Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems (SMINS-2), p.391 - 400, 2012/12
Optimization of composition for high Cr-W-Si Ni base alloy has been studied to apply to a nitric acid with high oxidation-reduction potential of advanced reprocessing plants. The corrosion resistance of the Ni base alloy is superior to that of conventional stainless steels. In addition, The Ni base alloy has an excellent resistance of weld crack and ability of plastic deformation caused by extra high purity (EHP) refining technology. However, the Ni base alloy has a technical limitation in hot working and welding for practical use. Several Ni base EHP alloys with different content of Si and W were manufactured to choose an optimum composition range without losing corrosion resistance. High strain rate tensile tests at high temperature, corrosion tests and weldability tests were carried out to examine the optimum composition range of Ni base EHP alloy.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems (SMINS-2), p.273 - 279, 2012/12
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/10
An Extra high purity Nb-W alloy (Nb-W EHP) that is superior to current Zr for cracking in severer environment is developed for reprocessing plants. Nb-W EHP has a technical limitation in weldability for practical use. To choose an optimum composition range of W, Nb-W EHP with different content of W were manufactured. Weld joint specimens were prepared by TIG welding. Tensile, corrosion and Charpy impact tests were carried out to examine the effect of W on chemical and mechanical properties of Nb-W EHP. There was little effect of W on corrosion rate of weld joint of Nb-W EHP. The increase in W improves ultimate tensile strength of Nb-W EHP. A ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) of Nb-W EHP increased with an increase in W. The increase in DBTT is a problem as a structural material. Moreover, DBTT of the weld joint was high about 150K in comparison with the base metal. It is necessary to adjust W content to 8wt% or less in Nb-W EHP from the obtained results.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1298, p.61 - 66, 2011/04
The irradiation behaviour in two different precipitation hardening types of Ni-base alloys with the ultra high purity grade (EHP), namely, the  ' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe
' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe or Ni
or Ni ) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni
) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni , 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP(
, 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP( ') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along
') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along 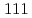 planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP(
planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP( '), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP(
'), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP( '), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
'), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2010/05
An Extra High Purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP alloy) was developed with conducting the new multiple refined melting in order to suppress the harmful impurities less than 100 ppm. EHP alloy has great intergranular corrosion resistance. It is considered that intergranular corrosion becomes initiation of SCC. So, we try to apply EHP alloy to weld overlay materials to prevent from SCC. EHP alloy was melted by the new multiple refined method. The conventional weld metals were also prepared as comparisons. Specimens were machined from the welded metal of each material. Intergranular corrosion tests were performed in boiling 8 kmol/m HNO
HNO solutions containing 1 kg/m
solutions containing 1 kg/m Cr(VI) ions. The intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals was severer than those of EHP alloys. Crevice Beam bending tests to evaluate susceptibility of SCC were carried out in high temperature water of 561 K with saturated oxygen for 1000 h. Cracks and intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals were much more than those of EHP alloys. It was confirmed that EHP alloy had excellent SCC resistance in comparison with conventional materials when EHP alloy was used as a weld metal.
Cr(VI) ions. The intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals was severer than those of EHP alloys. Crevice Beam bending tests to evaluate susceptibility of SCC were carried out in high temperature water of 561 K with saturated oxygen for 1000 h. Cracks and intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals were much more than those of EHP alloys. It was confirmed that EHP alloy had excellent SCC resistance in comparison with conventional materials when EHP alloy was used as a weld metal.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Materia, 49(3), p.122 - 124, 2010/03
In reprocessing plants, it is known that the corrosion environment for structural materials is extremely severe to be used boiling nitric acid with oxidized ions related to fission products (FP). Ultra low carbon stainless steels (SUS304ULC) were developed from the experience of corrosion troubles in foreign plants and the operation of domestic plant. In an advanced reprocessing plant, it is predicted that the corrosion environment will be more severe because of the advanced spent fuels which contain much FP than an existing spent fuel. Therefore, it is necessary to develop the new stainless steel with excellent corrosion resistance in comparison with SUS304ULC. We developed an extra high purity stainless steel (EHP alloy) having superior corrosion resistance in the strong acid environment for the advanced reprocessing plant. In the production process of EHP alloy, the practical use was taken into consideration. This report introduces the present conditions of EHP alloy.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Motooka, Takafumi; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 4(1), p.105 - 112, 2010/02
An intergranular corrosion is an important degradation mechanism of austenitic stainless steels for use in a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant. The intergranular corrosion is caused by the segregation of impurities to grain boundaries. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP) was developed with conducting the new multiple refined melting to suppress the impurities less than 100ppm. The intergranular corrosion behavior of EHP alloys added various impurities was examined in boiling nitric acid solution with highly oxidizing ions. A multi regression analysis was performed using the obtained data. The degree of influence of the impurities on intergranular corrosion was shown from the analysis. The influence on corrosion rate became small in order of B, P, Si, C, S and Mn. There is little effect of Mn on corrosion rate of EHP-SSs in case of 10000appm or less.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Motooka, Takafumi; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-17) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2009/06
An intergranular corrosion is an important degradation mechanism of austenitic stainless steels for use in a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant. The intergranular corrosion is caused by the segregation of impurities to grain boundaries. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP ) was developed with conducting the new multiple refining to suppress the impurities less than 100 ppm. The intergranular corrosion behavior of EHP alloys with various impurities was examined in boiling nitric acid solution. The intergranular corrosion was observed in impurity doped EHP alloys, although no intergranular corrosion was observed in EHP alloy. From the obtained results, an empirical equation between susceptibility of intergranular corrosion and impurities was established by means of the regression analysis. The degree of influence of the impurities on intergranular corrosion was shown.
) was developed with conducting the new multiple refining to suppress the impurities less than 100 ppm. The intergranular corrosion behavior of EHP alloys with various impurities was examined in boiling nitric acid solution. The intergranular corrosion was observed in impurity doped EHP alloys, although no intergranular corrosion was observed in EHP alloy. From the obtained results, an empirical equation between susceptibility of intergranular corrosion and impurities was established by means of the regression analysis. The degree of influence of the impurities on intergranular corrosion was shown.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 3(1), p.31 - 37, 2009/00
Austenitic stainless steels suffer intergranular attack in boiling HNO with oxidants. The intergranular corrosion is mainly caused by impurities at the grain. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP alloys) was developed with conducting the new technique in order to suppress harmful impurities less than 100 ppm. The corrosion behavior of type 310 EHP alloy in HNO
with oxidants. The intergranular corrosion is mainly caused by impurities at the grain. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP alloys) was developed with conducting the new technique in order to suppress harmful impurities less than 100 ppm. The corrosion behavior of type 310 EHP alloy in HNO with highly oxidants was investigated. The straining, aging and recrystallizing (SAR) treated type 310 EHP alloy showed superior corrosion resistance for intergranular attack than solution annealed (ST) type 310 EHP alloy with same impurity level. Boron segregation at the grain boundary was detected in only ST specimen using a FTE method. It is believed that the segregated boron along the grain boundaries in type 310 EHP alloy was one of main factor of intergranular corrosion. The SAR treatment was effective to restrain the intergranular corrosion for type 310 EHP alloy with B up to 7 ppm.
with highly oxidants was investigated. The straining, aging and recrystallizing (SAR) treated type 310 EHP alloy showed superior corrosion resistance for intergranular attack than solution annealed (ST) type 310 EHP alloy with same impurity level. Boron segregation at the grain boundary was detected in only ST specimen using a FTE method. It is believed that the segregated boron along the grain boundaries in type 310 EHP alloy was one of main factor of intergranular corrosion. The SAR treatment was effective to restrain the intergranular corrosion for type 310 EHP alloy with B up to 7 ppm.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2008/05
Austenitic stainless steels suffer intergranular attack in boiling nitric acid with oxidants. The intergranular corrosion is mainly caused by the segregation of impurities to grain. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP alloys) was developed with conducting the new multiple refined melting technique in order to suppress the total harmful impurities less than 100ppm. The basically corrosion behavior of type 310 EHP alloy with respect to nitric acid solution with highly oxidizing ions was investigated. The straining, aging and recrystallizing (SAR) treated type 310 EHP alloy showed superior corrosion resistance for intergranular attack. The segregated boron along the grain boundaries was one of main factor of intergranular corrosion from fission track etching results. The SAR treatment was effective to restrain the intergranular attack for type 310 EHP alloy with B less than 7ppm.
Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Nakamura, Hideo; Kukita, Yutaka*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(2), p.183 - 193, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:51.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 5th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-5), p.226 - 233, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Meguro, Yoshihiro; Tomioka, Osamu; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Wada, Ryutaro*; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Fukuzato, Ryuichi*
Proceedings of 8th International Symposium on Supercritical Fluids (ISSF 2006) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2006/11
A large-scale apparatus having a reaction vessel of ca. 4000 cm was developed for supercritical CO
was developed for supercritical CO leaching. An ultrasonic wave oscillator, stirring device, and piston compressor were equipped to the apparatus to enhance mass transfer rate of substances in supercritical CO
leaching. An ultrasonic wave oscillator, stirring device, and piston compressor were equipped to the apparatus to enhance mass transfer rate of substances in supercritical CO . A sea sand sample, an incinerated ash sample, and a porous alumina brick sample, in which uranium oxide was adsorbed, were prepared as simulated samples of radioactive wastes and uranium was tried to remove from these samples to supercritical CO
. A sea sand sample, an incinerated ash sample, and a porous alumina brick sample, in which uranium oxide was adsorbed, were prepared as simulated samples of radioactive wastes and uranium was tried to remove from these samples to supercritical CO including nitric acid - tri-n-butyl phosphate complex as a reactant using the apparatus. By several times of the uranium separation, more than 99% of uranium was removed from the sea sand sample and the ash sample. When the mass transfer enhanced system was operated, it was confirmed that separation efficiency of uranium was improved and then 99% of uranium could be removed form the ash sample.
including nitric acid - tri-n-butyl phosphate complex as a reactant using the apparatus. By several times of the uranium separation, more than 99% of uranium was removed from the sea sand sample and the ash sample. When the mass transfer enhanced system was operated, it was confirmed that separation efficiency of uranium was improved and then 99% of uranium could be removed form the ash sample.
Meguro, Yoshihiro; Tomioka, Osamu; Imai, Tomoki*; Fujimoto, Shigeyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio; Yoshida, Zenko; Honda, Tadashi*; Koya, Fumio*; Kitamura, Nobu*; Wada, Ryutaro*; et al.
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposium 2004 (WM '04) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/03
Supercritical CO fluid leaching (SFL) method using supercritical CO
fluid leaching (SFL) method using supercritical CO fluid containing a complex of HNO
fluid containing a complex of HNO - tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) was applied to removal of uranium from radioactive solid wastes. Sea sands, incineration ashes and porous alumina bricks were employed as matrixes of simulated solid wastes. Real radioactive incineration ash wastes and firebrick wastes were also subjected to the SFL treatment. It was found that uranium could be efficiently removed from both of the simulated wastes and real wastes by the SFL method. The removal efficiency of uranium from the real waste was lower than that from the corresponding artificial waste. About 1 g and 35 mg of uranium were recovered from 10 g of the real ash waste and 37 g of the real firebrick waste, respectively.
- tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) was applied to removal of uranium from radioactive solid wastes. Sea sands, incineration ashes and porous alumina bricks were employed as matrixes of simulated solid wastes. Real radioactive incineration ash wastes and firebrick wastes were also subjected to the SFL treatment. It was found that uranium could be efficiently removed from both of the simulated wastes and real wastes by the SFL method. The removal efficiency of uranium from the real waste was lower than that from the corresponding artificial waste. About 1 g and 35 mg of uranium were recovered from 10 g of the real ash waste and 37 g of the real firebrick waste, respectively.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Nakanishi, Tomoaki*; Nakayama, Takenori*; Sakashita, Shinji*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2005-001, 224 Pages, 2004/02
For repository container material of high-level radioactive waste, titanium and nickel-base alloys have been investigated as high corrosion resistance metal. In this study, the effects of environmental and material factors on hydrogen absorption of titanium were investigated experimentally. As for nickel-base allys, previous studies on corrosion behavior were serched.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2004-017, 71 Pages, 2004/02
Research on changes of nitrate by interactions with metals under the wastes disposal environment containing TRU nuclide
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2004-016, 194 Pages, 2004/02
Research on Changes of Nitrate by Chemical Interactions with Metals under the wastes Disposal Environment Contaioning TRU Nucride
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Nakanishi, Tomoaki*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Inoue, Takao*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-092, 246 Pages, 2003/02
Titanium is being studied for the high-level radioactive waste package material. Titanium has good corrosion resistance, however there is the possibility of hydrogen embrittlement with absorption of hydrogen in reducing condition. Experimental studies were performed to evaluate the hydrogen absorption behaviors of titanium in reducing condition. The failure model of the titanium overpack was also examined from the viewpoint of fracture mechanism in order to evaluate the fracture behavior of the titanium overpack caused by the hydrogen absorption. (1) Scratch test was conducted in reduce condition. The surface films on the titanium specimen were analyzed to examine the changes of the existing films and the growth phenomena of the regenerated films on the titanium specimen. (2)The long-term reaction test of the titanium specimen using the glass-seal ampoules maintaining reducing condition was conducted and analyses of the hydrogen gas generation and absorption quantitative as well as the generated film evaluation were performed. (3) Under reducing condition, the electrochemical acceleration tests of the titanium specimen were conducted. The effect of acceleration rate on the hydrogen absorption and surface film was evaluated, and the prediction as to the hydrogen absorption behavior at a natural state was also made. (4) The prediction of the maximum residual stress and the evaluation of crack growth of the titanium overpack based on the previous studies were performed. Feasibility of the modeling of fracture phenomenon with existing analysis technique was examined and the items to be developed were also discussed.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-080, 153 Pages, 2003/02
There exists the waste including a nitrate ion as a salt in the TRU waste materials. This nitrate ion can be transferred to the nitrite ion and/or ammonia by reducing materials such as metals in the waste disposal environment, and has the possibility to affect on the disposal environment and nuclide transfer parameters.Therefore, electrochemical tests were conducted to evaluate the reaction rate parameters of the nitrate ion and metals under the low oxygen environment. The long-term reaction test using the glass-seal vessel was also conducted to grasp precisely the nitrate ion transition reaction rate and the gas generation rate caused by the reaction of metal and the nitrate ion coexist solution. (1) Reaction rate constants under various environments were obtained performing the potentiostatic holding tests with the parameters of the solution pH, temperature, and the nitrate and nitrite ion concentrations. The formula of the nitrate ion transition reaction rate was also examined based on these obtained data. (2) Conducting the immersion tests under the environment of the low oxygen and high-pH rainfall underground water site, the long-term reaction rate data were obtained on the reaction products (ammonia, hydrogen gas etc.) of metals (carbon steel, stainless steel and zircaloy etc.) with nitrate ion. The tests under the same conditions as in the past were also conducted to evaluate the test accuracy and error range of the long-term reaction test with the glass-seal vessels.
Wada, Ryutaro*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
JNC TJ8400 2003-079, 252 Pages, 2003/02
There exists the waste including a nitrate ion as a salt in the TRU waste materials. This nitrate ion can be transferred to the nitrite ion and/or ammonia by reducing materials such as metals in the waste disposal environment, and has the possibility to affect on the disposal environment and nuclide transfer parameters. Therefore, electrochemical tests were conducted to evaluate the reaction rate parameters of the nitrate ion and metals under the low oxygen environment. The long-term reaction test using the glass-seal vessel was also conducted to grasp precisely the nitrate ion transition reaction rate and the gas generation rate caused by the reaction of metal and the nitrate ion coexist solution. (1)}Reaction rate constants under various environments were obtained performing the potentiostatic holding tests with the parameters of the solution pH, temperature, and the nitrate and nitrite ion concentrations. The formula of the nitrate ion transition reaction rate was also examined based on these obtained data. (2) Conducting the immersion tests under the environment of the low oxygen and high-pH rainfall underground water site, the long-term reaction rate data were obtained on the reaction products (ammonia, hydrogen gas etc.) of metals (carbon steel, stainless steel and zircaloy etc.) with nitrate ion. The tests under the same conditions as in the past were also conducted to evaluate the test accuracy and error range of the long-term reaction test with the glass-seal vessels.