Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Bucalossi, J.*; Marty, V.*; Urano, Hajime; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Masaki, Kei; Kaminaga, Atsushi
Nuclear Fusion, 50(11), p.115003_1 - 115003_10, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:58.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The supersonic molecular beam injection (SMBI) was successfully operated in JT-60U. Frequent density jumps were clearly observed in the main plasma against the SMBI pulses with the background gas pressure (
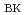 ) of 2-6 bar. Fuelling efficiency exhibited weak dependence on
) of 2-6 bar. Fuelling efficiency exhibited weak dependence on 
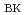 and the injection direction (high- and low-field-side injections). The amount of the fuelling necessary for achieving the same density level is much smaller for the SMBI than for the gas-puffing. It is comparable for the SMBI and the pellet injection even with shallower penetration of the SMBI as discussed below. The SMBI ionization area was estimated based on emission measured using the fast TV camera with a time resolution of 0.167 ms. The estimations indicated similar penetration position for
and the injection direction (high- and low-field-side injections). The amount of the fuelling necessary for achieving the same density level is much smaller for the SMBI than for the gas-puffing. It is comparable for the SMBI and the pellet injection even with shallower penetration of the SMBI as discussed below. The SMBI ionization area was estimated based on emission measured using the fast TV camera with a time resolution of 0.167 ms. The estimations indicated similar penetration position for 
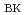 = 6 and 2 bar, although the ionization area was larger for 6 bar. This result supports the weak
= 6 and 2 bar, although the ionization area was larger for 6 bar. This result supports the weak 
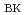 dependence of the fuelling efficiency. The front of the ionization area moved between first and second frames of the fast TV camera and it reached just inside the separatrix in the second frame. The ionization area was significantly expanded from the expected SMB size and the expansion was also enhanced between two frames. These relatively slow changes between two frames suggest that interaction between SMB and plasma significantly influences the fuelling characteristics.
dependence of the fuelling efficiency. The front of the ionization area moved between first and second frames of the fast TV camera and it reached just inside the separatrix in the second frame. The ionization area was significantly expanded from the expected SMB size and the expansion was also enhanced between two frames. These relatively slow changes between two frames suggest that interaction between SMB and plasma significantly influences the fuelling characteristics.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; JT-60 Team
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.869 - 875, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Particle control is important for burning plasma control, because fuel density is one of a few controllable parameters in a burning plasma. First, mechanisms responsible for determining density profiles and dependence of impurity transport on density profiles were investigated. Peakedness of density profiles increased with decreasing collisionality, which is consistent with ITG/TEM turbulence theory. However, other hidden parameters, such as toroidal rotation, existed. Metal impurity accumulation was observed with peaked density profile, while light impurity accumulation was not. Next, effects of fuelling on confinement was investigated using newly installed supersonic molecular beam injection (SMBI). SMBI directly affected the plasma parameters at r/a 0.8 as similar as pellet injection. However, confinement degraded with constant pedestal pressure in contrast to pellet injection. Using the burning plasma simulation scheme, it was demonstrated to reduce the simulated a-heating with SMBI due to confinement degradation and flattening of pressure profile.
Miyo, Yasuhiko; Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Urano, Hajime; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Masaki, Kei; Bucalossi, J.*; Marty, V.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English