Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Co gamma irradiation test results with calculated results
Co gamma irradiation test results with calculated resultsTakeda, Ryoma; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Seki, Misaki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Testing 2024-007, 33 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. In this report, we compare and verify these test results with the theoretical output results obtained by the calculation code created in the JAEA report (JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018). The comparison was made with the irradiation test results of SPGD, a cobalt-60 gamma irradiation facility. As a result, it was found that the calculation results reproduced the test results well when the emitter diameter was relatively small compared to the range of Compton scattered electrons by the gamma rays. On the other hand, when the emitter diameter is relatively large, the output current in the test results is only about half of the calculated output current. The self-shielding effect of the emitter may be one of the reasons for the difference in the emitter diameter, and a new formulation, such as incorporating the effect of self-shielding caused by a larger emitter diameter or a non-isotropic  -ray field as a change in the mean electron range or mean minimum energy in the calculation code, is necessary. The new formulation is necessary.
-ray field as a change in the mean electron range or mean minimum energy in the calculation code, is necessary. The new formulation is necessary.
Miyazaki, Yasunori; Sano, Yuichi; Ishigami, Ryoya*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 317, p.01006_1 - 01006_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The gamma-ray and He ion beam (which is simulated for alpha-ray from
ion beam (which is simulated for alpha-ray from  Am, for example) were irradiated on the TEHDGA adsorbent to evaluate the hydrogen gas production, leaching amount of organics in the immersed 3 M HNO
Am, for example) were irradiated on the TEHDGA adsorbent to evaluate the hydrogen gas production, leaching amount of organics in the immersed 3 M HNO solution, thermal characteristics and speciation of the degradation products. These were combined to assess the safety of the 1st run of the MA separation process from the raffinate at a dose rate of 1 kGy/h.
solution, thermal characteristics and speciation of the degradation products. These were combined to assess the safety of the 1st run of the MA separation process from the raffinate at a dose rate of 1 kGy/h.
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 226, p.112198_1 - 112198_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In recent years, the use of radiation-resistant resins of polyimide and polyether ether ketone becomes increasing as vessels for irradiation and unsealed radioisotope experiments. However, in our radiolysis experiments, the possibility of interaction between radiolysis products of water and the resin was found, suggesting concerns that the resin may affect reactions in water in radiation fields. To clarify the interaction, dichromate (Cr O
O
 ) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H
) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) formation in
) formation in  -radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr
-radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr O
O
 reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr
reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr O
O
 reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H
reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H O
O formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
Kitamura, Yoshimasa; Oka, Toshitaka; Seito, Hajime*; Yokozuka, Eri*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1660 - 1665, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)In this work, we evaluated the applicability of hydroxyapatite, which is a main component of tooth enamel, as individual dosimeters that can detect from less than 1 Gy to several tens Gy. Commercially available hydroxyapatite was irradiated by  Co gamma-ray up to 75 Gy and ESR spectrum of the irradiated sample was observed. The relationship between the intensity of produced carbonated radical and the absorbed dose shows a good linearity (
Co gamma-ray up to 75 Gy and ESR spectrum of the irradiated sample was observed. The relationship between the intensity of produced carbonated radical and the absorbed dose shows a good linearity (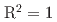 ) from 0 to 75 Gy. The detection limit of this samples was estimated to be 99.7 mGy, and the radical intensity do not change for eight month from the irradiation. These results suggest that this sample can be used as a candidate of the individual dosimeter.
) from 0 to 75 Gy. The detection limit of this samples was estimated to be 99.7 mGy, and the radical intensity do not change for eight month from the irradiation. These results suggest that this sample can be used as a candidate of the individual dosimeter.
Seito, Hajime*; Yokozuka, Eri*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1656 - 1659, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)We have examined dosimetric characteristics of bio-inspired carbonated hydroxyapatite (CO HAp), which is a main component of calcified tissues like tooth enamel. CO
HAp), which is a main component of calcified tissues like tooth enamel. CO HAp powder samples were exposed to gamma-ray with radiation doses ranging from 1 Gy to 1000 Gy at room temperature, and ESR spectra were measured immediately after irradiation and subsequently measured each 1 day during 90 days. The post-irradiation fading resulted in significant 20% decay of the signal amplitude, which stabilised within 7 days after irradiation, and the intensity approached a constant. The sample has good linear dose response in the experiment range of 10 Gy - 1000 Gy. Our results indicate that the CO
HAp powder samples were exposed to gamma-ray with radiation doses ranging from 1 Gy to 1000 Gy at room temperature, and ESR spectra were measured immediately after irradiation and subsequently measured each 1 day during 90 days. The post-irradiation fading resulted in significant 20% decay of the signal amplitude, which stabilised within 7 days after irradiation, and the intensity approached a constant. The sample has good linear dose response in the experiment range of 10 Gy - 1000 Gy. Our results indicate that the CO HAp materials is suitable for chemical dosimetry.
HAp materials is suitable for chemical dosimetry.
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
Nuclear Technology, 210(8), p.1427 - 1443, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The retention of hydrogen (H ) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H
) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H
retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H
O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H
O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H
bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H observed with and without stirring the slurry after
observed with and without stirring the slurry after  Co
Co  -irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H2 bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
-irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H2 bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
Hata, Kuniki; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Watanabe, Yutaka*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(4), p.126 - 130, 2023/04
Gamma-radiolysis experiments with gas-liquid coexistent samples were carried out to investigate effects of gas-phase radiolysis on corrosive environment for materials in solutions under irradiation. After gamma-ray irradiation, hydrogen peroxide, nitrate ion, nitrite ion were detected in the liquid phase. The production yields of nitrate ion and nitrite ion increased with increasing gas-phase volume and oxygen concentration. This result indicated that chemical reactions including oxygen and nitrogen in the gas phase were required for the production of nitrate ion and nitrite ion. To magnify the effects of gas-phase radiolysis in the gas-liquid coexistent samples, absorption dose rate in the liquid phase was reduced by one-hundredth using lead shield. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide and the pH in the shielded liquid phase were similar to those in the irradiated pure water, which did not contact with gas phase. This result indicated that the effects of nitrate ion and nitrite ion dissolved in the liquid phase on water radiolysis were not important in the current experimental system, in which the effects of gas-phase radiolysis were increased by 100-times.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Suzuki, Shunichi*
Isotope News, (782), p.40 - 44, 2022/08
The stagnant water in the reactor building at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is exposed to the radiation from fuel debris and radioactive species. This water contains much amounts of impurities from the seawater which was injected in the emergency cooling. The impurities will affect the radiolysis and corrosive conditions in the water under irradiation. So, the water radiolysis data, corrosion data of steels under irradiations, and the evaluated potential impacts of corrosion in the decommissioning process of 1F are arranged as the database for corrosion under irradiation. This paper introduces the outline of this database.
Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 191, p.109831_1 - 109831_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, we investigated and compared the effects of a high-silica zeolite (HMOR) on the radiation-induced degradation of three aromatic chlorides, 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh), 2-chloroaniline (2-ClAn), and 2-chlorobenzoic acid (2-ClBA), in order to examine its potential to reduce the influence of ions in water matrix in the irradiation treatment of water-soluble organic compounds. In the presence of ions reactive to radicals, the degradation of 2-ClPh in water was inhibited, but the combined use of HMOR much improved the degradation yield. This improvement was attributed to high performance of HMOR in adsorption of 2-ClPh. Similarly, HMOR was effective for adsorption of 2-ClAn and facilitated the 2-ClAn degradation by irradiation. In contrast, HMOR was poor at adsorption of 2-ClBA and consistently the degradation of 2-ClBA in the water-HMOR mixture was inhibited by the radical scavenger. These results demonstrate that HMOR can mitigate the influence of radical scavengers in water.
Kato, Chiaki; Yamagishi, Isao; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.441 - 447, 2021/12
Zeolite particles have been used in a Cs adsorption vessel for purification of contaminated water in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The used Cs adsorption vessels were kept in storage space on 1F site. The risk of localized corrosion of stainless steel used in the vessel was worried. To evaluate the risk of localized corrosion, using specially designed electrochemical testing apparatus was used under gamma-ray irradiation test. And, real size mock-up test conducted. The results showed the potential change caused by creation of H O
O by water radiolysis decreased by zeolite particles and the enrichment of chloride ion concentration in the vessel do not propagate during dry up procedure of Cs adsorption vessel. These data indicate the risk of localized corrosion of Cs adsorption vessel may stay at considerably low level.
by water radiolysis decreased by zeolite particles and the enrichment of chloride ion concentration in the vessel do not propagate during dry up procedure of Cs adsorption vessel. These data indicate the risk of localized corrosion of Cs adsorption vessel may stay at considerably low level.
Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.457 - 461, 2021/12
The Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F) have been exposed to a corrosive environment containing seawater components under irradiation condition. In such conditions, the hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H
) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H O
O concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N
concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O
gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O and H
and H O
O concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O
concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O and H
and H O
O as well as that of carbon steel in the O
as well as that of carbon steel in the O and H
and H O
O coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
Miyazaki, Yasunori; Sano, Yuichi
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (112), p.27 - 32, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Ogawa, Toru
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.37 - 45, 2021/10
Zeolite adsorbents are to be used for decontamination of radioactive water in Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station. Evaluation of hydrogen production by water radiolysis during decontamination is important for safe operation. Thus hydrogen production from the mixture of zeolite adsorbents and seawater was studied because seawater was urgently used as a coolant for the fuels. The hydrogen yield from the mixture decreased at a high weight fraction of zeolites. However, the measured yield was higher than the yield expected from the direct radiolysis of seawater in the mixture, which would decrease proportional to the weight fraction of seawater. The result suggests that the radiation energy deposited to zeolites was involved in the hydrogen formation. From the results, the hydrogen production rate was evaluated to be 3.6 mL/h per ton of radioactive water before decontamination. After the process, it was evaluated to be 1.5 L/h per ton of waste adsorbents due to the high dose rate.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-001, 123 Pages, 2021/06
In the implement of the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), there are many problems to be solved. Specially, the mitigation of the aging degradation by the corrosion of the structural materials is important to implement the decommissioning safely and continuously. However, there are limited data for the environmental factors of corrosion in 1F, and the condition of 1F is continuously changing. So, the literature data for the water radiolysis and the corrosion under irradiation are listed as the database of corrosion under irradiation in this report. And the new obtained radiolysis and corrosion data, which have not been reported in the literature and will be required in the decommissioning of 1F, are reported.
Miyazaki, Yasunori; Sano, Yuichi; Okamura, Nobuo; Watanabe, Masayuki; Koka, Masashi*
QST-M-29; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2019, P. 72, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Cantarel, V.; Arisaka, Makoto; Yamagishi, Isao
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 102(12), p.7553 - 7563, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:52.00(Materials Science, Ceramics)The hydrogen gas (H ) production of wasteforms is a major safety concern for encapsulating nuclear wastes. For geopolymers, the H
) production of wasteforms is a major safety concern for encapsulating nuclear wastes. For geopolymers, the H produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the hydrogen production was measured under
produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the hydrogen production was measured under  Co gamma irradiation. The effect of water saturation and sample size were studied for pure geopolymers, or using zeolites as an example waste. When geopolymer monolithic samples were large and saturated by water, the hydrogen released was measured up to two orders of magnitude lower with a 40 cm long cylinder samples (1.9
Co gamma irradiation. The effect of water saturation and sample size were studied for pure geopolymers, or using zeolites as an example waste. When geopolymer monolithic samples were large and saturated by water, the hydrogen released was measured up to two orders of magnitude lower with a 40 cm long cylinder samples (1.9 10
10 mol/J) than a sample in powder form (2.2
mol/J) than a sample in powder form (2.2 10
10 mol/J). To interpret results, a simple model was used, considering only hydrogen production, a potential recombination and its diffusion in the geopolymer matrix. Knowing the diffusion constant of the matrix, the model was able to reproduce the evolution of the hydrogen release as a function of the water saturation level and predict the evolution when sample size is increased up to 40 cm.
mol/J). To interpret results, a simple model was used, considering only hydrogen production, a potential recombination and its diffusion in the geopolymer matrix. Knowing the diffusion constant of the matrix, the model was able to reproduce the evolution of the hydrogen release as a function of the water saturation level and predict the evolution when sample size is increased up to 40 cm.
Watanabe, Takashi*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ozawa, Osamu*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Akahori, Tomoyuki*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 2019 International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW 2019) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/06
Radiation hard image sensors have been developed past decades among the world. Almost papers discussed properties before and after radiation but images during radiation were not described yet. We have developed a new type of rad-hard pixel and integrated to 1.3M-pixel, 18-bit digital CMOS image sensor. Pixel area consists of several types of variation and the sensor has been analyzed during gamma ray radiation higher than 1 kGy/h up to 200 kGy. As the result, one type of pixel showed almost zero dark current increase at whole period.
Sato, Fuminori; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Ito, Yoshiyuki
QST-M-16; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2017, P. 60, 2019/03
Hydrogen gas generation by  -radiation from cement solidified products loading low-level radioactive liquid waste generated at LWTF in Tokai Reprocessing Facility was studied.
-radiation from cement solidified products loading low-level radioactive liquid waste generated at LWTF in Tokai Reprocessing Facility was studied.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Iida, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Osamu*; Shibagaki, Taro*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
QST-M-16; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2017, P. 67, 2019/03
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Keisuke; Wakaida, Ikuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
A high-radiation resistant optical fiber has been developed in order to investigate the interiors of the reactor pressure vessels and the primary containment vessels at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The tentative dose rate in the reactor pressure vessels is assumed to be up to 1 kGy/h. We developed a radiation resistant optical fiber consisting of a 1000 ppm hydroxyl doped pure silica core and 4 % fluorine doped pure silica cladding. We attempted to apply the optical fiber to remote imaging technique by means of fiberscope. The number of core image fibers was increased from 2000 to 22000 for practical use. The transmissive rate of infrared images was not affected after irradiation of 1 MGy. No change in the spatial resolution of the view scope by means of image fiber was noted between pre- and post-irradiation. We confirmed the applicability of the probing system, which consists of a view scope using radiation-resistant optical fibers.