Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Keya, Hiromichi; Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-001, 49 Pages, 2019/03
A wide range of geoscientific research aims to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock. The Regional Hydrogeological Study (RHS) project is a one of the geoscientific research program at Tono Geoscience Center. This project started since April 1992 and main investigations were finished to March 2004. Since 2005, hydrogeological and hydrochemical monitoring have been continued using the existing monitoring system. This report describes the results of the long term hydro-pressure monitoring from April 2017 to March 2018.
Kato, Tomoko; Fukaya, Yukiko*; Sugiyama, Takeshi*; Nakai, Kunihiro*; Oda, Chie; Oi, Takao
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-002, 162 Pages, 2019/03
The radioactive waste generated from Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station (FDNPS) accident have features such as wide range of radioactivity level (from low to high) and huge amount etc. It would be necessary for the waste from the FDNPS accident to develop suitable disposal concept and to be disposed safely and reasonably. When considering such appropriate disposal concepts in site-generic phase, it is necessary to appropriately develop models and parameters depending on the disposal concepts, such as disposal depth and specification of engineered barrier. In addition, it is desirable to evaluate the safety of repository with common models and parameters independent on the disposal concepts. In the safety assessment of disposal, it is useful to show the difference in performance of repository with "dose" as an indicator of safety assessment. Biosphere model and parameter set and flux-to-dose conversion factors calculated using them are originally dependent on the disposal concepts. However, the biosphere models and the parameter set in safety assessment of near-surface disposal, sub-surface disposal and geological disposal are prepared in each case, and are different according to the age and purpose of the discussion. In this study, an example of biosphere model and parameter-set of groundwater sceinario commonly applicable to various disposal concepts were shown, to calculate flux-to-dose conversion factors, as common indicators independent to disposal concept. And, a set of flux-to-dose conversion factors was also calculated by using the commonly available biosphere model and parameter set. By applying the flux-to-dose conversion factors, it is possible to compare the performance of disposal concepts to the waste generated from FDNPS accident, focusing on the parts depending on the disposal concepts.
Nakayama, Masashi; Ono, Hirokazu; Nakayama, Mariko*; Kobayashi, Masato*
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-003, 57 Pages, 2019/03
The Horonobe URL Project has being pursued by JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. The URL Project consists of two major research areas, Geoscientific Research and Research and Development on Geological Disposal Technologies, and proceeds in 3 overlapping phases, Phase I: Surface-based investigations, Phase II: Investigations during tunnel excavation and Phase III: Investigations in the URL, over a period of around 20 years. Phase III investigation was started in 2010 FY. The in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system had been prepared from 2013 to 2014 FY at GL-350 m gallery, and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack had started in January, 2015. One of objectives of the experiment is acquiring data concerned with THMC coupled behavior. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. This report summarizes the measurement data acquired from the experiment from December, 2014 to March, 2018. The summarized data of the EBS experiment will be published periodically.
Haraga, Tomoko; Shimomura, Yusuke; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-004, 48 Pages, 2019/10
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Hashidate, Ryuta; Kato, Shoichi; Kurihara, Akikazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-005, 117 Pages, 2019/07
SUS316 and SUS321 are used for structural materials of the Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs), because of excellent high creep strength. This report summarized the mechanical properties data on SUS316 and SUS321 obtained in various tests including the long-term material tests and the material tests in sodium.
Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-006, 17 Pages, 2019/07
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NOx) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NOx with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis program has been developed to simulate chemical reaction coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building.
Sakai, Toshihiro; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-007, 29 Pages, 2019/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is performing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project, which includes a scientific study of the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for the geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes, in order to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in the sedimentary rock. This report summarize numerical data of 3D geological model in regional-scale constructed by Maptek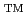 Vulcan
Vulcan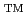 .
.
Samata, Yoichi; Iwata, Tatsuya*; Ishii, Eiichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-008, 19 Pages, 2019/09
In Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project, hydraulic tests for the excavation damaged zone have been performed in order to characterize the hydrological properties of the zone. In PB-V01 borehole, pore pressure observation started in October 2008, but the pore pressure is currently reduced by about 3 MPa compared to that time. In this report, in order to evaluate the influence that this pore pressure drop has on the permeability of the rock, the results of the in-situ permeability test using the long-term hydraulic pressure monitoring device installed in the same hole are summarized.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-009, 22 Pages, 2019/10
Tono Geoscience Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). As for The MIU Project (Phase II) was carried out from 2004 fiscal year, and has been started the Phase III in 2010 fiscal year. The groundwater inflow monitoring into shafts and research galleries, has been maintained to achieve the Phase II goals, begins in 2004 fiscal year and follows now. This document presents the results of the groundwater inflow monitoring from fiscal year 2016 to 2018.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-010, 41 Pages, 2019/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a wide range of geoscientific research in order to build scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of nuclear wastes. This study aims to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock. The Regional Hydrogeological Study (RHS) project is a one of the geoscientific research program at Tono Geoscience Center. This project started since April 1992 and main investigations were finished to FY 2004. Since FY 2005, hydrogeological and hydrochemical monitoring have been continued using the existing monitoring system. This report describes the results of the long term hydro-pressure monitoring from April 2018 to March 2019.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Takino, Kazuo
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-011, 110 Pages, 2020/01
A deterministic discrete ordinates method (SN method) transport calculation code for three-dimensional hexagonal geometry has been developed as the MINISTRI code (Ver. 7.0). MINISTRI is based on the triangle-mesh finite difference method, which can perform neutron transport calculations with high accuracy for cores of fast power reactors and assemblies of the Russian BFS critical facility. The present study has derived a proper scheme for remarkably improving the convergence of MINISTRI by investigating the issue of previous MINISTRI (Ver. 1.1), which sometimes plays a poor convergence performance in calculations for large-scale power reactor cores. The verification test of improved MINISTRI has been carried out for various cores by setting the reference result as the multi-group Monte-Carlo calculation with the same cross-sections as used in MINISTRI. As a result, it is found that the agreements are within 0.1% for eigenvalues and within 0.7% for power distributions. Thus, the satisfying accuracy of MINISTRI has been confirmed. In order to reduce the calculation time, the initial diffusion calculation scheme and the parallel processing have been implemented. As a result, the calculation time is reduced to the approximately one tenth compared with previous MINISTRI. Furthermore, adoption of the treatment of the anisotropic cell streaming effect, preparation of the perturbation calculation tool, implementation of the function for specification of the triangle-mesh-wise material and merging of the hexagonal-mesh calculation code MINIHEX have been carried out. Thus, the versatility of MINISTRI has been enhanced.
Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-012, 70 Pages, 2020/02
It is necessary to establish practical evaluation methods to determine radioactivity concentration of radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from Post Irradiation Examination Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Miyara, Nobukatsu; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-013, 8 Pages, 2020/01
As part of the research and development program on the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW), the Horonobe Underground Research Center, a division of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), is implementing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Horonobe URL Project) with the aim at investigating sedimentary rock formations. This data collection is a compilation of Earthquake observation data acquired in the Horonobe Underground Research Project (Phase II).
Mochizuki, Akihito; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-014, 56 Pages, 2020/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "geoscientific study" and "research and development on geological disposal" in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) for safe geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Groundwater pressure and geochemical parameters such as pH and oxidation-reduction potential in the deep groundwater have been continuously monitored with monitoring systems which were developed in the Horonobe URL Project. This report presents the data of groundwater pressure which have been obtained by the monitoring systems installed at the 350 m gallery. The data obtained from April 1, 2016 until March 31, 2019 was summarized along with related information such as the specifications of boreholes and the excavation of the URL.
Morita, Yasuji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-015, 45 Pages, 2020/01
Decay heat from radioactive elements in high-level liquid waste (HLLW) and separated solutions in partitioning process was evaluated as a basic data for safety assessment of partitioning process. In the evaluation of HLLW from spent UO fuel burned-up to 45 GWd/t in light water reactor, decay heat value from fission products decreased as the cooling period become longer but heat from actinides, Am and Cm, was almost constant until 50-year cooling. Decay heat density in solutions of Am, Cm and rare earth elements and of Am and Cm without concentration for volume reduction does not exceed the heat density of HLLW, but the concentration should be required to minimize the scale of the partitioning process. Separated solution of Am and Cm must be concentrated to convert the two elements to a solid state to make fuel for transmutation, and the decay heat density of the concentrated solution of Am and Cm is 10 times higher compared with the Pu solution of same element concentration. Higher burn-up UO
fuel burned-up to 45 GWd/t in light water reactor, decay heat value from fission products decreased as the cooling period become longer but heat from actinides, Am and Cm, was almost constant until 50-year cooling. Decay heat density in solutions of Am, Cm and rare earth elements and of Am and Cm without concentration for volume reduction does not exceed the heat density of HLLW, but the concentration should be required to minimize the scale of the partitioning process. Separated solution of Am and Cm must be concentrated to convert the two elements to a solid state to make fuel for transmutation, and the decay heat density of the concentrated solution of Am and Cm is 10 times higher compared with the Pu solution of same element concentration. Higher burn-up UO fuel and MOX fuel in light water reactor and minor-actinide-recycled MOX fuel in fast reactor were also considered and the evaluated decay heat was compared among the spent fuels.
fuel and MOX fuel in light water reactor and minor-actinide-recycled MOX fuel in fast reactor were also considered and the evaluated decay heat was compared among the spent fuels.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Seki, Kotaro*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kochiyama, Mami; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-016, 72 Pages, 2020/02
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 25 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Mo,
Mo,  Tc,
Tc, 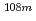 Ag,
Ag,  Sn,
Sn,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Development Group for LWR Advanced Technology
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-017, 59 Pages, 2020/03
ECUME (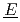 ffective
ffective 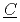 hemistry database of fission products
hemistry database of fission products 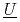 nder
nder 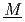 ultiphase r
ultiphase r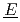 action) is the database for the analyses of FP chemistry which strongly affects all the FP behaviors in a severe accident (SA) of nuclear facility like LWR. ECUME consists of three kinds of datasets: CRK (dataset for
action) is the database for the analyses of FP chemistry which strongly affects all the FP behaviors in a severe accident (SA) of nuclear facility like LWR. ECUME consists of three kinds of datasets: CRK (dataset for 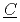 hemical
hemical 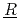 eaction
eaction 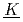 inetics), EM (
inetics), EM (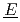 lemental
lemental 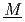 odel set) and TD (
odel set) and TD (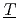 hermo
hermo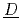 ynamic dataset). The present version of ECUME is prepared especially for the more accurate evaluation of cesium and iodine distribution in a reactor and release amount into an environment which should be of crucial importance towards the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (1F) and the enhancement of LWR safety after the 1F SA.
ynamic dataset). The present version of ECUME is prepared especially for the more accurate evaluation of cesium and iodine distribution in a reactor and release amount into an environment which should be of crucial importance towards the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (1F) and the enhancement of LWR safety after the 1F SA.
Aihara, Jun; Goto, Minoru; Ueta, Shohei; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-018, 22 Pages, 2020/01
Concept of Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) was proposed for purpose of more safely reducing amount of recovered Pu. In Pu-burner HTGR concept, coated fuel particle (CFP), with ZrC coated yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) containing PuO (PuO
(PuO -YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. On the other hand, we have developed Code-B-2.5.2 for prediction of pressure vessel failure probabilities of SiC-tri-isotropic (TRISO) coated fuel particles for HTGRs under operation by modification of an existing code, Code-B-2. The main purpose of modification is preparation of applying code for CFPs of Pu-burner HTGR. In this report, basic formulae are described.
-YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. On the other hand, we have developed Code-B-2.5.2 for prediction of pressure vessel failure probabilities of SiC-tri-isotropic (TRISO) coated fuel particles for HTGRs under operation by modification of an existing code, Code-B-2. The main purpose of modification is preparation of applying code for CFPs of Pu-burner HTGR. In this report, basic formulae are described.
Fukuda, Kenji; Watanabe, Yusuke; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Aosai, Daisuke*; Kumamoto, Yoshiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-019, 74 Pages, 2020/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the influence of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2018. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Samata, Yoichi; Ishii, Eiichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-020, 69 Pages, 2020/03
In Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project, hydraulic tests for the excavation damaged zone have been performed in order to characterize the hydrological properties of the zone. This report summarized the results of the hydraulic tests and pore-pressure monitoring which have been done from April 2016 to March 2019.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Mihara, Morihiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-021, 101 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption of radionuclides in cement and bentonite as engineered barrier materials, and rocks as natural barrier is the one of key processes in the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU and high-level waste. The magnitude of sorption, expressed normally by a distribution coefficient (K ), needs to be measured and determined taking into account the properties of barrier materials and geochemical conditions and associated uncertainty in the performance assessment. The basic concept for TRU waste disposal contains cementitious materials as an engineered barrier materials, in addition to bentonite and rock. It is therefore needed to consider the effects of the cement degradation and co-existing substances such as nitrates on radionuclide sorption. This report focused on data acquisition of distribution coefficient (K
), needs to be measured and determined taking into account the properties of barrier materials and geochemical conditions and associated uncertainty in the performance assessment. The basic concept for TRU waste disposal contains cementitious materials as an engineered barrier materials, in addition to bentonite and rock. It is therefore needed to consider the effects of the cement degradation and co-existing substances such as nitrates on radionuclide sorption. This report focused on data acquisition of distribution coefficient (K ) by batch sorption experiments for the systems coupling barrier material-chemical condition-radionuclides that are needed to consider for the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. The barrier materials considered are ordinary Portland cement (OPC), degraded OPC and tuff rock. The chemical conditions are distilled water and synthetic seawater equilibrated with OPC and those containing nitrates and ammonium salts, etc. The radionuclides considered are organic carbon, inorganic carbon, Cl, I, Cs, Ni, Se, Sr, Sn, Nb, Am and Th. Although K
) by batch sorption experiments for the systems coupling barrier material-chemical condition-radionuclides that are needed to consider for the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. The barrier materials considered are ordinary Portland cement (OPC), degraded OPC and tuff rock. The chemical conditions are distilled water and synthetic seawater equilibrated with OPC and those containing nitrates and ammonium salts, etc. The radionuclides considered are organic carbon, inorganic carbon, Cl, I, Cs, Ni, Se, Sr, Sn, Nb, Am and Th. Although K values have been partly reported previously as RAMDA (Radionuclide Migration Datasets) for the performance assessment in the TRU-2 report, these results and addition K
values have been partly reported previously as RAMDA (Radionuclide Migration Datasets) for the performance assessment in the TRU-2 report, these results and addition K data are reported with the details of experimental methods and conditions.
data are reported with the details of experimental methods and conditions.
Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-022, 40 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption behavior of radionuclides (RNs) in buffer materials, rocks and cementitious materials is one of the key processes in a safe geological disposal. This report focuses on updating of JAEA sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as a basis of integrated approach for the performance assessment (PA)-related distribution coefficient (K ) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K
) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K
data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K
setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K data from 60 references were added and the total number of K
data from 60 references were added and the total number of K values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K
values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K data reached about 72% for all K
data reached about 72% for all K data in JAEA-SDB.
data in JAEA-SDB.
Shibata, Hiroki; Saito, Hiroaki; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Takano, Masahide
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-023, 138 Pages, 2020/03
Transmutation of minor actinides in the form of nitride fuel by the accelerator driven system has been developed to reduce the radiotoxicity and volume in the radioactive wastes. Nitride fuel behavior under irradiation condition is necessary for its design and development. Nitride fuel performance analysis module based on light water reactor fuel performance code, FEMAXI-7, was developed by introducing fundamental properties of nitride pellet, 9Cr-1Mo ferrite cladding, and Pi-Bi coolant. As a result of test analysis with this module, we have understood that the nitride fuel shows excellent behavior under irradiation due to its high thermal conductivity. We found that, however, it may be a main concern that fuel cladding integrity is maintained during irradiation in which pellet-cladding mechanical interaction is increased by He gas release, low creep rate of nitride pellet at low temperatures, and high creep rate of cladding above 873 K.