Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 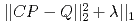 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
Onizawa, Kunio; Masaki, Koichi; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-9-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.374 - 379, 2012/07
To assure the structural integrity of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is known as one of the critical issues to maintain the safe long-term operation of a nuclear power plant. In Japan, the assessment methods for RPV integrity, stipulated in the codes and standards, have been endorsed by the regulatory body. Authors have initiated extensive research on the improvement of structural integrity assessment methods of RPVs. In this paper, we describe some research results obtained from the first-year activity. These include the study on revisiting the technical background of the methods, such as loading conditions, postulated crack definition, the other evaluation methods. In addition, studies on probabilistic methods for the applicability to the current rules and the standardization of the probabilistic analysis methods have been presented.
Yabuta, Naohiro*; Kawai, Jun*; Hikawa, Tamae*; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Sato, Kazuhiko; Koga, Osamu
JAEA-Review 2008-015, 92 Pages, 2008/11
On the closure of uranium mine site at Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the action plans for risk communication with residence and local governments were developed and implemented. Under a practical program of the risk communication, an ethnographical research on Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center has been conducted by local high school students. The research was focused on several social groups such as engineers at the Center and residents around Ningyo-Toge and described their circumstances from the past to the present, since the discovery of the uranium outcrop 1955. In the second year of the program, the results of the research were presented at symposium and the students had opportunities to exchange their views with others from different high schools that held in similar programs. Through those activities, the importance of the program was rediscovered and some new issues were also identified.
Yabuta, Naohiro*; Kawai, Jun*; Hikawa, Tamae*; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Sato, Kazuhiko; Koga, Osamu
JAEA-Review 2008-014, 133 Pages, 2008/11
On the closure of uranium mine site at Ningyo-Toge, the action plans for risk communication with residence and local governments were developed and implemented. Under a practical program of the risk communication, an ethnographical research on Ningyo-toge has been conducted by local high school students. The research was focused on several social groups such as engineers at the Center and residents around Ningyo-toge and described their circumstances from the past to the present. In addition, it should be noted that as a results, the research project led several effects listed below; (1) High school students understood significance of the uranium development projects implemented at Ningyo-toge, (2) Differences of standpoints between local residents and Ningyo-toge became clearer, (3) Foundation to communicate between local communities and Ningyo-toge was found out, (4) The educational program on an ethnographical research was conducted autonomously by local high school students.
Yabuta, Nohiro*; Kawai, Jun*; Hikawa, Tamae*
JNC TJ6420 2005-001, 88 Pages, 2005/02
On the closure of uranium production facilities, settled at Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center and other area in Okayama and Tottori prefectures, action plans for risk communication with residence and local governments were developed and implemented. With the direction of the action plans for risk communication,
Yabuta, Naohiro*; Takizawa, Masayuki*; Hikawa, Tamae*; Kawai, Jun*
JNC TN6400 2004-004, 89 Pages, 2004/03
On the closure of uranium production facilities, settled at Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center (NTEEC) and other area in Okayama and Tottori prefectures, Action Plans for risk communication with residence and local governments were developed. Firstly, to clarify requirements for risk communication plans, extensive case study for resemblance project of other fields were performed, such as chemical hazards exposure, industrial waste disposal, metal mining site closure and overseas uranium mining site closure. Secondly, with the understanding of societal environment issues around NTEEC, missions of risk communication at NTEEC case were listed. After considerations above, action plans for risk communication on the uranium mining sites remedy at NTEEC were developed. Plans involves several alternatives and were to be performed in building blocks manner. Emergency management plans during pursuing of risk communication plans were also developed.
Konishi, Yasuya*; Sonoyama, Minoru*; Suzuki, Atsushi*
JNC TJ9400 2005-004, 150 Pages, 2004/02
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has development FBR achievement analysis system by the last fiscal year and has enforced the investigation of its functional expansion. That system is based on the AHP (Analytic Hierarghy Process) to do comparative evaluation mulltilatelly between proposed concepts of FBR cycle or between FBR cycle and other power source systems. This fiscal year, we enforced achievement analysis for 22 cases of proposed concepts of FBR cycle and between FBR cycle and other power source systems (LWR, thermal power generation, hydraulic power generation, etc.). The evaluation items related with technical feasibility and social acceptability were included in addition to those of economy, resource utilization effectiveness, environmental burden reduction, nuclear proliferation resistance and safety. Also, we investigated social changes that could happen in our country in the future, and we drew 4 future scenarios combining likely changes, then we investigated classifications of weight that seem to be adequate under each scenario with its calculation logic. In establishing points of view or structure of evaluation, and in the process of drawing scenarios, we collected comments from experts in OR (Operation Research) field and energy field.
Okubo, Hiroo*
JNC TJ8400 2004-009, 84 Pages, 2004/02
In H12 Project to Establish Technical Basis for HLW Disposal in Japan an approach that is based on an international consensus was adopted to develop scenarios to be considered in performance assessment. Adequacy of the approach was, in general term, appreciated through the peer review. However it was also suggested that there are issues related to improving transparency and traceability of the procedure.Therefore, in the current financial year, in the first place a scenario development methodology was constructed taking into account the requirements identified last year. Furthermore a practical work-frame was developed to support the activities related to the scenario development. This work-frame was applied to an example scenario to check its applicability and identify issues for further research. Secondly, scenario analysis method with regard to perturbation scenario has been studied. First of all, a survey of perturbation scenario discussed in different countries has been carried out and its assessment has been examined. Especially, in Japan, technical information has been classified in order to assess three scenarios, which are seismic activity, faulting and igneous activity. Then, on the basis of assumed occurrence pattern and influence pattern for each perturbation scenario, variant type that should be considered in this analysis has been identified, and the concept of treatment, modeling data and requirements have been clarified. As a result of these researches, a future direction for advanced scenario analysis on performance assessment has been indicated, as well as associated issues to be discussed have been clarified.
Okubo, Hiroo*
JNC TJ8400 2004-008, 264 Pages, 2004/02
In H12 Project to Establish Technical Basis for HLW Disposal in Japan an approach that is based on an international consensus was adopted to develop scenarios to be considered in performance assessment. Adequacy of the approach was, in general term, appreciated through the peer review. However it was also suggested that there are issues related to improving transparency and traceability of the procedure.Therefore, in the current financial year, in the first place a scenario development methodology was constructed taking into account the requirements identified last year. Furthermore a practical work-frame was developed to support the activities related to the scenario development. This work-frame was applied to an example scenario to check its applicability and identify issues for further research. Secondly, scenario analysis method with regard to perturbation scenario has been studied. First of all, a survey of perturbation scenario discussed in different countries has been carried out and its assessment has been examined. Especially, in Japan, technical information has been classified in order to assess three scenarios, which are seismic activity, faulting and igneous activity. Then, on the basis of assumed occurrence pattern and influence pattern for each perturbation scenario, variant type that should be considered in this analysis has been identified, and the concept of treatment, modeling data and requirements have been clarified. As a result of these researches, a future direction for advanced scenario analysis on performance assessment has been indicated, as well as associated issues to be discussed have been clarified.
Sato, Osamu*; Maeda, Akio*
JNC TJ9400 2003-008, 139 Pages, 2003/03
Two-dimensional cell calculation is necessary to exactly treat the major heterogeneous structure of fuel pins and a wrapper tube in fast reactor fuel assemblies. JNC has been developing the new SLAROM, which includes a two-dimensional cell calculation routine. In this report, validity and effect of two-dimensional calculation were investigated. The validity was checked by comparing neutron flux in fuel assemblies and assembly averaged cross sections with those calculated by Monte Carlo code GMVP. The comparisons were made for the calculation model called "concentric layers of hexagon with equi-distance pin-rod array"(IGT=13) with a fuel assembly of JOYO and were also made for the model of a two-dimensional slab called "Quadrant of an octant symmetric assembly" (IGT=8) with SCF and DCF fuel cells in ZPPR=9. The calculated results with the new SLAROM and GMVP were agreed within statistical errors for the JOYO fuel assembly and the adequacy of the collision probability calculations in the new SLAROM was proved for a hexagonal fuel assembly. For a two-dimensional slab geometry, the assembly averaged absorption cross sections and total cross sections were 20% higher than those with Monte Carlo calculations below 24keV at which the large resonance of sodium exist. Further investigations are required to explain the differences. The results of core calculations with CITATION were performed and compared with the assembly-averaged cross sections using one-dimensional cell model and with the cross sections using two-dimentional cell model. THe differences caused by the cell calculation model were larger for radial blanket regions than for fuel regions. It revealed that the fewer numbers of fuel pins in radial blanket bring out the larger error of one-dimensional cell model.
Kobe, Mitsuru*; Tsunoda, Hirokazu*; Mishima, Kaichiro*; Kawasaki, Akira*; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Tech 2003-016, 68 Pages, 2003/03
The 200 kWe uranium nitride fueled lithium cooled fast reactor "RAPID-L" combined with thermoelectric power conversion system that can be operated unmanned without refueling for up to ten years has been demonstrated. The RAPID refueling concept enables quick and simplified refueling, and achieves plant design lifetime over 20 years. A significant advantage of the RAPID-L design, which does not require the use of control rods - is the introduction of the innovative reactivity control systems: lithium expansion module (LEM), lithium injection module (LIM) and lithium release module (LRM). LEM is the most promisiong candidate for improving inherent reactivity feedback. LEMs could realize burnup compensation. LIMs assure sufficient negative reactivity feedback in unprotected transients. LRMs enable an automated reactor startup by detecting the hot standby temperature of the primary coolant. All these systems use  Li as liquid poison and are actuated by highly reliable physical properties (volume expansion of
Li as liquid poison and are actuated by highly reliable physical properties (volume expansion of  Li for LEM, and freeze seal melting for LIM and LRM).
Li for LEM, and freeze seal melting for LIM and LRM).
Okubo, Hiroo*
JNC TJ8400 2003-052, 67 Pages, 2003/02
As the first step of this study, description level and content of the FEPs with regard to the FEP information data on the Natural Barrier System developed by JNC have been examined from various angles on the basis of the latest research information. Each content of the FEP data has been classified and modified by means of integrating descriptive items, checking detail levels and correlations with other FEPs, collating with the H12 report, and adding technical information after H12 report. Secondly, scenario analysis method has been studied. As an illustrated example, a procedure for deriving a calculation case by using Connectivity Matrix and PPM (Parameters, Processes, Models) database was applied for buffer in base scenario and then volcanism scenario. Also, another approach based on Correlation Matrix has been comparatively discussed to list up future subjects. Lastly, in relation to the geological disposal system, assessment techniques have been examined for more practical scenario analysis on variant scenario. Possible conceptual models have been proposed for uplift and erosion scenario. As a result of these researches, a future direction for advanced scenario analysis on performance assessment has been indicated, as well as associated issues to be discussed have been clarified.
Okubo, Hiroo*
JNC TJ8400 2003-051, 298 Pages, 2003/02
As the first step of this study, description level and content of the FEPs with regard to the FEP information data on the Natural Barrier System developed by JNC have been examined from various angles on the basis of the latest research information. Each content of the FEP data has been classified and modified by means of integrating descriptive items, checking detail levels and correlations with other FEPs, collating with the H12 report, and adding technical information after H12 report. Secondly, scenario analysis method has been studied. As an illustrated example, a procedure for deriving a calculation case by using Connectivity Matrix and PPM (Parameters, Processes, Models) database was applied for buffer in base scenario and then volcanism scenario. Also, another approach based on Correlation Matrix has been comparatively discussed to list up future subjects.Lastly, in relation to the geological disposal system, assessment techniques have been examined for more practical scenario analysis on variant scenario. Possible conceptual models have been proposed for uplift and erosion scenario. As a result of these researches, a future direction for advanced scenario analysis on performance assessment has been indicated, as well as associated issues to be discussed have been clarified.
Shiba, Tsuyoshi*; *; *
JNC TJ9400 2003-007, 126 Pages, 2003/01
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development lnstitute(JNC) has developed FBR achievement analysis system by the end of the last fiscal year, and has been improving it to be capable to assess other power generation systems than FBR, in view of public acceptance. In this study, we conducted a trial analysis on various aspects of other energy systems with an obJective of functional expansion of the analysis system to obtain generally agreeable results. Trial analysis was performed on LNG fueled thermal power generation and wind power generation in comparison with FBR systems with large power (1 GW x 50-100 plants) and small (50-200MW) power output, respectively. The impact of the weight attached to input data and indices on the analysis results was analyzed to get to know the characteristics of this analysis system, and the system was further improved in terms of simplification of the analysis structure and the way to handle pair comparison. Then, we again conducted trial analysis using the improved analysis system, in which indices were weighted assuming several societies with different sense of values. Then we calculated the various aspects of values each energy system would gain in the settmg of each society. The results for each of the assumed societies were considered to be qualitatively reasonable, but the need for further discussion on the analysis structure, weighting of indices, etc. was pointed out.
*; *
JNC TJ9410 2002-001, 96 Pages, 2002/03
The following codes were developed to enhance the applicability of the three-dimensional Hex-Z geometry codes that can model the BN and BFS reactor core accurately. The neutron flux reconstruction method in the three-dimensional transport-based perturbation code SNPERT-HEXZ was modified to improve the calculation accuracy. New functions to calculate design parameters, such as peaking coefficients, maximum linear power etc., based on the reconstructed neutron flux were added to the three dimensional Hex-Z geometry transport burn-up code NSHEX-BURN. The three-dimensional Hex-Z finite difference transport code MINIHEX was modified to improve the computational performance. First, cash-tuning and a flux extrapolation method were applied to MINIHEX. This modification reduced the computational time by a factor of 3.8 at most. Second, the modified MINIHEX was parallelized with MPI by an angular space decomposition method. A series of performance check calculations was performed on GP7000 and DEC/alpha EWS cluster. Speed-up obtained on GP7000 was at most 5.3 for 9 PE and that on DEC/alpha cluster was at most 1.5 for 4 PE. The parallelization of MINIHEX also enhanced the applicability of the code to larger scale computational problems and more detailed reactor core modeling. An interface to MINIHEX was added to the three-dimensional Hex-Z geometry reaction rate calculation code LAGOON-HEXZ. The added interface enables the code to calculate reaction rates using neutron flux obtained by MINIHEX. A three-dimensional transport-based perturbation code for MINIHEX was developed based on the three-dimensional tansport-based perturbation code NSHEX-HEXZ. This code makes it possible to evaluate reactivity cbange from the neutron flux and eigenvalue obtained by MINIHEX.