Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Kazushige*
JNC TJ7420 2005-092, 99 Pages, 2002/02
Permafrost Occurrence induces the drastic changes of ground water condition in considerable depths of bedrocks.
Takebe, Akimitsu*; Higashihara, Masami*; Takami, Akira*
JNC TJ7420 2005-067, 132 Pages, 2001/03
The comprehensive studies are being carried out for the deep structure of the active fault, characteristics of the fault fracture zone and stress states of the rock nearby the fault. As one of them, an in-situ rock stress measurement by hydrofracturing method was attempted on a nearby active fault in the survey tunnel at Kamioka Mine. This report describes the hydrofracturing method and results of the in-situ rock stress measurement.
Takebe, Akimitsu*; Higashihara, Masami*; Takami, Akira*
JNC TJ7420 2005-060, 211 Pages, 2001/03
One of purposes in the Inland Underground Structure Frontier Investigation is the development of the dry-fracture method to get basic data on in-situ stress states around an active fault. In previous experiments using concrete specimen and steel pipe, the dry-fracture method was determined to be reasonable. This report describes the laboratory validation test of dry-fracture method by re-boring in the difficult case to maintain the naked borehole in the bad ground situation.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Takebe, Akimitsu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-052, 97 Pages, 2001/03
In this study, artificial earthquake is triggered by gunpowder explosion near the surficial part of the Mozumi-Sukenobu Fault in the Atotsugawa Fault System, for the purpose of the basic data collection about the underground structure of the fault. And seismic wave derived from the explosion is observed on the surface and in the investigation tunnel across the fault.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-066, 99 Pages, 2000/03
The active fault survey tunnel across the Mozumi-Sukenobu Fault is located at the Kamioka Mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. At present, the comprehensive studies of the active fault are being carried out in this tunnel. In this report, the results of the laboratory test using steel pipes and numerical simulation for the new ground stress measuring instrument were presented in order to inspect the stress state around the active fault.
Sakogaichi, Kaoru*; Takebe, Akimitsu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-040, 62 Pages, 2000/03
The Atotsugawa active fault system (AFS) extends 60km or more in the northern Hida Mountains of central Japan, traced ENE to WSW trend. The Hietsu earthquake occurred along the AFS. The studies on the AFS started in April 1996 as
Shingu, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-063, 242 Pages, 1999/03
The active fault survey tunnel across the Mozumi-Sukenobu Fault is located at the Kamioka Mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. At present, The comprehensive studies of the active fault are being carried out in this tunnel. The results of the laboratory test and numerical simulation for the new ground stress measuring instrument were presented in order to inspect the stress state around the active fault.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Sakogaichi, Kaoru*; Takebe, Akimitsu*; Inoue, Motoi*; Niimi, Ken*; Kinoshita, Hirohisa*
JNC TJ7420 2005-051, 93 Pages, 1999/03
The Atotsugawa active fault system (AFS) extends 60km or more in the northern Hida Mountains of central Japan, traced ENE to WSW trend. The Hietsu earthquake occurred along the AFS. The studies on the AFS started in April 1996 as
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Sakogaichi, Kaoru*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Takebe, Akimitsu*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*; Yamanouchi, Hirofumi*
JNC TJ7420 2005-041, 129 Pages, 1999/03
The active fault survey tunnel that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (a member of the Atotsugawa fault system) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault such as the earthquake mechanism is done by using this tunnel. The purpose of this investigation is to define the hydrological characteristics inside and around the Mozumi - Sukenobu fault crush zones. The investigation is mainly Lugeon test and simple permeability test inside and around the crush zones.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-038, 39 Pages, 1998/03
The active fault study drift that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (a member of the Atotsugawa fault system) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault is done in this drift. The purpose of this investigation is to obtain the data of the basis to clear the hydro-geological structure around the active fault. From December 1, 1997 to March 13, 1998, the pore pressure was measured using the hole.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Shingu, Kazuki*; Sakogaichi, Kaoru*; Nishikawa, Yuji*; Okada, Yoichi*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-035, 152 Pages, 1998/03
The active fault survey tunnel that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (MSF) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault, such as the study of the earthquake mechanism and the development of the new initial stress measurement method is done by using this tunnel. One of the purposes of this investigation is to define the three-dimensional distribution of the MSF by geological survey, on the basis of the seismic and geophysical studies on this fault. The other purpose is to develop the new initial stress measurement method.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Shingu, Kazuki*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Okada, Yoichi*; Takebe, Akimitsu*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Inoue, Toshio*
JNC TJ7420 2005-033, 128 Pages, 1998/03
The active fault survey tunnel that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (a member of the Atotsugawa fault system) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault is done by using this tunnel. The purpose of this investigation is to define the hydrological characteristics of the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault crush zones. The permeability of the crush zones is measured by the Lugeon test and the simple injection test.
*; Shingu, Kazuki*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*; *; *
PNC TJ7187 97-002, 586 Pages, 1997/11
None
Shingu, Kazuki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*
PNC TJ7187 97-001, 170 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
Hama, Hiroshi*; Yamada, Tsuyoshi*; Ide, Mitsuyoshi*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Yamamoto, Katsuya*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Watabe, Takeo*
JNC TJ7440 2005-074, 270 Pages, 1995/05
In 1997, DH-5 hole was drilled at P.N.C.(present J.N.C.) Toki Branch of Tono Geoscience Centr in Gifu prefecture. The borehole was drilled to a depth of 502.3 meters in Toki granite in order to investigate the deep groundwater. This report describes the investigation of the groundwater conducted at depth from 323.8 to 330.8 meters to make clear geological, hydrogeological and geochemical characteristics of study area. The investigation includes the following items;i) Sampling of the groundwaterii) Measurement of physical chemistry parameters of the groundwater in the borehole iii) Chemicaal analysis of the main composition of the groundwater during the continuous samplingiv) Chemical analysis of the groundwater It has become clear the following points;* The physical chemistry parameters of groundwater was alkalic, low deoxidize and buffer ability. There were few total ions and sulfide ions in the groundwater.* The isotopic analysis showed that the groundwater was regarded as rainwater in origin on the side of the Pacific Ocean and was relatively young with the age of a few decades.* According to the tri-linear diagram, the groundwater was classified into Ca(HCO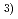
 type. Based on hydrochemical facies, the groundwater was classified into Ca
type. Based on hydrochemical facies, the groundwater was classified into Ca sup+ Na
sup+ Na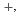 and HCO
and HCO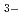 Cl
Cl SO
SO

 in the cation and anion facies, respectively.* Nitrite oxidizing bacteria, nitrite reducing bacteria and nitrate reducing bacteria were detected in the groundwater by the bacteria analysis.
in the cation and anion facies, respectively.* Nitrite oxidizing bacteria, nitrite reducing bacteria and nitrate reducing bacteria were detected in the groundwater by the bacteria analysis.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Sato, Eitaro*; Adachi, Kazuhiro*; Kudo, Masakatsu*; Ishizuka, Yoshiaki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*
JNC TJ7400 2005-007, 214 Pages, 1995/03
The objective of this study is to prove the long-term geoscientific stability of the geological environment. The survey will clarify the extent and degree of mechanical change influenced by fault movement deep underground as well as the surface. The study was conducted in Mozumi of the Kamioka mining district, located in the Atotsu active fault system zone. This year, a study was carried out by measuring stress state and rock properties around the active fault. At first, stress measurement by double fracturing was conducted at Nagato No.1 borehole in order to compare a newly measured stress state with the one done last year. The difference between them was very little. Secondly, the first stress measurement was carried out on the Nagato No.3 borehole.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Furumori, Hisayoshi*
JNC TJ7400 2005-005, 250 Pages, 1994/03
The objective of this study is to prove the long-term geoscientific stability of a geological environment. This was accomplished by measurement of stress and study of rock properties around an active fault in the Atotsu fault system near Mozumi in the Kamioka mining district. A future goal of the project is to clarify the areal extent and degree to which fault movement at the surface and at depth affects mechanical changes.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Adachi, Kazuhiro*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Tomita, Teruo*
JNC TJ7400 2005-006, 358 Pages, 1993/03
The objective of this study is to prove a long-term geoscientific stability of geological environment by means of measuring stress state and rock property around the active fault in order to investigate geological environment influenced by fault movement in underground as well as surface. The study was conducted in Mozumi mine of the Kamioka mining district, located in the Atotsu active faults system zone.