waste management: development of record keeping system for land burial and a new management system for mid-level radioactive waste packages. Decommissioning activities were carried out as planned for the JAEA's Reprocessing Test Facility, the Ceramic Fuel Laboratory, the Plutonium Laboratory No.2 and the Metallurgical Laboratory. As for the R&D activities, studies were conducted on radiochemical analyses of wastes for land burial, and decommissioning. As for the clearance was applied for approval of nuclide measureing.
of liquid wastes. After adequate treatment 2,111 waste packages were generated. Two new approaches were conducted for radioactive waste management: development of record keeping system for land burial and a new management system for mid-level radioactive waste packages. Decommissioning activities were carried out as planned for the JAEA's Reprocessing Test Facility, the Ceramic Fuel Laboratory, the Plutonium Laboratory No.2 and the Metallurgical Laboratory. As for the R&D activities, studies were conducted on radiochemical analyses of wastes for land burial, and decommissioning. As for the clearance was applied for approval of nuclide measureing.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2009-008, 233 Pages, 2009/06
The Department of Research Reactors and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3, JRR-4, NSRR and Tandem Accelerator. This report is a summary of technical developments of The Department of Research Reactors and Tandem Accelerator in 2007.
Shimada, Taro; Shiraishi, Kunio; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Ishigami, Tsutomu
JAEA-Review 2009-009, 42 Pages, 2009/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA: the former Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute) has been collecting wide variety of information on decommissioning nuclear facilities by the cooperative program with US Department of Energy (DOE) since 1988. In the course of the cooperation, the cooperative program has continued under the newly established specific memorandum in the field of decontamination and decommissioning nuclear facilities since 2001 on the framework agreement of USDOE and JAERI. On the other hand, the US DOE environmental management program, which was initiated in 1989, has developed resulting in achievement of dismantlement, decontamination and cleanup of nuclear facilities mainly used for Manhattan project and demonstration of various technologies developed for this program. In the cooperative activities, information on decommissioning activities including innovated technology developments has been exchanged with CP-5 and Mound plant as designated main facilities of DOE, and with JRR-2 and the reprocessing test facility of JAERI. The experiences and technologies applied in the environmental management program are expected to contribute to planning and implementing decommissioning nuclear facilities in JAEA. This report describes the summary of the information on decommissioning activities and technology development and deployment of the environmental management program in DOE obtained through the cooperation under the specific memorandum agreement.
Takahashi, Kuniaki; Kawato, Yoshimi; Hanada, Keiji
JAEA-Review 2009-010, 37 Pages, 2009/07
Regulatory matters for transportation of radioactive waste, legislation, regulations and standards, are checked. We have conducted a study on cost and transportation measure for waste packages from Tokai reprocessing plant and MOX fuel fabrication facilities in Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories. Here, the number, radioactive inventory and properties of the waste packages are quoted from the second progress report on research and development for TRU waste disposal in Japan. We sorted out the waste packages by the type of packages based on the legislation for transportation of radioactive material. We have studied the packaging for each type of package, and have estimated number of the packages of a conveyance, number of conveyances for transportation of all waste packages. As a result, the waste packages constitutes ca.86% of Industrial package Type 2, ca.2% of Type A package and ca.12% of Type B package. Number of transport by sea for the waste packages is estimated as about 120 times.
Hemmi, Ko
JAEA-Review 2009-011, 50 Pages, 2009/07
NSC has proposed a renewed basic concept for safety regulation of LLW disposal as an interim report. They also redefined the concept for upper bounds of radioactivity concentration and revised the recommended values accordingly. This revision of the upper bounds gave the border values between intermediate-depth disposal and geological disposal. Since very long-lived radionuclides are included in radioactive wastes for intermediate-depth disposal, the long-term safety assessment is required and the uncertainty for the far future is needed to be considered in the scenario development. Therefore, the risk-based categorization of safety assessment scenarios was proposed in the interim report. This report organizes information from governmental reports to review the regulatory progression of radioactive waste disposal, and provides commentary on the background, the how and why, and the resulting regulatory concept of the intermediate-depth disposal.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sano, Michiaki; Sugita, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2009-012, 29 Pages, 2009/06
As part of the R&D program on geological disposal of HLW, the Horonobe Underground Research Center, a division of the JAEA, is implementing the Horonobe URL Project with the aim at investigating sedimentary rock formations. According to the research plan described in the Midterm Plan of JAEA, geological investigations are to be carried out during the drilling of a shaft down to intermediate depth, while R&D in the areas of engineering technology and safety assessment are to be promoted by collaboration with other research organizations. The results of the R&D activities will be systematized as a "knowledge base" that supports a wide range of arguments related to the safety of geological disposal. The Horonobe URL Project is planned to extend over a period of 20 years. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). This report summarizes the investigation program for the 2009 fiscal year, the 5th year of the Phase 2 investigations. In the 2009 fiscal year, investigations in "geoscientific research", including "development of techniques for investigating the geological environment", "development of techniques for long-term monitoring of the geological environment", "development of engineering techniques for use in the deep underground environment" and "studies on the long-term stability of the geological environment", are continuously carried out. Investigations in "research and development on geological disposal technology", including "improving the reliability of disposal technologies" and "enhancement of safety assessment methodologies", are also continuously carried out. Construction of the underground facilities is ongoing at Access Shaft (East) and 140 m depth drift.
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Tachibana, Yukio; Sun, Y.*
JAEA-Review 2009-013, 11 Pages, 2009/07
The worldwide interests in the HTGR (High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor) have been growing because the high temperature heat produced by the reactor can be utilized not only for efficient power generation but also for broad process heat applications, especially for thermo-chemical hydrogen production to fuel a prospective hydrogen economy in future. Presently only two HTGR reactors are operational in the world, including the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the HTR-10 in the Institute of Nuclear and New Energy Technology (INET) of Tsinghua University in China. JAEA and INET have cooperated since 1986 in the field of HTGR development, particularly on the HTTR and HTR-10 projects. This report describes the cooperation activities on HTGR and nuclear hydrogen technology between JAEA and INET in 2008.
Arai, Masatoshi; Aizawa, Kazuya; Nakajima, Kenji; Shibata, Kaoru; Takahashi, Nobuaki
JAEA-Review 2009-014, 84 Pages, 2009/07
The 2nd International Advisory Committee on "Biomolecular Dynamics Backscattering Spectrometer DNA" was held on November 12th - 13th, 2008 at J-PARC Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This IAC has been organized for aiming to realize an innovative neutron backscattering instrument in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) at the J-PARC and therefore four leading scientists in the field of neutron backscattering instruments has been selected as the member (Dr. Dan Neumann (Chair), Prof. Ferenc Mezei, Dr. Hannu Mutka, Dr. Philip Tregenna-Piggott), and the 1st IAC had been held on February 27th - 29th, 2008. This report includes the executive summary and materials of the presentations in the 2nd IAC.
Itazu, Toru; Inagaki, Manabu; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebina, Takanori*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Review 2009-015, 59 Pages, 2009/07
The project of high-level radioactive waste disposal is in the stage of site selection in Japan, and the site-specific performance assessment using the methodology of site-generic study has been developed after the publication of the second progress report (H12). In the same way, biosphere assessment using the behavior of radionuclides, which depends on the site-specific condition, has been started. In this paper, the following issues have been addressed. (1) Survey of the foreign literature relating to the surface and near- surface hydrology for biosphere assessments. (2) Survey of the domestic literature of flow and transport in subsurface systems valuable for biosphere assessments. (3) Trial of transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment of the model site. (4) The setting and boundary conditions of model used for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis. About the fist issue, from literature of Sweden, we studied the calculation of the dose with account to radionuclides migration in the Quaternary. Concerning the second item, collecting and compiling the useful information for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis from literature related to groundwater flow and pollution survey in Japan, we learned about the environmental tracer method and so on. Concerning the third point, transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment using site-specific data for sensitivity analysis after this has been carried out to check out the influence of some parameters on transport phenomena, and the relative high sensitivity of the difference of the source positions were shown. Concerning the fourth item, we examined the setting and the boundary conditions of model whose outputs include groundwater flow and transport rate into river, lake, sea. These outputs are used as inputs of biosphere assessment model.
 Superconductors (IRiSes 2009); January 25, 2009, Center for Computational Science & e-System, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Higashi-Ueno, Tokyo, Japan
Superconductors (IRiSes 2009); January 25, 2009, Center for Computational Science & e-System, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Higashi-Ueno, Tokyo, JapanShamoto, Shinichi
JAEA-Review 2009-016, 276 Pages, 2009/08
The 1st workshop of the International Workshop on Iron Related High-T Superconductors (IRiSes 2009) was held on January 25, 2009 at Center for Computational Science and e-Systems, Japan Atomic Energy Agency mainly under sponsorship of Transformative Research-Project on Iron Pnictides (TRIP) of Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST). This workshop is aimed to reveal the mechanism of iron related high-Tc superconductivity partly on the basis of the NIMS-RIKEN-JAEA Cooperative Research Program on Quantum Beam Science and Technology. This report includes abstracts and materials of the presentations in the workshop.
Superconductors (IRiSes 2009) was held on January 25, 2009 at Center for Computational Science and e-Systems, Japan Atomic Energy Agency mainly under sponsorship of Transformative Research-Project on Iron Pnictides (TRIP) of Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST). This workshop is aimed to reveal the mechanism of iron related high-Tc superconductivity partly on the basis of the NIMS-RIKEN-JAEA Cooperative Research Program on Quantum Beam Science and Technology. This report includes abstracts and materials of the presentations in the workshop.
Takeuchi, Shinji; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-017, 29 Pages, 2009/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at the MIU project is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following 2009 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation Plan, (2) Construction Plan, (3) Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
Nagane, Satoru; Matsuno, Satoru; Yamamoto, Makoto; Tobinai, Kazuhito; Ozaki, Shinji; Sato, Yasuo; Kitahara, Katsumi; Yoshikawa, Seiji
JAEA-Review 2009-018, 39 Pages, 2009/08
Nuclear Facilities Management Section is, Liquid nuclear waste facility, a small nuclear fuel treatment facility, operation, maintenance and decommissioning of the nuclear ship "MUTSU", which carried out the operation and maintenance services of solid waste facilities. This paper, the nuclear facilities Management Section, Office of FY2008 year (April 2008-March 2009) summarized results of operations.
Department of JMTR Operation
JAEA-Review 2009-019, 30 Pages, 2009/09
As for the refurbishment, the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has been stopped since its 165th cycle operation was finished, and the JMTR is advancing its refurbishment aiming at the reoperation from FY2011. Regarding the management and operation of the JMTR, inspection based on the law, maintenance and preservation works of facilities were carried out. Moreover, in the irradiation facility, maintenance and preservation works on the management and operation were also carried out. In the hot laboratory, post-irradiation examinations using irradiated materials and fuels were carried out. In addition, maintenance and preservation works of facilities and building were also carried out. This report describes the FY2008 activities relating to above mentions.
Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-020, 25 Pages, 2009/10
The preliminary investigation of direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel was conducted for the current Nuclear Energy Policy by Japan Atomic Energy Commission to compare the cost between direct disposal and nuclear fuel cycle. One of important point for the cost estimation was a diameter of the disposal tunnel. In this study, the preliminary design of disposal tunnel was conducted from an engineering viewpoint based on the status of direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel in Finland and Sweden. As a result, the excavated cross section of disposal tunnel could be decreased to approximately half of the above investigation. In order to improve these results, further investigation is needed.
Research Cooperation Section
JAEA-Review 2009-021, 214 Pages, 2009/09
This report includes a summary of the results of the research carried out in fiscal year 2008 on 32 research collaboration subjects for preceding basic engineering research related to fast breeder reactors, the nuclear fuel cycle, radiation safety and geological disposal/geoscience; twelve of which ended in 2008.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Ito, Keishiro*; Katsuki, Chisato*; Kawashima, Kei*; Shirabe, Masashi*
JAEA-Review 2009-022, 26 Pages, 2009/09
An outcome of nuclear safety research done by JAERI was case studied by the bibliometric method. (1) For LOCA (loss-of-coolant accident) a domestic share of JAERI in monoclinic research paper was 63% at the past (20) 1978-1982 but was decreased to 40% at the present 1998-2002. For co-authored papers a domestic share between JAERI and PS (public sectors) is almost zero at past (20) but increased to 4% at the present. Research cooperation is active between Tokyo University and JAERI or between JAERI and Nagoya University. (2) Project-type research is to have a large monopolization in papers and that of basic-type research is to have a large DRN. (3)For reprocessing, PS had a monopolistic position with a domestic share of 71% and a share of JAERI was about 20%. (4) LOCA and RIA outputs born by NSR-JAERI coincided partly to those of the Safety Licensing Guidelines but a share of contribution done by JAERI was difficult to obtain due to the lack of necessary information.
Kanamori, Masashi; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Omura, Akiko; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-023, 61 Pages, 2009/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are Designated Public Organizations conforming to the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the Joint Council of Nuclear Disaster Countermeasures, which meets at the Off-Site Center. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2008.
Torata, Shinichiro; Numata, Yoshiaki; Kawase, Keiichi; Manabe, Tatefumi
JAEA-Review 2009-024, 12 Pages, 2009/09
To continue utilizing nuclear energy in the future, a key issue still remains concerned with the public's perception of generating radioactive waste and its subsequent safe disposal. Despite undertaking long term research and development to implement a program of geological disposal of radioactive waste, the social recognition and public understanding is still insufficient. Consequently, JAEA has been trying to extend the public's scientific understanding by showing its research facilities. In this report, the content of more than 1000 answer sheets have been analyzed from members of the public who visited the JAEA research facilities. Several important findings were obtained, in particular, notable differences were found in the answers of those who had also visited an underground tunnel compared with those who had not. This and other findings are significant in promoting the social recognition of the ongoing research and development of the geological disposal of radioactive waste.
Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center
JAEA-Review 2009-025, 37 Pages, 2009/09
The JMTR, one of the most high flux test reactors in the world, has been used for the irradiation experiments of fuels and materials related to LWRs, fundamental research and radioisotope productions. The JMTR was stopped at the beginning of August 2006 to conduct refurbishment works, and the reoperation will be planned from FY 2011. After reoperation, the JMTR will contribute to many fields, such as the lifetime extension of LWRs, expansion of industrial use, progress of science and technology. This report summarizes the activities on refurbishment works, development of new irradiation techniques, enhancement of reactor availability, etc.
Ikezoe, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-026, 55 Pages, 2009/09
The summaries of the 8 research projects conducted through the Reimei Research Program are published for the growth and development of the new researches.
Sakaba, Nariaki
JAEA-Review 2009-027, 135 Pages, 2009/09
Chemistry control is important for the helium coolant of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) because impurities cause oxidation of the graphite applied to the core structure and corrosion of high-temperature materials utilized at the intermediate heat exchanger (IHX). This thesis describes the helium chemistry which should be maintained adequately during reactor operations not only for the safety and stability of operations, but also for the increase of economic competitiveness by reducing replacing times of IHXs and simplifying helium purification systems. In this paper the chemical impurity behaviour was clarified by the obtained chemistry data by the Japan's HTTR and the criteria of chemical impurities for the GTHTR300C, which can supply both of electricity and hydrogen for the future hydrogen society, was proposed with its control technologies. In this R&D, the chemical impurity behavior, purification abilities, emitted impurities from graphite and thermal insulator, and hydrogen permeation at the heat transfer tube of the IHX during the 950 C operation of the HTTR were evaluated. Utilizing these results, radical reactions at the core were identified. Also, chemical impurity criteria were proposed to avoid structural degradation of the Hastelloy XR and thermophysical properties deterioration at the heat transfer tubes. As a result, active chemistry control technologies where the necessary chemical impurity will be injected in response to the chemical balance at the core are proposed for the GTHTR300C. The proposing technology is expected to contribute economically to the purification systems of the future HTGRs.
C operation of the HTTR were evaluated. Utilizing these results, radical reactions at the core were identified. Also, chemical impurity criteria were proposed to avoid structural degradation of the Hastelloy XR and thermophysical properties deterioration at the heat transfer tubes. As a result, active chemistry control technologies where the necessary chemical impurity will be injected in response to the chemical balance at the core are proposed for the GTHTR300C. The proposing technology is expected to contribute economically to the purification systems of the future HTGRs.
Yasue, Kenichi; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji
JAEA-Review 2009-028, 15 Pages, 2009/09
The Japanese islands are located in the tectonically active Circum-Pacific Mobile Belt. As a result, Japan has a high frequency of earthquakes and eruptions. Special consideration is given to the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. Development of investigation technologies for geotectonic events has been carried out to evaluate the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. The research activity in fiscal year 2009 composes of the following contents. Concerning earthquakes and fault movement, we continue to develop investigation techniques for evolutional history and activity of fault, and carry out case studies for development of effective assessment models in the fault zones. For volcanological and geothermal studies, we plan to provide an integrated approach for detecting crustal magma and/or geothermal fluid in deep underground using geophysical and geochemical data, and models assessing the likelihood of future volcanism and its influence on the geological environments. Concerning uplift, denudation, climatic change and sea-level change, we plan to arrange investigation techniques for reconstruction of paleo-topography and paleo-climate, and to establish modeling techniques for landform changes. In addition, we develop dating methods that are necessary for these studies.
Subcommittee of Research on Performance Goals for Nuclear Fuel Facilities
JAEA-Review 2009-029, 57 Pages, 2009/10
A lot of efforts have been carried out recently for researches on development of PSA methodology and its applications, and trials of risk-informed operation and maintenance in nuclear fuel facilities in Japan. Quantitative performance goals consistent with Nuclear Safety Goals, which is essential for risk-informed decision making, however, have not been discussed yet for those nuclear installations. A Subcommittee under the Nuclear Safety Research Committee has been organized by Nuclear Research Center of Japan Atomic Energy Institute to prepare the technical basis and a typical procedure to derive the quantitative performance goals for further discussions by the regulatory bodies to establish the objectives. The activities in 2008 fiscal year have been summarized in this report carried by the Subcommittee of research on performance goals for nuclear fuel facilities.
Information Technology Systems' Management and Operating Office
JAEA-Review 2009-030, 210 Pages, 2009/09
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) installed and operated super-computers in order to support nuclear research and development activities in JAEA. This report presents the status of usage of the JAEA super-computers and research and development activities by using the computer systems in FY2008 (April 1, 2008 - March 31, 2009).
Editorial Committee of R&D Results
JAEA-Review 2009-031, 77 Pages, 2009/09
It is an important issue to take measures against the matters on decommissioning of retired nuclear facilities and management of low-level radioactive waste, and the measures must be taken with rational way by ensuring the safety. As the development, improvement, and proper deployment of technologies will be key factors, a technology development program is under way in Nuclear Cycle Backend Directorate in cooperation with each institutes/centers in JAEA. The technology development items are selected from the viewpoint of cost reduction; these include the development of computer systems for planning and evaluation of decommissioning programs, supercritical CO fluid leaching method for decontamination, nitrate-ion degradation method, rapid and simplified method for radiochemical analysis, safety assessment for waste disposal and so on. This report describes outline and progress of the technology development program conducted in FY2008 by the research and development unit.
fluid leaching method for decontamination, nitrate-ion degradation method, rapid and simplified method for radiochemical analysis, safety assessment for waste disposal and so on. This report describes outline and progress of the technology development program conducted in FY2008 by the research and development unit.
Division of Fusion Energy Technology
JAEA-Review 2009-032, 100 Pages, 2009/11
The Division of Fusion Energy Technology of the Fusion Research and Development Directorate is carrying out cooperating researches with universities, research institutes and industries using five fusion engineering facilities; Caisson Assembly for Tritium Safety Study (CATS), Fusion Neutronics Source (FNS), JAEA Electron Beam Irradiation System (JEBIS), RF Test Stand (RFTS). In the fiscal year 2007 (from April 1, 2008 to March 31, 2009), 19 activities were carried out as the cooperating researches. This report reviews the results of 8 activities which were completed in the fiscal year 2008.
Working Group on NuTEC's 50th Anniversary, Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAEA-Review 2009-033, 183 Pages, 2009/12
This report summarizes the activities that Nuclear Technology and Education Center (NuTEC), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted since its first training course started at Radioisotope School of Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), in 1958. NuTEC was founded by consolidation of JAERI and Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Corporation (JNC) in October, 2005 and this report also describes the recent activities of NuTEC since then. There have been many people concerned with the NuTEC's training activities for 50 years, such as lecturers, trainees, and technical or administrative staff of NuTEC. This report also includes their contributed articles.
Hayashi, Naomi
JAEA-Review 2009-034, 208 Pages, 2009/11
The activities of Safety Administration Department covers many fields in Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories such as the management of a safety and health, the crisis management and the security, and the management of a quality assurance. This report is the summary of the activities of Safety Administration Department since October, 2007 until March, 2008.
Kobayashi, Naoki*; Naoi, Yosuke; Wakabayashi, Shuji; Tazaki, Makiko; Senzaki, Masao
JAEA-Review 2009-035, 88 Pages, 2010/03
In order to facilitate the international discussion of the assurance of supply (AOS) system, authors have been conducted studies of AOS. We focused and based our study on Japanese proposal "IAEA Standby Arrangement System (INFCIRC/683)". In this paper, we have been able to show the feasibility of AOS system more specifically by supposing additional costs and the required period necessary for the AOS and present a system we made that we hope as a practical system. And we studied the issues surrounding AOS and presented our proposal of their solutions. The issues we are tackling here are the definitions of AOS; issues on consumer states, supplier states, IAEA and the nuclear industries. The proposals we present here are the broadening the cause of AOS, the declaration of the supplier states on AOS, the advisory committee on the initiation of AOS of IAEA and setting up a IAEA fund for AOS.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2009-036, 163 Pages, 2009/11
The JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator complex has been used in various research fields such as nuclear science and material science not only by JAEA but also by universities, research institutes and industrial companies. This annual report covers developments of accelerators and research activities carried out using the tandem accelerator, superconducting booster, and radioactive nuclear beam accelerator, from April 1, 2008 to March 31, 2009. Fifty-five summary reports were categorized into seven research/development fields: (1) accelerator operation and development, (2) nuclear structure, (3) nuclear reaction, (4) nuclear chemistry, (5) nuclear theory, (6) atomic physics and solid state physics, and (7) radiation effects in materials. This report also lists publications, meetings, personnel, committee members, cooperative researches and common use programs.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Ishihara, Masahiro
JAEA-Review 2009-037, 37 Pages, 2009/12
The JMTR, one of the most high flux test reactors in the world, has been used for the irradiation experiments of fuels and materials related to LWRs, fundamental research and radioisotope productions. The JMTR was stopped at the beginning of August 2006 to conduct refurbishment works, and the reoperation will be planned from FY 2011. After reoperation, the JMTR will contribute to many fields, such as the lifetime extension of LWRs, expansion of industrial use, progress of science and technology. This report summarizes the activities on refurbishment works, development of new irradiation techniques, enhancement of reactor availability, etc.
Yang, J.-E.*; Homma, Toshimitsu
JAEA-Review 2009-038, 765 Pages, 2009/12
The tenth Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on Probabilistic Safety Assessment (PSA) was held in the Jeju Island of Korea, on May 18-20, 2009 organized by Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI). The purpose of the workshop was to provide a forum for presentation and discussions on experiences and technical achievements related to PSA, risk-informed and performance-based approach, and other relevant issues in both countries. Since the first Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on PSA started in 1992, the workshops have provided an important and timely opportunity for exchange and discussion of the relevant information to all PSA practitioners and users of risk information in the industry, research, academia and regulatory arena. This was the tenth anniversary of the Joint Workshop with the main theme of "For Asian PSA Network" and participants include those from China, Taiwan and the United States of America besides Korea and Japan.
Takeishi, Minoru; Matsuura, Kenichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Kono, Takahiko; Hiyama, Yoshinori; Fujii, Jun*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sagawa, Fumiaki*; Otani, Kazunori*
JAEA-Review 2009-039, 131 Pages, 2009/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and byelaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2008, from 1st April 2008 to 31st March 2009. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactive liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Department of Radiation Protection, Nuclear Science Research Institute; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institut; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Kansai Photon Science Institute; Operation Safety Administration Section, Mutsu Office, Aomori Research and Development Center; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Naka Fusion Institute
JAEA-Review 2009-040, 168 Pages, 2010/01
This annual report describes the activities of Radiation Protection Sector in Department of Radiation Protection in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Safety Section in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Safety Section in Kansai Photon Science Institute, Operation Safety Administration Section in Aomori Research and Development Center and Safety Section in Naka Fusion Institute.
Tanaka, Shigeru
JAEA-Review 2009-041, 218 Pages, 2009/12
JAEA Takasaki annual report 2008 describes research and development activities performed from April 1, 2008 to March 31, 2009 with Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA, four ion accelerators), and electron/ -ray irradiation facilities(an electron accelerator and three
-ray irradiation facilities(an electron accelerator and three  Co
Co  -ray irradiation facilities) at Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Takasaki). These activities are classified into four research fields: (1) space, nuclear and energy engineering, (2) environmental conservation and resource security, (3) biotechnology and medical application, and (4) advanced materials, analysis and novel technology. This annual report contains 161 reports consisting of 153 research papers and 8 status reports on operation/maintenance of the irradiation facilities described above, and a list of publications, related press-releases, TV programs, patents, and the type of research collaborations as Appendices.
-ray irradiation facilities) at Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Takasaki). These activities are classified into four research fields: (1) space, nuclear and energy engineering, (2) environmental conservation and resource security, (3) biotechnology and medical application, and (4) advanced materials, analysis and novel technology. This annual report contains 161 reports consisting of 153 research papers and 8 status reports on operation/maintenance of the irradiation facilities described above, and a list of publications, related press-releases, TV programs, patents, and the type of research collaborations as Appendices.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Review 2009-042, 87 Pages, 2010/01
This report provides an overview of research and development activities in Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), JAEA, during the fiscal years 2007 and 2008 (Apr 1, 2007 - March 31, 2009). These research and development activities have been performed by the Simulation Technology R&D Office and Computer Science R&D Office.
Shobu, Nobuhiro; Takashita, Hirofumi; Horikoshi, Hidehiko*; Osawa, Yukiko*
JAEA-Review 2009-043, 160 Pages, 2010/01
This report summarizes the review work to paraphrase nuclear technical terms with clear and brief explanations. Explanation with nuclear technical terms was not very acceptable to the public in a variety of contexts. The objective of this study is to paraphrase from the public point of view. JAEA has conducted a survey on public attitudes toward fifty-nine nuclear technical terms by using an online questionnaire. Most of them were frequently used in the brochures of JAEA. The survey clarified the public awareness and comprehension of each term. Thirty-two terms, which was subject to paraphrase on a priority basis, were selected from fifty-nine nuclear technical terms based on our importance rating. At the work to paraphrase thirty-two terms, emphasis was placed more on clearness and briefness than on scientific accuracy. They are reviewed through focus group interviews. This study brought results on recognizable style and thirty-two well-polished paraphrases.
Hanakawa, Hiroki; Sato, Shinichi; Kusunoki, Hidehiko; Fukasaku, Akitomi; Tobita, Kenji
JAEA-Review 2009-044, 24 Pages, 2010/01
Electric power supply system of JMTR consists of commercial power supply system and emergency power supply system. In the periodical assessment of JMTR, it was concluded that the integrity of the emergency generators were confirmed and the aging effects were to be watching continuously in future. Therefore, prior to the restart of the JMTR, verification on integrity of the generators were carried out in order to confirm the integrity and to determine maintenance plans which run before and after the restart. As a result, the integrity of the generators were confirmed because the electrical degradation was not found. Maintenance plan is determined before JMTR restart. Also it is possible to maintain the integrity of the generators by carrying on the current maintenance plan with periodical overhaul.
JT-60 Team
JAEA-Review 2009-045, 177 Pages, 2010/02
Results in JT-60U experiments in 2007 and 2008 are reviewed. In this campaign, which is the final experimental period in JT-60U, development of advanced tokamak plasma was extensively performed toward establishment of physics basis of ITER and DEMO. High integrated performance plasma with high normalized beta (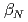
 2.6) and high confinement enhancement factor (
2.6) and high confinement enhancement factor (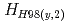 =1.0-1.1), which are comparable to those in the ITER Hybrid Scenario, and at the same time with high bootstrap current fraction (
=1.0-1.1), which are comparable to those in the ITER Hybrid Scenario, and at the same time with high bootstrap current fraction ( 40%) was sustained for 25 s. High density and high radiation loss fraction plasma was sustained for 12 s by adding argon and neon to a deuterium plasma. The duration of the high-performance plasmas is more than 10 times longer than the current diffusion time,
40%) was sustained for 25 s. High density and high radiation loss fraction plasma was sustained for 12 s by adding argon and neon to a deuterium plasma. The duration of the high-performance plasmas is more than 10 times longer than the current diffusion time, 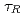 . In a high beta regime exceeding the ideal MHD limit without conducting wall (no-wall limit), a new instability was observed. By suppressing the instability a high beta plasma was sustained for 5 s, which corresponds to several times longer than
. In a high beta regime exceeding the ideal MHD limit without conducting wall (no-wall limit), a new instability was observed. By suppressing the instability a high beta plasma was sustained for 5 s, which corresponds to several times longer than 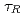 . Performance of reversed shear plasmas was significantly improved by utilizing the stabilizing effect of the conducting wall, and
. Performance of reversed shear plasmas was significantly improved by utilizing the stabilizing effect of the conducting wall, and 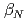
 2.7 and
2.7 and 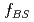
 90% were obtained. These results significantly exceed those in the previous experimental campaign.
90% were obtained. These results significantly exceed those in the previous experimental campaign.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Review 2009-046, 45 Pages, 2010/02
Research on simulation engineering for nuclear applications, based on "the plan for meeting the mid-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed at Center for Computational Science & e-Systems, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (CCSE/JAEA). CCSE established the committee consisting outside experts and authorities which does research evaluation and advices for the assistance of the research and development. This report summarizes the result of the evaluation by the committee on the research on simulation engineering performed at CCSE/JAEA in FY2009.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-047, 26 Pages, 2010/01
Within the scope of the JAEA thermodynamic database project for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes, refinement of the thermodynamic data for the inorganic compounds and complexes of actinium, plutonium(III), americium, curium and samarium was carried out. Refinement of thermodynamic data of these elements was performed on a basis of the thermodynamic database for americium published by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). Based on the similarity of chemical properties among trivalent actinides and samarium, complementary thermodynamic data for their species expected under the geological disposal condition were selected to complete the thermodynamic data set for the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive wastes.
Takeishi, Minoru; Sumiya, Shuichi; Matsuura, Kenichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Isozaki, Hisaaki*; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Fujita, Hiroki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-048, 177 Pages, 2009/12
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV; Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2008 to March 2009. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Iyatomi, Yosuke; Shimada, Akiomi
JAEA-Review 2009-049, 159 Pages, 2010/03
The Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a geoscientific studies in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. Information and Opinion Exchange Conference on Geoscientific Study has been held by TGC annually. The conference provides technical information and an opportunity for peer review and exchange of opinions on the geoscientific studies conducted at TGC. Research specialists and engineers from Japanese universities, research organizations and private companies usually participate the conference. This document compiles research presentations, posters of the conference on October 27th, 2009 at Mizunami.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Kawashima, Kei*; Katsuki, Chisato*; Ito, Keishiro*
JAEA-Review 2009-050, 13 Pages, 2010/02
Bibliometric study by means of research papers revealed the followings; (1) Nuclear Safety Research (NSR) performed in Japan is the 2nd highest in the world followed by USA. The share of JAERI for safety paper publication is about 25% in Japan (2) During past 25 years, JAERI is predominant at 39 safety fields out of 97, that is, 40% to the total. This is the fact revealed from comparison of published number of research papers with those of other organizations. (3) JAERI is recently changing its stress point from reactor-oriented accidents to the down stream of nuclear fuel cycling. There existed impact of TMI-2 accident on NSR-JAERI, especially in the field of thermal hydraulics, LOCA, severe accident and risk analysis.
Doi, Reisuke; Kitamura, Akira; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-051, 18 Pages, 2010/02
Within the scope of the JAEA thermodynamic database project for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU radioactive wastes, the selection of the thermodynamic data on the inorganic compounds and complexes of selenium have been carried out. Selection of thermodynamic data of selenium has been based on a thermodynamic database of selenium published by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). The remarks of a thermodynamic database by OECD/NEA found by the authors were noted in this report and then thermodynamic data have been reviewed after surveying latest literatures. Some thermodynamic values of iron selenides not selected by OECD/NEA due to low reliability, which are important for the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive wastes, were selected as a tentative value with specifying reliability and needs of the value to be determined.
Kato, Tomoko
JAEA-Review 2009-052, 23 Pages, 2010/02
It is difficult to assume future evaluations of surface environments and human activities accurately and to describe them in a biosphere assessment scenario of geological disposal. Accurate assumption on their evolution is not necessary, because a biosphere assessment aims to illustrate the radiological impact to human as an index of performance for repository. Consequently, it is important to develop the methodology to describe the biosphere system with long-term evolution of geosphere according to a regulatory guideline or an assessment purpose, that is, the methodology to stylize evaluations of surface environments and human activities. In this report, we reviewed regulatory guidelines and scenarios of performance assessment applied to natural processes and human intrusion in foreign countries, and discussed the view-points when evolution of biosphere and future human activity are stylized in performance assessment of geological disposal.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nozawa, Takashi; Ando, Masami
JAEA-Review 2009-053, 89 Pages, 2010/03
R&D on DEMO engineering was started from 2007 as the main activity of a DEMO design and R&D coordination center activity which was one of the international nuclear fusion energy research center (IFERC) activity of "Broader Approach" (BA) activity. In the DEMO engineering R&D activity, five "generic" R&D items were selected, which attract both Japan and EU interest and not specific to a DEMO design, i.e., (1) R&D on SiC/SiC Composites: (2) R&D on Tritium Technology: (3) R&D on Materials Engineering for DEMO Blanket: (R&D on reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel: RAFM) (4) R&D on Advanced Neutron Multiplier for DEMO Blanket: (5) R&D on Advanced Tritium Breeders for DEMO Blanket. In first phase (2007 -2009), some part of preliminary R&D, which was defined in procurement arrangement (PA) between Japan and EU, is conducted by JAEA university collaboration. This report summarized the results from joint research activities about R&D on SiC/SiC composite and RAFM in 2008.
Kimura, Tadashi; Oto, Tsutomu; Miyauchi, Masaru; Nemoto, Nobuaki; Tobita, Kenji; Fukasaku, Akitomi; Takahashi, Kunihiro
JAEA-Review 2009-054, 73 Pages, 2010/03
An integrity investigation was carried out for the JMTR reactor building, which was the concrete structure and would be used for the long-term after JMTR restart, before the repair or replacement work of the JMTR related facilities that had begun in FY2007. In the integrity investigation, the concrete surface deterioration, the rebound number (nondestructive strength test), compressive strength using drilled concrete core test piece, the static modules of elasticity, the carbonation depth, the reinforced bar corrosion and the chloride ion content were investigated respectively and the integrity of concrete was confirmed. In order to use the JMTR reactor building continuously for long-term, it is important for maintaining the integrity of a concrete structure by the periodical maintenance and the repairing work including the building outer-wall surface painting that has been conducted up to now.
Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Tobita, Kenji; Fukasaku, Akitomi; Kaminaga, Masanori
JAEA-Review 2009-055, 24 Pages, 2010/02
The condition of facilities and components to be used for re-operation of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) from FY2011, was investigated before the refurbishment work. An investigation of aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, trench, canal, filter banks and for aged components of tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out from the beginning of FY2007. As a result, cracks of concrete structures such as the exhaust stack, a foundation of the UCL (Utility Cooling Line) elevated water tank were repaired and pipe linings of secondary cooling system were replaced. Motors of primary cooling pumps, pumps in the secondary cooling system and in other systems were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability. Other components and the reactor building were decided to use continuously for a long-term by appropriate maintenance activities based on the long-term maintenance plan. In this paper, the aged-investigation for the JMTR reactor building, heat exchangers and emergency generators is presented.
Kaminaga, Masanori; Niimi, Motoji; Hori, Naohiko; Takahashi, Kunihiro; Kanno, Masaru; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-056, 20 Pages, 2010/02
The JMTR is a light water moderated and cooled, beryllium reflected tank- type reactor using LUE silicide plate-type fuels. Its thermal power is 50 MW, maximum thermal and fast neutron flux is 4  10
10 m
m s
s . First criticality was achieved in March 1968, and its operation was stopped from August, 2006 for the refurbishment. The refurbishment is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. The renewed and upgraded JMTR will be re-started from FY2011. An investigation on aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, etc., and for tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out at the beginning of FY2007. As a result, some components were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability, and some components or structures were decided to repair. A visual inspection of inner side of the pressure vessel was carried out using an underwater camera in FY2008, and no serious damage was observed. Up to now, refurbishment works are in progress according to the planned schedule. In this paper, current status of JMTR refurbishment project is presented.
. First criticality was achieved in March 1968, and its operation was stopped from August, 2006 for the refurbishment. The refurbishment is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. The renewed and upgraded JMTR will be re-started from FY2011. An investigation on aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, etc., and for tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out at the beginning of FY2007. As a result, some components were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability, and some components or structures were decided to repair. A visual inspection of inner side of the pressure vessel was carried out using an underwater camera in FY2008, and no serious damage was observed. Up to now, refurbishment works are in progress according to the planned schedule. In this paper, current status of JMTR refurbishment project is presented.
Ishihara, Masahiro; Yanagihara, Satoshi; Karlsson, M.*; Stenmark, A.*
JAEA-Review 2009-057, 149 Pages, 2010/03
The second annual meeting was held at Studsvik AB in Sweden to exchange information on radioactive waste treatment technology including recycling of materials and technical developments for the neutron irradiation experiments in materials testing reactors. The information exchange meeting was held on the basis of the implemental agreement between the Studsvik AB and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) for cooperation in nuclear energy research and development. The major items of the information exchange were the present status of waste treatment in both organizations including acceptance criteria of wastes in Studsvik facilities, experience and current status of RI production technology in both organizations as well as the sensor development. The future plan in cooperative program was also discussed. This report describes contents of the information exchange and discussions in two cooperation areas.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akira; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-058, 17 Pages, 2010/03
Within the scope of the JAEA thermodynamic database project for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU radioactive wastes, the refinement of the thermodynamic data for the inorganic compounds and complexes of tetravalent zirconium was carried out. Refinement of thermodynamic data for the element was performed on a basis of the thermodynamic database for zirconium published by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD-NEA). About the paper published after the thermodynamic database for zirconium published, the data was checked and refined.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akira; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-059, 23 Pages, 2010/03
Within the scope of the JAEA thermodynamic database project for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU radioactive wastes, the refinement of the thermodynamic data for the inorganic compounds and complexes of thorium(IV), uranium(IV), neptunium(IV) and plutonium(IV) was carried out. Refinement of thermodynamic data for the element was performed on a basis of the thermodynamic database for actinide published by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). About the paper published after the thermodynamic database for actinide ion published, the data was checked and refined.
Mihara, Morihiro
JAEA-Review 2009-060, 27 Pages, 2010/03
It is planned that JAEA-TDB has been developed modifying JNC-TDB released in 1999 by the end of FYJ 2009. The JAEA-TDB is planned to include thermodynamic data of compounds and complexes of metal elements with organic ligands which were not included in JNC-TDB. This report shows the selected thermodynamic data of compounds and complexes of metal elements with organic ligands which might be included in TRU waste in JAEA-TDB. Selected organics are oxalic acid, citric acid, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and iso-saccharinic acid (ISA) which were of interest in the OECD/NEA. The thermodynamic data evaluated by OECD/NEA were selected for JAEA-TDB. However, selected values by OECD/NEA are limited to evaluate the solubility calculation. Therefore, other published values and estimated values by LFER are also selected as tentative values for JAEA-TDB.
Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities
JAEA-Review 2009-061, 95 Pages, 2010/03
This is an annual report in a fiscal year 2008 that describes activities of RFEF, WASTEF, RHL and the other research hot facilities in the Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities. In RFEF, various PIEs were performed related to the advanced high burn-up fuel cladding, Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program, the Advanced LWR fuel Performance and Safety research program and the new cross over research program. In WASTEF, various material tests were performed, such as basic characteristic examinations for stainless steel under high temperature water environment, stress corrosion cracking tests for high-performance fuel claddings. In RHL, attached equipments were uninstalled and dismantled from each lead cells according to the decommissioning plan. And un-irradiated fuels from decommissioning facilities were carried in. In addition, managements of the other research hot facilities were carried out.
Sasaki, Yuji; Koyama, Shinichi; Ozawa, Masaki
JAEA-Review 2009-062, 158 Pages, 2010/03
The 3rd Seminar of R&D on advanced ORIENT (International) was held at Tohoku University, on October 30th, 2009 organized by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The first meeting of this seminar was held at Oarai, Ibaraki on May, 2007, and the second seminar was held at Tokai, Ibaraki on November, 2008. This seminar has the world-wide concept and includes the main topics from foreign researchers. Spent nuclear fuel should be recognized not only mass of radioactive elements but also potentially useful materials including platinum metals and rare earth elements. Taking the cooperation with universities related companies and research institutes, into consideration, we aimed at expanding and progressing the basic researches.
Environmental Management Section, Safety Administration Department
JAEA-Review 2009-063, 161 Pages, 2010/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency published the Environmental Report 2009 concerning the activities of FY 2008 in July, 2009 under "Law Concerning the Promotion of Business Activities with Environmental Consideration by Specified Corporations, etc, by Facilitating Access to Environmental Information, and Other Measures". This report has been edited to show detailed environmental performance data in FY 2008 as the base of the Environmental Report 2009. This report would environmental report, but also make useful measures for promoting activities of environmental considerations in JAEA.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Matsuura, Kenichi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Morisawa, Masato; Onuma, Toshimitsu; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Watanabe, Hajime*; Sugai, Masamitsu*
JAEA-Review 2009-064, 166 Pages, 2010/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been conducted by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Chapter IV; Environmental monitoring" and Environmental Radiation Monitoring Program decided by the Ibaraki prefectural government. The radiation monitoring installations and equipments were also prepared for emergency. This manual describes; (1) the installations of radiological measurement, (2) the installations of meteorological observation, and (3) environmental data processing system for executing the terrestrial environmental monitoring by Environmental Protection Section, Radiation Protection Department. The environmental monitoring has been operated through the manual published in 1993 (PNC TN8520 93-001). Then the whole articles were revised because the partially of installations and equipments having been updated in recent years.
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Review 2009-065, 30 Pages, 2010/03
Lead-210 is one of the important elements for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Equilibrium constants of lead species and compounds are required to estimate their migration behavior in the geological disposal system. The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) developed thermodynamic data for lead species and compounds in the JNC's thermodynamic database (JNC-TDB) published in 1999. In the present paper we reviewed latest literatures after publishing the JNC-TDB, and confirmed the reliability of their experimental values and obtained equilibrium constants for Pb(OH)
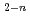 and PbCl
and PbCl
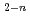 (n = 1-3). Furthermore, we re-evaluated the equilibrium constants at zero ionic strength for Pb(OH)
(n = 1-3). Furthermore, we re-evaluated the equilibrium constants at zero ionic strength for Pb(OH)
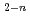 and PbCl
and PbCl
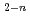 (n = 1-3) using the presently reviewed data and the previously confirmed literature data as shown below. We improved the reliability of thermodynamic data for these species.
(n = 1-3) using the presently reviewed data and the previously confirmed literature data as shown below. We improved the reliability of thermodynamic data for these species.
Saito, Yuichi; Shibata, Hiromi*
JAEA-Review 2009-066, 118 Pages, 2010/07
This review covers results of the "Study of interaction of swift cluster ion beam with matter and its irradiation effect" supported by the Interorganization Atomic Energy Research Program from FY2006 to FY2008 (Representative; Tomihiro Kamiya (FY2006), Wataru Yokota (FY2007), Takuji Kojima (FY2008) (JAEA), Hiromi Shibata (Kyoto Univ.)). The review is composed of a research abstract of each sub-group with viewgraphs which were presented at the group meeting held on March 2009 and at "Meeting of High LET radiation -From fundamental study among physics, chemistry and biology to medical applications-" sponsored by Japan Society of Radiation Chemistry, cosponsored by our research group.
Soma, Susumu; Tago, Itaru; Ono, Takayuki; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawasaki, Satoru
JAEA-Review 2009-067, 20 Pages, 2010/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency performs the environmental monitoring around the Ningyo-toge and the waste rock sites according to the agreements with local governments, Okayama and Tottori prefectures. Each prefectural committee on the environmental monitoring evaluates the monitoring data annually. This report summarized the results of the environmental monitoring in Tottori prefecture in the fiscal year 2007. The results show that the levels of the radiation doses and the radioactive concentrations in the environment were within natural variations, and the waste rock sites have been well maintained. The committee concluded the environmental impacts from the sites were negligible.
Soma, Susumu; Ono, Takayuki; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawasaki, Satoru
JAEA-Review 2009-068, 20 Pages, 2010/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency performs the environmental monitoring around the Ningyo-toge and the waste rock sites according to the agreements with local governments, Okayama and Tottori prefectures. Each prefectural committee on the environmental monitoring evaluates the monitoring data annually. This report summarized the results of the environmental monitoring in Tottori prefecture in the fiscal year 2008. The results show that the levels of the radiation doses and the radioactive concentrations in the environment were within natural variations, and the waste rock sites have been well maintained. The committee concluded the environmental impacts from the sites were negligible.
Soma, Susumu; Tago, Itaru; Ono, Takayuki; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawasaki, Satoru
JAEA-Review 2009-069, 43 Pages, 2010/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Ningyo-Toge) performs the environmental monitoring around the Ningyo-toge and the waste rock sites according to the agreements with local governments, Okayama and Tottori prefectures. Environmental monitoring of plutonium has been also performed around the Ningyo-toge regarding the practical application study on the reprocessed uranium conversion, which was carried out from 1994 to 1999 at the Ningyo-toge. Each prefectural committee on the environmental monitoring evaluates the monitoring data annually. This report summarized the results of the environmental monitoring in Okayama prefecture in the fiscal year 2007. The results show that the levels of the radiation and the radioactive concentrations in the environment were within natural variations, and the committee concluded the environmental impacts from the sites were negligible. Therefore, the site of the JAEA Ningyo-Toge has been well operated, and the waste rock sites have been well maintained.
Soma, Susumu; Ono, Takayuki; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawasaki, Satoru
JAEA-Review 2009-070, 43 Pages, 2010/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Ningyo-toge) performs the environmental monitoring around the Ningyo-toge and the waste rock sites according to the agreements with local governments, Okayama and Tottori prefectures. Environmental monitoring of plutonium has been also performed around the Ningyo-toge regarding the practical application study on the reprocessed uranium conversion, which was carried out from 1994 to 1999 at the Ningyo-toge. Each prefectural committee on the environmental monitoring evaluates the monitoring data annually. This report summarized the results of the environmental monitoring in Okayama prefecture in the fiscal year 2008. The results show that the levels of the radiation doses and the radioactive concentrations in the environment were within natural variations, and the committee concluded the environmental impacts from the sites were negligible. Therefore, the site of the JAEA Ningyo-toge has been well operated, and the waste rock sites have been well maintained.
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAEA-Review 2009-071, 102 Pages, 2010/03
This annual report summarizes the activities of Nuclear Technology and Education Center (NuTEC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the fiscal year 2008. This year is the 50th anniversary of NuTEC since the starting of the first training course in January, 1958 at the Radioisotope-School in Tokyo. On this occasion, a commemorative symposium was held and attended by around 150 participants. NuTEC flexibly designed and conducted out new training courses upon requests while conducting the annually scheduled training programs.
 Mo-production facility in JMTR
Mo-production facility in JMTRKimura, Akihiro; Iimura, Koichi; Hosokawa, Jinsaku; Izumo, Hironobu; Hori, Naohiko; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Kanno, Masaru; Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-072, 18 Pages, 2010/03
JAEA has a plan to produce  Mo, a parent nuclide of
Mo, a parent nuclide of  Tc. At present, radioisotopes are indispensable for a diagnosis and treatment in the medical field. Demand of
Tc. At present, radioisotopes are indispensable for a diagnosis and treatment in the medical field. Demand of  Tc (half life 6h) used as a radiopharmaceutical increases up year by year. Moreover, the expansion of demand will be expected in future. However, the supply of
Tc (half life 6h) used as a radiopharmaceutical increases up year by year. Moreover, the expansion of demand will be expected in future. However, the supply of  Mo in Japan depends fully on the import from foreign countries. Therefore, it is necessary to supply
Mo in Japan depends fully on the import from foreign countries. Therefore, it is necessary to supply  Mo stably by the domestic production. There are two methods of
Mo stably by the domestic production. There are two methods of  Mo (half life 65.9h) production; the one is the nuclear fission (n,fiss) method, and the other is the (n,
Mo (half life 65.9h) production; the one is the nuclear fission (n,fiss) method, and the other is the (n, ) method using the
) method using the  Mo target.
Mo target.  Mo production in the JMTR with the (n,
Mo production in the JMTR with the (n, ) method was studied and evaluated. As a result, it was found that the partial amount of
) method was studied and evaluated. As a result, it was found that the partial amount of  Mo demand is possible to supply stably if a new hydraulic-rabbit-irradiation-facility (HR) is used.
Mo demand is possible to supply stably if a new hydraulic-rabbit-irradiation-facility (HR) is used.
Tachi, Yukio; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Review 2009-073, 183 Pages, 2010/03
The international workshop on mechanistic understanding of radionuclide migration in compacted/intact systems was held at ENTRY, JAEA, Tokai on 21st - 23rd January, 2009. The objective of the workshop is to integrate the state-of-the-art of mechanistic sorption and diffusion model, and discuss the JAEA's mechanistic approaches and future challenges. This report includes workshop program, overview and materials of each presentation, summary of discussions.
Imaizumi, Tomomi; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-074, 20 Pages, 2010/03
For the neutronic calculation in JMTR, an error of only thermal-neutron-flux tends to extend in specific region, i.e. an irradiation region in beryllium reflectors surrounding the fuel region. From our former investigation, the reason is thought to be the neutron scattering and absorption in the thermal energy region. Therefore, the effect on the thermal neutron scattering law S( ,
, ) to hydrogen in light water and to beryllium metal was investigated. As a result, it was confirmed that the error could be caused by the treatment in inelastic scattering within coherent scattering in the beryllium metal, whereas no error factor was found to the hydrogen in light water.
) to hydrogen in light water and to beryllium metal was investigated. As a result, it was confirmed that the error could be caused by the treatment in inelastic scattering within coherent scattering in the beryllium metal, whereas no error factor was found to the hydrogen in light water.
Sukegawa, Takenori; Shimada, Taro; Katsurai, Kiyomichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAEA-Review 2009-075, 86 Pages, 2010/03
In the field of safety regulation systems for nuclear facilities after completion of operation, criteria of residual radioactivities and confirmation and verification procedures for termination of decommissioning are important problems that should concretely be made a study. Safety standards and criteria in IAEA, USA, etc., and practical examples of site release of power reactors in USA were studied, therefore, problems for introducing the regulation system in Japan were discussed. In this report, final status survey of Trojan power plant were investigated as a particular case of site release, and, concept of specifying survey areas to be measured radioactivities and demonstrated to compliance with release criteria was discussed. In addition, the idea of confirmation and verification procedure for termination of decommissioning in Japan was proposed referring to the US guidance (MARSSIM).
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2009-076, 131 Pages, 2010/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and seven departments such as Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities, Department of Criticality and Fuel Cycle Research Facilities, Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and Engineering Services Department. This annual report of JFY 2007 summarizes the activities of NSRI, the R&D activities of the Research and Development Directorates and human resources development at site, and is expected to be referred to and utilized by R&D departments and project promotion sectors at NSRI site for the enhancement of their own research and management activities to attain their goals according to "Middle-term Plan" successfully and effectively.
Geoscience Facility Construction Section, Tono Geoscience Center
JAEA-Review 2009-077, 38 Pages, 2010/03
This technical committee was organized for the purpose of obtaining technical comments and recommendations from specialists belonging to universities and research institutes, and for deliberating on specific matters concerning the measures for reducing water inflow into the deep shafts at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. This report presents an outline compilation of the minutes of meetings held in FY2008.
Radiation Protection Department
JAEA-Review 2009-078, 154 Pages, 2010/03
This annual report summarizes the various activities on radiation control at the nuclear fuel cycle facilities in Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, which were undertaken by the Radiation Protection Department in fiscal 2008.
Kusano, Tomohiro; Yasue, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Miyahara, Tomoya*
JAEA-Review 2009-079, 56 Pages, 2010/03
We paid attention to near-surface hydrology which influence the change of groundwater flow characteristic to grasp generally the width of long-term change of the geological environment condition with climatic / sea-level changes, and collected the data of evapotranspiration of 84 districts shown in about 50 parts domestic and foreign documents about evapotranspiration that it was difficult in the data of near-surface hydrology and arranged information about annual evapotranspiration. We collected the data of current Japan and the world district in a high latitude area (an area resemble climate of Japan of the glacial epoch) to consider the width of the change of near-surface hydrology with the climate change because data of the warmness period chilliness period in Japan were necessary. We compiled these information to the table which showed calculation technique or quantity of position / basin characteristic / evapotranspiration / precipitation every district.
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Review 2009-080, 23 Pages, 2010/03
Reliable thermodynamic data of strontium and radium are required for performance assessment of geological disposal system. Strontium is one of the important elements for performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. Radium is an important element in HLW disposal system as a daughter of actinides. Review of thermodynamic data of strontium and radium obtained from literature survey has been performed, and those of hydrolysis species, sulfate complexes, carbonates and sulfates have been selected.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2009-081, 193 Pages, 2010/03
The Department of Research Reactors and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3, JRR-4, NSRR and Tandem Accelerator. This report is a summary of technical developments of The Department of Research Reactors and Tandem Accelerator in 2008.