Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishii, Junya*; Shimizu, Morihito*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tsuji, Tomoya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Watabe, Hiroshi*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 44(3), p.031516_1 - 031516_8, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Yamazaki, Takumi*; Hirai, Takamasa*; Yagi, Takashi*; Yamashita, Yuichiro*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 21(2), p.024039_1 - 024039_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Physics, Applied)Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
KEK Proceedings 2023-2, p.132 - 137, 2023/11
New analytical method of a combination of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) for quantification of Zr isotopes in a solid sample was investigated. Solid Zr-isotope reference was added to a simulated radioactive waste sample as a spike, then Zr isotope ratio was measured by LA-ICP-MS. As a result, we successfully quantify Zr isotopes in the simulated radioactive waste sample by new IDMS. There is a possibility that this new method can be applied for quantification of Zr-93 in difficult to dissolve radioactive wastes.
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 72(10.11), p.441 - 448, 2023/10
Rapid analytical method for the determination of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes has been developed. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS was applied to the analysis of Zr isotopes in simulated high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Sample preparation time was dramatically reduced by using a DGA resin as the adsorbent for Zr. Direct quantification of Zr isotopes in this resin sample was carried out by LA-ICP-MS. Laser settings were optimized to obtain a reliable isotope ratio of the sample by LA-ICP-MS. Quantification of Zr isotopes in the simulated HLW solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was examined. The amount of Zr-90 in the sample obtained by IDMS corresponded to a value calculated from the given concentration of Zr in the sample within uncertainty. Thus, this method can be applied for the quantification of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Manabe, Kentaro; Ochi, Kotaro; Kono, Takahiko; Sasaki, Michiya*; Yoshida, Hiroko*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(2), p.105 - 111, 2023/08
This article gives the report on participation in the 6th Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP6), which was held in Mumbai, India on between February 7th and 11th, 2023.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2023-003, 72 Pages, 2023/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of radiation hardened diamond image sensing devices" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. The present study aims to develop image sensing devices which work under the high radiation condition. The devices will be realized using radiation hard diamond semiconductor devices as charge transfer devices and photodetectors. The research project has mainly two targets such as to confirm charge coupled devices operation on diamond unipolar devices and to characterize photo conductivity of diamond detectors.
Suzuki, Tomoya*; Otsubo, Ukyo*; Ogata, Takeshi*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Matsuoka, Mitsuaki*; Murayama, Norihiro*; Narita, Hirokazu*
Separation and Purification Technology, 308, p.122943_1 - 122943_7, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.39(Engineering, Chemical)HNO leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO
solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,
solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,  90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO
90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
 with [Pd(NO
with [Pd(NO )
) ]
] . The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
. The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
Uchino, Seiko*; Narita, Hirokazu*; Kita, Keisuke*; Suzuki, Hideya*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Naganawa, Hirochika*; Sakaguchi, Koichi*; Oto, Keisuke*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 30(1), p.39 - 46, 2023/00
The extraction of trivalent rare earth ions (RE ) from HNO
) from HNO solution using a triamide amine, tris(N,N-di-2-ethylhexyl-ethylamide)amine (DEHTAA), was conducted, and the extraction mechanism was estimated from extraction behavior of HNO
solution using a triamide amine, tris(N,N-di-2-ethylhexyl-ethylamide)amine (DEHTAA), was conducted, and the extraction mechanism was estimated from extraction behavior of HNO and RE
and RE and the relationship between atomic number and extraction percentages (E%) for RE
and the relationship between atomic number and extraction percentages (E%) for RE . A DEHTAA molecule dominantly formed a DEHTAA HNO
. A DEHTAA molecule dominantly formed a DEHTAA HNO at 1.0 M HNO
at 1.0 M HNO and a DEHTAA(HNO
and a DEHTAA(HNO )
) at 6.0 M HNO
at 6.0 M HNO in the acid-equilibrated organic phase. This would provide the unique dependence of E% for the light RE
in the acid-equilibrated organic phase. This would provide the unique dependence of E% for the light RE on the HNO
on the HNO concentration, in which the E% value had a minimum and maximum at
concentration, in which the E% value had a minimum and maximum at  0.5 M and
0.5 M and  2 M HNO
2 M HNO , respectively. The results of the slope analyses for the distribution ratios for RE
, respectively. The results of the slope analyses for the distribution ratios for RE suggested that the dominant RE
suggested that the dominant RE complex was RE(NO
complex was RE(NO )
) DEHTAA(DEHTAA HNO
DEHTAA(DEHTAA HNO ) at 1.0 M HNO
) at 1.0 M HNO . The E% for RE
. The E% for RE decreased from La
decreased from La to Lu
to Lu at 1.0 M HNO
at 1.0 M HNO ; on the other hand, those increased from La
; on the other hand, those increased from La to Nd
to Nd at 0.25 M and from La
at 0.25 M and from La to Sm
to Sm and 6.0 M HNO
and 6.0 M HNO .
.
Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sun, L.*; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Otsu, Iwao*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), p.10750_1 - 10750_14, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.49(Environmental Sciences)Reactive sulfur species (RSS) involve oxidative stress deeply and contribute anti-inflammatory effect, but no studied have focused on RSS changes after irradiation. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed the metabolites, focusing on RSS in mouse brain following radon inhalation. The ratio of oxidized glutathione to reduced glutathione and proportion of RSS in GSH or cysteine increased by radon inhalation. The sulfur ion might bind to GSH or cysteine chemically under conditions of oxidative stress, even at very low-dose exposure. We performed the overall assessment of high-dimensional data by applying machine learning and showed the specific characteristics of the effects by the exposure conditions. Our results suggested that RSS could produce a biological defense against oxidative stress following radon inhalation.
Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; Machida, Akihiko*; Watanuki, Tetsu*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Mizuno, Masataka*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Acta Materialia, 234, p.118055_1 - 118055_10, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:84.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wada, Yuki; Furuichi, Noriyuki*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*
European Journal of Mechanics B, Fluids, 91, p.233 - 243, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.16(Mechanics)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-026, 47 Pages, 2021/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of radiation hardened diamond image sensing devices" conducted in FY2020. The research objective of this project is to develop image sensing devices which work under the high radiation condition. The devices will be realized using radiation hardened diamond semiconductor devices as charge transfer devices and photodetectors. The research project has mainly two targets such as to confirm charge coupled devices operation on diamond unipolar devices and to characterize photo conductivity of diamond detectors.
Kanzaki, Norie
Hoshasen Seibutsu Kenkyu, 56(3), p.295 - 307, 2021/09
The biological effects of low-dose radiation are confusing due to the various intertwined factors. The vital body responses are complex. In this review, we visualized the results of animal experiments using Self-organizing maps (SOM) and reported the results of the low-dose radiation biological effect assessment from a different viewpoint. For example, although the classification of these data which were the biological effects by low-dose radiation were impossible, SOM got the overall assessment and the intuitive understanding. We reported the results and the usefulness of data visualization of radiation biological effects using machine learning.
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 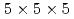
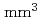 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0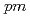 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-027, 27 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of radiation hard diamond image sensing devices". The research objective of this project is to develop image sensing devices which work under the high radiation condition. The devices will be realized using radiation hard diamond semiconductor devices as charge transfer devices and photodetectors. The research project has mainly two targets such as to confirm charge coupled devices operation on diamond unipolar devices and to characterize photo conductivity of diamond detectors.
Narita, Hirokazu*; Kasuya, Ryo*; Suzuki, Tomoya*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Tanaka, Mikiya*
Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry (Internet), 28 Pages, 2020/12
Naito, Wataru*; Uesaka, Motoki*; Kuroda, Yujiro*; Kono, Takahiko; Sakoda, Akihiro; Yoshida, Hiroko*
Radioprotection, 55(4), p.297 - 307, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:66.37(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima nuclear accident in Japan, a number of practical activities related to public understanding (PU) of radiation risks were implemented inside and outside Fukushima Prefecture. The various noteworthy approaches and strategies behind those practical activities have not been organized and made explicit thus far. In this study, we have organized the noteworthy practical activities related to PU of radiation risks following the Fukushima nuclear accident, and discussed them mainly from the standpoints of communication strategies and approaches. As several examples demonstrate, efforts to contextualize and localize radiation risk in various forms were observed during post-accident recovery in Fukushima, and these efforts were confirmed, through actual experiences, to be an important component of effective PU activities of radiation risks. Community-based or citizen science approaches, such as having affected residents or citizens to measure radioactivity, have contributed to the PU of radiological situations, but some challenges, such as ethical aspects and the handling of uncertainty, have also been revealed. In the era of information and communications technology, a number of citizens, experts, and agencies have made social media a popular platform for disseminating radiation risk messages to the public and have demonstrated that social media can play an important role in providing radiological risk information. The knowledge and lessons learned from the practical activities discussed in this study can be useful in enhancing PU of risks not only radiation but also other stressors such as toxic chemicals, preparing future disasters and supporting risk communication plans during recovery periods after disasters.
 RuO
RuO proved by spin resonance
proved by spin resonanceIida, Kazuki*; Kofu, Maiko; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Murai, Naoki; Kawamura, Seiko; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Hasegawa, Shunsuke*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(5), p.053702_1 - 053702_5, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:78.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)