Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ohashi, Yusuke
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 141, p.107299_1 - 107299_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)A large amount of general steel waste is generated during decommissioning and dismantling of nuclear facilities. Very low-contaminated radioactive waste, whose radioactivity is below clearance level, generated from the demolition process may be reused for general use. We examined the feasibility of the clearance verification system for uranium waste. The relative error of uranium determination was within 30% for 1 g of uranium when measuring steel materials (angle bar, channel steel, pipe steel, square steel tube, fragments of metal tube).
Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.509 - 521, 2018/00
In-situ electrochemical measurement within crevice of stainless steel in 288 C water has been conducted to analyze crevice water chemistry. Small sensors (
C water has been conducted to analyze crevice water chemistry. Small sensors (
 250
250 m) measured local solution electrical conductivity,
m) measured local solution electrical conductivity, 
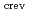 , polarization resistance, and electrochemical corrosion potential. Real-time response of the
, polarization resistance, and electrochemical corrosion potential. Real-time response of the 
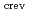 as functions of bulk water conductivity, dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration has been quantitatively analyzed. The effect of geometrical factors on the crevice environment was also studied. The
as functions of bulk water conductivity, dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration has been quantitatively analyzed. The effect of geometrical factors on the crevice environment was also studied. The 
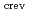 differ more than an order of magnitude depending on the oxygen potential inside the crevice. The
differ more than an order of magnitude depending on the oxygen potential inside the crevice. The 
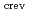 increased by small amount of bulk DO (e.g. 30 ppb). Maximum
increased by small amount of bulk DO (e.g. 30 ppb). Maximum 
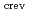 was observed with DO of 32000 ppb and became more than 100 times higher than that of bulk water. Crevice geometry affected significantly on the water chemistry inside.
was observed with DO of 32000 ppb and became more than 100 times higher than that of bulk water. Crevice geometry affected significantly on the water chemistry inside.
Ueda, Minoru*; Hashizume, Masahiro *
JNC TJ6430 2005-001, 36 Pages, 2005/03
We are developing the method of prospecting underground openings using microtremors around our service area in order to prospect underground openings of closed lignite mines effectively at Electric Power Research & Development Center of CHUBU Electric Power Co.,Inc. We have few results in the mountainous area. So we made the field survey preliminary to inspection of the application of the method at the formar Yotsugi open-pit in Ningyo- toge Environmental Engineering Center. We also tried two dimensions numerical analysis in order to reproduce results of measurement of microtremors there.As a result it could be confirmed that the results of analysis were harmonious with those of measurements, in which velocity spectrums on measurement points changed remarkably in the symmetry shape with respect to the point above the openings along the measurement lines while they didn't change along the measurement lines with backfilled underground openings.Therefore it could be confirmed that it was able to judge the situation of falling ground above openings on this point by using microtremors.
Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Aoki, So; Inagaki, Hiromitsu*
no journal, ,
Crevice environment was measured by electrochemical sensors in high temperature pure water. Crevice environment and surface oxide layer on the crevice surface was analyzed in terms of crevice's geometrical factors (crevice gap, g and depth, d). The results were plotted on the g-d plane. It was shown that electrical conductivity of crevice solution was very high in oxygen depleted zone and the zone shrinked with increasing crevice gap, g.
Soma, Yasutaka
no journal, ,
Crevice corrosion have been studied.
Soma, Yasutaka; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Inagaki, Hiromitsu*
no journal, ,
Effect of crevice geometry on corrosion environment within crevice of stainless steel in high temperature water was studied.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Inagaki, Hiromitsu*
no journal, ,
Corrosion condition within crevice of stainless steel is important to understand dissolution mechanisms of crack tip of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) in high-temperature water. We have reported that electrical conductivity of solution within crevice of stainless steel ( crev) exposed to high temperature and high purity water containing sufficient dissolved oxygen (DO) become more than 2 orders of magnitude higher than that for bulk pure water. In this study effect of conductivity and DO concentration of bulk water on
crev) exposed to high temperature and high purity water containing sufficient dissolved oxygen (DO) become more than 2 orders of magnitude higher than that for bulk pure water. In this study effect of conductivity and DO concentration of bulk water on  crev of Type-316L stainless steel have been studied in 288
crev of Type-316L stainless steel have been studied in 288 C water. Following conclusion have been obtained: (1)
C water. Following conclusion have been obtained: (1)  crev increased with increasing DO concentration from 3 ppb to approximately 300 ppb. Above 300 ppb,
crev increased with increasing DO concentration from 3 ppb to approximately 300 ppb. Above 300 ppb,  crev did not simply increased with DO concentraion. (2) maximum
crev did not simply increased with DO concentraion. (2) maximum  crev was not affected by bulk water conductivity suggested that
crev was not affected by bulk water conductivity suggested that  crev would be determined by chemical equilibrium reaction. (3)
crev would be determined by chemical equilibrium reaction. (3)  crev-time curves were not affected by crevice depth. It was assumed that anion required to increase
crev-time curves were not affected by crevice depth. It was assumed that anion required to increase  crev generated within the crevice.
crev generated within the crevice.
Muramatsu, Toshiharu*; Kamei, Naomitsu*; Aoyagi, Yuji*; Kitagawa, Yoshihiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Ozono, Shinji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki; Kadowaki, Masanao
no journal, ,
In local-scale atmospheric dispersion problems, an important issue is the accurate analysis of airborne radioactive materials released from nuclear facilities for safety and consequence assessment. At distances of up to several kilometers from the emission source, inhomogeneous distributions of air concentration and surface deposition around the evaluation point should be investigated considering the turbulent effects induced by individual buildings and local terrain variability. In this study, we perform a numerical simulation of unsteady behaviors of turbulent flow and plume dispersion over a 2-dimensional hill by a local-scale high-resolution atmospheric dispersion and dose assessment system (LHADDAS). Then, we investigate the formation processes of air concentration and dose rate distributions over the hill from the viewpoint of the turbulent structures.