Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Masatoshi; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-001, 32 Pages, 2008/02
We have developed the probabilistic assessment code system (PASCLR ver.2) for derivation of clearance levels of radioactive materials for the uranium and transuranium (TRU) wastes. This code supports the dose estimation for the exposure pathways in two different scenarios; landfill disposal as industrial waste and recycle or reuse of materials. Thirty one external exposure pathways were considered in the two scenarios. The irradiation geometry for specific individuals in the external exposure pathways are divided into anteroposterior, isotoropic and rotational conditions. We employed the EGS4 code to estimate the effective dose buildup factors of these irradiation conditions for QAD-CGGP2 code. This report provides estimated values of the effective dose buildup factors, and the calculating process and the results of the external effective dose conversion factors with QAD-CGGP2 code.
Ebina, Takanori*; Oi, Takao
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-002, 53 Pages, 2008/03
In order to obtain the information concerning the safety of the geological disposal, the sensitivity analysis considers the uncertainty of parameters resulting from the insufficiency of knowledge and information plays an important role. TIGER allows the physical and chemical properties within the system to vary with time and this function is useful for understanding the effect of the property change in sensitivity analysis. Therefore, at this study, some typical processing methods with the engineered barrier system and the host rock were developed, and through the comparison with the calculation time, the step of processing, the most suitable method was considered. After this, the interrelation between the calculation accuracy and the calculation time was examined for the purpose of using this method to the uncertain analysis. Through this consideration, the information of the best processing method, the calculation accuracy, and the analysis tool was arranged for an uncertain analysis used TIGER.
Sasaki, Toshihisa; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Takeda, Seiji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Ochiai, Toru; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-003, 29 Pages, 2008/02
In this report, external effective dose conversion factors necessary for examining the activity concentration limits are derived for three disposal concepts. After this, the activity concentration limits that constitute a permissible range of radioactive concentration to typical land disposal concept (for radioactive wastes containing transuranic nuclides from reprocessing and MOX fuel manufacturing and uranium waste from enrichment and fuel manufacturing) are calculated. External effective dose conversion factors are derived in consideration with analysis that conforms to laws that use the conversion coefficients of ICRP Publication 74 for effective dose conversion, and adoption of the latest data i.e.  -ray's and X-ray's energies and intensities of "JAERI-Data/Code 2001-004" as photon energy data. This document summarizes calculation method, conditions, and results of external effective dose conversion factors for transuranium and uranium wastes disposal.
-ray's and X-ray's energies and intensities of "JAERI-Data/Code 2001-004" as photon energy data. This document summarizes calculation method, conditions, and results of external effective dose conversion factors for transuranium and uranium wastes disposal.
Liu, Q.; Muramatsu, Ken; Uchiyama, Tomoaki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-004, 70 Pages, 2008/03
SECOM2-DQFM is developed for seismic reliability analysis of complex engineering systems, such as nuclear power plants. Suppose that the seismic hazard curve of the location site of a plant, the fault tree model and the event tree model of this plant are known. If the capacities and responses of components are available, the conditional occurrence probability (and frequency) of the top event of the fault tree model can be estimated by using SECOM2-DQFM. In addition, the importance of each basic event as well as the occurrence probability (and frequency) of each accident sequence can also be calculated. One feature of SECOM2-DQFM is that the method of Direct Quantification of Fault Tree using Monte Carlo simulation (DQFM) is adopted to evaluate the concurrent failure probability of multiple components. This report is summarized as the user manual of SECOM2-DQFM.
Liu, Q.; Muramatsu, Ken; Uchiyama, Tomoaki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-005, 76 Pages, 2008/03
SECOM2-DQFM is developed for seismic reliability analysis of complex engineering systems, such as nuclear power plants. Given that the seismic hazard curve of the location site of a plant, the fault tree and event tree models of this plant were known, if the capacities and responses of components were available, the conditional occurrence probability (or frequency) of the top event of the FT models could be estimated by using SECOM2-DQFM. In addition, the importance of each basic event as well as the occurrence frequency of each accident sequence could also be obtained. Further, the concurrent failure probability of multiple components due to earthquake is considered in SECOM2-DQFM by using the method of Direct Quantification of Fault Tree with Monte Carlo simulation. This report is the English translation of the Japanese version of the user's manual of SECOM2-DQFM.
Kawachi, Susumu; Oi, Takao; Kawamura, Makoto; Ishihara, Yoshinao*; Ebina, Takanori*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-006, 55 Pages, 2008/03
The investigation and studies of site-specific geological conditions provide much information and data. A system for managing and integrating the technical information was developed (JGIS: JAEA Geological Disposal Information Integration System). In this study we built the conceptual design in order to implement the function of quality management and project management to JGIS. We considered that researchers could access the portal site of the research projects which were set as the WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) items and could confirm which WBS item the research project belonged to in the whole plan. We also considered that the research projects could be managed by using the conformity sheets which were adopted in the quality management system.
Suyama, Tadahiro; Ueno, Kenichi; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-007, 39 Pages, 2008/03
To evaluate long term corrosion behavior of carbon steel in compacted bentonite, experiment was carried out using artificial seawater and groundwater at 50 C and 80
C and 80 C for 10 years. In this study, alteration behavior of bentonite for Fe-bentonite interaction was investigated for compacted bentonite after this experiment. Until now, batch experiment carried out to change temperature, solution and period to understand behavior of altered bentonite contacted with iron. These result showed a change for Fe-type smectite and alteration of non-expandable clay mineral. But, in this study, initial Na-type smectite did not exchange after experiment, while it was confirmed that iron permeated in compacted bentonite. Therefore, for estimation of influence that is interaction of Fe-bentonite on compacted condition like a repository, it is important to estimate sufficiently understanding phenomenon for compacted bentonite, not to adapt directly to batch experimental results.
C for 10 years. In this study, alteration behavior of bentonite for Fe-bentonite interaction was investigated for compacted bentonite after this experiment. Until now, batch experiment carried out to change temperature, solution and period to understand behavior of altered bentonite contacted with iron. These result showed a change for Fe-type smectite and alteration of non-expandable clay mineral. But, in this study, initial Na-type smectite did not exchange after experiment, while it was confirmed that iron permeated in compacted bentonite. Therefore, for estimation of influence that is interaction of Fe-bentonite on compacted condition like a repository, it is important to estimate sufficiently understanding phenomenon for compacted bentonite, not to adapt directly to batch experimental results.
Hayashi, Maki*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Hideki
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-008, 17 Pages, 2008/03
In geological disposal system, high-level radioactive waste (HLW) glass is expected to retain radionuclide for the long term as the first barrier to prevent radionuclide release. The advancement of its performance assessment technology leads to the reliability improvement of the safety assessment of entire geological disposal system. For this purpose, phenomenological studies for improvement of scientific understanding of dissolution/alteration mechanisms, and development of robust dissolution/alteration model based on the study outcomes are indispensable. The database on glass dissolution has been developed for supporting these studies. This report describes improvement of the prototype glass database. Also, this report gives an example of the application of the database for verification of glass dissolution model.
Sukegawa, Takenori; Shimada, Taro; Shiraishi, Kunio; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Ishigami, Tsutomu
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-009, 57 Pages, 2008/03
We developed the RADO code system for evaluating residual radioactive inventory in decommissioning of nuclear reactor. The code system consists of computer programs which calculate macroscopic effective cross section, neutron flux, and radioactive inventory. This report describes an evaluation method of radioactive inventory, structure and functions of RADO, input and output of RADO, and sample run with RADO.
Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Asakura, Toshihide; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-010, 145 Pages, 2008/04
A computer code PARC was developed for simulating liquid-liquid extraction process in the PUREX reprocessing plant. PARC is able to predict transient behavior and profiles at equilibrium of uranium, plutonium, neptunium and fission products in several units of pulsed columns and mixer-settlers, which are connected each other in the PUREX plant. In this report, mathematical models of mass transfer and chemical reactions employed in PARC are described and an example of PUREX simulation is given.
Fukaya, Yuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-011, 44 Pages, 2008/05
The assistance interface of calculation for innovative water reactor for flexible fuel cycle (FLWR) had been developed. The interface system should have an ability to display the output of core calculation code, graphically and simply. Generally, nuclear reactor analysis codes, e.g, SRAC, has text base interface. Input and output using text files have high flexibility to use for research of various objectives. However, for a single objective, the text base interface complicates to understand the result of analysis, because almost only the condition of fuel composition would be changed, and the other conditions, e.g, geometry data, would be fixed. In this case, the manipulation of the output wastes the time. Therefore, the interface which can easily treat the output data is very useful. Moreover, the interface provides the function to illustrate the result intuitively. Thus the outcome of developing the EVIRA code is benefit for the research on FLWR.
Otsuka, Naohiko*; Zukeran, Atsushi*; Takano, Hideki*; Chiba, Go; Ishikawa, Makoto
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-012, 17 Pages, 2008/06
A computer code, ERRORF, was developed for calculation of covariance of self-shielding factor and its temperature gradient. This code is based on several modules. With this code, covariance of self-shielding factor and its temperature gradient can be calculated from evaluated nuclear library in the ENDF format.
Funaki, Hironori; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Ishii, Eiichi; Hatsuyama, Yoshihiro*; Matsuo, Shigeaki*; Tsuda, Kazuyasu*; Koizumi, Akira*; Ishikawa, Taiki*; Daijo, Yuichi*; Sugiyama, Kazutoshi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-013, 65 Pages, 2008/08
We conducted geological investigation of the pilot borehole of the ventilation shaft in Horonobe during October 2007 and March 2008. This report describes the field operations (core description, core photograph, and core sampling) and laboratory measurements (modal analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis), equipments as well as processing procedures, and shows the obtained results. The information obtained from this investigation will be reflected in spring water control plan on shaft excavation and additional plan of drainage treatment facilities.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-014, 118 Pages, 2008/07
A steam explosion occurs when hot liquid contacts with cold volatile liquid. In this phenomenon, fine fragmentation of the hot liquid causes extremely rapid heat transfer from the hot liquid to the cold volatile liquid, and explosive vaporization, bringing shock waves and destructive forces. The steam explosion due to the contact of the molten core material and coolant water during severe accidents of light water reactors has been regarded as a potential threat to the integrity of the containment vessel. We developed a mechanistic steam explosion simulation code, JASMINE, that is applicable to plant scale assessment of the steam explosion loads. This document, as a manual for users of JASMINE code, describes the models, numerical solution methods, and also some verification and example calculations, as well as practical instructions for input preparation and usage of the code.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Takeda, Tetsuaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-015, 94 Pages, 2008/10
A reactor kinetics analysis code called the TAC/BLOOST code was developed for High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors (HTGRs). The TAC/BLOOST code can use a divided core model with region temperature coefficients. In this study, a validation of the TAC/BLOOST code was conducted with the experimental data of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). As a result, some improved points of the property changes of the fuels and the structures according to the burnup effect, the gap changes among the blocks, the gap changes between the fuel compact and the graphite sleeve, and the cross section changes of the coolant were clarified. Moreover, prediction analyses of the gas circulator tripping tests can be showed within 3% accuracy.
Sato, Kaoru; Endo, Akira; Saito, Kimiaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-016, 173 Pages, 2008/10
At the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, high-resolution five Japanese adult voxel phantoms have been constructed up to now to clarify the variation of organ doses due to the anatomical characteristics of Japanese. This report presents a complete set of conversion coefficients of organ doses and effective doses calculated for external photon exposure using five Japanese voxel phantoms. The calculated conversion coefficients are compared with those of Caucasian voxel phantoms and the recommended values in ICRP74 in order to discuss variation of organ doses due to the body size and individual anatomy, and effect of posture on organ doses. The present report provides valuable data to study the influence of the body characteristics of Japanese upon the organ doses and to discuss developing reference Japanese and Asian phantoms.
Saegusa, Jun
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-017, 72 Pages, 2008/10
The representative point method is a novel method which enables efficiency calibrations with a standard point source. A calculation code for implementing the method has been developed. The code is named CREPT-MCNP ((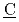 )alibration Code for the (
)alibration Code for the (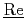 )presentative (
)presentative (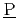 )oin(
)oin(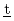 ) Method with MCNP). The code estimates the position of the representative point which is intrinsic to each shape of volume sample, and also gives the self-absorption factors to make correction on the efficiencies measured at the representative point with a standard point source. It can deal with photons between 20 keV and 2 MeV with p- or n-type germanium semiconductor detectors. CREPT-MCNP can be operated under the Windows PC environment as a GUI based application. This manual describes features of CREPT-MCNP code.
) Method with MCNP). The code estimates the position of the representative point which is intrinsic to each shape of volume sample, and also gives the self-absorption factors to make correction on the efficiencies measured at the representative point with a standard point source. It can deal with photons between 20 keV and 2 MeV with p- or n-type germanium semiconductor detectors. CREPT-MCNP can be operated under the Windows PC environment as a GUI based application. This manual describes features of CREPT-MCNP code.
Nakada, Akira; Miyauchi, Toru; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Momose, Takumaro; Kozawa, Tomoyasu*; Yokota, Tomokazu*; Otomo, Hiroyuki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-018, 134 Pages, 2008/10
This report provides the data set of atmospheric discharges from Tokai reprocessing plant in Tokai-mura, Japan over the period from 1998 to 2007. Daily and weekly data are shown for  Kr that is continuously monitored and for the other nuclide (Alpha emitters, Beta emitters,
Kr that is continuously monitored and for the other nuclide (Alpha emitters, Beta emitters,  H,
H,  C,
C,  I,
I,  I) whose activities are evaluated based on weekly batch-samplings, respectively. The data contained in this report are expected to apply for studying the behavior of the radioactive airborne effluent in the environment.
I) whose activities are evaluated based on weekly batch-samplings, respectively. The data contained in this report are expected to apply for studying the behavior of the radioactive airborne effluent in the environment.
Sato, Koichi; Seki, Fumiko*; Hasegawa, Shiori*; Sengoku, Akio; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Koizumi, Koichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-019, 43 Pages, 2008/09
On October 24th, 2007, the Agreement on the Establishment of the ITER International Fusion Energy Organization for the Joint Implementation of the ITER Project (the "ITER Agreement") came into force, and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was appointed to a Domestic Agency (DA). The DA will contribute to the ITER construction in cooperation with ITER Organization (IO) where many ITER-specific technical terms and abbreviations were used. This book is a collection of those terms and abbreviations translated to Japanese.
Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-020, 188 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency promotes development of innovative analysis methods and models in fundamental studies for next-generation nuclear reactor systems. In order to efficiently and effectively reflect the latest analysis methods and models to primary design of prototype reactor and/or in-core fuel management for power reactors, a next-generation analysis system MARBLE has been developed. In this study, detailed design of a framework, its implementation and tests are conducted so that a Python system layer can drive calculation codes written in C++ and/or Fortran. It is confirmed that various type of calculation codes such as diffusion, transport and burnup codes can be treated in the same manner on the platform for unified management system for calculation codes with a data exchange mechanism for abstracted data model between the Python and the calculation code layers.
Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Yokoyama, Kenji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-021, 110 Pages, 2008/10
Development of burnup analysis system for fast reactors with modularity and flexibility is being done that would contribute to actual core design work and improvement of prediction accuracy. In the previous study on "Development of Burnup Analysis System for Fast Reactors (2)" in FY2006, design and implementation of models for detailed geometry of assembly, fuel loading pattern and so on, accompanied with specification and implementation of input file handling to construct data models. In this study, a prototype system has been implemented in which functionalities are embedded for calculation of macroscopic cross section, core calculation and burnup calculation applying the fruits of the study "Development of a Framework for the Neutronics Analysis System for Next Generation (2)". It also implements a fuel reloading/shuffling function controlled with simple description in user input for multi-cycle burnup analysis.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Sugawara, Takanori; Kosako, Kazuaki*; Fukahori, Tokio
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-022, 18 Pages, 2008/11
The latest JENDL High Energy File (JENDL/HE) was released in 2007 to respond the requirements of reaction data in high energy range up to several GeV to design accelerator facilities such as accelerator-driven systems and research complex like J-PARC. To apply the JENDL/HE-2007 file to the design study, the cross section library of FXJH7 series was constructed from the JENDL/HE file for the calculation using MCNP and MCNPX codes which are widely used in the field of nuclear reactors, fusion reactors, accelerator facilities, medical applications, and so on. In this report, the outline of the JENDL/HE-2007 file, modification of nuclear data processing code NJOY99, construction of FXJH7 library and test calculations for shielding and eigenvalue analyses are summarized.
Yamazaki, Masanao; Funaki, Hironori; Yamaguchi, Takehiro*; Niinuma, Hiroaki; Fujikawa, Daisuke; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Hiraga, Naoto; Tsusaka, Kimikazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-023, 136 Pages, 2008/11
This report summarizes the measurements data acquired at the Ventilation Shaft, the East Shaft and the drifts in 2007 based on the Observational Construction Program. The report summarizes for the purpose of the followings: sharing the investigation and measurements data, preventing the loss of them and acquisition the basic data for carrying out the Observational Construction Program.
Yoshikawa, Shinji; Minami, Masaki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-024, 28 Pages, 2009/01
A series of information required for numerical simulation of sodium thermal stratification observed at the plant trip test of "Monju" conducted in 1995 is provided, which consists of the test outline, geometry data of the reactor vessel upper plenum between the reactor core top and reactor outlet nozzles, and flow inlet boundary conditions at the reactor core top surface.
Soukhovitski, E.*; Chiba, Satoshi; Capote, R.*; Quesada, J.*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Morogovskij, G.*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-025, 55 Pages, 2008/12
A coupled-channel code to calculate nuclear cross sections, OPTMAN, has been improved after OPTMAN version 8 was published as JAERI-Data/Code 2005-002. The most important addition is the inclusion of dispersive relationships between imaginary and real parts of the optical potential within a Lane consistent formalism. The obtained CCOM potentials allow for the description of nucleon induced reactions up to 200 MeV, including (p,n) reactions with excitation of isobaric analog states. Relativistic corrections consistent with those used in the ECIS06 code are also added.
Yabuuchi, Satoshi; Kunimaru, Takanori; Ishii, Eiichi; Hatsuyama, Yoshihiro*; Ijiri, Yuji*; Matsuoka, Kiyoyuki*; Ibara, Tetsuo*; Matsunami, Shinjiro*; Makino, Akiya*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-026, 62 Pages, 2009/02
The Pilot Borehole Investigation of the Ventilation Shaft was conducted in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan from October 2007 to March 2008. Main purpose of the investigation is to understand geological, hydrogeological and hydrochemical properties of the formation where the Ventilation Shaft has been excavated. Hydraulic packer tests show that hydraulic conductivity lies in the range from 1.1E-11 to 1.4E-7 m/sec down to 500 m in depth. This heterogeneity mainly depends on the distribution and permeability of groundwater inflow points, which were detected by Fluid Electric Conductivity logging. High conductive zones were found between 263 m and 290 m, 355 m and 370 m of the depth in the pilot borehole. An effective method for reducing groundwater inflow should be considered for the deeper Ventilation Shaft excavation.
Iwai, Yasunori; Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Tamada, Masao
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-027, 69 Pages, 2009/02
This document presents the radiation durability of various polymeric materials applicable to a solid-polymer-electrolyte (SPE) water electrolyzer in the tritium facility of fusion reactor. In the ITER, an electrolyzer should keep its performance during two years operation in the tritiated water of 9 TBq/kg. The condition corresponds to the irradiation of no less than 530 kGy. In this study, the polymeric materials were irradiated with  -rays or with electron beams at various conditions up to 1600 kGy at room temperature or at 343 K. The change in mechanical and functional properties were investigated by stress-strain measurement, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS), and so on. Our selection of polymeric materials for a SPE water electrolyzer used in a radiation environment was Pt + Ir applied Nafion N117 membrane, VITON O-ring seal and polyimide insulator.
-rays or with electron beams at various conditions up to 1600 kGy at room temperature or at 343 K. The change in mechanical and functional properties were investigated by stress-strain measurement, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS), and so on. Our selection of polymeric materials for a SPE water electrolyzer used in a radiation environment was Pt + Ir applied Nafion N117 membrane, VITON O-ring seal and polyimide insulator.
Tanai, Kenji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-028, 15 Pages, 2009/02
Carbon steel is a candidate material for an overpack for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in Japan. The corrosion of the carbon steel overpack in aqueous solution under anoxic conditions will cause the generation of hydrogen gas, which may affect hydrological and mechanical properties of the bentonite buffer. To evaluate such an effect of gas generation, it is necessary to develop a model of gas migration through bentonite buffer material taking account of data obtained from experiments. The gas migration experiments under both unsaturated and saturated conditions have been carried out to clarify the fundamental characteristics of bentonite for gas migration. This report compilles the experimental data obtained from gas migration tests for buffer material which has been conducted by JAEA until December, 2007.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Okumura, Keisuke; Katakura, Junichi; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-029, 24 Pages, 2009/02
The continuous energy cross section library for the Monte Carlo transport code MCNP, JAC08T1, has been generated from the latest version of Japanese evaluated nuclear data library JENDL/AC released in March, 2008. The latest version of NJOY (NJOY99.259), the evaluated nuclear data processing system, has been employed to produce the library after necessary modifications in order to process JENDL/AC.
Kato, Shoichi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yoshida, Eiichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-030, 89 Pages, 2009/02
Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel is a candidate for structural materials of future advanced Fast Breeder Reactors (FBR), because of good thermal properties and high creep strength. Material test of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel, which was candidated for structure materials of the future advanced FBR has been performed in Technology Development Department. In this report, the result of test obtained up to this time was collected.
Hato, Shinji; Terakado, Masato*; Tomita, Kenichi*; Homma, Toshimitsu
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-031, 75 Pages, 2009/03
This is the user's manual of DSYS-GUI, which calculates the internal dose coefficients by the models of International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). The DSYS-GUI consists of two programs. One is a program for setting calculation conditions and executing. The other is a program for displaying results to figures and tables. The displaying them are used the Microsoft Excel. Anyone can easily calculate the internal dose coefficients and quickly display results as figures and tables with DSYS-GUI.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Nakamura, Ario*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-032, 13 Pages, 2009/03
In geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, overpack is required to prevent vitrified waste from the contacting groundwater with during a certain period of time. At present, the period is defined as 1000 years for complete containment and developments of technologies for design, manufacturing and quality assurance and researches for improving long-term performance have been carried out. Each R&D results have been published as a reports or journal papers by each individual institute. However, it is necessary to integrate these results so as to develop a practical knowledge base that would be useful for design of an overpack for a specific repository site, establishment of the codes and standards or other general purposes. Accordingly, we have been developing a database, which integrate R&D results on design concepts of overpack, technologies for design and manufacturing, test data of the characteristics as an overpack and so on. This report presents a current status of the overpack database using a commercial application software basic structure and an example of a menu for the database.
Katata, Genki
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-033, 64 Pages, 2009/02
In order to predict energy and water balances between the biosphere and atmosphere accurately, sophisticated schemes to calculate evaporation and adsorption processes in the soil and cloud (fog) water deposition on vegetation were implemented in the one-dimensional atmosphere-soil-vegetation model including CO exchange process (SOLVEG2). Performance tests in arid areas showed that the above schemes have a significant effect on surface energy and water balances. The framework of the above schemes incorporated to the SOLVEG2 and instruction for running the model are documented. With further modifications of the model to implement the carbon exchanges between the vegetation and soil, deposition processes of materials on the land surface, vegetation stress-growth-dynamics etc., the model is suited to evaluate environmental loads to ecosystems by atmospheric pollutants and radioactive substances under climate changes such as global warming and drought.
exchange process (SOLVEG2). Performance tests in arid areas showed that the above schemes have a significant effect on surface energy and water balances. The framework of the above schemes incorporated to the SOLVEG2 and instruction for running the model are documented. With further modifications of the model to implement the carbon exchanges between the vegetation and soil, deposition processes of materials on the land surface, vegetation stress-growth-dynamics etc., the model is suited to evaluate environmental loads to ecosystems by atmospheric pollutants and radioactive substances under climate changes such as global warming and drought.
Tachi, Yukio; Tochigi, Yoshikatsu; Suyama, Tadahiro; Saito, Yoshihiko; Ochs, M.*; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-034, 36 Pages, 2009/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing databases of sorption and diffusion parameters in buffer material and rock, which are key parameters for safety assessment of the geological disposal. The new web-based sorption and diffusion database system (JAEA-SDB/DDB) has been developed to utilize quality assuring procedure and to allow effective application for parameter setting, based on the existing database. In the present report, practical examples were illustrated regarding the applicability of the database system to the parameter setting by using additional functions such as QA information and parameter estimation. This database system is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data from the database, and to have suitable access to the respective data for parameter-setting for performance assessment and parameter-deriving for mechanistic modeling in traceable and transparence manner.
Tochigi, Yoshikatsu; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-035, 57 Pages, 2009/02
The database for utilizing the data related to the diffusion coefficient of nuclides in the buffer material and rock was improved on the basis of the existing diffusion database. Renewals of database definition include maintenance of database contents, extension of stored data scope, etc. The database was updated with especially emphasis on introduction of estimated value in data evaluation and description concerning reliability of information. Existing data of domestic rock were updated by implementation of the result of literature survey in accordance with the definition of updated database and new data of domestic bentonite. As the result of data addition, total data count of effective diffusion coefficient is about 450 and that of apparent diffusion coefficient is about 1,350. As an example of practical use of the improved database, the example of evaluation for the plot of a diffusion coefficient of dry density or porosity was discussed.