Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Honda, Masaki*; Saiki, Yohei*; Takahashi, Masashi*; Ohira, Koichi*; Nakano, Masaaki*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 357, p.110419_1 - 110419_10, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concept of a plutonium (Pu) burner HTGR is proposed to incarnate highly-effective Pu utilization by its inherent safety features. The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Mizuta, Naoki; Goto, Minoru; Fukaya, Yuji; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. Especially, a zirconium carbide (ZrC) coating is one of key technologies of the 3S-TRISO, which performs as an oxygen getter to reduce the fuel failure due to internal pressure during the irradiation. R&Ds on ZrC coating directly on the dummy CeO
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. Especially, a zirconium carbide (ZrC) coating is one of key technologies of the 3S-TRISO, which performs as an oxygen getter to reduce the fuel failure due to internal pressure during the irradiation. R&Ds on ZrC coating directly on the dummy CeO -YSZ kernel have been carried in the Japanese fiscal year 2017. As results of ZrC coating tests by the bromide chemical vapor deposition process, stoichiometric ZrC coatings with 3 - 18 microns of thicknesses were obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight.
-YSZ kernel have been carried in the Japanese fiscal year 2017. As results of ZrC coating tests by the bromide chemical vapor deposition process, stoichiometric ZrC coatings with 3 - 18 microns of thicknesses were obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight.
Yokoi, Shinobu*; Kamishima, Yoshio*; Sadahiro, Daisuke*; Takaya, Shigeru
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-002, 38 Pages, 2016/07
Many efforts have been made to implement the System Based Code concept aiming at optimizing margins dispersed in existing codes and standards. Failure probability calculated based on statistical information such as a type of probability distribution, mean (or median) and variance (or standard deviation) for random variables is expected to be a promising quantitative index for margin optimization. Statistical information on material strength, which is also required to calculate the failure probability, has been already reported in JAEA-Data/Code 2015-002 "Structural Properties of Material Strength for Reliability Evaluation of Components of Fast Reactors -Austenitic Stainless Steels-" whereas others have not been identified yet. This report provides methodologies and basic ideas to determine statistical parameters of other random variables, especially variable loads, necessary for reliability evaluation.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Tazawa, Yujiro*; Tachibana, Yukio; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
FAPIG, (190), p.20 - 24, 2015/07
In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat in HTGRs must be removed by radiation, thermal conduction and natural convection. Passive heat removal performance is of primary concern for enhancing inherent safety features of HTGRs. Therefore, the thermal hydraulic analyses for normal operation and a loss of forced cooling accident are conducted by using thermal hydraulic CFD code. And further, a multi-hole type fuel block of MHTGR is also modeled and the flow and heat transfer characteristics are compared with a pin-in-block type fuel block.
Ooka, Makoto; Maekawa, Yasunari; Tomizuka, Chiaki; Murakami, Tomoyuki*; Katagiri, Genichi*; Ozaki, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2015-003, 31 Pages, 2015/03
An action for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (Tokyo Electric Power Company) is pushed forward now. For fuel debris Remove, it is necessary to fill the Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) with water. Because a coolant leaks out from the PCV, it becomes the most important problem to seal leak the coolant. Nuclear Plant Decommissioning Safety Research Establishment has examined the method of seal leak using the photocoagulation resin. However, originally the photocoagulation resin is used as coating or the painting, and the applicability to seal leak water is unknown. This report describes the result that examined the applicability to seal leak using photocoagulation resin.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Nakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/10
Passive heat removal performance of the reactor vessel cavity cooling system (RCCS) is of primary concern for enhanced inherent safety of HTGR. In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat must be removed by radiation and natural convection of RCCS. Thus thermal hydraulic analysis of reactor internals and RCCS is powerful means for evaluation of the heat removal performance of RCCS. The thermal hydraulic analyses using CFD computation tools are conducted for normal operation of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and are compared to the temperature distribution of measured data. The calculated temperatures on outer faces of the permanent side reflector (PSR) blocks are in fair agreement with measured data. The transient analysis for decay heat removal mode in HTTR is also conducted.
 C high temperature gas-cooled reactor
C high temperature gas-cooled reactorNakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The conceptual core design study of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is performed. The major specifications are 600 MW thermal output, 950 C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release,
C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release, 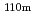 Ag and
Ag and  Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Imaizumi, Tomomi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Ito, Masayasu; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Nagata, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Naka, Michihiro; Kawamata, Kazuo; Yamaura, Takayuki; Ide, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-031, 123 Pages, 2012/01
The number of research reactors in the world is decreasing because of their aging. However, the planning to introduce the nuclear power plants is increasing in Asian countries. In these Asian countries, the key issue is the human resource development for operation and management of nuclear power plants after constructed them, and also the necessity of research reactor, which is used for lifetime extension of LWRs, progress of the science and technology, expansion of industry use, human resources training and so on, is increasing. From above backgrounds, the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center began to discuss basic concept of a multipurpose low-power research reactor for education and training, etc. This design study is expected to contribute not only to design tool improvement and human resources development in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center but also to maintain and upgrade the technology on research reactors in nuclear power-related companies. This report treats the activities of the working group from July 2010 to June 2011 on the multipurpose low-power research reactor in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center and nuclear power-related companies.
Sakakibara, Tetsuro; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamaguchi, Hiromi; Sasaki, Naoto*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Murata, Minoru*; Park, J.*; Taniguchi, Shoji*; Fujita, Michiru*; Fukuda, Tomoyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposium 2009 (WM '09) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2009/03
The volume reduction treatment of solid waste system by ultra-high frequency induction furnace (UHFIF) was developed from FY2005 to FY2007. Basic data for melting performance were collected by non-radioactive experiments using the bench scale UHFIF with a crucible capacity of 10 liters. Based on the obtained data, engineering specifications were evaluated for a demonstration scale UHFIF with a crucible capacity of 30 liters. A new demonstration scale UHFIF was constructed and melting experiments of surrogate wastes were carried out by this furnace. It was confirmed that the demonstration scale UHFIF can melt ferrous metal, ceramics and aluminum all together and stabilize aluminum by oxidation to alumina. Density, chemical composition, and surface condition of the solidified substances were analyzed, and homogeneity of the solidified substances was confirmed. Melting behavior in the demonstration scale UHFIF was analyzed by computer simulation and simulation results agreed well with the experimental ones. From the design study for a full scale UHFIF with a crucible capacity of 100 liters, basic specifications were evaluated for the full scale UHFIF. Based on the obtained specification, melting behavior in the full scale UHFIF was analyzed by computer simulation.
Yan, X.; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Ohashi, Kazutaka; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*
Nuclear Technology, 163(3), p.401 - 415, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)A rupture of primary piping in HTGR represents a design basis event. In such a loss of coolant event a safety issue remains graphite oxidation damage to fuel and core should major air ingress take place through the breached primary boundary. The present study deals with the two most probable cases of air ingress. The first results from rupture of a standpipe. A design change proposed in the vessel top structure intends to rule out any probability of a standpipe rupture. The feasibility of the modified structure is evaluated. The second case results from rupture of a main coolant pipe. Experiment and analysis are performed to gain understanding of the multi-phased air ingress phenomena and accordingly a new mechanism of sustained counter-air diffusion is proposed that is fully passive and effective in preventing major air ingress in the event of main coolant pipe rupture. The results of the present study may lead to improved safety and economic design of the HTGR.
Ohashi, Kazutaka; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Nakano, Masaaki*; Tazawa, Yujiro*; Okamoto, Futoshi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(1), p.32 - 43, 2008/03
Interests on the development of the Very High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor (VHTR), of which the reactor outlet temperature is 950 C or much higher, are recently increasing world-widely and it was selected as one of the candidate reactor types of the GIF. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has already initiated R&D efforts on the electricity and hydrogen co-generation plant with VHTR system, GTHTR300C. Although technical feasibility of its VHTR reactor using Pin-in-block fuel, which has experience to be already used in the HTTR, has been shown fundamentally, more improvements of the core performances, such as decrease of the occupational exposure doses during the plant maintenance, are desired. This report presents the results of the conceptual core design study using Multi-hole type fuel and the study on the occupational exposure doses. The latter results shows much better plant maintainability compared to the previous results of the GTHTR-300.
C or much higher, are recently increasing world-widely and it was selected as one of the candidate reactor types of the GIF. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has already initiated R&D efforts on the electricity and hydrogen co-generation plant with VHTR system, GTHTR300C. Although technical feasibility of its VHTR reactor using Pin-in-block fuel, which has experience to be already used in the HTTR, has been shown fundamentally, more improvements of the core performances, such as decrease of the occupational exposure doses during the plant maintenance, are desired. This report presents the results of the conceptual core design study using Multi-hole type fuel and the study on the occupational exposure doses. The latter results shows much better plant maintainability compared to the previous results of the GTHTR-300.
Tozawa, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Hiroyuki*; Ozaki, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Yoshihiro*
JNC TJ9420 2005-006, 133 Pages, 2005/02
Hexagonal block fuel subassembly dispersing coated particle nitride fuel fabrication facility for Helium gas cooled reactor on the Feasibility Study for FBR fuel cycle systems has been investigated to reflect plant design considering detail effect of nitride fuel and remote handling and to evaluate waste production and plant cost. Results of the study are follows.(1) Research for hexagonal block fuel fabrication plant concept Material balance was settled considering with coated particle with TiN layer and SiC layer. System configuration was settled based on capacity and number of each equipments. Production method of the hexagonal block is hexagonal block flame capped SiC plate after vibration compaction in vertical position at core particle section and vibration compaction in horizontal position at blanket particle section. Production facility of the hexagonal block is embodied.Fuel subassembly is made by the hexagonal block screwed shut with entrance nozzle and handling head. Inspection items of hexagonal block are picked up and density inspection method is settled in X-ray CT scanning.Reagent recovery system is settled based on the system of sphere packing method.(2) Data evaluation for system assessment Radioactive gaseous waste, liquid waste, and solid waste in the main process, analysis process and maintenance process are evaluated. From the result, it made clear that radioactive gaseous waste and liquid waste are decreased by recovering IPA, nitric acid, ammonia water in reagent recovery process.Cost of equipment of the plant and operation cost have been estimated. Main process equipment cost occupies 21% of construction cost. Cost of radioactive waste treatment process, analysis process, maintenance facilities, instrumentation facilities and utility, occupy 35% of it. Cost of building, electrical equipment and ventilating system occupy 34% of it. New fuel storage facility occupies 10% of it.
Tozawa, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Hiroyuki*; Ozaki, Hiroshi*; Nakano, Masaaki*
JNC TJ9420 2005-007, 104 Pages, 2004/02
Coated particle nitride fuel fabrication facility for He gas cooled reactor on the Feasibility Study for FBR and Related Fuel Cycle has been investigated to reflect plant design considering detail effect of nitride fuel and remote handling and to evaluate waste production and plant cost.
Sadahiro, Daisuke*
JNC TJ9400 2001-020, 91 Pages, 2002/03
Plant economics is one of important items in FBR development. In present FBR design, large design factor provided in design standards is considered to be one of restriction for the improvement of FBR economics. From such a background, FBR Integrity System Code (FISC), which is for settlement of appropriate design margin, is now under development. Aim of this study is to contribute to the development of this code, and investigation study on inspection technique and flame of code for inspection has been performed. The results of this studyare as follows. (1)Study of position of code for inspection. The present code and standard for inspection and evaluation examples for risk assessment, which is one of method fbr margin exchange, have been investigated, and inspection accuracy, inspection interval, type of inspection and inspection procedure etc. have been extracted as the standardization item. In these items, first two items, in particular, have a large contribution to rationalization. (2)Investigation of inspection technique. Because the inspection accuracy is one of important item from study item (1), present status of Ultrasonic Testing (UT) technique, which is the one of the method used for ISI, has been investigated. And, monitoring technique, which is effective for rationalization of inspection, has been also investigated. Concerning UT, estimation of detection limit is difficult, but it is considered that detection of 1-2mm depth crack can be detected by present UT technique. On monitoring technique, fatigue or crack monitoring can contribute to maintenance schedule. (3)Study of flame of code for inspection. Based on the above study results, the standardization items in code for inspection have been extractcd, and area and flame of this code have been studied. Because FISC is considered to provide the concrete design procedures, present code and guideline such JEAC and JEAG is considered to be covered in this code. Material inspection included ...
*; *; *; *; *
JNC TJ9410 2001-003, 432 Pages, 2001/08
This report describes the result of study of manufacture and test of the Alcohol Waste Processing test Equipment. The experimental fast Reactor, JOYO, stores the radioactive alcohol waste at storage tank. As this alcohol waste can not be processed with existing equipment, about 5 m of alcohol waste is stored. And the amount of this waste increases every year. So it is necessary to process this alcohol waste by appropriate method, for example, chemical resolution. In this fiscal year, based on the study results in the last fiscal year on catalytic oxidation method, the test equipment is manufactured and conclusive test is performed. And the investigation and tests on applicability of the other sodium removal technologies is also performed. The study results obtained in this fiscal year are as follows. [(1)Conclusive Test of the alcohol waste processing] (a)As a result of 1/2 scale test, target processing performance of 1.25
of alcohol waste is stored. And the amount of this waste increases every year. So it is necessary to process this alcohol waste by appropriate method, for example, chemical resolution. In this fiscal year, based on the study results in the last fiscal year on catalytic oxidation method, the test equipment is manufactured and conclusive test is performed. And the investigation and tests on applicability of the other sodium removal technologies is also performed. The study results obtained in this fiscal year are as follows. [(1)Conclusive Test of the alcohol waste processing] (a)As a result of 1/2 scale test, target processing performance of 1.25 /h can be obtained for simulative alcohol waste of 80% alcohol, but processing performance for simulative alcohol waste of 20% could not satisfy the target value. (b)In case that high temperature pipes, which are under condition of 350 deg C in actual plant, are arranged, it is difficult to arrange equipment in alcohol waste tank room (A-106). [(2)Investigative and Test about Sodium removal] (a)The sodium in alcohol waste can be separated and removed from carbonate compound. (b)A sodium (carbonate compound and metals) in alcohol waste could be removed by wired-film evaporator, and it is considered to be possible that this equipment is applied to actual plant. (c)ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) is considered to be effective method as one of alcohol resolution processes. [(3)Basic Design of alcohol waste process equipment] In this basic design, as far evaporation-dry process, the components, process ability, properties of waste, chemical mass balance, safety for fire and explosion, and the plot plan are investigated. As a result, ...
/h can be obtained for simulative alcohol waste of 80% alcohol, but processing performance for simulative alcohol waste of 20% could not satisfy the target value. (b)In case that high temperature pipes, which are under condition of 350 deg C in actual plant, are arranged, it is difficult to arrange equipment in alcohol waste tank room (A-106). [(2)Investigative and Test about Sodium removal] (a)The sodium in alcohol waste can be separated and removed from carbonate compound. (b)A sodium (carbonate compound and metals) in alcohol waste could be removed by wired-film evaporator, and it is considered to be possible that this equipment is applied to actual plant. (c)ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) is considered to be effective method as one of alcohol resolution processes. [(3)Basic Design of alcohol waste process equipment] In this basic design, as far evaporation-dry process, the components, process ability, properties of waste, chemical mass balance, safety for fire and explosion, and the plot plan are investigated. As a result, ...
*; *; *; *
JNC TJ9410 2000-002, 412 Pages, 2000/12
This report describes the result of Conceptual Design of the Alcohol Waste Treatment Equipment. The experimental fast Reactor, JOYO, saves the radioactive alcohol waste at storage tank. As this alcohol waste is not able to treat with existing equipment, it is stored about 5m . And the amount of this is increasing every year. So it is necessary to treat the alcohol waste by chemical resolution for example. On account of this, the investigative test about filtration and dialyzer, and conceptual design about catalyst oxidation process, which is composed from head end process to resolution, are done. The results of investigation show as follows. [(1)Investigative Test about filtration and dialyzer] (a)The electric conduction is suitable for the judgement of alkyl sodium hydrolysis. Alkyl sodium hydrolysis is completed below 39% alcohol concentration. (b)The microfiltration is likely to separate the solid in alcohol waste. (c)From laboratory test, the electrodialyzer is effective for sodium separation in alcohol waste. And sodium remove rate, 96
. And the amount of this is increasing every year. So it is necessary to treat the alcohol waste by chemical resolution for example. On account of this, the investigative test about filtration and dialyzer, and conceptual design about catalyst oxidation process, which is composed from head end process to resolution, are done. The results of investigation show as follows. [(1)Investigative Test about filtration and dialyzer] (a)The electric conduction is suitable for the judgement of alkyl sodium hydrolysis. Alkyl sodium hydrolysis is completed below 39% alcohol concentration. (b)The microfiltration is likely to separate the solid in alcohol waste. (c)From laboratory test, the electrodialyzer is effective for sodium separation in alcohol waste. And sodium remove rate, 96 99%, is confirmed. [(2)Conceptual Design] The candidate process is as follows. (a)The head end process is electrodialyzer, and chemical resolution process is catalyst oxidation. (b)The head end process is not installed, and chemical resolution process is catalyst oxidation. (c)The head end process is electrodialyzer, and alcohol extracted by pervaporation. In this Conceptual Design, as far these process, the components, treatment ability, properties of waste, chemical mass balance, safety for fire and explosion, and the plot plan are investigated. As a result, remodeling the existing facility into catalyst oxidation process is effective to treat the alcohol waste, and treatment ability is about 1.25
99%, is confirmed. [(2)Conceptual Design] The candidate process is as follows. (a)The head end process is electrodialyzer, and chemical resolution process is catalyst oxidation. (b)The head end process is not installed, and chemical resolution process is catalyst oxidation. (c)The head end process is electrodialyzer, and alcohol extracted by pervaporation. In this Conceptual Design, as far these process, the components, treatment ability, properties of waste, chemical mass balance, safety for fire and explosion, and the plot plan are investigated. As a result, remodeling the existing facility into catalyst oxidation process is effective to treat the alcohol waste, and treatment ability is about 1.25 /h.
/h.
*; *; *
PNC TJ9068 88-002, 150 Pages, 1988/03
With a purpose of operating effectively JOYO as a fuel irradiation bed, studies have been conducted for reduction of fuel handling time and prevention of troubles resulted in delay of fuel handling time. This report describes of results of following studies. (1)Increase of numbers of fuel assembly received in the transfer rotor tank as a buffer storage (2)Abandonment of fuel cooling pot and addition of fuel transfer pot in the in-vessel storage rack (3)Necessity of the guide sleeve and maintenability of the hold-down mechanism of in-core charge machine (4)Addition of rotating function to the gripper of in-core charge machine (5)Reduction of gas-purge time of the guide sleeve connected with ex-vessel transfer machine (6)Reduction of spent fuel cleaning time and spent fuel canning time. As a result of the above-mentioned studies, the feasibility of increasing numbers of fuel assembly received in the transfer rotor tank was proved and the refueling time undetr reactor shutdown was prospected to reduce as follows; (1)Abandonment of fuel cooling pot reduces about 2.5days per one refueling period. (2)Abandonment of the guide sleeve of in-core charge machine reduces about 2days per one refueling period. (3)Gas-purge time of the guide sleeve connected with ex-vessel transfer machine reduces one half as compared with the present gas-purge time by means of the ex-vessel transfer guide sleeve attached door-valve.