Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Mezawa, Tetsuya*; Mochizuki, Akihito; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-001, 41 Pages, 2020/03
Development of technologies to investigate properties of deep geological environment and model development of geological environment have been pursued in "Geoscientific Research" in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (Horonobe URL) project. A geochemical model which is a part of geological environment model requires the data of groundwater chemistry around the Horonobe URL for the development. This report summarizes the data obtained for 3 years from the fiscal year 2017 to 2019, especially for the results for measurement of physico-chemical parameters and analysis of groundwater chemistry, in the Horonobe URL project.
Kimura, Masanori; Munakata, Masahiro; Hato, Shinji*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-002, 38 Pages, 2020/03
To consider the method of implementing urgent protective actions in a nuclear accident appropriately, the authors have been assessing the effects of reducing doses by taking urgent protective actions using a Level 3 Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) code, the OSCAAR, developed by the JAEA. Iodine thyroid blocking is an effective urgent protective action to reduce equivalent doses to the thyroid due to inhalation of radioactive iodine. However, the timing of the administration of stable iodine (SI) is important to maximize the effectiveness for thyroidal blocking. Therefore, the careful consideration should be given to the most effective way of iodine thyroid blocking when preparing off-site emergency plans. In the present study, the authors developed a new metabolic model for thyroid by combining the respiratory tract model (Publ.66) and gastrointestinal tract model (Publ.30) of the ICRP with a metabolic model for thyroid (Johnson's model) in order to calculate the behavior of radioiodine and stable iodine in the body more realistically. The model is useful to evaluate the effect of the administration of SI for reducing equivalent doses to the thyroid depending on the its timing. We also calculated the reduction factor for equivalent doses to the thyroid in order to the thyroid by using the model, and then developed the its database for the OSCAAR. Consequently, the OSCAAR can evaluate the effectiveness for thyroidal blocking realistically and promptly.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Konno, Chikara; Ikehara, Tadashi; Okumura, Keisuke; Suyama, Kenya*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-003, 33 Pages, 2020/03
Data handling modules for the radioactivity calculation code, ORIGEN-S, are developed for the reliable evaluations of radioactivity inventory. By using these modules, an activation cross-section data library for the ORIGEN-S code is updated easily and effectively based on a facility-specific neutron spectrum and multi-group neutron activation cross-section library for decommissioning of nuclear facilities, MAXS2015. In order to guarantee the reliability of the radioactivity calculations, functions of data verification in a visual way and numerical comparison between before and after the data processing are also prepared.
Abe, Tomohisa; Ogiya, Takashi*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Hanawa, Tatsuaki*; Sanada, Yukihisa
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-004, 280 Pages, 2020/08
After the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency has carried on survey for distribution situation of radiation materials under the direction of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (later the Nuclear Regulatory Agency) from June 2011 to FY2019. This report is mainly summarized as data-base of air dose rate, integrated dose and radionuclide concentration of some types of environmental sample (airborne dust, soil, pine needles) in the radiation monitoring in Fukushima Prefecture (20 km far from FDNPS). The results of radiation monitoring were analyzed for temporal change at each measurement site under the unification format. Furthermore, the effective half-life and the dispersion at each location and sample were evaluated based on these big data.
Nishihara, Kenji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-005, 48 Pages, 2020/07
In order to discuss the technological development and human resource development necessary for the future nuclear fuel cycle, various quantitative analyzes were conducted assuming a wide range of future nuclear power generation scenarios. In the evaluation of quantities, the future power generation of LWR and fast reactor, the amount of spent fuel reprocessing, etc. were assumed, and the amount of uranium demand, the accumulation of spent fuel, plutonium, vitrified waste etc. were estimated.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-006, 70 Pages, 2020/08
Radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried at the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JPDR and JRR-4. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Takai, Shizuka; Kimura, Hideo*; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Munakata, Masahiro; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-007, 174 Pages, 2020/09
The MIG2DF computer code is a computer program that simulates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport in porous media for the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The original version of MIG2DF was released in 1992. The original code employs a two-dimensional (vertical or horizontal cross-section, or an axisymmetric configuration) finite-element method to approximate the governing equations for density-dependent saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Meanwhile, for geological disposal of radioactive wastes, landscape evolution such as uplift and erosion needs to be assessed as a long-term geological and climate events, considering site conditions. In coastal areas, the impact to groundwater flow by change of salinity distribution to sea level change also needs to be considered. To deal with these events in the assessment, we have revised the original version of MIG2DF and developed the external program which enables MIG2DF to consider unsteady landscape evolution. In these developments, this report describes an upgrade of MIG2DF (Version 2) and presents the configuration, equations, methods, and verification. This reports also give the explanation external programs of MIG2DF: PASS-TRAC (the particle tracking code), PASS-PRE (the code for dataset preparation), and PASS-POST (the post-processing visualization system).
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-008, 41 Pages, 2020/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a wide range of geoscientific research in order to build scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of nuclear wastes. This study aims to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock. The Regional Hydrogeological Study (RHS) project is a one of the geoscientific research program at Tono Geoscience Center. This project started since April 1992 and main investigations were finished to FY2004. Since FY2005, hydrogeological and hydrochemical monitoring have been continued using the existing monitoring system. Furthermore, these monitoring were ceased at the end of FY2019 due to the completion of the RHS project. This report describes the results of the long term hydro-pressure monitoring for FY2019.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-009, 98 Pages, 2020/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC (Highly Fly-ash contained Silicafume Cement), in order to decrease the effect on geological environment of cementitious material. HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete (140m, 250m and 350m depth gallery) and lining concrete (GL-374m to GL-380m of east access shaft) in construction part of Horonobe URL. In order to evaluate the effect of HFSC on the surrounding rock and groundwater, concrete and rock cores were periodically sampled from the site where the in-situ construction test was conducted, and various analyzes were conducted. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) was used for part of 140m depth gallery, and the same analysis as HFSC was conducted, in order to compare the effect of OPC and HFSC. This report summarizes the results of analyzes conducted on core samples from 2009 to 2018.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-010, 112 Pages, 2020/10
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III), the project is being carried out under the Phase III. The main goals of the MIU Project from Phase I to Phase III are: to establish techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment, and to develop a base of engineering for deep underground application. One of the Phase III goals is to construct geological environment models and grasp deep geological changes when expanding the research gallery by research and investigations using research galleries. The long term hydro-pressure monitoring has been continued to achieve the Phase III goals. Furthermore, these monitoring were ceased at the end of FY2019 due to the completion of the MIU project. This report describes the results of the long term hydro-pressure monitoring from April 2017 to March 2020.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-011, 50 Pages, 2020/11
This report summarize the results of the single borehole hydraulic test carried out at the -300 m Stage and the -500 m Stage of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory from FY 2016 to FY 2019. The details of each test (test interval depth, geology, etc.) as well as the interpreted hydraulic parameters and analytical methods used are presented in this report. Furthermore, the previous results of the single borehole hydraulic tests carried out in the Regional Hydrogeological Study Project and the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project before FY 2016 are also summarized in this report.
Fukuda, Kenji; Watanabe, Yusuke; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Aosai, Daisuke*; Hara, Naohiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-012, 80 Pages, 2020/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the influence of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2019. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Morita, Yasuji; Fukushima, Masahiro; Kashima, Takao*; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-013, 38 Pages, 2020/09
Critical Masses of Cm, Am and the mixture were calculated in metal-water mixtures with water reflector as a basic data for criticality safety assessment of minor actinide separation process. In the mixture of Cm-244 and Cm-245, higher ratio of Cm-245 gives smaller critical mass, but the amount of Cm-245 in the critical mass can be obtained by concentration of Cm-245 in the Cm mixture without depending on the Cm-245 ratio. Critical mass of Cm isotope mixture with 30% Cm-245 was smaller than that of Pu isotope mixture in the practical reprocessing (71% Pu-239 + 17% Pu-240 + 12% Pu-241). When Cm is separated from other element including Am and the solution is concentrated, measure for the critical accident has to be taken. Critical mass of Am-242m is smaller than that of Cm-245, but the ratio of Am-242m in the Am contained in practical spent fuel is small enough, about several percent, and therefore the critical accident by Am does not have to be considered. That by the mixture of Am and Cm does not either.
Tada, Kenichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-014, 30 Pages, 2020/10
The decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident is one of the most important issues in Japan. In the process of the decommissioning, preventing radiation exposure of workers is imperative originating in nuclear criticality of fuel debris. This study provides the handy tool enabling the analysis on nuclear criticality of fuel debris. The developed analysis tool named as HAND enables estimation of the criticality of fuel debris in short time. HAND deduces the range of parameters such as the size and composition, in which the criticality of fuel debris is specified. By selecting the range of the parameters using HAND in advance, total calculation time of the detail analysis will be reduced. Since the input data of HAND is designed to be simple and the output of HAND is to be user friendly, this tool is expected to be also an intuitive tool to study the criticality of fuel debris. This report explains the outline of the HAND and input instructions for HAND.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-015, 22 Pages, 2020/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project, which is a broad scientific study of the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, targeting in crystalline rock. The main goals of the MIU Project from Phase I to Phase III are: to establish techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment, and to develop a base of engineering for deep underground application. The groundwater inflow monitoring into shafts and research galleries, has been conducted to achieve the Phase II goals. Furthermore, these monitoring were ceased at the end of FY2019 due to the completion of the MIU project. This report describes the results of the groundwater inflow monitoring from April 2019 to March 2020.
Onoe, Hironori
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-016, 15 Pages, 2020/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project, which is a broad scientific study of the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, targeting in crystalline rock. This report summarized the digital data of local scale and site scale geological model and hydrogeological model constructed in the MIU project and the Regional hydraulic study.
Sugita, Yutaka; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Hoshino, Emiko*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-017, 39 Pages, 2021/01
In Japan, high-level radioactive waste (HLW) will be buried in a purpose built repository in deep underground. In the vertical disposal concept of HLW, nuclear waste canisters will be emplaced in excavated vertical disposal holes, surrounded by bentonite/sand mixture. And the galleries will be backfilled with bentonite/excavated rock mixture, which will be isolated with a concrete plug. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has performed swelling test, permeability test, thermal property measurement, uniaxial compression test, water potential measurement and infiltration tests to identify coupled thermal-hydraulic-mechanical-chemical behavior that will operate in the backfill material using excavated rock in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL). The obtained data will be used to support an ongoing full scale, in-situ experiment being conducted in the Horonobe URL.
Aoki, Katsunori; Yamanaka, Hiroki*; Watanabe, Kazuhiko*; Sugihara, Kozo
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-018, 45 Pages, 2021/02
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is pursued by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the crystalline host rock (granite) as a part of geoscientific study of JAEA, and underground facilities of MIU are constructed down to 500m blow the ground surface. As small amount of Uranium is normally contained in granite, high concentration of radon is sometimes detected in the air of the underground facilities constructed in granitic rocks depending on their ventilation conditions. Radon concentrations in underground facilities of MIU have been measured according to the excavation progress of underground facilities or the change of ventilation system. It is recognized that the data obtained by the actual measurement of radon concentration in such underground facilities are rare and valuable. This repot summarizes the measured data from fiscal 2010 to fiscal 2020, together with the information of ventilation conditions and air temperature which affect radon concentrations in underground facilities. The variation of the equilibrium factors of radon is also examined with the actually measured data. As a result, it has been found that radon concentration in the drift is high in summer and low in winter according to the natural ventilation caused by the seasonal temperature difference between in and out of the underground facilities. Furthermore, the temporary increase in the equilibrium factor of radon in the drift at the start of ventilation is supposed to be due to the aerosol increase by the ventilation flow, such as the dust blown up.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-019, 58 Pages, 2021/01
An experiment denoted as SB-SL-01 was conducted on March 27, 1990 using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in the Rig of Safety Assessment-IV (ROSA-IV) Program. The ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-SL-01 simulated a main steam line break (MSLB) accident in a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The test assumptions were made such as auxiliary feedwater (AFW) injection into secondary-side of both steam generators (SGs) and coolant injection from high pressure injection (HPI) system of emergency core cooling system into cold legs in both loops. The MSLB led to a fast depressurization of broken SG, which caused a decrease in the broken SG secondary-side wide-range liquid level. The broken SG secondary-side wide-range liquid level recovered because of the AFW injection into the broken SG secondary-side. The primary pressure temporarily decreased a little just after the MSLB, and increased up to 16.1 MPa following the closure of the SG main steam isolation valves. Coolant was manually injected from the HPI system into cold legs in both loops a few minutes after the primary pressure reduced to below 10 MPa. The primary pressure raised due to the HPI coolant injection, but was kept at less than 16.2 MPa by fully opening a power-operated relief valve of pressurizer. The core was filled with subcooled liquid through the experiment. Thermal stratification was seen in intact loop cold leg during the HPI coolant injection owing to the flow stagnation. On the other hand, significant natural circulation prevailed in broken loop. When the continuous core cooling was ensured by the successive coolant injection from the HPI system, the experiment was terminated. The experimental data obtained would be useful to consider recovery actions and procedures in the multiple fault accident with the MSLB of PWR. This report summarizes the test procedures, conditions, and major observations in the ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-SL-01.
Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-020, 164 Pages, 2021/03
Part of JAEA's Thermodynamic Database (JAEA-TDB) for solubility and speciation of radionuclides (JAEA-TDB-RN) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes has been updated with subsuming the database for geochemical calculations (JAEA-TDB-GC). This report has focused to update JAEA-TDB-RN after selecting change in standard Gibbs free energy of formation (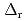
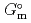 ), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (
), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (


 ), standard molar entropy (
), standard molar entropy (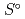
 ) and, heat capacity (
) and, heat capacity (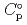 ), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (
), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (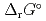
 ), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
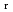


 ) and standard entropy change of reaction (
) and standard entropy change of reaction (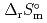 ) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
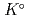 ) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
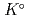 have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Mano, Akihiro; Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi*; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Li, Y.
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-021, 176 Pages, 2021/02
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, as a part of researches on the structural integrity assessment and seismic safety assessment of aged components in nuclear power plants, a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL-SP (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR - Stress Corrosion Cracking at Welded Joints of Piping) has been developed to evaluate failure probability of piping. The initial version was released in 2010, and after that, the evaluation targets have been expanded and analysis functions have been improved based on the state-of-the art technology. Now, it is released as Ver. 2.0. In the latest version, primary water stress corrosion cracking in the environment of Pressurized Water Reactor, nickel based alloy stress corrosion cracking in the environment of Boiling Water Reactor, and thermal embrittlement can be taken into account as target age-related degradation. Also, many analysis functions have been improved such as incorporations of the latest stress intensity factor solutions and uncertainty evaluation model of weld residual stress. Moreover, seismic fragility evaluation function has been developed by introducing evaluation methods including crack growth analysis model considering excessive cyclic loading due to large earthquake. Furthermore, confidence level evaluation function has been incorporated by considering the epistemic and aleatory uncertainties related to influence parameters in the probabilistic evaluation. This report provides the user's manual and analysis methodology of PASCAL-SP Ver. 2.0.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Omori, Takeshi*; Murakami, Hideaki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-022, 34 Pages, 2021/03
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3 and JPDR. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 22 radionuclides( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Ba,
Ba,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-023, 32 Pages, 2021/03
Nuclear Material Balance code (NMB code) have been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The NMB code will be updated with the function of mass balance analysis at the backend process such as reprocessing, vitrification and geological disposal. In order to perform its analysis with high accuracy, it is necessary to expand the number of FP nuclides calculated in the NMB code. In this study, depletion calculation by ORIGEN code was performed under 3 different burn-up conditions such as spent uranium fuel from light water reactor, and nuclides were selected from 5 evaluation indexes such as mass and heat generation. In addition, the FP nuclides required to configure a simple burnup chain with the same calculation accuracy as ORIGEN in the NMB code was selected. As the result, two lists with different number of nuclides, such as "Detailed list" and a "Simplified list", were created.