Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebihara, Kenichi; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Toda, Hiroyuki*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 136, p.751 - 756, 2025/06
It has been experimentally reported that adding tin (Sn) to high-strength aluminum-zinc-magnesium (Al-Zn-Mg) alloys effectively suppresses hydrogen (H) embrittlement, which may be attributed to H absorption by the second-phase particles of Sn. To verify this fact, a simulation of H entry into the Sn phase in Al was performed using a model based on the reaction-diffusion equation that incorporates the solid solution energy of H evaluated by first-principles calculations. The results showed that the H solid solution site concentration of the second-phase particles must be at least five times higher than that of the Al phase for H absorption by the Sn second-phase particles to suppress H embrittlement. Therefore, the actual H embrittlement suppression effect of Sn second-phase particles is limited, and other factors may influence the suppression of H embrittlement in the experiment.
Meguro, Tomonari*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Kobayashi, Koji*; Araki, Yasufumi; Nomura, Kentaro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022065_1 - L022065_8, 2025/06
 Be activity concentrations in Dazaifu (western Japan)
Be activity concentrations in Dazaifu (western Japan)Narazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 284, p.107612_1 - 107612_7, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Atmospheric  Be activity concentration was continuously measured in Dazaifu, western Japan, from 1999 to 2020, and its variation was analyzed. Daily
Be activity concentration was continuously measured in Dazaifu, western Japan, from 1999 to 2020, and its variation was analyzed. Daily  Be data analysis, encompassing an analysis for 22 years, revealed a concentration range of not detected - 18 mBq/m
Be data analysis, encompassing an analysis for 22 years, revealed a concentration range of not detected - 18 mBq/m , characterized by substantial monthly variation and smoothed annual variation. An average daily
, characterized by substantial monthly variation and smoothed annual variation. An average daily  Be activity concentration of 5.0
Be activity concentration of 5.0  2.6 mBq/m
2.6 mBq/m was considered to be representative at the ground-surface-level in 30-40
was considered to be representative at the ground-surface-level in 30-40 N. Results from a two-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated statistical significance in monthly and annual
N. Results from a two-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated statistical significance in monthly and annual  Be variabilities. The monthly variability of
Be variabilities. The monthly variability of  Be activity concentration was approximately four times greater than the annual variability. Frequency analysis revealed that the monthly variability comprised major 12-month and minor 6-month periodicities. The substantial decrease in
Be activity concentration was approximately four times greater than the annual variability. Frequency analysis revealed that the monthly variability comprised major 12-month and minor 6-month periodicities. The substantial decrease in  Be activity concentration during summer, a primary driver of monthly variation, was also observed at other locations in Japan, attributed to a stable high-pressure system in the Pacific Ocean that stalled over Japan's southern seas, followed by the inflow of air masses containing low
Be activity concentration during summer, a primary driver of monthly variation, was also observed at other locations in Japan, attributed to a stable high-pressure system in the Pacific Ocean that stalled over Japan's southern seas, followed by the inflow of air masses containing low  Be activity concentrations. The annual variation was primarily influenced by the 11-year solar activity cycle, which affects the intensity of cosmic rays that produce
Be activity concentrations. The annual variation was primarily influenced by the 11-year solar activity cycle, which affects the intensity of cosmic rays that produce  Be.
Be.
Moon, J. Y.*; Ito, Yuta; 13 of others*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 9 Pages, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sumita, Takehiro*; Osawa, Takahito; Chiu, I.-H.; Ikeda, Atsushi
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1329, p.343256_1 - 343256_10, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
Wen, J.*; Kamada, Yuto*; Yokoyama, Kosei*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Liu, W.*; Morita, Koji*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 13th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS13) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/11
Mikhail, M. A. G.*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Eto, Taisei*; Tsukada, Kazuaki
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.27132_1 - 27132_10, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We have studied a straightforward and robust single-step cation exchange separation method to isolate medical copper radioisotopes  Cu and
Cu and  Cu produced in the
Cu produced in the  Zn(n, x) reaction with an accelerator neutrons technique. This study revealed the key role of a phosphate buffer pre-treatment of the cation exchange column in the separation process. It was found that incorporating the phosphate buffer into the column pre-treatment markedly enhances the retention of copper isotopes within the column throughout the separation procedure. This approach yields a high-purity radioactive copper sample with a high extraction efficiency of 94.4% of the initially produced copper, all within a relatively short experimental time frame of approximately 5 h for 100 g of starting material.
Zn(n, x) reaction with an accelerator neutrons technique. This study revealed the key role of a phosphate buffer pre-treatment of the cation exchange column in the separation process. It was found that incorporating the phosphate buffer into the column pre-treatment markedly enhances the retention of copper isotopes within the column throughout the separation procedure. This approach yields a high-purity radioactive copper sample with a high extraction efficiency of 94.4% of the initially produced copper, all within a relatively short experimental time frame of approximately 5 h for 100 g of starting material.
Toyama, Takeshi*; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Otsuka, Satoshi; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Nakashima, Hideharu*; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155252_1 - 155252_14, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the stability of oxide nano particles in oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, which is a promising candidate material for next-generation reactors, under neutron irradiation at high temperature to high doses. MA957, a 14Cr-ODS steel, was irradiated with Joyo in Japan Atomic Energy Agency under irradiation conditions of 130 dpa at 502 C, 154 dpa at 589
C, 154 dpa at 589 C, and 158 dpa at 709
C, and 158 dpa at 709 C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502
C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502 C and to 154 dpa at 589
C and to 154 dpa at 589 C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709
C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709 CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of
CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of  160 dpa at high temperature up to 700
160 dpa at high temperature up to 700 C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
 Cf fission fragments with MRTOF-MS and detailed study of masses of neutron-rich Ce isotopes
Cf fission fragments with MRTOF-MS and detailed study of masses of neutron-rich Ce isotopesKimura, Sota*; Ito, Yuta; 8 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(4), p.045810_1 - 045810_9, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.81(Physics, Nuclear)Ozawa, Akihiro*; Araki, Yasufumi; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.094704_1 - 094704_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Modulation of magnetization in magnetic Weyl semimetals leads to the shift of Weyl points in momentum space, which effectively serves as the chirality-dependent gauge field for the Weyl fermions. Here, we theoretically study such a magnetization-induced chiral gauge field, in a fully spin-polarized Weyl ferromagnet Co Sn
Sn S
S . From a tight-binding model of Co
. From a tight-binding model of Co Sn
Sn S
S on stacked kagome lattice with magnetism, we calculate the magnetization-dependent evolution of the Weyl points in momentum space, resulting in the chiral gauge field. In the presence of the magnetic domain wall structure, we evaluate the chiral magnetic field arising from the spatial profile of the chiral gauge field. We find that a magnetic domain wall in Co
on stacked kagome lattice with magnetism, we calculate the magnetization-dependent evolution of the Weyl points in momentum space, resulting in the chiral gauge field. In the presence of the magnetic domain wall structure, we evaluate the chiral magnetic field arising from the spatial profile of the chiral gauge field. We find that a magnetic domain wall in Co Sn
Sn S
S gives rise to a giant chiral magnetic field for the Weyl fermions, which reaches the order of a few hundred tesla to induce the Landau quantization. Such a giant chiral magnetic field may also influence the novel transport phenomena, such as the charge pumping by the domain wall motion, compatible with the spinmotive force.
gives rise to a giant chiral magnetic field for the Weyl fermions, which reaches the order of a few hundred tesla to induce the Landau quantization. Such a giant chiral magnetic field may also influence the novel transport phenomena, such as the charge pumping by the domain wall motion, compatible with the spinmotive force.
Higa, Ryota*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
Materials Transactions, 65(8), p.899 - 906, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)It is indispensable to suppress hydrogen embrittlement (HE) to develop the strength of the Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Because intergranular fracture (IGF) is mainly observed when HE occurs in the alloy, we need to understand the IGF initiation to suppress HE. In the present study, we investigated the stress, strain, and H concentration, which influence the IGF initiation, in actual fractured regions by simulation of a crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis in a 3D image-based model, which was created based on 3D polycrystalline microstructure data obtained from X-ray imaging technique. Combining the simulation and in-situ observation of the tensile test sample by X-ray CT, we examined the stress, strain, and H concentration, and discussed the IG crack initiation condition. As a result, it is revealed that stress normal to grain boundary induced by crystal plasticity dominates IG crack initiation while the accumulation of H due to stress has little impact on it.
 Be activity concentrations with respect to precipitation
Be activity concentrations with respect to precipitationNarazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 277, p.107432_1 - 107432_7, 2024/07
Beryllium-7 activity concentrations in the atmosphere and precipitation were continuously measured every day between April 2011 and December 2015 in Dazaifu, western Japan. The measured data were quantitatively analyzed to determine the precipitation-induced variation in  Be activity concentrations. The average concentrations on nonprecipitation and precipitation days were 5.5 and 3.8 mBq/m
Be activity concentrations. The average concentrations on nonprecipitation and precipitation days were 5.5 and 3.8 mBq/m , respectively. This difference of 31% (1.7 mBq/m
, respectively. This difference of 31% (1.7 mBq/m ) on average, was attributable to the washout effect, which was more significant in the summer. Regarding the association between
) on average, was attributable to the washout effect, which was more significant in the summer. Regarding the association between  Be activity concentration and precipitation, the concentration remained at a similar level for the small precipitation amount of
Be activity concentration and precipitation, the concentration remained at a similar level for the small precipitation amount of  5.0 mm/day and showed a decreasing trend (but was insignificant) for the precipitation of 5.0-10.0 mm/day. A significant decrease in the concentration was observed for
5.0 mm/day and showed a decreasing trend (but was insignificant) for the precipitation of 5.0-10.0 mm/day. A significant decrease in the concentration was observed for 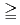 10 mm/day. Furthermore, when precipitation occurred on two successive days, the
10 mm/day. Furthermore, when precipitation occurred on two successive days, the  Be activity concentrations on the second day significantly decreased regardless of precipitation.
Be activity concentrations on the second day significantly decreased regardless of precipitation.
 complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transition
complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transitionJi, T.*; Su, S.*; Wu, S.*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Huang, Y.*; Zheng, W.*; Xu, W.*; Zhang, X.*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 63(25), p.e202404843_1 - e202404843_6, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:94.71(Engineering, Mechanical)Hydrogen(H) embrittlement in high-strength aluminum(Al) alloys is a crucial problem. H accumulation at the interface of precipitates in Al alloy is considered to cause embrittlement. However, there is no quantitative knowledge regarding the interaction between H distribution and stress field near cracks. In this study, using a multi-modal three-dimensional image-based simulation combining the crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis, we tried to capture the stress distribution near the crack, its influence on the H distribution, and the probability of crack initiation in the experimental condition. As a result, it was found that grain boundary cracks transition to quasi-cleavage cracks in the region where the cohesive energy of the semi-coherent interface of MgZn precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
 nuclei constrain element abundances
nuclei constrain element abundancesXian, W.*; Ito, Yuta; 30 of others*
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.035804_1 - 035804_10, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear) particle impinging on Al at 230 MeV/u
particle impinging on Al at 230 MeV/uFuruta, Toshimasa*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Koba, Yusuke*; Velicheva, E.*; Kalinnikov, V.*; Tsamalaidze, Z.*; Evtoukhovitch, P.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.230 - 236, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Charged particle production from  particle fragmentation reactions was investigated experimentally by measurement of 230-MeV/u
particle fragmentation reactions was investigated experimentally by measurement of 230-MeV/u  particles bombarding an aluminum target. Double differential cross sections were measured for each ejectile of p, d, t,
particles bombarding an aluminum target. Double differential cross sections were measured for each ejectile of p, d, t,  He, and
He, and  He at laboratory angles between 15 and 60 deg. The results of analyzed data found the following common characteristics: (1) spectra of proton- and neutron-emission are similar in high energy region at forward angle, (2) triton-to-
He at laboratory angles between 15 and 60 deg. The results of analyzed data found the following common characteristics: (1) spectra of proton- and neutron-emission are similar in high energy region at forward angle, (2) triton-to- He ratio of
He ratio of  -breakup yield is 1:2, which is similar to lower incident energy experiment, and (3) the shape of broad peak formed by
-breakup yield is 1:2, which is similar to lower incident energy experiment, and (3) the shape of broad peak formed by  He and
He and  particles could be explained by the process with collision between induced
particles could be explained by the process with collision between induced  particle and target nucleus.
particle and target nucleus.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:129 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:82.25(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
 ,
,  , and X-ray spectrum analysis
, and X-ray spectrum analysisOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Kin, Tadahiro*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*
Isotope News, (790), p.19 - 23, 2023/12
When analyzing samples that contain many radionuclides at various concentrations, such as radioactive waste or fuel debris, it is difficult to apply general spectrum analysis methods and is necessary to chemically separate each nuclide before quantifying it. The chemical separation is especially essential for analysis using a liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In this report, the authors explain the newly developed spectral determination method (SDM) in which the entire spectrum is fitted to quantify radioactivity of nuclides mixed in a sample. By applying the SDM to  - and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and
- and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and  -ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
-ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.