Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kim, B. K.*; Tan, L.*; Sakasegawa, Hideo; Parish, C. M.*; Zhong, W.*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu*; Kato, Yutai*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 545, p.152634_1 - 152634_12, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 97(2), p.86 - 92, 2021/02
The 5D gyrokinetic simulation data has been analyzed with the data-driven analysis methods. By defining an entropy-like quantity with singular values, we have quantitatively evaluated the randomness of the plasma state. We found that the randomness of plasma increases after the avalanche like transport and then gradually decrease. Since the decrease of the randomness is expected to be relevant to the phase space structure formation, we have developed a method to extract the phase space structures from the time series of 5D data. The relationship between the avalanche-like transport and phase space structures is discussed based on the contribution of each principal component to the energy transport.
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*; Heim, D. M.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Garbet, X.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Masatoshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 28(1), p.012304_1 - 012304_21, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This article demonstrates a data compression technique for the time series of five dimensional distribution function data based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Phase space bases and corresponding coefficients are constructed by PCA in order to reduce the data size and the dimensionality. It is shown that about 83% of the variance of the original five dimensional distribution can be expressed with 64 components. This leads to the compression of the degrees of freedom from 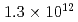 to
to 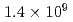 . One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
. One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
Uenaga, Issei; Furukawa, Masaru*
Physics of Plasmas, 27(9), p.092501_1 - 092501_11, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This work uses the Rutherford model for a cylindrical plasma to study the dynamics of magnetic islands under external magnetic perturbations, including both applied rotational magnetic fields and static error magnetic fields. The results show that, in an unstable tearing situation, magnetic islands are completely suppressed by modulating the frequency of the externally applied rotational magnetic field to maintain the phase of the combined external magnetic field to be opposite (or nearly opposite) that of the magnetic islands. The frequency is modulated by using a proportional controller in the simulation, where the frequency of the rotational field is determined by using the island rotation frequency "measured" in the simulation.
Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Park, C. H.*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 146(Part A), p.285 - 288, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)Herein, the wall shear stress in a double contraction nozzle has been evaluated experimentally to produce a liquid lithium (Li) target as a beam target for intense fusion neutron sources such as the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), the Advanced Fusion Neutron Source (A-FNS), and the DEMO Oriented Neutron Source (DONES). The boundary layer thickness and wall shear stress are essential physical parameters to understand erosion-corrosion by the high-speed liquid Li flow in the nozzle, which is the key component in producing a stable Li target. Therefore, these parameters were experimentally evaluated using an acrylic mock-up of the target assembly. The velocity distribution in the nozzle was measured by a laser-doppler velocimeter and the momentum thickness along the nozzle wall was calculated using an empirical prediction method. The resulting momentum thickness was used to estimate the variation of the wall shear stress along the nozzle wall. Consequently, the wall shear stress was at the maximum in the second convergent section in front of the nozzle exit.
Donnel, P.*; Garbet, X.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Asahi, Yuichi; Wilczynski, F.*; Caschera, E.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Gillot, C.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 61(1), p.014003_1 - 014003_11, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:60.80(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Poloidal asymmetries of the 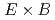 plasma flow are known to play a role in neoclassical transport. According to conventional neoclassical theory, the level of poloidal asymmetry of the electric potential is expected to be very small. In the present work, a general framework for the generation of axisymmetric structures of potential by turbulence is presented. Zonal flows, geodesic acoustic modes and convective cells are described by a single model. This is done by solving the gyrokinetic equation coupled to the quasi-neutrality equation. This calculation provides a predictive calculation of the frequency spectrum of flows given a specified forcing due to turbulence. It also shows that the dominant mechanism comes from zonal flow compression at intermediate frequencies, while ballooning of the turbulence Reynolds stress appears to be the main drive at low frequency.
plasma flow are known to play a role in neoclassical transport. According to conventional neoclassical theory, the level of poloidal asymmetry of the electric potential is expected to be very small. In the present work, a general framework for the generation of axisymmetric structures of potential by turbulence is presented. Zonal flows, geodesic acoustic modes and convective cells are described by a single model. This is done by solving the gyrokinetic equation coupled to the quasi-neutrality equation. This calculation provides a predictive calculation of the frequency spectrum of flows given a specified forcing due to turbulence. It also shows that the dominant mechanism comes from zonal flow compression at intermediate frequencies, while ballooning of the turbulence Reynolds stress appears to be the main drive at low frequency.
Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 136(Part A), p.24 - 28, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the IFMIF-EVEDA project, we designed and constructed the IFMIF-EVEDA Li Test Loop (ELTL), and we performed experiments to validate the stability of the Li target. This project required a diagnostic tool to be developed in order to examine the Li target; as such, we developed a unique laser-based method that we call the laser-probe method; this method combines a high-precision laser distance meter with a statistical data analysis method. Following the successful development of the laser-probe method, we proposes a long-distance-measurement of the laser probe method (long-distance LP method) as a diagnostics tool in off-beam conditions for IFMIF or the relevant neutron sources. In this study, the measurement uncertainty resulting from coherency of the laser in a long-distance-measurement has been verified by using stationary objects and a water jet simulating the liquid Li target.
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku*; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.14971_1 - 14971_8, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:78.94(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 9, p.286 - 291, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to exchange the components which received irradiation damage during the operation at the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility, the adhered lithium, which is partially converted to lithium compounds such as lithium oxide and lithium hydroxide, should be removed from the components. In this study, the dissolution experiments of lithium compounds (lithium nitride, lithium hydroxide, and lithium oxide) were performed in a candidate solvent, allowing the clarification of time and temperature dependence. Based on the results, a cleaning procedure for adhered lithium on the inner surface of the components was proposed.
Kim, Jae-Hwan; Nakamichi, Masaru
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1764 - 1768, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:77.12(Nuclear Science & Technology) TiO
TiO during DT neutron irradiation by use of an improved tritium collection method
during DT neutron irradiation by use of an improved tritium collection methodEdao, Yuki; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 112, p.480 - 485, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)The accurate measurement of behavior of bred tritium released from a tritium breeder is indispensable to understand the behavior for a design of a tritium extraction system. The tritium collection method combined a CuO bed and water bubbles was not suitable to measure transient behavior of tritium released from Li TiO
TiO during neutron irradiation because tritium released behavior was changed to be delayed due to adsorption of oxidized tritium on the CuO. Hence, the tritium collection method with hydrophobic catalyst instead of the CuO was demonstrated and succeeded the accurate release measurement of tritium from Li
during neutron irradiation because tritium released behavior was changed to be delayed due to adsorption of oxidized tritium on the CuO. Hence, the tritium collection method with hydrophobic catalyst instead of the CuO was demonstrated and succeeded the accurate release measurement of tritium from Li TiO
TiO . With the method, we assessed the behavior of tritium release under the various conditions since tritium should be released from Li
. With the method, we assessed the behavior of tritium release under the various conditions since tritium should be released from Li TiO
TiO as the form of HT as much as possible from the view point of the fuel cycle. Our results indicated; promotion of isotopic exchange reaction on the surface of Li
as the form of HT as much as possible from the view point of the fuel cycle. Our results indicated; promotion of isotopic exchange reaction on the surface of Li TiO
TiO by addition of hydrogen in sweep gas is mandatory in order to release tritium smoothly from Li
by addition of hydrogen in sweep gas is mandatory in order to release tritium smoothly from Li TiO
TiO irradiated with neutrons; the favorable sweep gas to release as the form of HT was hydrogen added inert gas; and the temperature of Li
irradiated with neutrons; the favorable sweep gas to release as the form of HT was hydrogen added inert gas; and the temperature of Li TiO
TiO was the dominant parameter to control the chemical form of tritium released from the Li
was the dominant parameter to control the chemical form of tritium released from the Li TiO
TiO .
.
Shirai, Hiroshi; Barabaschi, P.*; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60SA Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1701 - 1708, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:87.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JT-60SA Project has shown steady progress toward the first plasma in 2019. JT-60SA is a superconducting tokamak designed to operate in the break-even conditions for a long pulse duration with a maximum plasma current of 5.5 MA. Design and fabrication of JT-60SA components shared by EU and Japan started in 2007. Assembly in the torus hall started in January 2013, and welding work of the vacuum vessel sectors is currently on going on the cryostat base. Other components such as TF coils, PF coils, power supplies, cryogenic system, cryostat vessel, thermal shields and so forth were or are being delivered to Naka site for installation, assembly and commissioning. This paper gives technical progress on fabrication, installation and assembly of tokamak components and ancillary systems, as well as progress of JT-60SA Research Plan being developed jointly by EU and Japanese fusion communities.
Noguchi, Yuto; Maruyama, Takahito; Ueno, Kenichi; Komai, Masafumi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1291 - 1295, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper reports the impact hammer test of the full-scale mock-up of ITER Blanket Remote Handling system (BRHS). Since the BRHS, which is composed of the articulated rail and the vehicle manipulator which travels on the rail deployed in the vacuum vessel, is subjected to the floor response spectrum with 14 G peak at 8 Hz, evaluation of dynamic response of the system is of essential importance. Recently impact hammer testing on the full-scale mock-up of the BRHS was carried out to verify the finite element method seismic analysis and to experimentally obtain the damping ratio of the system. The results showed that the mock-up has a vertical major natural mode with a natural frequency of 7.5 Hz and a damping ratio of 0.5%. While higher structural damping ratios is predicted in a high amplitude excitation such as major earthquake, it was confirmed that the experimental natural major frequencies are in agreement with the major frequencies obtained by elastic dynamic analysis.
Konno, Chikara; Sato, Satoshi; Ota, Masayuki; Kwon, Saerom; Ochiai, Kentaro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1649 - 1652, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently we have examined KERMA factors and DPA cross section data in the latest official ACE files of JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1, JEFF-3.2 and FENDL-3.0 in more detail and we found out the following new problems on the KERMA factors and DPA cross section data. (1) NJOY bugs and incorrect nuclear data generated KERMA factors and DPA cross section data of no increase with decreasing neutron energy in low neutron energy. (2) Huge helium production data caused drastically large KERMA factors and DPA cross section data in low neutron energy. (3) It seemed that NJOY could not adequately process capture cross section data in File 6, not File 12-15. (4) KERMA factors with the kinematics method are not correct for nuclear data libraries without detailed secondary particle data (energy-angular distribution data). These problems should be resolved based on our study.
Edao, Yuki; Sato, Katsumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Hayashi, Takumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(11), p.1831 - 1838, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:59.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wakai, Eiichi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi*; Ito, Yuzuru*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yagi, Juro*; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 11, p.2405112_1 - 2405112_4, 2016/11
Konno, Chikara; Kwon, Saerom; Ota, Masayuki; Sato, Satoshi
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.239 - 242, 2016/09
In order to specify reasons of the discrepancy between the calculated and measured results in analyses of benchmark experiments, some parts of some isotope data in nuclear data files are often modified and the modifies nuclear data files are processed with the NJOY code and the new ACE or MATXS files are used. However it is not easy to modify capture and elastic scattering data below 1 MeV with resonance data. Thus we devised a simple method to use capture and elastic scattering cross section data generated from resonance data with the NJOY code. This method was applied to detailed analyses of copper and molybdenum benchmark experiments at JAEA/FNS and it was demonstrated that this method was a very powerful tool.
Konno, Chikara; Kwon, Saerom; Ota, Masayuki; Sato, Satoshi
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.233 - 238, 2016/09
We compared the KERMA factors and DPA cross section data included in the official ACE and MATXS files of JENDL-4.0 with those of ENDF/B-VII.1 and JEFF-3.2. As a result, they were different from those of ENDF/B-VII.1 and JEFF-3.2 in a lot of nuclei, which was considered to be caused by the following new problems; (1) NJOY bugs, (2) huge helium production cross section data, (3)  production data format in the nuclear data, (4) no detailed secondary particle data (energy-angular distribution data). The ACE and MATXS files of JENDL-4.0 with these problems should be revised based on this study.
production data format in the nuclear data, (4) no detailed secondary particle data (energy-angular distribution data). The ACE and MATXS files of JENDL-4.0 with these problems should be revised based on this study.
Edao, Yuki; Iwai, Yasunori; Sato, Katsumi; Hayashi, Takumi
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 114, p.40 - 44, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.75(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have focused on bacterial oxidation of tritium by hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria in natural soil to realize a passive reactor for tritium oxidation at room temperature. The purpose of this study was to examine the feasibility of a bioreactor with hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria for detritiation system from a point of view of engineering. The efficiency of the bioreactor was evaluated by kinetics. The bioreactor packed with natural soil shows a relative high conversion rate of tritium under the saturated moisture condition at room temperature, which is obviously superior to that of a Pt/Al O
O catalyst generally used for tritium oxidation in the existing tritium handling facilities. The order of reaction for tritium oxidation with soil was the pseudo-first order as assessed with Michaelis-Menten kinetics model. Our engineering suggestion to increase the reaction rate is the intentional addition of hydrogen at a small concentration in the feed gas on condition that the oxidation of tritium with soil is expressed by the Michaelis-Menten kinetics model. We reach a conclusion that a bioreactor using hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria in natural soil has the feasibility to be applied in the DS as a passive reactor.
catalyst generally used for tritium oxidation in the existing tritium handling facilities. The order of reaction for tritium oxidation with soil was the pseudo-first order as assessed with Michaelis-Menten kinetics model. Our engineering suggestion to increase the reaction rate is the intentional addition of hydrogen at a small concentration in the feed gas on condition that the oxidation of tritium with soil is expressed by the Michaelis-Menten kinetics model. We reach a conclusion that a bioreactor using hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria in natural soil has the feasibility to be applied in the DS as a passive reactor.
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.30720_1 - 30720_7, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.65(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In this Letter, we report model verifications for a key physics for the L-H transition. Radial electric field excitation, using discharges having a two-step transition. Examining time derivative of Poissons equation, it is found that the sum of the loss cone loss current and neoclassical bulk viscosity current agrees the experimentally observed current in the order of magnitude at the first transition. Following second transition and an ambipolar condition in the L-mode cannot be explained by the models.