Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Huang, Y.-C.*; Kikkawa, Takashi; 5 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 126(9), p.092403_1 - 092403_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Suzuki, Seiya; Katsube, Daiki*; Yano, Masahiro; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Terasawa, Tomoo; Ozawa, Takahiro*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Kim, Y.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yuhara, Junji*; et al.
Small Methods, 9(3), p.2400863_1 - 2400863_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)Moon, J. Y.*; Ito, Yuta; 13 of others*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 9 Pages, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cf fission fragments with MRTOF-MS and detailed study of masses of neutron-rich Ce isotopes
Cf fission fragments with MRTOF-MS and detailed study of masses of neutron-rich Ce isotopesKimura, Sota*; Ito, Yuta; 8 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(4), p.045810_1 - 045810_9, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Journal of Neutron Research, 26(2-3), p.69 - 74, 2024/09
Slow neutrons, such as cold neutrons, are important non-destructive probes not only for basic physics but also for the structural genomics advancements in the life sciences and the battery technology advancements needed for the transition to a hydrogen society. Neutron-based science is also known as high-neutron-intensity-dependent science. A new unique method focusing on nanosized particle aggregation has been proposed to increase neutron intensity in that energy region. The method is based on intensity enhancement by multiple coherent scatterings with nanosized particle aggregation. The aggregation of nanosized particles matches the wavelength of below cold neutrons, causing a similar effect to coherent scattering, so-called Bragg scattering, leading to neutron intensity enhancement by several orders of magnitude. Nanodiamonds and magnesium hydride have recently been studied numerically and experimentally. The major challenge with nanodiamonds in practical applications is the molding method. Another carbon structure, graphene is focused on to find a solution to this problem. It is hypothesized that nanosized graphene could aid coherent neutron scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamonds. We report the potential of nanosized graphene as a reflector material below cold neutrons, together with experimental results.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt bilayer disk
/Pt bilayer diskEmdi, G.*; Hioki, Tomosato*; Makiuchi, Takahiko*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 22(3), p.L031002_1 - L031002_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied) C
C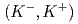 reaction at 1.8 GeV/
reaction at 1.8 GeV/ with the Superconducting Kaon spectrometer
with the Superconducting Kaon spectrometerIchikawa, Yudai; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sato, Susumu; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.091D01_1 - 091D01_13, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)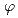 Josephson junctions and synchronized precession
Josephson junctions and synchronized precessionNakata, Koki; Zou, J.*; Klinovaja, J.*; Loss, D.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.033207_1 - 033207_11, 2024/08
Hosokawa, Kaiji*; Yama, Masaki*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kato, Takeo*
Physical Review B, 110(3), p.035309_1 - 035309_12, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sano, Ryotaro*; Ominato, Yuya*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review Letters, 132(23), p.236302_1 - 236302_9, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Funato, Takumi*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kato, Takeo*
Physical Review Letters, 132(23), p.236201_1 - 236201_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:82.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yao, D.*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Yokoyama, Takehito*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(16), p.162603_1 - 162603_5, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.60(Physics, Applied)Warashina, Tomoro*; Sato, Asako*; Hinai, Hiroshi; Shaikhutdinov, N.*; Shagimardanova, E.*; Mori, Hiroshi*; Tamaki, Satoshi*; Saito, Motofumi*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 90(4), p.e02113-23_1 - e02113-23_23, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology) Fe
Fe O
O
Kawamoto, Yo*; Kikkawa, Takashi; Saito, Eiji; 9 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(13), p.132406_1 - 132406_7, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.60(Physics, Applied)Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H.; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ominato, Yuya*; Yamakage, Ai*; Matsuo, Mamoru
Physical Review B, 109(12), p.L121405_1 - L121405_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)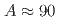 nuclei constrain element abundances
nuclei constrain element abundancesXian, W.*; Ito, Yuta; 30 of others*
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.035804_1 - 035804_10, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Taniguchi, Koji*; Huang, P.-J.*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oishi, Kazuki*; Kito, Shunsuke*; Nakamura, Yuiga*; Miyasaka, Hitoshi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(2), p.024409_1 - 024409_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:51.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsushima, Yu*; Zhang, Z.*; Ohashi, Yuri*; Hatakeyama, Tsunagu*; Xiao, G.*; Funato, Takumi*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kaiju, Hideo*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(2), p.022404_1 - 022404_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:70.50(Physics, Applied)Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.245110_1 - 245110_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a mean-field theory of a novel Kondo effect emerging in systems without a Fermi surface, which instead emerges under strong magnetic fields. We determine the magnitude of the Kondo condensate, which is a particle pairing composed of conducting Dirac fermions and localized impurities. We focus on the competition between the Kondo effect and the energy gap formation that stems from the pairing among the Dirac fermions leading to the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking. We find that this competition induces a quantum critical point. We also investigate finite-temperature effects. This system at vanishing fermion density can be studied with Monte Carlo lattice simulations, which do not suffer from the sign problem.