Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ozawa, Tatsuya; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Nakayama, Shinichi; Hotta, Katsutoshi*
JAEA-Technology 2006-001, 11 Pages, 2006/02
Melting treatment is a candidate solidification technique for nonflammable low-level radioactive wastes including metals, incineration ashes, and glasses. Simulated incineration ashes of a wide range of chemical compositions were molten at 1,600 C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Nakamichi, Masaru
JAEA-Technology 2006-002, 36 Pages, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Yamamura, Toshio*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-003, 89 Pages, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Kozo; Toyoda, Hiromasa*; Nagamine, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-004, 30 Pages, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
Tochio, Daisuke; Watanabe, Shuji; Saikusa, Akio; Oyama, Sunao; Nemoto, Takahiro; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Shinohara, Masanori; Isozaki, Minoru; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-005, 83 Pages, 2006/02
In High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the rated thermal power of 30MW, the generated heat at reactor core is finally dissipated at the air-cooler by way of the heat exchangers of the primary cooling system, such as the intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) and the secondary pressurized water cooler (SPWC). The heat exchangers in the main cooling system are required the heat exchange performance to remove the reactor-generated-heat of 30MW under the condition of reactor coolant outlet temperature of 850  C/ 950
C/ 950  C. Therefore, the heat exchanges are required to satisfy the design criteria of heat exchange performance. In this report, heat exchange performance of the SPWC in the main cooling system was evaluated with the rise-to-power-up test and the in-service operation data. Moreover, evaluated value is compared with designed one, it is confirmed that the SPWC has required heat exchange performance.
C. Therefore, the heat exchanges are required to satisfy the design criteria of heat exchange performance. In this report, heat exchange performance of the SPWC in the main cooling system was evaluated with the rise-to-power-up test and the in-service operation data. Moreover, evaluated value is compared with designed one, it is confirmed that the SPWC has required heat exchange performance.
Sato, Kazuyoshi; Hashimoto, Masayoshi*; Nagamatsu, Nobuhide*; Yagenji, Akira; Sekiya, Shigeki*; Takahashi, Hideo*; Motohashi, Keiichi*; Ogino, Shunji*; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Ohashi, Hironori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-006, 587 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Nishizawa, Hidetoshi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sonoda, Takashi; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Shimizu, Kaori; Haga, Takahisa; Sakai, Yutaka*; Akutsu, Hideyuki*; Niitsuma, Yasushi; Inoue, Takeshi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-007, 24 Pages, 2006/03
Analysis of the uranyl nitrate solution fuel is carried out at the analytical laboratory of NUCEF(Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Research Facility), which provides essential data for operation of STACY(Static Experiment Critical Facility), TRACY(Transient Experiment Critical Facility)and the fuel treatment system. Analyzed in FY 2004 were uranyl nitrate solution fuel samples taker before and after experiments of STACY and TRACY, samples for the preparation of uranyl nitrate solution fuel, and samples for nuclear material accountancy purpose. Also analyzed were the samples from raffinate treatment and its preliminary tests. The raffinate was generated, since FY 2000, during preliminary experiments on U/Pu extraction-pulification to fix the operation condition to prepare plutonium solution fuel to be used for criticality experiments at STACY. The total number of the samples analyzed in FY 2004 was 160. This report summarizes works related to the analysis and management of the analytical laboratory in the FY 2004.
Nakano, Masanao; Onuma, Toshimitsu*; Takeyasu, Masanori; Takeishi, Minoru
JAEA-Technology 2006-008, 26 Pages, 2006/03
The meteorological observation has been performed since 1960's. After 1974, this observation came to measure on the top of the meteorological observation tower, which is 100m high above the sea level, for the environmental assessment of radioactive wastes with the atmospheric discharge from the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. The meteorological observation data has been applied for the calculation of the atmospheric diffusion of radioactive wastes since the hot examination was started at 1977. The previous report, named "Analysis of Meteorological Observation Data for the Atmosphere Diffusion Calculation" was published in 1996, and mentioned to the data from 1977 to 1995. This report presents a statistic result of meteorological observation based on the decadal data from fiscal year 1995 to 2004. The characteristics of the atmosperic diffusion around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant are also discussed in this report.
Iwai, Takashi; Kikuchi, Hironobu; Arai, Yasuo
JAEA-Technology 2006-009, 31 Pages, 2006/03
Both gloveboxes No.121-D and No.122-D for metallography were installed twenty seven years ago in the room No.101 of Plutonium Fuel Research Facility in Oarai Research Establishment of former Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). It was planed to scrap the old gloveboxes and build new ones for starting new research on advanced fuel. This report summarizes the scrapping work of the gloveboxes from the technical viewpoints.
Onozawa, Atsushi; Harada, Akio; Honda, Junichi; Yasuda, Ryo; Nakata, Masahito; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Nishino, Yasuharu
JAEA-Technology 2006-010, 19 Pages, 2006/03
A measurement technique for hydrogen concentration using Backscattered Electron Image analysis (BEI method) had been developed by Studsvik Nuclear AB, Sweden. The hydrides in claddings are identified using BEIs which are imaged with Scanning Electron Microscope, and the hydrogen concentrations are calculated from the area fractions of the hydrides in the matrix. The BEI method is very useful for the measurement in local hydrogen concentrations of fuel claddings. In the Reactor Fuel Examination Facility, a sample preparation, imaging conditions of SEM and image analysis procedures for the BEI method were improved. In addition, the hydrogen concentrations obtained by the improved BEI method and Hot Vacuum Extraction (HVE) method were compared to confirm the reliability of the improved BEI method. The results showed, the improved BEI method has the same reliability as that of HVE method and can be applied for the Post-Irradiation Examination.
Hayashi, Koji; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Kato, Michio; Aita, Hideki; Morisaki, Norihiro; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takada, Shoji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-011, 132 Pages, 2006/03
This report describes 2002 fiscal-year experimental test operations of the mock-up test facility with a full-scale reaction tube for the HTTR hydrogen production system. The improvement works were performed in May 2002. The second experimental test operation was performed from June 2002 and the performances of the improved parts were confirmed. Periodic inspections on boiler equipment and high-pressure gas production facilities were performed from end of July 2002. The third experimental test operation was performed, from October 2002, for (a)start-up and shutdown test, (b)process change test, (c)chemical reaction shutdown test and (d)characteristics test on steam reformer. It was confirmed that the changes of helium gas temperature, caused at steam reformer, could be mitigated into the target range by the steam generator. Maintenance works of high-pressure gas production facilities were also performed in February 2003. This report is summarized with the outline and the results of the test, maintenance works and inspections, and operation records in mentioned above.
Hayashi, Koji; Morisaki, Norihiro; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Kato, Michio; Aita, Hideki; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Takada, Shoji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-012, 98 Pages, 2006/03
This is a report on the experimental operations and maintenances of the mock-up test facility with a full-scale reaction tube for the HTTR hydrogen production system in 2003 fiscal year. The fourth and fifth experimental test operations were performed, from May to July and from October to December in 2003, for the following tests; (a)start-up and shutdown operation test, (b)process change test, (c)continuous hydrogen-production test and (d)chemical reaction shutdown test. From the results, a long time-range stability of the hydrogen production system was confirmed, a behavior of the helium-gas cooling system, consists of steam generator and radiator, during chemical reaction shutdown, was understanded, and so on. Periodic inspections on boiler equipment and high-pressure gas production facilities were performed from end of July 2003. This report is summarized on outlines and results of the tests, outlines and results of the periodic inspections, and operation records of the mock-up test facility.
Hayashi, Koji; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Morisaki, Norihiro; Kato, Michio; Aita, Hideki; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Takada, Shoji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-013, 73 Pages, 2006/03
This is annual report on the experimental test operations and maintenances of the mock-up test facility with a full-scale reaction tube for the HTTR hydrogen production system in 2004 fiscal year. The improvement work of catalyst dust filter in combustion system was performed in May 2004, and the performance was confirmed. The sixth experimental test operation was performed from June to July 2004. Periodic inspections on boiler equipment and high-pressure gas production facilities were performed from end of July to September 2004. The seventh experimental test operation was performed from October to December 2004 for chemical reaction shutdown test. From the results, a behavior of the helium-gas cooling system, consists of steam generator and radiator, during chemical reaction shutdown was confirmed. This report is summarized with the outline and the results of the test, maintenance works and inspections, and operation records in mentioned above.
Takahashi, Toshio*; Terada, Atsuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2006-014, 60 Pages, 2006/03
In the corrosive process environment of thermochemical hydrogen production Iodine-Sulfur process plant, there is a difficulty in the direct measurement of surface temperature of the structural materials. An inverse problem method can effectively be applied for this problem, which enables estimation of the surface temperature using the temperature data at the inside of structural materials. This paper shows analytical results of steady state temperature distributions in a two-dimensional cylindrical system cooled by impinging jet flow, and clarifies necessary order of multiple-valued function from the viewpoint of engineeringly satisfactory precision.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Kasai, Satoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-015, 119 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Katsumi; Akino, Noboru; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Usui, Katsutomi; Umeda, Naotaka; Oga, Tokumichi; Kawai, Mikito; Mogaki, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2006-016, 25 Pages, 2006/03
The 500 keV negative-ion based neutral beam injector (NBI) has been operated to heat plasma and drive plasma current on JT-60U since 1996. The ion source was designed to accelerate the negative ions up to 500 keV. During the last 10 years, the accelerated voltage of the negative ion beam has been limited to  400 keV by breakdowns in the accelerator. To understand the breakdown phenomena, the characteristics of the voltage holding of the ion source were studied without beam extraction. Outgassing with the main species of m/e=28 was observed when high voltage was applied even without breakdowns. It was noticed that the fraction of the main species at breakdown was almost the same as without breakdowns. Conditioning reduced the outgassing and resulted in improvement of the voltage holding capability. Inside the ion source, a brightening was observed even without breakdown. The brightening intensity was suppressed by increasing the D
400 keV by breakdowns in the accelerator. To understand the breakdown phenomena, the characteristics of the voltage holding of the ion source were studied without beam extraction. Outgassing with the main species of m/e=28 was observed when high voltage was applied even without breakdowns. It was noticed that the fraction of the main species at breakdown was almost the same as without breakdowns. Conditioning reduced the outgassing and resulted in improvement of the voltage holding capability. Inside the ion source, a brightening was observed even without breakdown. The brightening intensity was suppressed by increasing the D pressure in the accelerator in the range of 10
pressure in the accelerator in the range of 10 Pa to 0.5 Pa. Since the voltage holding was also improved with D
Pa to 0.5 Pa. Since the voltage holding was also improved with D pressure, breakdowns seemed to correlate with the brightening phenomena in the accelerator. This report gives the preliminary results of outgassing and brightening measurements when the high voltage was applied on the accelerator without beam extraction.
pressure, breakdowns seemed to correlate with the brightening phenomena in the accelerator. This report gives the preliminary results of outgassing and brightening measurements when the high voltage was applied on the accelerator without beam extraction.
Omori, Junji; Nakahira, Masataka; Takeda, Nobukazu; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sago, Hiromi*; Onozuka, Masanori*
JAEA-Technology 2006-017, 134 Pages, 2006/03
In order to improve the fabricability of the vacuum vessel (VV) of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), applicability of plug weld between VV outer shell and stiffening ribs/blanket support housings has been assessed using crack propagation analysis for the plug weld. The ITER VV is a double-wall structure of inner and outer shells with ribs and housings between the shells. For the fabrication of VV, ribs and housings are welded to outer shell after welding to inner shell. A lot of weld grooves should be adjusted for the outer shell weld. The plug weld can allow larger tolerance of weld groove gaps than ordinary butt weld. However, un-welded lengths parallel to outer shell surface remain in the plug weld region. It is necessary to evaluate the allowable un-welded length to apply the plug weld to ITER vacuum vessel fabrication. For the assessment the allowable un-welded lengths have been calculated by crack propagation analyses for the load conditions, conservatively assuming the un-welded region is a crack. The analyses have been carried out for typical inboard straight region and inboard upper curved region with maximum housing stress. The allowable cracks of ribs are estimated to be 8.8mm and 38mm for the rib and the housing, respectively, considering inspection error of 4.4mm. Plug welding for welding between outer shell and ribs/housings could be applicable.
Suzuki, Takashi; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; Kabuto, Shoji; Togawa, Orihiko; Kinoshita, Naoki; Amano, Hikaru
JAEA-Technology 2006-018, 40 Pages, 2006/03
An accelerator mass spectrometry has been set up at the Mutsu Establishment of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This AMS has two independent beam lines, optimized for  C and
C and  I measurements. For the
I measurements. For the  I measurement, precision and reproducibility was 2.0 - 1.5% and 1.5 - 0.7%, respectively at the acceptance test in July 2000, and after that, exchange of MCP and re-alignment improved precision and reproducibility to 0.6% and 0.26%, respectively. The results of testing standard materials, which have a variety of iodine isotopic ratios (
I measurement, precision and reproducibility was 2.0 - 1.5% and 1.5 - 0.7%, respectively at the acceptance test in July 2000, and after that, exchange of MCP and re-alignment improved precision and reproducibility to 0.6% and 0.26%, respectively. The results of testing standard materials, which have a variety of iodine isotopic ratios ( I/
I/ I), showed that this beam line has excellent measurement accuracy between 10
I), showed that this beam line has excellent measurement accuracy between 10 and 10
and 10 iodine isotopic ratios, and the detection limit is substantially below the 10
iodine isotopic ratios, and the detection limit is substantially below the 10 iodine isotopic ratio. Sub-standard samples were normalized to NIST SRM 3230 standard reference material, and the iodine isotopic ratio was (1.21
iodine isotopic ratio. Sub-standard samples were normalized to NIST SRM 3230 standard reference material, and the iodine isotopic ratio was (1.21 0.01)
0.01) 10
10 for Iso Trace Lab. Standard, (7.22
for Iso Trace Lab. Standard, (7.22 0.03)
0.03) 10
10 for Standard No. 3K and (2.77
for Standard No. 3K and (2.77 0.03)
0.03) 10
10 for Standard No. 3i.
for Standard No. 3i.
Wakai, Eiichi; Otsuka, Hideo; Matsukawa, Shingo*; Ando, Masami; Jitsukawa, Shiro
JAEA-Technology 2006-019, 58 Pages, 2006/03
Small specimen test technology (SSTT) has been developed to investigate mechanical properties of nuclear materials. SSTT has been driven by limited availability of effective irradiation volumes in test reactors and accelerator-based neutron and charged particle sources, and it is very useful for the reduction of waste materials produced in nuclear engineering. In this study new bend test machines have been developed to obtain fracture behaviors of F82H steel for very small bend specimens of pre-cracked 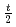 -
-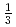 CVN (Charpy V-notch) with 20 mm-length and DFMB (deformation and fracture mini bend specimen) with 9 mm-length and disk compact tension of 0.18DCT type, and fracture behaviors were examined to evaluate DBTT (ductile-brittle transition temperature) at temperatures from -180 to 250
CVN (Charpy V-notch) with 20 mm-length and DFMB (deformation and fracture mini bend specimen) with 9 mm-length and disk compact tension of 0.18DCT type, and fracture behaviors were examined to evaluate DBTT (ductile-brittle transition temperature) at temperatures from -180 to 250 C. The effect of specimen size on DBTT of F82H steel was also examined by using Charpy type specimens such as
C. The effect of specimen size on DBTT of F82H steel was also examined by using Charpy type specimens such as 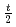 -CVN,
-CVN, 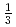 CVN and
CVN and 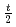 -
-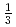 CVN. In this paper, it also provides the information of the specimens irradiated at 250
CVN. In this paper, it also provides the information of the specimens irradiated at 250 C and 350
C and 350 C to about 2 dpa in the capsules of 04M-67A and 04M-68A of JMTR experiments.
C to about 2 dpa in the capsules of 04M-67A and 04M-68A of JMTR experiments.
Honda, Atsushi; Okano, Fuminori; Oshima, Katsumi; Akino, Noboru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Tanai, Yutaka; Takenouchi, Tadashi; Numazawa, Susumu*
JAEA-Technology 2006-020, 20 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; Kubomura, Hiroyuki*; Matsuoka, Shinichi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
JAEA-Technology 2006-021, 22 Pages, 2006/06
A high output energy (5J) and high repetition rate (100Hz) laser system is required for the edge Thomson scattering system in ITER. A YAG laser (Nd:YAG laser) is a first candidate for the laser system having the performances. It is important to develop a high beam quality and single longitudinal mode (SLM) laser oscillator in order to realize this high power laser system. In this design work, following activities relating to the SLM laser oscillator have been carried out: design of the laser head and the resonator, estimation of the output power for the SLM laser oscillator, consideration of the feedback control scheme and consideration of interface for amplification system to achieve final performance (5J, 100Hz). It is expected that the designed laser diode (LD) pumped SLM laser oscillator realizes: 100 Hz of repetition rate, 10 mJ of output energy, 10 ns of pulse width, single longitudinal mode, TEM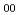 of transversal mode, less than 4 times of the diffraction limit for divergence, within 5% of energy stability.
of transversal mode, less than 4 times of the diffraction limit for divergence, within 5% of energy stability.
Sueoka, Michiharu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hosoyama, Hiroki
JAEA-Technology 2006-022, 44 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Obara, Kenjiro; Kakudate, Satoshi; Yagi, Toshiaki; Morishita, Norio; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-023, 38 Pages, 2006/03
The components in the vacuum vessel of ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor), e.g. blanket and divertor, are replaced using the dedicated remote handling systems. The environment conditions inside the vacuum vessel during the operation are temperature of 50 C, gamma ray radiation and air or inert gas atmosphere at 1 atm. ; therefore multiple elements are required as durability of the remote handling systems. In addition, the remote handling system it is desired to be able to operate over a long time. The radiation resistance motor driving equipment, which comprises parts with different radiation resistance levels, was designed simulating mechanisms of the ITER remote handling systems. The equipment being the servomotor, turns the weight (dummy load) of 8 kgf and controls, and continuous running test under high gamma ray irradiation was started from March, 2000. Irradiation conditions on the test were the dose rate of 3.6 kGy/h, the target accumulation dose of 30 MGy at the minimum. The irradiation test was performed two stages which was divided by overhaul of the equipment. The achieved accumulation dose and running time in these stages were approximately 47.6 MGy/13,200 hours and 23.9 MGy/6,640 hours, respectively. As a result, it has been confirmed that sufficient radiation resistance of the equipment, which is required from the latest dose rate of 0.5 kGy/h inside the vacuum vessel was achieved. In this report, we describe design conditions of the equipment and the results of the 1st and 2nd irradiation tests and the overhaul after the 1st irradiation test.
C, gamma ray radiation and air or inert gas atmosphere at 1 atm. ; therefore multiple elements are required as durability of the remote handling systems. In addition, the remote handling system it is desired to be able to operate over a long time. The radiation resistance motor driving equipment, which comprises parts with different radiation resistance levels, was designed simulating mechanisms of the ITER remote handling systems. The equipment being the servomotor, turns the weight (dummy load) of 8 kgf and controls, and continuous running test under high gamma ray irradiation was started from March, 2000. Irradiation conditions on the test were the dose rate of 3.6 kGy/h, the target accumulation dose of 30 MGy at the minimum. The irradiation test was performed two stages which was divided by overhaul of the equipment. The achieved accumulation dose and running time in these stages were approximately 47.6 MGy/13,200 hours and 23.9 MGy/6,640 hours, respectively. As a result, it has been confirmed that sufficient radiation resistance of the equipment, which is required from the latest dose rate of 0.5 kGy/h inside the vacuum vessel was achieved. In this report, we describe design conditions of the equipment and the results of the 1st and 2nd irradiation tests and the overhaul after the 1st irradiation test.
Sato, Kazuyoshi; Uehara, Masaharu*; Tamura, Kosaku*; Hashimoto, Masayoshi*; Ogino, Shunji*; Yagenji, Akira; Nagamatsu, Nobuhide*; Sekiya, Shigeki*; Takahashi, Hideo*; Motohashi, Keiichi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-024, 114 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi; Nakahira, Masataka; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-025, 52 Pages, 2006/03
In the ITER, the neutrons created by D-T reactions activate structural materials, and thereby, the circumstance in the vacuum vessel is under intense  radiation field. Thus, the in-vessel components such as blanket are handled and replaced by remote handling equipment. The objective of this report is to study the compactness of the remote handling equipment (a vehicle/manipulator) for the ITER blanket maintenance. In order to avoid the interferences between the blanket and the equipment during blanket replacement in the restricted vacuum vessel, a compact design of the equipment is required. Therefore, the compact design is performed, including kinematic analyses aiming at the reduction of the sizes of the vehicle equipped with a manipulator handling the blanket and the rail for the vehicle traveling in the vacuum vessel. The compact vehicle/manipulator is designed concentrating on the reduction of the rail size and simplification of the guide roller mechanism as well as the reduction of the gear diameter for vehicle rotation around the rail. As a result, the manipulator becomes about 30% lighter, 8 tons, than the original weight, 11.2 tons. Based on the compact design of the vehicle/manipulator, the structural analysis for the rail and the kinematical analysis for replacement of blanket are also performed. It is confirmed that every blanket can be replaced without any interferences in the vessel.
radiation field. Thus, the in-vessel components such as blanket are handled and replaced by remote handling equipment. The objective of this report is to study the compactness of the remote handling equipment (a vehicle/manipulator) for the ITER blanket maintenance. In order to avoid the interferences between the blanket and the equipment during blanket replacement in the restricted vacuum vessel, a compact design of the equipment is required. Therefore, the compact design is performed, including kinematic analyses aiming at the reduction of the sizes of the vehicle equipped with a manipulator handling the blanket and the rail for the vehicle traveling in the vacuum vessel. The compact vehicle/manipulator is designed concentrating on the reduction of the rail size and simplification of the guide roller mechanism as well as the reduction of the gear diameter for vehicle rotation around the rail. As a result, the manipulator becomes about 30% lighter, 8 tons, than the original weight, 11.2 tons. Based on the compact design of the vehicle/manipulator, the structural analysis for the rail and the kinematical analysis for replacement of blanket are also performed. It is confirmed that every blanket can be replaced without any interferences in the vessel.
Ozawa, Takayuki; Abe, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-026, 300 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Nakabayashi, Hiroki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Sato, Koji; Niwa, Hajime; Aoki, Kazuo*
JAEA-Technology 2006-027, 119 Pages, 2006/03
This report describes a study about the criticality safety design for the large-scale electrorefiner, which is designed in the activities of "The Design Study of Metal Fuel Recycle System (2002)", under the collaboration with Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, and the continuation of "A Study of the Criticality Safety Design for the Metal Fuel Recycle System", which was published at September 2003. The report includes a detail design and quantitative criticality parameter limits based on "the mass control supported with chemical form control" concept which is proposed in "A Study of the Criticality Safety Design for the Metal Fuel Recycle System". Furthermore procedures to determine these limits are presented in the report. Next we studied contingencies anticipated under the critical control and executed quantitative criticality safety analyses of models based on these abnormal conditions. The analytical result shows adequate safety margins are existed in the criticality safety design even if many of these contingencies could occur. Moreover we propose a concept of material transfer and production control system, we call it as "Operation by wire", which all equipment and handling machines are electrified and the control system provides completely automated process control and operation. The control system eliminates human errors and violations like over batching error or transfer error in the commercial scale metal fuel recycle system with complicated operation procedures.
Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Nemoto, Takumi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Yagi, Masahiro; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Watanabe, Shukichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-028, 115 Pages, 2006/03
JRR-4, a light-water-moderated and cooled, swimming pool type research reactor using high-enriched uranium plate-type fuels had been operated from 1965 to 1996. In order to convert to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels, modification work had been carried out for 2 years, from 1996 to 1998. After the modification, start-up experiments were carried out to obtain characteristics of the low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuel core. The measured excess reactivity, reactor shutdown margin and the maximum reactivity addition rate satisfied the nuclear limitation of the safety report for licensing. It was confirmed that conversion to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels was carried out properly. Besides, the necessary data for reactor operation were obtained, such as nuclear, thermal hydraulic and reactor control characteristics. This report describes the results of start-up experiments and burnup experiments. The first criticality of low-enriched-uranium-silicied core was achieved on 14th July 1998, and the operation for joint-use has been carried out since 6th October 1998.
Motegi, Toshihiro; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Saito, Kenji; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Shibutani, Hideki; Ogawa, Satoru; Shinozaki, Masayuki; Mizushima, Toshihiko; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-029, 67 Pages, 2006/06
The plant control performance of the IHX helium flow rate control system, the PPWC helium flow rate control system, the secondary helium flow rate control system, the inlet temperature control system, the reactor power control system and the outlet temperature control system of the HTTR are obtained through function tests and power-up tests. As the test results, the control systems show stable control response under transient condition. Both of inlet temperature control system and reactor power control system shows stable operation from 30% to 100%, respectively. This report describes the outline of control systems and test results.
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Kondo, Makoto; Oyama, Sunao; Kawano, Shuichi; Kobayashi, Shoichi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Suzuki, Hisashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-030, 58 Pages, 2006/03
During normal operation of High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the reactivity is controlled by the Control Rods (CRs) system which consists of 32 CRs (16 pairs) and 16 Control Rod Drive Mechanisms (CRDMs). The CR system is located in stand-pipes accompanied by the Reserved Shutdown System (RSS). In the unlikely event that the CRs fail to be inserted, the RSS is provided to insert B C/C pellets into the core. The RSS shall be designed so that the reactor should be held subcriticality from any operation condition by dropping in the pellets. The RSS consists of B
C/C pellets into the core. The RSS shall be designed so that the reactor should be held subcriticality from any operation condition by dropping in the pellets. The RSS consists of B C/C pellets, hoppers which contain the pellets, electric plug, driving mechanisms, guide tubes and so on. In accidents when the CRs cannot be inserted, an electric plug is pulled out by a motor and the absorber pellets fall into the core by gravity. A trouble, malfunction of one RSS out of sixteen, occurred during a series of the pre-start up checks of HTTR on February 21, 2005. We investigated the cause of the RSS trouble and took countermeasures to prevent the issue. As the result of investigation, the cause of the trouble was attributed to the following reason: In the motor inside, The Oil of grease of the multiplying gear flowed down from a gap of the oil seal which has been deformed and was mixed with abrasion powder of brake disk. Therefore the adhesive mixture prevented a motor from rotating.
C/C pellets, hoppers which contain the pellets, electric plug, driving mechanisms, guide tubes and so on. In accidents when the CRs cannot be inserted, an electric plug is pulled out by a motor and the absorber pellets fall into the core by gravity. A trouble, malfunction of one RSS out of sixteen, occurred during a series of the pre-start up checks of HTTR on February 21, 2005. We investigated the cause of the RSS trouble and took countermeasures to prevent the issue. As the result of investigation, the cause of the trouble was attributed to the following reason: In the motor inside, The Oil of grease of the multiplying gear flowed down from a gap of the oil seal which has been deformed and was mixed with abrasion powder of brake disk. Therefore the adhesive mixture prevented a motor from rotating.
Kitagawa, Osamu; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-031, 29 Pages, 2006/03
Using the correlation between electric conductivity and acidity in solution, we have investigated an analytical method that is able to determine acidity in the nitric acid solution by measuring electric conductivity of sample diluted with distilled water, and correcting the electric conductivity for plutonium(Pu) and uranium(U) using multivariate analysis method. We obtained good results as follows, (1) Acidity in the nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U obtained by this method was good agreement, within 10%, compared with the acidity measured by potentiometric titration method. (2) For plutonium nitrate solution and plutonium-uranium mixed nitrate solution, the repeatability and reproducibility for the measurement of electric conductivity at 25.0 C were less than 0.52%, and 1.53% respectively. (3) Impurities such as americium and iron in the solutions did not influence to the measurement of electric conductivity, if total amounts of these impurities were less than 1% compared with those of Pu and U. From the results described above, electric conductivity measuring method has been applying to analysis of acidity in the nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U at high concentration handled in Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. Furthermore, this method can be expected for the application to analysis of acidity in nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U for reprocessing process.
C were less than 0.52%, and 1.53% respectively. (3) Impurities such as americium and iron in the solutions did not influence to the measurement of electric conductivity, if total amounts of these impurities were less than 1% compared with those of Pu and U. From the results described above, electric conductivity measuring method has been applying to analysis of acidity in the nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U at high concentration handled in Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. Furthermore, this method can be expected for the application to analysis of acidity in nitric acid solutions containing Pu and U for reprocessing process.
Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishitani, Takeo; Ioki, Kimihiro; Iida, Hiromasa; Kataoka, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-032, 91 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Hirakawa, Yasushi; Yoshida, Eiichi; Gunji, Shigeru*
JAEA-Technology 2006-033, 22 Pages, 2006/06
The sodium removal technology containing radioactive nuclides is required for inspection and repair of sodium system components and decommissioning of sodium cooled fast reactors. In order to evaluate the efficient sodium removal conditions, the sodium removal rate by the moisture gas cleaning process was examined. Experiments were conducted by simulating residual sodium in the bottom of a vessel and in the crevice parts of components. The experimental parameters were sodium temperature, moisture concentration in career gas (N ), and surface area of sodium. (1)The effect of the moisture gas cleansing parameters has been investigated and quantitative data for the sodium removal rate were obtained in this study. (2)Sodium temperature and sodium-phase (liquid or solid) did not affect sodium removal rate from 80
), and surface area of sodium. (1)The effect of the moisture gas cleansing parameters has been investigated and quantitative data for the sodium removal rate were obtained in this study. (2)Sodium temperature and sodium-phase (liquid or solid) did not affect sodium removal rate from 80  C to 150
C to 150  C sodium temperature. However, at the 180
C sodium temperature. However, at the 180  C sodium temperature of sodium removal rate declined. (3)Moisture concentration in the nitrogen gas greatly affected the sodium removal rate increased with increasing moisture. (4)The sodium removal rate was influenced of sodium surface direction (facing upward or downward). Facing upward the sodium surface had higher sodium removal rate than facing downward. (5)The unstable rapid reaction similar to combustion was observed in some cases during experiments of sodium removal by wet nitrogen gas.
C sodium temperature of sodium removal rate declined. (3)Moisture concentration in the nitrogen gas greatly affected the sodium removal rate increased with increasing moisture. (4)The sodium removal rate was influenced of sodium surface direction (facing upward or downward). Facing upward the sodium surface had higher sodium removal rate than facing downward. (5)The unstable rapid reaction similar to combustion was observed in some cases during experiments of sodium removal by wet nitrogen gas.
Obara, Kenjiro; Kakudate, Satoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sago, Hiromi*; Ue, Koichi*; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Onozuka, Masanori*
JAEA-Technology 2006-034, 85 Pages, 2006/06
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) tokamak is composed of many kinds of components. The dimensions and weight of the respective components are around a few ten-meters and several hundred-tons. In addition, the whole tokamak assembly, which are composed of these components, are roughly estimated, 26 m in diameter, 18 m in height and over 16,500 tons in total weight. On the other hand, as for positioning and assembly tolerances of these components are required to be a high accuracy of  3mm in spite of large size and heavy weight. The assembly procedures and techniques of the ITER tokamak are therefore studied, taking account of the tolerance requirements. Based on the above background, the assembly procedures and techniques, which are able to assemble the tokamak with high accuracy, are described in the present report. The following newly developed tokamak assembly procedures and techniques, jigs and tools for assembly and metrology concept based on the available knowledge and experiences of the installation of the large components, in order to improve the IT (International Team) design toward the more realistic one. As a result, we show the realistic tokamak assembly procedures and techniques to be able to assemble the large and heavy ITER tokamak with high accuracy. (1)Assembly and alignment of the toroidal field coil with high accuracy. (2)Simplification of the assembly procedures, and the jigs/tools and procedures to reduce the misalignment. (3)Assembly procedures and techniques for the vacuum vessel to reduce the weld distortion. (4)Supporting procedures and techniques of the vacuum vessel sector to prevent the toridal field coil from the deformation due to the dead weight of the vacuum vessel sector. (5)Datum points and lines for the required positions and assembly tolerances during tokamak assembly.
3mm in spite of large size and heavy weight. The assembly procedures and techniques of the ITER tokamak are therefore studied, taking account of the tolerance requirements. Based on the above background, the assembly procedures and techniques, which are able to assemble the tokamak with high accuracy, are described in the present report. The following newly developed tokamak assembly procedures and techniques, jigs and tools for assembly and metrology concept based on the available knowledge and experiences of the installation of the large components, in order to improve the IT (International Team) design toward the more realistic one. As a result, we show the realistic tokamak assembly procedures and techniques to be able to assemble the large and heavy ITER tokamak with high accuracy. (1)Assembly and alignment of the toroidal field coil with high accuracy. (2)Simplification of the assembly procedures, and the jigs/tools and procedures to reduce the misalignment. (3)Assembly procedures and techniques for the vacuum vessel to reduce the weld distortion. (4)Supporting procedures and techniques of the vacuum vessel sector to prevent the toridal field coil from the deformation due to the dead weight of the vacuum vessel sector. (5)Datum points and lines for the required positions and assembly tolerances during tokamak assembly.
Saito, Kosuke; Maeda, Seiichiro; Higuchi, Masashi*; Takano, Mitsuhiro*; Nakazawa, Hiroaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-035, 76 Pages, 2006/06
Because of the revision on the standardized strength of the ODS steel, the previous design study of MONJU demonstrative core has been obliged to be reconsidered. For economical advantages, only a 127 pins-bundle core was selected to be redesigned. For the sake of cladding endurance, the ratio of cladding thickness to outer diameter was reset incrementally followed by the determination of the basic specification of a pin. Notwithstanding some deterioration thanks to the reduction of a fuel volume fraction, the prospect in neutronics was obtained. Coolant flow distribution design which was based on power distribution was successfully carried out without overheating cladding. Average burn-up of 150 GWd/t and 380 days-long operational period per cycle are to be attained, and the designed core can thermally afford to receive test fuels. The study has necessity to be advanced extensively for the purpose of materialization according to the circumstances of MONJU in future.
Miyaji, Noriko; Nagamine, Tsuyoshi; Katsuyama, Kozo
JAEA-Technology 2006-036, 41 Pages, 2006/06
Eddy current testing (ECT) technique has been developed in order to check the soundness of irradiated fuel pins non-destructively. This paper describes the results that it was examined if corrosions were detected using an imitation fuel pin, made of 15Ni-15Cr-Ti and same type of the fuel pins irradiated in JOYO. As the results of experimental for an imitation pin, ECT detected the corrosions using frecquency 32kHz. And, the signal of eddy current became larger as the thickness of the cladding became smaller, because there was some correlation between the signal and thickness. As for the irradiated fuel pins, inner corrosions were not recognized from the signal because their sizes were too small. However, outside corrosions by sodium as coolant might have an influence on the signal. And, as well as a change of the electromagnetic characteristics of cladding by irradiation, inner pressure by FP gas and PCMI might have an influence on the signal.
Narita, Osamu; Iwata, Noboru; Isobe, Yoshihiro; Seki, Masakazu; Kadosaka, Hidetake; Ninomiya, Kazushige; Sato, Osamu
JAEA-Technology 2006-037, 102 Pages, 2006/06
We edited and published the Environmental Report according to the law on Promotion of the Environmental Concerning Activity by means of the Publish of Environmental Concerning Data. The report included the environmental concerning activity at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and the Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute (JNC) in the first half year of 2005. This report is the first one which is regulated and obligated by the law. We have made much effort for gathering the data and gained a lot of experience on editing the report. We hope this paper is useful not only for the back data of our environmental report, but also for the organization which is planning to publish the similar environmental report.
Kakudate, Satoshi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Nakahira, Masataka; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-038, 38 Pages, 2006/06
Transportation of the in-vessel components to be repaired in the ITER hot cell is carried by two kinds of transporters, i.e., overhead cranes and floor vehicles. The access area for repair operations in the hot cell is duplicated by these transporters. Clear sharing of the respective roles of these transporters with the minimum duplication is therefore useful for rationalization. The overhead crane has an adapter for change of the end-effectors, which can be easily changed, to grasp many kinds of components to be repaired. The floor vehicle, which is equipped with wheel mechanisms for transportation, is just to pass through the components between cells with only straight (linear) motion on the floor. Rescue scenarios and procedures in the hot cell are also studied in this report. The proposed rescue crane has major two functions for rescue operations of the hot cell facility, i.e., one for the overhead crane and the other for refurbishment equipment such as workstation for divertor repair. Especially, for the rescue of the workstation, the rescue crane consists of a telescopic manipulator (maximum length of 6500 mm) with rescue tool such as wrench for operation of the faulty driving mechanism through the redundant mechanism in order to release the activated component.
Hirao, Norie*; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao
JAEA-Technology 2006-039, 39 Pages, 2006/08
The present report summarizes the outline and details of synchrotron soft X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) system installed at the synchrotron beamline (BL-27) of the Photon Factory (PF), High Energy Accelerator Research organization (KEK). This system was installed at the soft X-ray beamline (BL-27A), one of the branch beamlines of the BL-27, which was constructed at the KEK-PF in 1992. Since then, various researches centering around the surface chemistry field have been conducted using this XPS system. Many parts of the system have been remodeled and improved in these 14 years. In addition, a new X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) microscopy system and its analysis chamber have been installed just at the down stream of XPS system in 2005, therefore considerable parts of the XPS system have been renewed. Under these circumstances, this report summarizes the outline and operation manual of the XPS system. The related data about XPS, XAFS, etc. are also added in appendix for the users who will use this XPS system from now on.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-040, 76 Pages, 2006/07
A spectrophotometric determination using neodymium as an internal standard has been developed for safeguards verification analysis of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste which is produced by the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical operation and the instrument conditions. The sample was mixed with a known amount of neodymium as an internal standard. Subsequently, plutonium was quantitatively oxidized to Pu(IV) by the addition of Ce(IV). Plutonium concentration was calculated from a relation between Nd(III)/Pu(VI) molar extinction coefficient ratio and their absorbance ratio. The expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis of plutonium (n=5) was found to be  15mgL
15mgL (confidence interval 95%) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample (173mgL
(confidence interval 95%) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample (173mgL ). The determination limit was calculated to be 6mgL
). The determination limit was calculated to be 6mgL (ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were agree well with values obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.nt on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
(ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were agree well with values obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.nt on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2006-041, 58 Pages, 2006/06
We have developed a method of spectrophotometric determination of plutonium ( 10
10 M) in highly radioactive liquid waste for safeguards verification analysis. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical scheme and the inspection procedure. The relative expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis (n = 5) was 8.9 % (coverage factor k = 2) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample(173 mgL
M) in highly radioactive liquid waste for safeguards verification analysis. The method offers reduced sample preparation and analysis time compared to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It uses neodymium as an internal standard, which allows for determining an index for the authentication of the analytical scheme and the inspection procedure. The relative expanded uncertainty of the repeated analysis (n = 5) was 8.9 % (coverage factor k = 2) for a highly radioactive liquid waste sample(173 mgL ). The determination limit was calculated to be 6 mgL
). The determination limit was calculated to be 6 mgL (ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were in good agreement with those obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It is to be noted that the neodymium standard is intended to be provided by the inspector so that an inspector can check the instrument conditions as well as the analytical scheme. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
(ten fold's the standard deviation). This method was validated through comparison experiments with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The analytical results of plutonium in highly radioactive liquid waste using this method were in good agreement with those obtained using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. It is to be noted that the neodymium standard is intended to be provided by the inspector so that an inspector can check the instrument conditions as well as the analytical scheme. The proposed method was successfully applied for the independent on-site safeguards analysis at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant.
Mori, Kensuke; Suzuki, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kakudate, Satoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Akiba, Masato
JAEA-Technology 2006-042, 72 Pages, 2006/08
A separable first wall from a shield block in ITER shield blanket module is required not only to be connected metallurgically to the shield block in order to withstand the electro-magnetic force and coolant pressure, but also to be able to replace the first wall more than 2 times in the hot cell during the life time of the reactor. Therefore, the consistent structure where remote handling equipment can be access to the joint and carry out the welding/cutting works perfectly to replace the first wall in the hot cell is required in the shield blanket design. This study shows an investigation of the blanket module design with a new type of the first wall support leg structure based on Disc-Cutter technology, which had been developed for the main pipe cutting in the maintenance phase and was selected out of a number of candidate methods, taking its large advantages into account, such as (1) a post-treatment can be eliminated in the hot cell because of no making material chips and of no need of lubricant, (2) the cut surface can be rewelded without any machining. In conclusion, not only the good performance of Disc-Cutter technology applied to the updated blanket module, but also consistent structure of the simplified shield blanket module including the first wall support leg in order to satisfy the requirements in the design have been proposed.
Imaizumi, Hirobumi; Ban, Yasutoshi; Asakura, Toshihide; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Technology 2006-043, 45 Pages, 2006/09
In JAEA, the solvent washing properties of n-butylamine compounds, which can be decomposed by incineration or electrolysis, have been investigated using simulated and real degraded tributylphosphate (TBP) solvent. Ion chromatography has been utilized as an analytical method to determine the concentration of dibutylphosphoric acid (DBP) in organic and aqueous phases. Recently, we met difficulty to maintain the reliability of analytical results. A gas chromatograph-mass spectroscope (GC-MS) was considered as new analytical method to solve these problems. As a result, it was confirmed that improved reliability of analysis can be obtained by utilizing a sample pre-treatment method to introduce tetra methyl silyl substituent to the target molecule, DBP. In a chromatogram, monobutylphosphoric acid also gave good peaks. I can be expected to analyze DBP and MBP simultaneously with only one sample in the TBP solvent.
Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Yamamura, Toshio*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-044, 39 Pages, 2006/10
In the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), the back-wall of target assembly is the part suffered the highest neutron-flux. The back-wall and the assembly are designed to have lips for cutting/welding at the back-wall replacement. To reduce thermal stress and deformation of the back-wall under neutron irradiation, contact pressure between the back-wall and the assembly is one of dominant factors. Therefore, an investigation was performed for feasible clamping pressure of a mechanical clamp set in limited space around the back-wall. It was clarified that the clamp can give a pressure difference up to 0.4 MPa between the contact pressure and atmosphere pressure in the test cell room. Also a research was performed for the dissimilar metal welding in the back-wall. Use of 309 steel was found adequate as the intermediate filler metal through the research of previous welding. Maintaining a temperature of the target assembly so as to avoid a freezing of liquid lithium is needed at the lithium charge into the loop before the beam injection. The assembly is covered with thermal insulation. Therefore, a research and an investigation were performed for compact and light thermal-insulation effective even under helium (i.e. high heat-conduction) condition of the test cell room. The result was as follows; in the case that a thermal conductivity 0.008 W/m K of one of found insulation materials is available in the temperature range up to 300
K of one of found insulation materials is available in the temperature range up to 300 C of the IFMIF target assembly, needed thickness and weight of the insulation were respectively only 8.2 mm and 32 kg. Also a research was performed for high-heat-density heaters to maintain temperature of the back-wall which can not be cover with insulation due to limited space. A heater made of silicon-nitride was found to be adequate. Total heat of 8.4kW on the back-wall was found to be achievable through an investigations of heater arrange.
C of the IFMIF target assembly, needed thickness and weight of the insulation were respectively only 8.2 mm and 32 kg. Also a research was performed for high-heat-density heaters to maintain temperature of the back-wall which can not be cover with insulation due to limited space. A heater made of silicon-nitride was found to be adequate. Total heat of 8.4kW on the back-wall was found to be achievable through an investigations of heater arrange.
Tochio, Daisuke; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Yamazaki, Kazunori; Shimizu, Yasunori; Aragaki, Etsushi; Ota, Yukimaru; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Technology 2006-045, 43 Pages, 2006/09
The auxiliary component cooling water system (ACCWS) is one of the cooling system in High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) The ACCWS has the features not only many facilities cooling but also heat sink of the vessel cooling system which is one of the engineering safety features. Therefore, the ACCWS is required to satisfy the design criteria of heat removal performance. In this report, heat exchange performance data of the rise-to-power-up test and the in-service operation for the ACCWS cooling tower was evaluated. Moreover, the evaluated values were compared with the design values, and it is confirmed that ACCWS cooling tower has the required heat exchange performance in the design.
Hazawa, Tomoya; Nagahori, Kazuhisa; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-046, 44 Pages, 2006/10
The moderator cell containing liquid hydrogen is made of stainless steel. The material irradiation lifetime is limited to 7 years due to irradiation brittleness. The survey and design for a renewal moderator cell were conducted with a view to domestic production by the JAEA. It was fabricated and replaced by a domestic company, and the replacement work was completed in February, 2006. Characteristic was measured after exchange, and it had the same performance as the moderator cell made in France, and succeeded in making to domestic production.
 Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO pebbles for a high Li-burnup irradiation test
pebbles for a high Li-burnup irradiation testTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2006-047, 18 Pages, 2006/10
Lithium titanate (Li TiO
TiO ) pebbles are considered to be a candidate material of tritium breeders for fusion reactor from viewpoints of easy tritium release at low temperatures (about 300
) pebbles are considered to be a candidate material of tritium breeders for fusion reactor from viewpoints of easy tritium release at low temperatures (about 300 ) and chemical stability. In the present study, trial fabrication tests of
) and chemical stability. In the present study, trial fabrication tests of  Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO pebbles of 1mm in diameter were carried out by a wet process with a dehydration reaction, and characteristics of the
pebbles of 1mm in diameter were carried out by a wet process with a dehydration reaction, and characteristics of the  Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO pebbles were evaluated for preparation of a high Li-burnup test in a testing reactor. Powder of 96at%
pebbles were evaluated for preparation of a high Li-burnup test in a testing reactor. Powder of 96at%  Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO was prepared by a solid state reaction, and two kinds of
was prepared by a solid state reaction, and two kinds of  Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO pebbles, namely un-doped and TiO
pebbles, namely un-doped and TiO -doped Li
-doped Li TiO
TiO pebbles, were fabricated by the wet process. Based on results of the pebble fabrication tests, two kinds of
pebbles, were fabricated by the wet process. Based on results of the pebble fabrication tests, two kinds of  Li-enriched Li
Li-enriched Li TiO
TiO pebbles were successfully fabricated with target values (density : 80-85%T.D., grain size :
pebbles were successfully fabricated with target values (density : 80-85%T.D., grain size :  5
5 m, diameter : 0.85-1.18mm). Physical, chemical and mechanical properties of these pebbles were also evaluated before neutron irradiation tests. Sphericity of these Li
m, diameter : 0.85-1.18mm). Physical, chemical and mechanical properties of these pebbles were also evaluated before neutron irradiation tests. Sphericity of these Li TiO
TiO pebbles was a satisfying value of about 1.05. Contact strength of these pebbles was about 6300MPa, which was almost the same as that of the Li
pebbles was a satisfying value of about 1.05. Contact strength of these pebbles was about 6300MPa, which was almost the same as that of the Li TiO
TiO pebbles with natural Li.
pebbles with natural Li.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ishihara, Masahiro; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2006-048, 19 Pages, 2006/10
IG-110 graphite is a fine-grained isotropic and nuclear-grade graphite with excellent resistivity on both irradiation and corrosion and with high strength. The IG-110 graphite is used for the graphite components of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) such as fuel and control rod guide blocks and support posts. In order to design and fabricate the graphite components in the HTTR, the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (the Japan Atomic Energy Agency at present) had established the graphite structural design code and design data on the basis of former research results. This report summarized the characteristics of the first loaded IG-110 graphite as basic data for surveillance test, measuring material characteristics changed by neutron irradiation and oxidation. By comparing the design data, it was shown that the first loaded IG-110 graphite had excellent strength properties and enough safety margins to the stress limits in the design code.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-049, 32 Pages, 2006/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a fast breeder reactor(FBR), and plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) having low density and 20-30%Pu content has used as a fuel of the FBR, Monju. In plutonium, Americium has been accumulated during long-term storage, and Am content will be increasing up to 2-3% in the MOX. It is essential to evaluate the influence of Am content on physical properties of MOX on the development of FBR in the future. In this study melting points and thermal conductivities which are important data on the fuel design were measured systematically in wide range of composition, and the effects of Am accumulated were evaluated. The solidus temperatures of MOX were measured as a function of Pu content, oxygen to metal ratio(O/M) and Am content using thermal arrest technique. The sample was sealed in a tungsten capsule in vacuum for measuring solidus temperature. In the measurements of MOX with Pu content of more than 30%, a rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction between MOX and tungsten. In the results, it was confirmed that the melting points of MOX decrease with as an increase of Pu content and increase slightly with a decrease of O/M ratio. The effect of Am content on the fuel design was negligible small in the range of Am content up to 3%. Thermal conductivities of MOX were evaluated from thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method and heat capacity calculated by Nuemann- Kopp's law. The thermal conductivity of MOX decreased slightly in the temperature of less than 1173K with increasing Am content. The effect of Am accumulated in long-term storage fuel was evaluated from melting points and thermal conductivities measured in this study. It is concluded that the increase of Am in the fuel barely affect the fuel design in the range of less than 3%Am content.
Ozawa, Tatsuya; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Suto, Makoto; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamaguchi, Hiromi
JAEA-Technology 2006-050, 88 Pages, 2006/11
Melting treatment is one of the volume reduction processes for nonflammable radioactive solid wastes. Though it is applied to the volume reduction process for the low-level radioactive wastes generated at nuclear power plants, it still has technical problems to be solved. The results of our previous investigation of existing melting treatment facilities and conceptual design of the melting treatment system for transuranic waste, made these technical problems clear. To solve them, we have been carrying out the experiments of melting treatment of the simulated transuranic wastes which are nonflammable solid wastes. This report describes the progress in investigating these problems, as well as the results of recent experiments.
Ozawa, Takayuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-051, 278 Pages, 2006/11
IFA-514 irradiation test was performed in Halden Reactor (HBWR) in Norway to study the irradiation performance of LWR MOX fuels. The fuel specifications for this irradiation test were decided in accordance with those of BWR 8  8 fuels, and plutonium content of MOX fuels was 5.8 wt.%. Six MOX fuel rods, of which parameters were pellet geometry (solid or annular) and surface roughness (grinded or as-sintered), were irradiated to the assembly average burn-up of 45 GWd/t, and the instrument data during irradiation, i.e,. cladding elongation, fuel stack elongation, fuel center temperature, and rod inner pressure, were obtained, and subsequent post-irradiation examinations indicated no remarkable corrosion and deformation on the irradiated fuel rods. The irradiation for three of six fuel rods irradiated in IFA-514 irradiation tests were continued to the assembly average burn-up of 56 GWd/t in IFA-565 irradiation tests, and the results of this irradiation test inditated no remarkable corrosion and deformation on the irradiated fuel rods. The FP gas release behavior of LWR MOX fuels was similar to that of BWR UO
8 fuels, and plutonium content of MOX fuels was 5.8 wt.%. Six MOX fuel rods, of which parameters were pellet geometry (solid or annular) and surface roughness (grinded or as-sintered), were irradiated to the assembly average burn-up of 45 GWd/t, and the instrument data during irradiation, i.e,. cladding elongation, fuel stack elongation, fuel center temperature, and rod inner pressure, were obtained, and subsequent post-irradiation examinations indicated no remarkable corrosion and deformation on the irradiated fuel rods. The irradiation for three of six fuel rods irradiated in IFA-514 irradiation tests were continued to the assembly average burn-up of 56 GWd/t in IFA-565 irradiation tests, and the results of this irradiation test inditated no remarkable corrosion and deformation on the irradiated fuel rods. The FP gas release behavior of LWR MOX fuels was similar to that of BWR UO and ATR MOX fuels, and no difference was confirmed in the FP gas release behavior. Also FP gas release rate of annular pellets (13 %) was lower than that of solid ones (16 %), and no difference in the effect of pellet geometry, i.e. solid and annular, on PCMI behavior was confirmed since no evidence of remarkable PCMI taking place was observed in any fuel rod from the instrument data of fuel stack elongation and the results of ceramography, but the pellet geometry is expected to have an effect of the cladding diameter change reduction since the cladding diameter change of annular fuel rods was less than that of solid ones.
and ATR MOX fuels, and no difference was confirmed in the FP gas release behavior. Also FP gas release rate of annular pellets (13 %) was lower than that of solid ones (16 %), and no difference in the effect of pellet geometry, i.e. solid and annular, on PCMI behavior was confirmed since no evidence of remarkable PCMI taking place was observed in any fuel rod from the instrument data of fuel stack elongation and the results of ceramography, but the pellet geometry is expected to have an effect of the cladding diameter change reduction since the cladding diameter change of annular fuel rods was less than that of solid ones.
Matsui, Hiroya; Sasaki, Manabu*
JAEA-Technology 2006-052, 101 Pages, 2006/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting the project with construction of the Underground Research Laboratory (URL) called "Horonobe URL Project" since FY2000/FY2001 in Horonobe-cho, Hokkaido in Japan. The project is divided into three major phase, such as surface-based investigation phase, construction phase and operation phase. Total duration of the project is about 20 years. In the surface-based investigation phase, the eleven deep borehole investigations, which were drilled until 1000m depth, have carried out to understand a geological environment in the selected URL area formed Neocence sedimentary formations in Horonobe-cho. This report describe summarized important experiences to perform the deep borehole investigations with max. 1000m depth. This information could be great helpful for future site investigations.
Baba, Shinichi; Shibata, Taiju; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2006-053, 84 Pages, 2006/12
This paper describes the outline of the neutron irradiation test on the thermal properties of zirconia material(3Y-TZP). The measured data of thermal diffusivity for the 3Y-TZP and the outlines of the thermal properties for zirconia-based materials applied to the Thermal Barrier Coating(TBC)/Inert Matrx Fuel(IMF) are also described in this report. The thermal diffusivity is measured by the laser flash method (L/F method). The analyses of the data are adopted with the 3-techniques regulated on Japan Industrial Standard (JIS). Namely, it is (1) the half-time method, (2) logarithmic and (3) regression analysis. The measurements of thermal diffusivity for the both materials isotropic graphite as reference materials and 3Y-TZP are carried out, and discussed to the heat loss. It is necessary to the correction of heat loss in the half-time method for measured at high temperature, and also especially need to the low-thermal diffusivity such as 3Y-TZP.
Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2006-054, 68 Pages, 2007/02
JAEA(Japan Atomic Energy Agency) has been conducting the project which is combined with construction of URL(Underground Research Laboratory) on Neocene sedimentary rock in Horonobe-cho, Hokkaido, Japan. This project, conjugate with the MIU project on crystalline rock in Mizunami-shi, Gifu-prefecture, Japan, was started FY1999/2000. The total duration of the project is about twenty years. The project consist of the following three phases; Surface-based investigation phase Construction phase Operation phase. This report summarizes the experience for deep borehole investigation in surface based investigation phase, which is most important investigation in the phase. The all deep borehole investigations had been planed and carried out in taking account of not only technical consideration but also practical and social aspects. Specifically, the report describes the important suggestions derived from the work of the deep borehole investigations.
Okano, Masanori; Kuno, Takehiko; Takahashi, Ichiro*; Shirozu, Hidetomo; Charlton, W. S.*; Wells, C. A.*; Hemberger, P. H.*; Yamada, Keiji; Sakai, Toshio
JAEA-Technology 2006-055, 38 Pages, 2006/12
The amount of Pu in the spent fuel was evaluated from Xe isotopic ratio in off-gas in reprocessing facility, is related to burnup. Six batches of dissolver off-gas at spent fuel dissolution process were sampled from the main stack in Tokai Reprocessing Plant during BWR fuel reprocessing campaign. Xenon isotopic ratio was determined with GC/MS. Burnup and generated amount of Pu were evaluated with Noble Gas Environmental Monitoring Application code (NOVA), developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory. Inferred burnup evaluated by Xe isotopic measurements and NOVA were in good agreement with those of the declared burnup in the range from -3.8% to 7.1%. Also, the inferred amount of Pu in spent fuel was in good agreed with those of the declared amount of Pu calculated by ORIGEN code in the range from -0.9% to 4.7%. The evaluation technique is applicable for both burnup credit to achieve efficient criticality safety control and a new measurement method for safeguards inspection.
Kiriyama, Koji; Mitsui, Takaya
JAEA-Technology 2006-056, 28 Pages, 2006/12
Crystal processing methods of high resolution monochromator (HRM) has been developed at Japanese Atomic Energy Agency/Quantum Beam Science Directorate/Synchrotron Radiation Research unit at SPring-8. For producing HRM, slicing machine has been installed as cutting device of crystal ingot, and X-ray diffractmetor to measure the crystal face of the ingot has set up. By installation of these devices, high energy resolution monochromator crystal for inelastic X-ray scattering and beam collimator are got ready to be used for nanotechnology studies.
Takai, Toshihide; Nakagiri, Toshio; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2006-057, 40 Pages, 2006/12
A new experimental apparatus by the thermo-chemical and electrolytic hybrid hydrogen production process was assembled for 1Nl/h (2.8 10
10 Nm
Nm /s) level hydrogen production. A SO
/s) level hydrogen production. A SO electrolysis cell and SO
electrolysis cell and SO solution electrolysis cell were developed to increase hydrogen production rate up to 1Nl/h (2.8
solution electrolysis cell were developed to increase hydrogen production rate up to 1Nl/h (2.8 10
10 Nm
Nm /s). To achieve higher cell current and durability of the SO
/s). To achieve higher cell current and durability of the SO cell, seven Yttria Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte tubes with platinum plated electrode which have twice length in comparison with the former tube are employed Flow type cell with MEA is used for the SO
cell, seven Yttria Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte tubes with platinum plated electrode which have twice length in comparison with the former tube are employed Flow type cell with MEA is used for the SO cell to increase cell current density. In this paper, outline of the newly developed experimental apparatus and future hydrogen production experimental plan are reported.
cell to increase cell current density. In this paper, outline of the newly developed experimental apparatus and future hydrogen production experimental plan are reported.
Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie*
JAEA-Technology 2006-058, 43 Pages, 2007/01
The present report summarizes the outline and details of synchrotron soft X-ray micro-XAFS (X-ray absorption fine structure) system installed at the synchrotron beamline (BL-27A) of the Photon Factory (PF), High Energy Accelerator Research organization (KEK). The system was installed for the purpose of measuring morphology, element-selective and chemical-state-selective mappings of solid surfaces at micrometer or nanometer scale. In this report, the detailed outlines, specification, and operation manual are firstly described. Then the experimental data about the observations on Si micro-pattern and estimation of spacial resolution using ultraviolet light are presented.Preliminary experimental results for chemical-state-selective mapping of Si/SiO micro-patterns using synchrotron radiation are also presented.
micro-patterns using synchrotron radiation are also presented.
Hirose, Akira; Wada, Shigeru; Sasajima, Fumio; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Kameyama, Iwao*; Aizawa, Ryoji*; Kikuchi, Naoyuki*
JAEA-Technology 2006-059, 122 Pages, 2007/01
It is expected that the demand for NTD-Si increases rapidly because of recent productive increase of hybrid-cars. In order to meet the demand, we have investigated the expansion technology of the NTD-Si productivity using the JRR3. This report describes the production of equipment for the external cooling device while proposed as one of the result of the investigation for the JRR-3 uniformity irradiation equipment. After an ingot was irradiated once, it is turned over manually and irradiated again in order irradiate the ingot uniformly. With the conventional equipment, it was necessary to wait the radioactivity of ingot decrease less than the permissible level with holding the ingot in the irradiation equipment. It was effective to shorten the waiting period by using an external cooling device for production increase of NTD-Si. It is expected that the productivity of NTD-Si will be increased by using the external cooling device.
Takada, Hiroshi; Kato, Takashi; Kaminaga, Masanori; Natsume, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2006-060, 103 Pages, 2007/02
We have planned an installation sequence of large structural components of the 1-MW spallation neutron source station with a high accuracy of an unit of mm with respect to the designed position and a tangential inclination of 1/1000 to horizontal level in Materials & Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) under the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). We have also carried out transportation and installation of some of structural components having a weight of heavier than 50 ton with a width of over 10 m and a height near 10 m and obtained perspectives to fulfill installation of whole components as designed sequence. In order to implement the surface transportation of such components to the construction site, we have carefully made a planning of the transportation, considering the structural strength of the bridge on the way to the site and temporal removal of structural interferences along the road.
Takasu, Tamio*; Maekawa, Keisuke
JAEA-Technology 2006-061, 34 Pages, 2007/02
It is necessary for safety assessment of high-level radioactive waste geologic disposal to understand groundwater flow in deep underground accurately. Groundwater flow in the coastal area especially considered to be quite complex that involves density and hydraulic gradient driven flow of freshwater and seawater. Furthermore, bentonite, which is one of the favored engineered barrier materials, may not swell very well in seawater as it does in freshwater, and therefore may not provide a reliable seal if salinity is high enough. Therefore it is important to understand saltwater behavior in deep underground. In order to understand the behavior of seawater intrusion into freshwater in deep underground, we constructed a laboratory equipment "Mini-MACRO" named after the original large scale MACRO (MAss transport Characterization in host ROck) and aimed to increase a precision and efficiency of experiment. In this report we summarize the procedures of the equipment construction and the results of preliminary tests of saltwater intrusion into a freshwater body.
Murao, Hiroyuki; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Okawara, Masami; Shibata, Isao
JAEA-Technology 2006-062, 32 Pages, 2007/02
In NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor) experiments, test fuels are inserted in the especial capsule and the capsule will be inserted into the experimental tube which is located in the center of reactor core. In NSRR, there are 17 types of atmospheric pressure capsule, and one of them Type X-IV atmospheric pressure capsule has been produced 6 times under authorization of Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). Application for the 7th time of authorization was submitted to the MEXT in June 2006. On this application, standard which is used to design was changed to The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers (JSME) S NC1-2005 from the Notification 501 of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). The JSME S NC1-2005 introduced the service condition in addition to the reactor condition which has been used in the Notification 501. In this application, stress limits were calculated based on the service condition. The JSME S NC1-2005 requires estimation of combined stress for Class1 support structures, which was unnecessary in the Notification 501. In this application, combined stresses were calculated and confirmed not to exceed the stress limits.