Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 thin film detector for neutrons
thin film detector for neutronsIshida, Takekazu*; Nishikawa, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Yoshifumi*; Okayasu, Satoru; Katagiri, Masaki*; Sato, Kazuo*; Yotsuya, Tsutomu*; Shimakage, Hisashi*; Miki, Shigehito*; Wang, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 151(3-4), p.1074 - 1079, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:78.05(Physics, Applied)The superconducting neutron detector using high-quality  B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB thin films at higher operating temperatures has been proposed, where a resistance change induced by the nuclear reaction of neutron and
thin films at higher operating temperatures has been proposed, where a resistance change induced by the nuclear reaction of neutron and  B in MgB
B in MgB is used to detect a neutron. Cold neutrons from a nuclear research reactor irradiated the MgB
is used to detect a neutron. Cold neutrons from a nuclear research reactor irradiated the MgB detector, and the output voltage was clearly observed through a low-noise amplifier by using a digital oscilloscope. The out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics was investigated by means of the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equations by using the Earth Simulator.
detector, and the output voltage was clearly observed through a low-noise amplifier by using a digital oscilloscope. The out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics was investigated by means of the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equations by using the Earth Simulator.
 neutron detectors
neutron detectorsMachida, Masahiko; Kano, Takuma*; Koyama, Tomio*; Kato, Masaru*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 151(1), p.58 - 63, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:46.07(Physics, Applied)We perform large-scale numerical simulations on the non-equilibrium superconducting dynamics after a neutron capture at the superconducting transition edge in MgB by solving the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation coupled with the Maxwell and the heat diffusion equations. The simulations are carried out under the current-biased condition in order to explain experimental results made in the JAEA reactor JRR-3, and the time scale of the obtained voltage signal is found tobe almost consistent with the experiments. Moreover, the time evolution of the voltage signal is connected with that of the spatial profile of the superconducting order parameter.
by solving the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation coupled with the Maxwell and the heat diffusion equations. The simulations are carried out under the current-biased condition in order to explain experimental results made in the JAEA reactor JRR-3, and the time scale of the obtained voltage signal is found tobe almost consistent with the experiments. Moreover, the time evolution of the voltage signal is connected with that of the spatial profile of the superconducting order parameter.
Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Hayashi, Masahiko*; Ebisawa, Hiromichi*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 403(5-9), p.996 - 998, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Condensed Matter)Using the Bogoliubov-de Gennes equation of a tight-binding electron model with attractive on-site and nearest-neighbor sites interactions, we investigate the superconducting structure of nano-structured anisotropic superconductors. Numerical results show that nano-scaled  /4-rotated square d-wave superconductors show various type of uperconductivities depending on the size. Especially,
/4-rotated square d-wave superconductors show various type of uperconductivities depending on the size. Especially,  +
+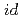 superconductivity, appears when size of superconductors is 10 times of coherence length.
superconductivity, appears when size of superconductors is 10 times of coherence length.
Nakajima, Susumu*; Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Ishida, Takekazu*; Nori, F.*
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.769 - 772, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.85(Physics, Applied)A d-dot is a superconducting composite structure of d- and s-wave superconductors, which shows spontaneous half-quantized magnetic fluxes. We developed numerical method to analyze the time development of these spontaneous magnetic fluxes, based on the twocomponents Ginzburg-Landau equation. The d-dot can be used as an element of quantum dot cellular automata logic gates. We show a simulation, which demonstrates the transfer of information between two d-dot's.
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.654 - 659, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.3(Physics, Applied)The terahertz wave emission from the intrinsic Josephson junctions is one of recent topics in high 
 superconductors. We investigate, by numerical simulation, properties of the electromagnetic waves excited by a constant bias current in the single- and multi-Josephson junctions. Nonlinear equations of phase-differences are solved numerically by treating the effects of the outside electromagnetic fields as dynamical boundary conditions. It is shown that the emitted power of the electromagnetic wave can become large near certain retrapping points of the I-V characteristics. An instability of the inside phase oscillation is related to large amplitude of the oscillatory waves. In the single- (or homogeneous mutli-) Josephson junctions, electromagnetic oscillations can occur either in a form of standing waves (shorter junctions) or by formation of vortex-antivortex pairs (longer junctions). How these two effects affects the behavior of electromagnetic waves in the intrinsic Josephson junctions is discussed.
superconductors. We investigate, by numerical simulation, properties of the electromagnetic waves excited by a constant bias current in the single- and multi-Josephson junctions. Nonlinear equations of phase-differences are solved numerically by treating the effects of the outside electromagnetic fields as dynamical boundary conditions. It is shown that the emitted power of the electromagnetic wave can become large near certain retrapping points of the I-V characteristics. An instability of the inside phase oscillation is related to large amplitude of the oscillatory waves. In the single- (or homogeneous mutli-) Josephson junctions, electromagnetic oscillations can occur either in a form of standing waves (shorter junctions) or by formation of vortex-antivortex pairs (longer junctions). How these two effects affects the behavior of electromagnetic waves in the intrinsic Josephson junctions is discussed.
Ishida, Takekazu*; Matsushima, Yoshiaki*; Shimizu, Makoto*; Hayashi, Masahiko*; Ebisawa, Hiromichi*; Sato, Osamu*; Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Sato, Kazuo*; et al.
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.576 - 580, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.18(Physics, Applied)The extended Little-Parks effect of superconducting network is known as a periodic 
 variation as a function of magnetic field. Superconducting Pb honeycomb networks of matching field 0.106 G and triangular microhole lattice of Pb of matching field 0.425 G have been fabricated by the combination of electron-beam lithography and a lift-off process of evaporated Pb films. The application of magnetic field corresponds to the vortex filling into superconducting networks. We measured the magnetization of the networks systematically by using a SQUID magnetometer. We found that flux jump appears rather periodically as a function of magnetic field. Flux jumps may be induced by a periodic decrease of the critical current density of the network. To the authors' knowledge, this is for the first time to observe the regular flux jumps due to the critical current modification coming from the extended Little-Parks effect of the superconducting networks.
variation as a function of magnetic field. Superconducting Pb honeycomb networks of matching field 0.106 G and triangular microhole lattice of Pb of matching field 0.425 G have been fabricated by the combination of electron-beam lithography and a lift-off process of evaporated Pb films. The application of magnetic field corresponds to the vortex filling into superconducting networks. We measured the magnetization of the networks systematically by using a SQUID magnetometer. We found that flux jump appears rather periodically as a function of magnetic field. Flux jumps may be induced by a periodic decrease of the critical current density of the network. To the authors' knowledge, this is for the first time to observe the regular flux jumps due to the critical current modification coming from the extended Little-Parks effect of the superconducting networks.
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Okumura, Masahiko; Igarashi, Ryo; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English