Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
上田 祐生; Micheau, C.; 阿久津 和宏*; 徳永 紘平; 山田 雅子*; 山田 悟史*; Bourgeois, D.*; 元川 竜平
Langmuir, 40(46), p.24257 - 24271, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)本研究では、パーフルオロヘキサン中のフルオラスリン酸エステル(TFP)からなるフルオラス抽出系において、n-ヘキサン中の有機リン酸エステル(THP)からなる類似の有機抽出系と比較して、より高い金属イオン抽出性能に寄与する主要因を分子レベルで理解するために、硝酸溶液からのZr(IV)イオンの抽出の巨視的挙動を微視的構造情報と相関させた。拡張X線吸収微細構造、中性子反射率測定、中性子小角散乱により、それぞれZr(IV)イオン周辺の局所配位構造、界面における抽出剤分子の蓄積、バルク抽出相における抽出剤分子の構造が明らかになった。その結果、いずれの抽出系においても、界面には抽出剤分子はあまり蓄積しなかった。フルオラス抽出系では、硝酸との接触により凝集体が形成され、Zr(IV)抽出後も残存した。一方、有機抽出系では、二量体のみが形成された。Zr(IV)イオン周辺の局所的な配位構造とバルク抽出相における抽出剤分子の構造の違いが、フルオラス抽出系における高いZr(IV)抽出性能に寄与していると推測している。特に、フルオラス相中のZr(IV)濃度が増加しても凝集体の大きさはほとんど変化せず、これはフルオラス抽出系で相分離が起こらないことと密接に関係していると考えられる。
Guerinoni, E.*; Giusti, F.*; Dourdain, S.*; Dufr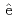 che, J.-F.*; 元川 竜平; 上田 祐生; 青柳 登; Zemb, T.*; Pellet-Rostaing, S.*
che, J.-F.*; 元川 竜平; 上田 祐生; 青柳 登; Zemb, T.*; Pellet-Rostaing, S.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 403, p.124820_1 - 124820_11, 2024/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In uranium production, liquid-liquid extraction using the AMEX (AMine EXtraction) process employs tertiary amines solubilized in an aliphatic diluent. Practical constraints as phase stability problems and co-extraction of competitive elements highlight the need for in-depth investigation and optimization. Modifying gradually the alkyl chain structure of tertiary amines, we investigate here the large variation in extraction performance in terms of Gibbs free energy of transfer using the ienaic decomposition taking into account long range interactions. We show hereby that structuration of the solvent phase can change uranium distribution by 2 orders of magnitude, which is incompatible with standard complexation theory of liquid-liquid extraction. We observe that co-extracted water is required to obtain extraction while extraction is quenched and no pair core can be formed when less than four as effective aggregation number. We conclude that the film term in the ienaic decomposition of the Gibbs energy of transfer, is the one that governs extraction performance. It shows that metal transfer is beyond complexation, and that organization of the solvent phase must be considered to quantitatively interpret the distribution coefficients.
Micheau, C.; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; 阿久津 和宏*; 山田 悟史*; 山田 雅子*; Moussaoui, S. A.*; Makombe, E.*; Meyer, D.*; Berthon, L.*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 401, p.124372_1 - 124372_12, 2024/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)Supramolecular organization of amphiphilic extractant molecules is involved in metal cation selectivity and separation kinetics during solvent extraction. The relationship between extractant associates/aggregates formed in the organic bulk phase and at the liquid-liquid interface is poorly understood even though it affects the extraction mechanism. The nanoscopic structures of the extraction systems N,N,N',N'-tetrahexylmalonamide (THMA) in toluene and N,N'-dibutyl-N,N'-dimethyl-2-tetradecylmalonamide (DBMA) in n-heptane, used for either Pd(II) or Nd(III) selective extraction from an acidic aqueous phase, were examined. These systems present markedly different affinity for Pd(II) and Nd(III), and extraction kinetics. Extractant organization in the organic bulk phase and at the interface were compared by small-angle X-ray scattering, interfacial tension, and neutron reflectivity. THMA in toluene forms small associates in the organic bulk phase and accumulates in a diffuse layer at the interface, decreasing Pd(II) coordination probability and resulting in slow extraction. DBMA in n-heptane forms large aggregates and a compact, dense interfacial layer, resulting in rapid Pd(II) and Nd(III) extraction. Thus, Pd(II) extraction is driven by interfacial coordination alone, whereas the incorporation of Nd(III) into the core of large aggregates governs Nd(III) extraction in the interfacial layer. These results suggest that the interface should be described as a nanoscale interphase containing a high extractant concentration compared with the organic bulk phase.
Micheau, C.; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; Bauduin, P.*; Girard, L.*; Diat, O.*
Langmuir, 39(31), p.10965 - 10977, 2023/07
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:71.78(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Understanding clay flotation mechanisms has become a major concern because of the increasing level of environmental contamination of soil and ground water by heavy metals and radionuclides. Clays are often used as sorbents for extracting metals in indirect flotation processes but can function simultaneously as defoamers. However, how foam generation and stability depend on the molecular interactions between the clays and surfactant is still controversial. In the present study, an amine polyethoxylated surfactant was used as a bifunctional surfactant that collected clay particles and acted as a foaming agent in the flotation process. The pH conditions strongly affected the surfactant physicochemical properties, allowing the clay extraction efficiency to be tuned. The interfacial recovery factor of the clays almost reached 100 percent under acidic (pH lower than 6) and neutral (pH 6-10) conditions, whereas it was negative under alkaline conditions (pH higher than 10), contrary to expectations. To elucidate the mechanisms involved in the particle flotation process for each of the pH conditions, the bulk and foam phases were analyzed. The effects of electrostatic interactions between the solutes and multiscale structure on the clay extraction behavior were investigated by electrophoretic measurements, dynamic light scattering, small-angle neutron scattering, and image analysis. Based on these results, three flotation processes were found depending on pH range: surfactant foam fractionation at pH higher than 10; clay particle foam flotation at pH 6-10; and particle froth flotation at pH lower than 6.
Micheau, C.; 上田 祐生; 阿久津 和宏*; Bourgeois, D.*; 元川 竜平
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 41(2), p.221 - 240, 2023/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:43.72(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Malonamide derivatives, which are among the most extensively investigated extractants in solvent extraction of lanthanoids, actinides, and platinum group metal ions, were deuterated by using Pd/C and Rh/C catalysts with a D O/2-propanol mixture. This method enables to replace the hydrogen atoms by deuterium atoms in the malonamide chemical structure with a controllable deuteration rate. The maximum rate reaches 75 percent approximately, determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. In addition, it has been demonstrated that extraction behavior of the malonamide molecules remains unchanged after the deuteration procedure. Deuterated malonamides should be a powerful tool for fundamental researches on solvent extraction systems, in particular, for structural analysis of the organic phases. The large difference in the neutron scattering cross-section between hydrogen and deuterium leads to a large difference in neutron scattering length density of the malonamide derivatives before and after the deuteration reaction. Therefore, using deuterated malonamides in small-angle neutron scattering and neutron reflectivity studies could give access to the nanoscopic structure of the specific solute species in the bulk organic phase and at the liquid-liquid interface, respectively. This deuteration method could become a general one and be extended to a wide variety of extractant molecules. In this way this work contributes to the development of the fundamental researches in solvent extraction systems.
O/2-propanol mixture. This method enables to replace the hydrogen atoms by deuterium atoms in the malonamide chemical structure with a controllable deuteration rate. The maximum rate reaches 75 percent approximately, determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. In addition, it has been demonstrated that extraction behavior of the malonamide molecules remains unchanged after the deuteration procedure. Deuterated malonamides should be a powerful tool for fundamental researches on solvent extraction systems, in particular, for structural analysis of the organic phases. The large difference in the neutron scattering cross-section between hydrogen and deuterium leads to a large difference in neutron scattering length density of the malonamide derivatives before and after the deuteration reaction. Therefore, using deuterated malonamides in small-angle neutron scattering and neutron reflectivity studies could give access to the nanoscopic structure of the specific solute species in the bulk organic phase and at the liquid-liquid interface, respectively. This deuteration method could become a general one and be extended to a wide variety of extractant molecules. In this way this work contributes to the development of the fundamental researches in solvent extraction systems.
Micheau, C.; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; Moussaoui, S.*; Makombe, E.*; Daniel, M.*; Berthon, L.*; Bourgeois, D.*; 阿久津 和宏*
no journal, ,
The DIAMEX process aims to separate minor f-elements using malonamide as extractant molecules such as N,N'-dimethyl-N,N'-dibutyl-tetradecyl-malonamide (DBMA). Recently, Poirot studied the effect of n-heptane and toluene on the selectivity of DBMA between Pd and Nd and have conclude that Pd extraction is driven by coordination whereas Nd extraction is driven by extractant aggregation. More recently, a specific study on tetrahexylmalonamide (THMA) in toluene demonstrated a superior selectivity for Pd compared to DBMA. THMA molecular structure suggests poor aptitude for aggregation compared with DBMA, and has been much less characterized. Supramolecular features of two different solvent extraction systems based on malonamide extractants, THMA in toluene and DBMA in heptane, have been studied using characterization techniques dedicated to bulk organic phase organisation, ie. small angle X-ray scattering, and to interface characterization, ie. neutron reflectivity and interfacial tension.