Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Takashi; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Kuwabara, Jun; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya
Biogeosciences, 10(6), p.3839 - 3847, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:57.84(Ecology)no abstracts in English
 Co in the digestive glands of the common octopus,
Co in the digestive glands of the common octopus,  , in the East China Sea
, in the East China SeaMorita, Takami*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Fujimoto, Ken*; Nishiuchi, Ko*; Kimoto, Katsunori*; Yamada, Haruya*; Kasai, Hiromi*; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Yoshida, Katsuhiko*
Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(8), p.1193 - 1199, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.23(Environmental Sciences)Significant concentrations of  Co,
Co,  Cs and
Cs and 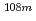 Ag were detected in common octopus specimens collected in the East China Sea during two periods, 1986-1989 and 1996-2005. The radionuclides detected in the former period were thought to originate from the global fallout. On the other hand, the source of
Ag were detected in common octopus specimens collected in the East China Sea during two periods, 1986-1989 and 1996-2005. The radionuclides detected in the former period were thought to originate from the global fallout. On the other hand, the source of  Co in the latter period has remained unclear because the
Co in the latter period has remained unclear because the  Co concentration decreased continuously with shorter half-lives than the physical half-lives. This tendency suggests that the source of
Co concentration decreased continuously with shorter half-lives than the physical half-lives. This tendency suggests that the source of  Co in 1996-2005 was identical and was temporary supplied to the East China Sea. Investigations of common octopus in the other area indicated that the origin of the pollutant source of
Co in 1996-2005 was identical and was temporary supplied to the East China Sea. Investigations of common octopus in the other area indicated that the origin of the pollutant source of  Co in 1996-2005 occurred locally in the restricted area in the East China Sea rather than in the coastal area of Japan.
Co in 1996-2005 occurred locally in the restricted area in the East China Sea rather than in the coastal area of Japan.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi; Tanaka, Takayuki; Ito, Toshimichi; Kobayashi, Takuya; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Senju, Tomoharu*; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-020, 27 Pages, 2010/02
The database for the Japan Sea parameters on marine environment and radionuclides (JASPER) has been established by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency as a product of the Japan Sea Expeditions. By the previous version of the database, data for representative anthropogenic radionuclides were opened to public. And now, data for radiocarbon and fundamental oceanographic properties (salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen) including nutrients (silicate, phosphate, nitrate and nitrite) are released as the second volume of the database. In the second volume, 20,398 data records are stored including 2,695 data for temperature, 2,883 data for salinity, 2,109 data for dissolved oxygen, 11,051 data for the nutrients, and 1,660 data for radiocarbon. The database will be a strong tool for the continuous monitoring for contamination by anthropogenic radionuclides, studies on biogeochemical cycle, and development and validation of models for numerical simulations in the sea.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Tanaka, Takayuki; Togawa, Orihiko; Amano, Hikaru; Karasev, E. V.*; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
Journal of Oceanography, 64(6), p.911 - 923, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:47.06(Oceanography)Transport processes of particulate organic carbon (POC) were inferred from sediment trap experiments in the three regions of the Japan Sea (western and eastern Japan Basin and Yamato Basin) and radiocarbon measurement. Annual mean  C/
C/ C isotopic ratio decreased with depth and the vertical changes in the isotopic signature were considered to indicate mixing of two fractions; labile POC produced in the surface and refractory POC. From seasonal variations of POC flux of the two fractions, transport processes of POC in the Japan Sea were summarized as follows: (1) In the Japan Basin, both labile and refractory POC were supplied in spring and a reservoir of refractory POC was formed, and (2) in the Yamato Basin, larger amount of refractory POC were carried the interior and accumulated rapidly.
C isotopic ratio decreased with depth and the vertical changes in the isotopic signature were considered to indicate mixing of two fractions; labile POC produced in the surface and refractory POC. From seasonal variations of POC flux of the two fractions, transport processes of POC in the Japan Sea were summarized as follows: (1) In the Japan Basin, both labile and refractory POC were supplied in spring and a reservoir of refractory POC was formed, and (2) in the Yamato Basin, larger amount of refractory POC were carried the interior and accumulated rapidly.
Suzuki, Takashi; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Amano, Hikaru; Togawa, Orihiko
Dai-10-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.147 - 150, 2008/00
no abstracts in English
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Tanaka, Takayuki; Togawa, Orihiko; Amano, Hikaru; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Khim, B.-K.*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
no journal, ,
A time-scale of particulate organic carbon (POC) in the Japan Sea, a marginal sea of the North Pacific, was quantified from radiocarbon (C-14) and stable carbon (C-13) measurements. Delta C-14 in POC decreased with depth, and the value was higher in the order of sinking POC, suspended POC and seabed sediment. delta C-13 values in suspended POC were higher than those in sinking POC obtained from the similar depth. From the radiocarbon signatures and elemental compositions of sinking POC, it was considered that Delta C-14 in sinking POC was determined by a mixing ratio of terrestrial and surface-produced POC. In addition, the difference of Delta C-14 and delta C-13 between the terrestrial and suspended POC was considered to indicate migration process of POC in the water column. From the difference of the C-14 age between terrestrial and suspended POC, it was estimated that an actual age of suspended POC at 3 km depth in the Japan Sea was about 300 years.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Oku, Shunsuke*; Minami, Hideki*; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
no journal, ,
The Japan Sea is regarded as a miniature of the ocean because of its bowl-like topography and unique seawater circulation. Recent studies have suggested that biogeochemical processes in the Japan Sea correspond with the global climate change. In this study, we assessed decadal changes in particulate flux and elemental composition of sinking particle in the Japan Sea by comparing results of a sediment trap experiment in September 1984 with those in 1999-2001. Total mass flux did not show remarkable temporal change, however, biogenic opal/carbonate ratios observed recently were lower than those from the previous observation. In addition, relative content of scavenging elements such as manganese and cobalt also showed a decrease between the 15 years. These results may indicate decadal changes in ecological characteristics at the surface and transport processes of particulate materials in the deep water.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Oku, Shunsuke*; Minami, Hideki*; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
no journal, ,
Many researchers pointed out that decadal change in deep-sea circulation in the Japan Sea are strongly related with the global climate change. However, little is known about changes in fluxes and elemental composition of sinking particles in the sea. In this study, we assessed temporal changes in elemental composition of sinking particle in the Japan Sea by comparing results of a sediment trap experiment in middle 1980s with those in end of 1990s. The result indicated that (1) the contribution of Asian dust in sinking particles decreased significantly, (2) horizontal transport of re-suspended particles from the slope regions was weakened, and (3) there was no significant increase in vertical transport of anthropogenic heavy metals to the interior of the Japan Sea.
Oku, Shunsuke*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Minakawa, Masayuki*; Minami, Hideki*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
no journal, ,
Autochthonous Ba (Ba-xs) in seawater is enriched in particulate materials by marine biota and settles down to the seabed. Therefore, Ba-xs is known as a proxy of export production in the surface ocean. However, it is necessary to discuss the effect of lateral transport of Ba-xs for the accurate estimation of the export flux. In this study, the authors investigated the effect of lateral transport of Mn-xs from a sediment trap experiment in the Japan Sea. Particulate fluxes of Ba-xs showed a positive relationship between flux of autochthonous Mn (Mn-xs). The flux of Mn-xs was higher in winter and it might be caused by the lateral transport of particulate materials from the shelf regions. The results indicated that Ba-xs is transported laterally and the effect was on a par with the sinking of biogenic particles.