Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hiramoto, Masayuki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Nakama, Shigeo; Mizutani, Kazuhiko*; Morita, Atsushi*
JAEA-Research 2008-001, 84 Pages, 2008/03
In this study, the following studies on the design method of multi-tunnels were performed. Study on the outbreak behavior of EDZ (Chapter 2) Study on the stability evaluation of the pillars (Chapter 3) In Chapter 2, analysis was carried out for "multi-tunnels model" that modeled the gallery group of a disposal panel scale. As a result, it is important to use multi-tunnels models for prediction evaluation of EDZ, because the outbreak behavior of EDZ was different from the model of the H12 report. In Chapter 3, a stability evaluation method of pillars was considered from two viewpoints of "pillar strength" and "pillar load" based on the similar structures. As a result, if numerical analysis by the multi-tunnels model was carried out, pillar strength and pillar load was estimated adequately. Therefore, a stability evaluation method of the pillars in a disposal institution was suggested.
Hiramoto, Masayuki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Okubo, Seisuke*
JAEA-Research 2008-002, 60 Pages, 2008/03
Strength recovery and generalized relaxation behavior of rock were examined. The sample rock was Wakkanai-formation shale. In Chapter 2, strength recovery characteristic of rocks was examined. It was found that strength recovery increases with increase of testing time or load-holding time. It was interesting that the sample with relatively small unconfined compressive strength showed higher strength recovery. These results were obtained for only two sample rocks. Therefore, the accumulation of the data is needed in future to evaluate the influence of the boring places quantitatively. In Chapter 3, the generalized relaxation behavior of rock was examined. As a result, scatter in obtained data is considerably large, so the accumulation of the data is needed in future to understand rightly the complicated generalized relaxation behavior.
Suzuki, Hideaki; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi; Fujita, Tomoo
JAEA-Research 2008-003, 48 Pages, 2008/03
The development of excavation disturbed zone (EDZ) around the disposal tunnel affects such as the corrosive environment of the over-pack and environmental condition of the nuclear species migration on the geological disposal for the high-level radioactive waste (HLW). It is necessary to consider aftermath of EDZ in initial condition of the realistic numerical simulation of the long-term behavior of near-filed HLW repository after emplacement of engineered barrier system. This report presents the analysis assessment geochemical reaction with the development of the unsaturated zone around the disposal tunnel by developed the coupled Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical and Chemical (THMC) processes model / analysis code. As a result, the THMC processes analysis model apply a change of the solution composition by degasification of the carbon dioxide gas to the pore water and the change of the oxidation-reduction potential due to unsaturated zone around the disposal tunnel.
Kitamura, Akira; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Sato, Haruo; Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Research 2008-004, 39 Pages, 2008/03
Distribution coefficient of cesium onto bentonite and sedimentary rocks was determined in saline groundwaters. Distribution coefficient of cesium onto the solid phases was also determined in sodium chloride and potassium chloride solutions in order to elucidate sorption behavior of cesium. It was expected that the sorption behavior of cesium was regarded as ion exchange reactions with sorption sites of the solid phases from the results of dependencies of distribution coefficient on pH and ionic strength. It was found that only potassium ion was competed with cesium for the sorption onto sedimentary rocks, while both sodium and potassium ions was competed with cesium for the sorption onto bentonite. It was also found that sorption behavior of cesium onto sedimentary rocks was well described using a model on the sorption of cesium onto illite. The present study was performed in Tokai Works, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (one of the predecessors of JAEA) in FY 2002-2003.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2008-005, 60 Pages, 2008/03
In this research we aim to clarify a long term behavior of crystalline rocks, and performed the following subjects: (1) Uniaxial and stress relaxation tests under observation of a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) by using granite specimens of Mizunami underground lab. (2) Pressure dissolution experiment using specimens of quartz single crystal and glass beads. (3) Theory establishment of pressure dissolution of quartz and a homogenization analysis for quartz dissolution. In Chapter 2 CLSM was used to acquire clearly focused three-dimensional images of granite specimens of Mizunami underground lab for uniaxial and stress relaxation tests, and observed the change of microscale structure including the mineral configuration under applying compression stress. The local strain distributions were calculated by using quadrilateral meshes of finite elements arranged on the surface of each specimen. In Chapter 3 we performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of quartz single crystal and glass beads, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. After applying stress the surface of contacted area of quartz was observed by CLSM and found traces of dissolution and reprecipitation. In Chapter 4 a reaction theory of pressure dissolution of quartz was proposed and by using a homogenization analysis the dissolution of quartz in bentonite was simulated.
Nakano, Yoshihiro; Akie, Hiroshi; Okumura, Keisuke; Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao
JAEA-Research 2008-006, 37 Pages, 2008/03
A core design of a high conversion type innovative water reactor for flexible fuel cycle (HC-FLWR) with thermal output of 3926 MW has been constructed. The design study of HC-FLWR consists of two steps of analyses. The first step was preliminary parametric survey calculations and the second step was more detailed calculations with a nuclear and thermal-hydraulic coupled calculation code MOSRA. Through the 1-D core burnup calculations, the following design values were obtained. The Puf enrichment of MOX fuel is 11%. The heights of upper blanket, MOX and lower blanket regions are 5 cm, 85 cm and 5 cm, respectively. With these values, 3-D core burnup calculations were performed. In this analysis, effects of the fuel loading pattern were also investigated. Finally, a neutronics design of HC-FLWR core with a negative void reactivity coefficient, a conversion ratio of 0.84 and a discharged burnup of 56 GWd/t was obtained.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Research 2008-007, 30 Pages, 2008/03
Neutron irradiation remarkably reduces the thermal conductivity of graphite components in HTGR. The reduced thermal conductivity is expected to be recovered by annealing of irradiation-induced defects, when the graphite components are heated above the irradiation temperature. The annealing effect is not considered in the maximum fuel temperature analysis of the HTTR design from a viewpoint of conservative evaluation for the maximum fuel temperature. Therefore, it is expected that the temperature evaluation at accident conditions could be carried out more accurately with a reasonable stand point by considering the annealing effect. In order to advance the evaluation method for temperature analysis of accident in the HTGR, the annealing effect on thermal conductivity of graphite was evaluated quantitatively and the design curve on the thermal conductivity for graphite components of HTGR was proposed in this study.
Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Matsunaga, Takeshi; Inoue, Takanobu*
JAEA-Research 2008-008, 31 Pages, 2008/03
The discharge of nitrate nitrogen from a forested catchment was analyzed using a distributed rainfall-runoff model. Observation in rainfall events were carried out in November, 2006 in the Ijira River. The distributed rainfall-runoff model carried out runoff simulation of ground water and rain water at the catchment. The model was verified by observed flow rate, and the hydrogen isotopic ratio of rain water and river water. The nitrate ion concentration in river water was shown as a function of the residence time of discharge water in the catchment calculated by the model. As a result, it was estimated that the nitric-acid ion in the river water was transported by the lateral flow of the rain water at the subsurface and the up-flow of ground water. Moreover, it was estimated that the residence time of the soil moisture influenced the discharge of nitrate nitrogen. This study was suggested that dynamic behavior of water in catchment was important when considering the balance of nitrate nitrogen in catchment.
Morioka, Hiroshi*; Yamazaki, Masanao; Matsui, Hiroya; Orukawa, Go*; Yamaguchi, Takehiro
JAEA-Research 2008-009, 263 Pages, 2008/07
On the "Development of engineering techniques for use in the deep underground environment" in Phase 1, based on the various type of data acquired on investigations from the surface, basic design of underground facilities in advance was carried out. This report summarizes the support design of underground facilities carried out in 2004.
Saito, Yuya; Tanai, Kenji; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Hirai, Takashi*; Nishimura, Mayuka*
JAEA-Research 2008-010, 35 Pages, 2008/03
Site with the potential to adversely affect the performance of the disposal system should be avoided by site selection in Japan. On the other hand, according to Atomic Energy Commission, the possibility to occur the natural and artificial events suddenly should be examined. So it is important to examine about the critical state of the engineering barrier system (EBS) when if the fault move across the EBS. And this study helps to be understood by the nation. In this paper, we examined the influence of the velocity of fault movement by the model test, and tried to improve the precision of the simulation analysis. Test results showed that the total pressure of the buffer inside was about 20% decreased when the velocity was a one-tenth. And it is important to set the permeability of the near-field rock appropriately when simulating the behavior of the buffer material affected by fault movement.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu*; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2008-011, 34 Pages, 2008/03
The deep underground environment where overpacks will be emplaced is expected to be anaerobic environment. It is necessary to understand the corrosion behavior of carbon steel in such environment for the assessment of corrosion lifetime of carbon steel overpacks. In this study, immersion tests of carbon steel were carried out in buffer material for 10 years duration in nitrogen atmosphere in which oxygen gas concentration was controlled to less than 1 ppm. Synthetic sea water and aqueous solution containing bicarbonate ion and chloride ion were selected as the test solution. The amount of corrosion of carbon steel was estimated from the weight loss of the specimen, and its change with time was investigated.
Kawasaki, Manabu*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2008-012, 55 Pages, 2008/03
Copper is one of the candidate materials for overpacks. The redox condition at the early stage of the post closure will be oxidizing. In order to understand the influence of environmental factors on the corrosion behavior of copper in such oxidizing environment, anodic polarization tests were performed in carbonate aqueous solution with varying the concentration of representative chemical species in groundwater. As the results of potentiodynamic and potentiostatic tests, anodic polarization behavior of pure copper was summarized as follows; (1) Carbonate ion and bicarbonate ion promoted the passivation of pure copper, and suppressed the initiation of film breakdown. (2) Chloride ion promoted both the active dissolution and initiation of film breakdown of pure copper. (3) The influence of sulfate ion and pH was small, but the action of sulfate ion to the pure copper was similar to that of chloride ion, and the increase of pH was likely to promote the passivation and suppress the initiation of film breakedown. (4) The film breakedown potential, Eb, was represented as a function of the ratio of aggressive ion and inhibiting ion such as [Cl ]/[ HCO
]/[ HCO
 ], [SO
], [SO
 ]/[HCO
]/[HCO
 ]. When the ratio exceeds a certain value, the anodic poralization curve becomes active dissolution type so that no macroscopic film breakedown can not be occured. The lower limit of Eb in passive type region was estimated to be about -200 mV vs. SCE. (5) As the results of potentio static tests, the corrosion form near the Eb was uniform dissolution over the surface, but pitting corrosion and non-uniform corrosion occurred according to the condition of the test solution. Neither pitting corrosion nor non-uniform corrosion occurred at the potential below Eb in every test cases.
]. When the ratio exceeds a certain value, the anodic poralization curve becomes active dissolution type so that no macroscopic film breakedown can not be occured. The lower limit of Eb in passive type region was estimated to be about -200 mV vs. SCE. (5) As the results of potentio static tests, the corrosion form near the Eb was uniform dissolution over the surface, but pitting corrosion and non-uniform corrosion occurred according to the condition of the test solution. Neither pitting corrosion nor non-uniform corrosion occurred at the potential below Eb in every test cases.
Hiramoto, Masayuki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Aoyagi, Shigeo*; Miyanomae, Shunichi*
JAEA-Research 2008-013, 62 Pages, 2008/03
For improvement of the credibility of evaluation method for the long-term dynamical behavior of near-field rock mass, the influence that swelling pressure caused by buffer material and expansion pressure caused by the erosion of overpack gave long-term stability of near-field rock mass was studied in this report. As a result, because swelling pressure caused by buffer material and expansion pressure caused by the erosion of overpack acted on near-field rock mass as inner pressure, long-term stability of near-field rock mass improved. And it was shown that conventional evaluation method gave results of safe side. But as an exception, when stiffness property of buffer material is large and initial stress of rock mass is small, a possibility that tensile fracture occurred in near field rock mass was shown. In such a case, a possibility that functional decline of artificial barrier happens is concerned, because buffer material flows out into the crack that occurred in rock mass.
Oi, Takao; Kato, Tomoko; Kawachi, Susumu; Kawamura, Makoto
JAEA-Research 2008-014, 14 Pages, 2008/03
The method contributing to the improvement of confidence and the systematization of the various information and knowledge under the responsibility of each researcher has examined. As a result, "a systematic compilation method to exhibit the level of the confidence on the assessments" has been developed based on the approach of the international quality management system. It is possible to manifest the aims, intention, contents, approach and process of the study by compiling and presenting the results of the studies using this method. In addition, transparency and traceability would be shown and the adequacy of the obtained result would be claimed by researcher through the conformity assessment for the result of the study. These results would contribute the understanding of reader and improvement of confidence.
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2008-015, 15 Pages, 2008/03
A concentration of Ra limited by coprecipitation with calcite used to be estimated by a model of distribution assuming that constant mol ratio of Ra/Ca is preserved in solid and liquid phase. According to experiments, it has been revealed that mol ratio of Ra/Ca in solid differs from that in liquid. This difference was evaluated by a partition coefficient(D). In this study, a partition model was established to evaluate an effect of coprecipitation of Ra in calcite with D. In the model, D was converted to a distribution coefficient(Kcp) and the effect of incorporation of Ra was examined. As an example, this model was adopted under a condition of FRHP porewater and a converted Kcp was conducted. Release rates of 4n+2 series nuclides from engineered barrier with this model were also calculated. As a result of calculation, release rate of  Ra was largest in their series on an outer surface of engineered barrier. This release rate was more than one order magnitude lower than that of
Ra was largest in their series on an outer surface of engineered barrier. This release rate was more than one order magnitude lower than that of  Cs.
Cs.
Kuno, Yoshio; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Research 2008-016, 21 Pages, 2008/03
In this study, the influence of chemical difference between in-situ condition and atmospheric condition on inorganic colloids was evaluated by carrying out the characterization of groundwater colloids in the Horonobe area. Remarkable amount of suspended substance including mainly Ca was observed in the groundwater collected from the HDB-10 borehole. Additional laboratory experiments were therefore conducted using this groundwater to investigate the impact on the groundwater composition and the colloidal properties by exposing to the atmosphere. Not only precipitation but also suspended particles composed mainly of CaCO were generated under the atmospheric condition. From the prediction using the DLVO theory, however, the suspended particles are not expected to have a dispersive stability in this groundwater. Formation of suspended particles seems to be a transient behavior caused by the change of chemical conditions and these particles would not exist in in-situ groundwater.
were generated under the atmospheric condition. From the prediction using the DLVO theory, however, the suspended particles are not expected to have a dispersive stability in this groundwater. Formation of suspended particles seems to be a transient behavior caused by the change of chemical conditions and these particles would not exist in in-situ groundwater.
 -setting for Horonobe rocks
-setting for Horonobe rocksOchs, M.*; Kunze, S.*; Saito, Yoshihiko; Kitamura, Akira; Tachi, Yukio; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2008-017, 89 Pages, 2008/03
In the present report, a first test and illustration was performed regarding the applicability of the JNC-SDB to the derivation of K -values for Th, Np, Cs, and Se valid for Horonobe rocks. The original experimental data selected from the JNC-SDB were converted to the application conditions using the semi-quantitative scaling procedures. To illustrate the effect of the scaling procedures, and of related uncertainties, on the magnitude of the derived K
-values for Th, Np, Cs, and Se valid for Horonobe rocks. The original experimental data selected from the JNC-SDB were converted to the application conditions using the semi-quantitative scaling procedures. To illustrate the effect of the scaling procedures, and of related uncertainties, on the magnitude of the derived K -values, scaling procedures taking into account mineralogy as well as surface and solution speciation were applied sequentially, and all results were discussed in detail. This K
-values, scaling procedures taking into account mineralogy as well as surface and solution speciation were applied sequentially, and all results were discussed in detail. This K -setting exercise allowed to predict the magnitude of K
-setting exercise allowed to predict the magnitude of K values under the in-situ conditions, however the availability of experimental data that closely match the application conditions is limited for some reasons.
values under the in-situ conditions, however the availability of experimental data that closely match the application conditions is limited for some reasons.
Kawamura, Makoto; Oi, Takao; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Kurosawa, Hideki; Asamori, Koichi; Kawachi, Susumu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-018, 47 Pages, 2008/03
In this report, we sophisticated the framework as a part of the total system performance assessment for two purposes: the first one is quantification of relationship of characteristic of natural phenomena between geological environmental conditions (THMCG), and the other one is quantification of relationship of THMCG condition between parameters of performance assessment. On the other hand, we applied the sophisticated framework to all natural phenomena. As a result, to apply the sophisticated framework, we could show that information integration could carry out efficiently. Moreover, we have checked that the framework was applicable to all phenomena. Furthermore, we could show that suitable scenarios might be chosen by information integration.
Ebashi, Takeshi; Koo, Shigeru*; Oi, Takao
JAEA-Research 2008-019, 142 Pages, 2008/03
In this study, comprehensive sensitivity analysis method was applied to HLW geological disposal concept. In this application, level of importance and successful condition for intended parameters on one barrier were extracted under conservative conditions of parameters on the other barrier, taking into account diverse uncertainties on initial stage of stepwise approach. We achieved analysis results with level of importance and successful condition for intended parameters. In conclusion, the comprehensive sensitivity analysis method can be applied to extraction of sensitivity characteristics on each barrier, under conservative conditions. Such study on the applicability of method and the extracted sensitivity characteristics will contribute to construction of a robust barrier and a scenario analysis for initial stage of stepwise approach.
Fujisaki, Kiyoshi; Suzuki, Hideaki; Fujita, Tomoo
JAEA-Research 2008-020, 62 Pages, 2008/03
In evaluating the behavior of near-field after emplacement of engineered barriers, it is necessary to understand quantitative changes of near-field over time and space. However, the coupled phenomena in near-field are complicated because thermo-, hydro-, mechanical, chemical process will interact, so that no comparison with real behavior will make it possible to find out if the applied model will represent the coupled behavior adequately or not. Hence, it is necessary to validate the model, based on the result of coupled behavior experiment in laboratory or in site. In this report, authors evaluated the applicability of coupled T-H model under the condition of simulated near-field, based on the results of coupled experiment in room. As a result, it has shown that the model which improved the fit to the measured data, is reasonable under this condition.
Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*
JAEA-Research 2008-021, 148 Pages, 2008/03
A great effort is necessary when all of the biosphere parameters need to be collected at the actual surface environment of any proposed repository, because a great number of biosphere parameters, such as element-specific parameters, parameters specific to the surface environment or human behavior, are used in the biosphere assessment. Therefore, it is helpful to identify the biosphere parameters that should be collected at the actual environment in advance. For this purpose, the following approaches were developed in this study: (1) Extraction of the significant biosphere parameters through sensitivity analysis including estimation of the influences of variation of element-specific parameters on flux-to-dose conversion factors. (2) Checking the data sources of the significant biosphere parameters on the present dataset. (3) Making the priority list in future data acquisition. So far, steps (1) and (2) have been done, therefore this report summarizes the results obtained from these steps.
Inagaki, Manabu; Ebina, Takanori*
JAEA-Research 2008-022, 37 Pages, 2008/03
The step-by-step progress for which a detailed investigation area(s) is chosen from the preliminary investigations area(s) in the volunteer sites is assumed on the high-level radioactive waste disposal in Japan. It's necessary to select an appropriate detailed investigation area from the preliminary investigation area, therefore, it's needed to combine the design options which have been assumed on the generic geological environment with the information of a limited investigation from the surface in the preliminary investigation area for evaluating the total performance of the investigation site. Requirements in the detailed investigation area are not only long term stability of geological environment but also stability of the engineered barrier system on influence by a flow of groundwater in major water conducting fracture, the correspondence by a site-design and the performance of the total system as a selection important matter in a detailed investigation area. I thought it was rational to build the scenario used by geological survey information, design situation and performance evaluations, the scenario which causes a model and data when combining geological information and design option as the early stage condition, and the frame able to make the model difference clear and feed this back to a design and a geological survey at the generic environment bottom considered up to now for it.
Oi, Takao; Inagaki, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto
JAEA-Research 2008-023, 23 Pages, 2008/03
In this study, a new concept of the scenario development method to be able to represent the importance of a scenario on geological disposal of HLW in an understandable way was examined with considering the versatility. By the carrying out the scenario development using this method, the information relation to the confidence building such as "the reason why the scenario is important scenario", "the argument which is able to claim completely the safety by the assessment according to the scenario" would be represented in the easy-understand format. Furthermore, the useful information for total performance assessment of geological disposal would be given with the role of each study and the relationship between the studies in the assessment.
Hayashi, Maki*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2008-024, 56 Pages, 2008/03
Corrosion analysis have carried out on forty iron-based archaeological remains, which had been dug out at seventeen relics in Japan. Although JAEA estimated the corrosion amount of the carbon steel to be 31mm for 1000 years by the second progress Report (H12), this analysis clarified the corrosion amount of the iron-based archaeological remain was lower than 31mm. Most of iron-based archaeological remains for this analysis had been buried in a oxidizing environment. Because the disposal environment is expected to be reducing condition, the corrosion data in conditions relevant for geological disposal are desirable. The purpose of this study is to investigate the corrosion of the soil solid sample that contains the plow excavated from the Oda castle. We want to use medical X-ray CT owned in the JAEA for metal natural analogue study. Therefore, same sample were measured by high energy industry machine for industry and medical X-ray tomography. And the comparison of each X-ray CT Image and measurement of thickness of rust were performed.
Tochigi, Yoshikatsu; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Yui, Mikazu; Asano, Takahiro*; Honjo, Hideko*; Haginuma, Masashi*; Kawakami, Yasushi*; Suzuki, Kazunori*
JAEA-Research 2008-025, 55 Pages, 2008/03
Results of joint research on fiscal year 2006 between Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Institute of Research and Innovative (IRI) titled as "Study on investigation of microbial effects for geological disposal" are described in this report. The objective of this study is to develop a method for estimating microbial effects for barrier performance of geological disposal site. The modeling was performed to examine the effect on the change in groundwater chemistry (mainly by electron acceptors) by microbial metabolism as well as microbial activities. In order to use the data (chemical composition, biomass, etc.) in the MINT code, groundwater was collected from the drilled well prepared for chemical and microbial analyses of groundwater. The well was prepared in observation field near Horonobe Underground Research Center of JAEA in fiscal year 2006. Then, numerical modeling using collected data of groundwater with numerical modeling program code "MINT" considering microbial effects was carried out. The modeling was carried out to evaluate the microbial effect for stability of chemical and microbial composition of groundwater. As the result of the modeling, relatively low microbial effect for groundwater composition was observed in particular for the concentration of dissolved methane, methanogen, sulfur reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfur ion. The result shows that low redox potential is stable in the well in spite of shallow depth.
Sugawara, Takanori; Suzuki, Kazuhiko; Nishihara, Kenji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Kurata, Yuji; Kikuchi, Kenji; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Research 2008-026, 91 Pages, 2008/03
The design acceptance of the beam window which is one of the most critical components for the Accelerator Driven System (ADS) was investigated. From the simplified overall assessment for nuclear power plant, it was clarified that the buckling failure was the most severe failure mode for the beam window. The parametric survey for the thickness of the ellipse model was carried out to prevent the buckling failure by using the Finite Element Method code, FINAS. The buckling analyses with initial imperfections were also performed to discuss the factor of safety (FS). The results showed that FS of 3 was enough conservative to ensure the integrity of the beam window. It was also shown that the ellipse shape concepts with the thickness of 2.0 2.4 [mm] at the top and the thickness of 2.0
2.4 [mm] at the top and the thickness of 2.0 4.0 [mm] at the transient part were acceptable under the current ADS design parameters.
4.0 [mm] at the transient part were acceptable under the current ADS design parameters.
Shibuya, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Takashi*; Kuroda, Hidetaka
JAEA-Research 2008-027, 274 Pages, 2008/03
Initial design of shafts and tunnels of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory was done in FY2002, and preliminary analysis of those of 0 to 300 m depth was done in FY2003 on the basis of geological survey results obtained then. We have recently completed boring of MIZ-1 borehole and obtained geological data to the depth of 1,000 m. In order to confirm validity of the design, we have reviewed geological model, rock property, initial stress and other characteristics and conducted corrective analysis (two-dimensional) on the basis of the new data. In junction of shaft and sub-stage (horizontal tunnel) (100 m and 300 m depth) where stress might be concentrated, three-dimensional analysis was done.
Tamura, Koji
JAEA-Research 2008-028, 9 Pages, 2008/03
A pulsed operation of a double-grating Ti:sapphire laser oscillator that consists of a gain medium, back mirror, and two gratings, was shown. A stable single longitudinal mode operation was achievable. From the calculation of the optical path, it can be explained by the increased beam walk-off from the gain medium by the introduction of the second grating compared with the conventional grazing incidence cavity geometry. The improved spectral property was also explained by the calculations of increased dispersion. The results indicate that the oscillator configuration was useful for the applications which require stable mode operation and narrow linewidth such as the high resolution spectroscopy or the laser isotope separation.
Shimo, Michito*; Kumamoto, So*; Karasaki, Kenji*; Sawada, Atsushi; Maekawa, Keisuke; Sato, Hisashi
JAEA-Research 2008-029, 95 Pages, 2008/03
It is important for safety assessment of HLW geological disposal to evaluate groundwater flow and mass transport in deep underground accurately. The objective of this study is to expand the data of flow and mass transport properties in fractured sedimentary rocks, and to estimate these properties in larger scale rocks, such as in situ test scale, using the results of the laboratory tests and the borehole investigations. This study was carried out under the following three tasks: (1) laboratory hydraulic and tracer experiments using the rock specimens of Koetoi formation obtained at underground research facility under construction in the Horonobe area, (2) a numerical study on the influence that a difference of the groundwater flow velocity in the fractures gives a mass transport in the fractured sedimentary rocks, (3) a numerical study on the contributing factors to groundwater flow such as effect of low permeability layers.
Takasu, Tamio*; Maekawa, Keisuke; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2008-030, 45 Pages, 2008/03
It is important to evaluate relevant processes in geosphere, such as groundwater flow, based on the actual conditions of geological environment. At the coastal area, it is needed to understand groundwater flow under the saltwater and freshwater mixing conditions. We conducted a set of laboratory experiments using mass transport visualization system with flow chamber representing homogeneous sedimentary rock filled with uniform glass beads and double layer filled with different size of glass beads, in order to observe saltwater intrusion process into fresh water and saltwater-freshwater interface behavior. From the horizontal intrusion length of saltwater, the result might not depend on the size of glass beads and might be categorized by the combination of hydraulic gradient and saline concentration. In case of low hydraulic gradient case, the saltwater intrusion length tends to be larger due to saline concentration increase.
 ion production and transport processes on the H
ion production and transport processes on the H ion beam intensity profile in the Cs-seeded negative ion source (Joint research)
ion beam intensity profile in the Cs-seeded negative ion source (Joint research)Takato, Naoyuki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Kato, Kyohei*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Sakamoto, Keishi
JAEA-Research 2008-031, 44 Pages, 2008/03
The origin of the H ion beam non-uniformity under the Cesium seeded condition was studied in the JAEA 10 Ampere negative ion source by measuring the profiles of the beam intensity and plasma parameters. The numerical analyses, such as the trace of particles (the electron, the H
ion beam non-uniformity under the Cesium seeded condition was studied in the JAEA 10 Ampere negative ion source by measuring the profiles of the beam intensity and plasma parameters. The numerical analyses, such as the trace of particles (the electron, the H atom and the H
atom and the H ion) trajectories using the Monte Carlo method, were also applied to consider the experimental results.
ion) trajectories using the Monte Carlo method, were also applied to consider the experimental results.
Hajima, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Norio*; Sakanaka, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Yukinori*
JAEA-Research 2008-032, 188 Pages, 2008/02
Energy-recovery linac (ERL) is a promising device for future X-ray light sources. In Japan, we organized a Japanese ERL collaboration team, consisting of the members of KEK, JAEA, ISSP and other laboratories, and then, started R&D efforts for the future ERL light source. In order to demonstrate accelerator technologies relevant to the ERL light source, we have decided to build a small facility, Compact ERL. This report presents a design study of the Compact ERL, which includes R&D issues for each accelerator component, studies on beam dynamics, performance of the Compact ERL as a light source of THz and X-ray.
Shibano, Kazunori; Orukawa, Go*; Yasue, Kenichi; Funaki, Hironori; Kurikami, Hiroshi
JAEA-Research 2008-033, 27 Pages, 2008/06
The hydrogeological model of shallow zone was built by using the data of core observation and permeability tests in the shallow boreholes drilled prior to the shaft excavation. Then, groundwater flow analysis of shaft excavation was performed using the hydrogeological model. By making a comparison between inflow rate into the shaft obtained by the analysis and measured inflow rate to the depth of 50m, the hydrogeological model and the performance of the cut-off wall established around the shaft were evaluated. The prediction analysis showed that the cut-off wall was the adequate performance and the hydraulic conductivity of fresh rock in the Koetoi Formation directly influenced the inflow rate below the cut-off wall. The simplified model in the report is efficient to reflect the excavation execution of the underground facility.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi
JAEA-Research 2008-034, 43 Pages, 2008/05
The authors developed a model for calculating the angular neutron fluence distributions for radionuclide neutron sources which are encapsulated in stainless steel capsules or surrounded by support structures as a source holder and a source movement system. These structures may cause an anisotropic neutron fluence distribution. This should be taken into account in the neutron-measuring instruments calibration procedure. The calculations were made for two types of widely used neutron sources,  Am-Be and
Am-Be and  Cf, by combining an in-house code simulating the
Cf, by combining an in-house code simulating the  Be(
Be( ,n) reactions and the Monte Carlo code MCNP-4C. As a result, anisotropy factors in the direction perpendicular to the source capsule axis for bare neutron sources were evaluated to be 1.012 for
,n) reactions and the Monte Carlo code MCNP-4C. As a result, anisotropy factors in the direction perpendicular to the source capsule axis for bare neutron sources were evaluated to be 1.012 for  Cf in a standard Amersham X1 capsule, 1.030, 1.039 and 1.045 for
Cf in a standard Amersham X1 capsule, 1.030, 1.039 and 1.045 for  Am-Be in a standard Amersham X3, X4 and X14 capsules, respectively. These values are in reasonable agreement with the published data.
Am-Be in a standard Amersham X3, X4 and X14 capsules, respectively. These values are in reasonable agreement with the published data.
Toida, Masaru*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Seno, Shoji*; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Ogata, Nobuhisa
JAEA-Research 2008-035, 89 Pages, 2008/03
"Geoscientific research" performed at the Tono Geoscience Center is developing site investigation, characterization and assessment techniques for understanding of geological environment. Their important themes are to establish a methodology for analyzing uncertainties in heterogeneous geological environment, and to develop investigation techniques for reducing the uncertainties efficiently. This study proposes a new approach where all the possible options in the models and data-sets that cannot be excluded in the light of the evidence available, are identified. This approach enables uncertainties associated with the understanding at a given stage of the site characterization to be made explicitly using an uncertainty analysis technique based on Fuzzy geostatistics. This, in turn, supports the design of the following investigation stage to reduce the uncertainties efficiently. In the study, current knowledge had been compiled, and the technique had been advanced through geological modeling and groundwater analyses in the Tono area. This report systematized the uncertainty analysis methodology associated with the characterization of the geological environment, and organized the procedure of the methodology with the application examples in the study. This report also dealt with investigation techniques for reducing the uncertainties efficiently, and underground facility design options for handling geological uncertainties based on the characterization of the geological environment.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Research 2008-036, 33 Pages, 2008/03
To advance the performance and safety of HTGR, heat-resistant ceramic materials are expected to be used as reactor internals of HTGR. C/C composite and superplastic zirconia are the promising materials for this purpose. In order to use these new materials as reactor internals in HTGR, it is necessary to establish a structure design method to guarantee the structural integrity under environmental and load conditions. Therefore, C/C composite expected as reactor internals of VHTR is focused and an investigation on the structural design method applicable to the C/C composite and a basic applicability of the C/C composite to representative structures of HTGR were carried out in this report. As the results, it is found that the competing risk theory for the strength evaluation of the C/C composite is applicable to design method and C/C composite is expected to be used as reactor internals of HTGR.
Nobuto, Jun*; Mikake, Shinichiro
JAEA-Research 2008-037, 240 Pages, 2008/03
In this study, the comprehensive performance of suspension type grouting materials to seal rock fractures encountered in excavation works at deep underground has been checked, and the clogging phenomenon at the entrance of rock fractures has been investigated. Research issues are as follows; Study on grouting concept to secure high-level water sealing, study on the test method to check grout clogging under high injection pressure, study on grouting material which can penetrate into finer fractures. Among these, in the study on penetrability test method, prototype test instruments were made and a series of preliminary tests were conducted.
Honda, Makoto*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Suzuki, Makoto*; Iwasa, Kengo*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-038, 73 Pages, 2008/06
The purpose of this study is to develop a geostatistical procedure for modeling on geological environments and to evaluate quantitative relationship between amount of geological information and reliability of the models using data sets obtained in surface-based investigation phase (Phase 1) of the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project. This study is a joint research with Shimizu Corporation carried out in four years from FY2003 to FY2006. In the first three years, by using the data sets obtained by the geological investigations in each FY, three dimensional models of the resistivity, the chemical composition of groundwater and the hydraulic conductivity were built and undated by the geostatistical method developed in this study. The relationship between the amount of information and the reliability of the models were demonstrated as well through comparisons of the models at each step which corresponds to the investigation stage in each FY. In FY2006, as a summary of this study in the final FY, to confirm the validity of the present method, the above three models were compared with models built by a conventional method. Relationship between the procedure of geological survey and the reliability of the models were also studied by newly computing three sets of models based on fictitious investigation plans, their procedures are different form the actual one, and comparing these four models.
Nobuto, Jun*; Mikake, Shinichiro
JAEA-Research 2008-039, 138 Pages, 2008/03
Research items are as follows: study on viscosity of high viscous grouting material, study of clogging phenomenon of suspension type grouting materials under high injection pressure, literature review on infiltration characteristics of grouting materials to point out research issues to be solved and summary of this research works to date. Among these, in high-pressure clogging test, prototype test equipment developed last year was improved completely to simulate grout flow accurately in actual grouting scene.
Uchikawa, Sadao; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kobayashi, Noboru
JAEA-Research 2008-040, 24 Pages, 2008/03
The present study deals with the potential effects of utilization of uranium recovered from LWR spent fuels as the axial blanket fuels in the core of the breeder type FLWR, which is characterized by the five-layer double-flat-core structure. Design studies shows that the adoption of recovered UO blanket can reduce the required plutonium inventory to attain the same core performances as the previous core design of depleted uranium blankets. Furthermore, the utilization of re-enriched recovered uranium with
blanket can reduce the required plutonium inventory to attain the same core performances as the previous core design of depleted uranium blankets. Furthermore, the utilization of re-enriched recovered uranium with  U enrichment of about 5wt% as the internal blanket fuel is evaluated to have a potential of a conversion ratio of 1.1. The core design with reduced plutonium inventory and high conversion ratio can contribute to realize a smooth and speedy transition from the LWR fuel cycle to the sustainable fuel cycle, as a core design for the transitioning period, during which a sufficient amount of uranium recovered from LWR spent fuels is available as resources.
U enrichment of about 5wt% as the internal blanket fuel is evaluated to have a potential of a conversion ratio of 1.1. The core design with reduced plutonium inventory and high conversion ratio can contribute to realize a smooth and speedy transition from the LWR fuel cycle to the sustainable fuel cycle, as a core design for the transitioning period, during which a sufficient amount of uranium recovered from LWR spent fuels is available as resources.
Fukaya, Yuji; Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao
JAEA-Research 2008-041, 98 Pages, 2008/03
The purpose of this research is to investigate spent fuel characteristics of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR). The characteristics should be investigated comparing with other types of reactor. It is important for the safety of spent fuel management to investigate the characteristics. The ORIGEN code was used in this research. Moreover, the ORIGEN libraries for RMWR were generated using SWAT code, because there are no open ORIGEN libraries for this purpose. To investigate the spent fuel characteristics, the decay heat and the radioactivity after a cooling time of 2 years and 4 years were evaluated. As a result, the decay heat and the radioactivity of the RMWR spent fuel are lower than those of full-MOX-LWRs and FBR, and the same levels as those of the high burn-up PWR. In addition, from the waste disposal point of view, the characteristics of spent fuel were also investigated.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-042, 236 Pages, 2008/04
The following study was done with the aim of systemizing the technology on the investigation and analysis to grasp deep underground geological environment in relation to the radioactive waste disposal. (1) The study on the research and development (R&D) subjects which turned to the practical investigation and analysis of deep underground geological environment. (2) The study on the advanced technical basis of the investigation and analysis of deep underground geological environment. It continued in the former year and got the following results. Concerning (1), the concrete investigation, measurements, numerical analyses and chemical analyses were enforced about the following item and extracted some subjects with the viewpoint of radioactive waste disposal. Concerning (2), the evaluation of the results and a way to the practical use were discussed on the R&D activities of the following item. The R&D activities of the study group concerning (2) are related to the fundamental and elemental technology. It was discussed if these results could be taken into the practical investigation programs which characterize the geological environment and engineering technology in the Tono Geoscience Center. The Study group also discussed and gave the comment on the 2nd phase (the shaft construction phase of the MIU (Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory) research program in the JAEA.
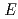 h analysis (Contract research)
h analysis (Contract research)Otsuka, Ichiro; Taki, Hiroshi*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamada, Fumika; Inada, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Tadao
JAEA-Research 2008-043, 101 Pages, 2008/03
The influence of carbon steel overpack corrosion on redox potential (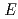 h) of bentonite pore water under geological disposal environment was investigated. The thermodynamics data of corrosion products, the corrosion rate of carbon steel, and the information on cathode reactions were acquired by experiments and literature survey. We conducted preliminary analysis of
h) of bentonite pore water under geological disposal environment was investigated. The thermodynamics data of corrosion products, the corrosion rate of carbon steel, and the information on cathode reactions were acquired by experiments and literature survey. We conducted preliminary analysis of 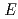 h, ascertained the validity of Phreeq C and identified important points on the analysis. Results were summarized as follows. (1) Thermodynamic data of Fe
h, ascertained the validity of Phreeq C and identified important points on the analysis. Results were summarized as follows. (1) Thermodynamic data of Fe , FeOH
, FeOH , Fe(OH)
, Fe(OH) (aq), Fe(OH)
(aq), Fe(OH)
 , Fe(OH)
, Fe(OH)
 , Fe
, Fe , FeS
, FeS (pyrite), FeCO
(pyrite), FeCO (siderite),Fe(OH)
(siderite),Fe(OH) (s), Fe
(s), Fe O
O (magnetite), Fe(cr) were determined by literature survey. The solubility product of Fe
(magnetite), Fe(cr) were determined by literature survey. The solubility product of Fe CO
CO (OH)
(OH) was determined experimentally, and thermodynamic data were estimated. (2) The corrosion rate of carbon steel was obtained as a function of pH and sulfide ion concentration. (3) After corrosion tests of carbon steel, no CH
was determined experimentally, and thermodynamic data were estimated. (2) The corrosion rate of carbon steel was obtained as a function of pH and sulfide ion concentration. (3) After corrosion tests of carbon steel, no CH , HS
, HS and H
and H S, the reduction product of CO
S, the reduction product of CO
 and SO
and SO
 ,were not detected in liquid and gas phases. (4) Preliminary analysis showed that the redox couple changed as HS
,were not detected in liquid and gas phases. (4) Preliminary analysis showed that the redox couple changed as HS (aq)/SO
(aq)/SO
 , CH
, CH (aq)/CO
(aq)/CO
 , H
, H (aq)/H
(aq)/H O during the evaluation period. After 1000 years,
O during the evaluation period. After 1000 years, 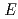 h attained about -500 to -600 mV (vs. NHE) or -750 mV controlled by CH
h attained about -500 to -600 mV (vs. NHE) or -750 mV controlled by CH (aq)/CO
(aq)/CO
 ,or H
,or H (aq)/H
(aq)/H O, respectively.
O, respectively.
Takeda, Seiji; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Sasaki, Toshihisa; Ochiai, Toru; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2008-044, 64 Pages, 2008/03
This document summaries the concept and method (scenario selection, model/code description and parameter selection) for estimation of the radioactivity concentration limits for trench disposal of transuranium and uranium wastes, and provide the derived values of the radioactivity concentration limit for each radionuclide in the wastes. The values for the transuranium waste are published in a Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan report.
Takeda, Seiji; Sasaki, Toshihisa; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Ochiai, Toru; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2008-045, 60 Pages, 2008/03
This document summaries the concept and method (scenario selection, model/code description and parameter selection) for estimation of the radioactivity concentration limits for intermediate depth disposal of transuranium and uranium wastes, and provide the derived values of the radioactivity concentration limit for each radionuclide in the wastes. The values for the transuranium waste are published in a Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan report.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji; Sasaki, Toshihisa; Ochiai, Toru; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2008-046, 62 Pages, 2008/03
The Atomic Energy Commission of Japan states that the transuranium waste and uranium waste are to be disposed of by either near surface disposal without artificial barrier (trench disposal), near surface disposal with artificial barrier (concrete vault disposal), or intermediate depth disposal, depending on the radionuclides and their radioactivity concentration in the wastes. The ranges of radioactivity concentration for these different disposal concepts are, therefore, required to be determined for the regulation. The radioactivity concentration limits define the upper bound of radioactivity concentrations for licensing application of the disposal of radioactive waste. This document summaries the concept and method for estimation of the radioactivity concentration limits for concrete vault disposal of transuranium and uranium wastes, and provides the derived values of the radioactivity concentration limits for each radionuclide in the wastes.
Kawashima, Katsuyuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JAEA-Research 2008-047, 12 Pages, 2008/04
As a part of the FaCT Project, the local feedback reactivities effect on power distributions during control rod withdrawal was studied for a large fast reactor. In the UTOP transient analysis based on the point reactor kinetics model, power distribution is usually given by the steady-state core neutronics calculation performed prior to the transient analysis. However, the power distribution during transient could be different from the one in the steady-state core condition because of local feedback reactivities effect induced by the temperature rise in the fuel assemblies adjacent to the withdrawn control rod. The core calculation model is configured to take into account the transient temperature rise. It is shown that the core radial power distribution skewing is significantly mitigated by considering the local feedback reactivities due to temperature rise. The calculated maximum power density ratio is 1.30, compared with 1.39 calculated under the steady-state core condition.
Kurosaki, Yukio*; Yamachi, Hiroshi*; Katsunuma, Yoshio*; Nakata, Masao*; Kuwahara, Hideki*; Yamada, Fumitaka*; Matsushita, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2008-048, 274 Pages, 2008/03
A junction space between a super deep shaft and horizontal drifts forms a 3-dimensional geo-structure, which would take a complicated mechanical behavior during a junction excavation. However, a quantitative design method for a deep junction has not yet established. In order to examine a collapse mechanism of super deep shaft junction, we have conducted literature surveys and interview studies concerned with a collapses. Considering the results of investigations with reviews of intellectuals, the collapse mechanism depends on both a construction procedure of shaft junction and a geological condition. On the other hand, where a deep junction intersects faults and/or fractures with a large angle, a collapse called taka-nuke may occur and a numerical studies that can simulate a practical rock mass behavior around a shaft junction should be carry out. We demonstrate finite difference method is most adequate for these simulations with intellectual review.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki; Kamide, Hideki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Ezure, Toshiki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Ito, Kei; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Okamoto, Koji*; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-049, 44 Pages, 2008/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has conducted a conceptional design study of a sodium-cooled fast reactor in a frame work of the FBR feasibility study. The plant system concept for a commercial step is intended to minimize a vessel diameter to achieve an economical competitiveness. Therefore, the coolant in the vessel has relatively higher velocity and gas entrainment (GE) prevention from a liquid surface in the reactor vessel becomes one of important issues for the thermal-hydraulic design. In order to establish a design criteria for the GE prevention, the GE from vortex dimples at the liquid surface was investigated by a working group. The 1st proposal of "Design Guideline for Gas Entrainment Prevention Using CFD Method" was established based on the knowledge gained from the working group activities. This report introduces each study in the working group to clarify the basis of the design guideline.
Iida, Hiromasa; Kawasaki, Nobuo*; Konno, Chikara; Sato, Satoshi; Seki, Akiyuki
JAEA-Research 2008-050, 26 Pages, 2008/04
An inconvenient experience was encountered, in which we have different answers depending on applied weight window values, in the nuclear analysis of the benchmark problem for CAD/MCNP interface programs, being developed under the ITER R&D task. Biasing can enhance calculation speed, but should not give different answers. Mechanism of this large underestimation is clarified. It is caused by the combination of the following two facts; (1) When one of particles in a history has got lost, MCNP cancels all tallies calculated during the history and all banked particles are thrown away (never tracked). (2) When we have distributed micro geometry errors in input data, important histories, which give significant contribution to tallies, will have many splitting and have "lost particle" with higher probability in the case of hard biasing. These two facts lead to selective canceling of important histories. An attempt to eliminate this inconvenience has been made, by modifying the subroutine "hstory" of MCNP. The modification has been done very successfully and eliminated the large underestimation, giving the same answer independently from applied weight window values.
Uehara, Kazuya; Nagashima, Takashi*
JAEA-Research 2008-051, 20 Pages, 2008/03
An optimum efficiency and the current profile on the lower-hybrid driven current in tokamaks are estimated in half-experimental by the modified quasi-linear theory including the mode conversion effect, the accessibility condition and the non-linear effect of the parametric instability so as to predict the experimentally obtained flowing current. The spectrum gap is bridged by the gap parameter depending on the electron temperature and the rf power density. It is shown that for the JT-60 parameter an optimum N parallel of the rf wave must be less smaller for the higher electron temperature not to destroy the accessibility condition and the driving efficiency depends on the electron temperature. The survey is also performed for the LHCD of the ITER parameter.
Shibuya, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Takashi*; Kuroda, Hidetaka
JAEA-Research 2008-052, 138 Pages, 2008/07
The soundness of the design of the support system for shafts and galleries and the effects of pre- and post-excavation grouting have been assessed to confirm the proposed technical solutions at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. For this purpose, design of the shafts above 1,000 m depth and the galleries above 500 m depth has been improved and grouting effects around the shafts has been calculated by means of seepage flow analysis. Additionally, analytical investigations on the concrete lining with respect to the influence of water pressure have been performed.
Aoyama, Takafumi
JAEA-Research 2008-053, 264 Pages, 2008/08
This thesis describes the research study to develop the core management method and irradiation field characterization method of the experimental fast reactor Joyo. Improvements of the methods through comparison with measured data from the reactor core physics performance tests of Joyo and post irradiation examination of tests conducted in the Joyo irradiation test facility complex are also described.
Kobayashi, Noboru; Onuki, Akira; Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu
JAEA-Research 2008-054, 145 Pages, 2008/05
A thermal-hydraulic design of the high-conversion (HC) type core of the innovative water reactor for flexible fuel cycle (FLWR) was constructed under the natural circulation core cooling, in order to achieve that HC-FLWR core can be converted to a breeder type one. The criteria on the thermal-hydraulic design of HC-FLWR were that the average void fractions in the core was smaller than 50%, and that the critical power ratio was larger than 1.3. The criterion on void fractions was determined from the nuclear design of HC-FLWR. The length of the chimney and the settings of the inlet orifice are common in both types of cores. The coefficient of the lower tie-plate of the HC-FLWR core and the temperature of the feed water were parametrically changed. Consequently, the design criteria were satisfied by adopting the setting of the form loss coefficients of the lower tie-plate comparable to those of the current BWRs and by lowering the feed water temperature to 505 K.
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Kurihara, Akikazu; Uchibori, Akihiro
JAEA-Research 2008-055, 24 Pages, 2008/06
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, thermal hydraulic studies on sodium-water reaction are being performed with the multi-component and multi-phase code SERAPHIM. The interfacial area concentration of sodium droplets in the steam is important for the accurate analysis of sodium-water reaction. In this report, the theoretical analysis and numerical models for gas jets were reviewed to understand the mixing process of sodium and water. As for theoretical analysis, existing critical flow rate, depressurization and entrainment analysis for jet flows were summarized. The applicability of critical flow rate equations for subcooled water at 17MPa were confirmed after investigating its effect of compressibility. Based on the available knowledge on entrained droplet sizes in gas jets, a transport equation of sodium droplet interfacial area concentration was constructed for multiphase flow simulation.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Wakaida, Ikuo; Watanabe, Kazuo
JAEA-Research 2008-056, 24 Pages, 2008/06
For remote isotope analysis of low-decontaminated TRU fuel, we are developing an analytical technique on the basis of the resonance absorption spectroscopy for the laser-ablation plume. To improve isotopic selectivity and detection sensitivity of this technique, we measured absorption spectra of Gd atom with various conditions. As a result, high resolution spectrum was obtained from the observation of slow component of the plume produced under low-pressure rare-gas ambient. The observed narrowest linewidth of about 0.85 GHz was found to be close to the Doppler width estimated for Gd atom of room temperature. Furthermore, relaxation rate of higher meta-stable state was found to be faster than that of ground state, suggesting that use of the transition arising from ground state or lower meta-stable state is preferable for highly sensitive isotope analysis.
Yokoyama, Sumi; Manabe, Kentaro
JAEA-Research 2008-057, 29 Pages, 2008/06
At Material and Life Science facility of J-PARC, a mercury target as spallation neutron source is used. In the mercury target, airborne radionuclides such as tritium and iodine are formed by spallation reaction with high energy and intensity proton beam. There is possibility that the airborne radionuclides leaked from the target vessel to the air of the facilities may cause internal exposure. However, there is insufficient information about these chemical forms and behavior in mercury to estimate internal doses. We clarified chemical forms and release rates of tritium and iodine from mercury by experiments and discussed from the viewpoint of internal radiation protection. In this study, we found that most tritium formed in mercury is released to the gas-phase as HTO, while iodine is not released under the condition of gas phase in the mercury target.
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Yanagisawa, Hideki*
JAEA-Research 2008-058, 29 Pages, 2008/06
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, investigations on heat transfer characteristics of steam generator are being performed for the development of Sodium-cooled Fast Breeder Reactor. In this report, the numerical methods were studied for two-phase flow instability analysis in steam generator. For numerical simulation purpose, the flow instability analysis code was developed with homogeneous equilibrium model on single heat transfer tube. The special algorithm to calculate inlet flow rate with inlet pressure, outlet pressure and heat flux as boundary conditions for the density-wave instability analysis has been established. The flow instability in single tube was successfully simulated with homogeneous equilibrium model. Then the drift-flux model including the effects of subcooled boiling and two phase slip was adopted to improve the accuracy. The capability of drift-flux model for simulating density-wave instability in single tube was confirmed.
Kamiyama, Kenji; Isozaki, Mikio; Imahori, Shinji; Konishi, Kensuke; Matsuba, Kenichi; Sato, Ikken
JAEA-Research 2008-059, 33 Pages, 2008/07
In CDA of LMFBR, molten core materials would discharge from the core region through the coolant paths. Rapid vaporization of the coolant by mixing of the molten core materials provides effective evacuation of the liquid coolant from the path and reduces significantly possibility of core-material freezing and blockage formation inside the paths. This characteristic enhances early discharge of molten-core materials and reduces possibility of severe re-criticality events. In this study, melt discharge experiments were conducted with a coolant channel simulating the discharge path with an enhanced length of the path compared with that of the realistic design structure. An alloy and water were used as simulant of the molten fuel and sodium respectively. This series of experiments showed that the discharge path can be entirely voided by vaporization of a part of the coolant at the initial melt discharge phase, followed by vapor expansion toward the end of the coolant channel. Furthermore, it was revealed that the condition where coolant void expansion started can be defined by melt-coolant sensible heats ratio and the heated height of the coolant. The heat balance evaluation during the coolant void expansion phase shows that the film condensation heat transfer should be considered. The coolant-void-expansion behavior in the discharge path of the realistic design condition was estimated based on an application of this knowledge to existing experiments with molten oxide and sodium.
Geological Isolation Research and Development Directorate; Advanced Waste System Research Project, Radioactive Waste Management Funding and Research Center*
JAEA-Research 2008-060, 72 Pages, 2008/06
JAEA and RWMC have carried out a joint research program on advanced technologies that could be used to support performance assessment and monitoring of geological disposal concepts for high-level radioactive waste. The 5 items regarding to performance assessment and 1 item for monitoring were considered in the program. The items were discussed in the context of technological experiences gained by JAEA and RWMC in previous repository-related studies. According to the results of these discussions, development strategies for each of the technology areas identified above were efficiently formulated by appropriate task allocations. Specific technical subjects requiring further investigation were identified using this approach, and a priority of subject was also discussed.
Sato, Isamu; Tanaka, Kosuke; Tanaka, Kenya
JAEA-Research 2008-061, 36 Pages, 2008/07
The diffusion coefficients of Pu and Am in UO fuel have been evaluated by use of a diffusion couple, in which a UO
fuel have been evaluated by use of a diffusion couple, in which a UO pellet and an Am containing MOX fuel contact each other. The heating temperature, time and atmosphere is 1650
pellet and an Am containing MOX fuel contact each other. The heating temperature, time and atmosphere is 1650 C 4.5h and Ar gas, respectively. We could catch the diffusion behavior of Pu and Am in UO
C 4.5h and Ar gas, respectively. We could catch the diffusion behavior of Pu and Am in UO . The value of diffusion coefficient of Pu and Am were evaluated to be 4-6
. The value of diffusion coefficient of Pu and Am were evaluated to be 4-6 10
10 m
m /sec. On the other hand, we try to estimate the tracer-diffusion coefficients with the molecular dynamics. Around 2000 K (close to the heating temperature), the coefficient was near 10
/sec. On the other hand, we try to estimate the tracer-diffusion coefficients with the molecular dynamics. Around 2000 K (close to the heating temperature), the coefficient was near 10 m
m /sec, which was agree with the value from Matzke's evaluation. This indicates the possibility of molecular dynamics for estimation of the diffusion coefficient. The gap between the coefficient from the test and reference (or estimation) might result from the affection of grain boundaries.
/sec, which was agree with the value from Matzke's evaluation. This indicates the possibility of molecular dynamics for estimation of the diffusion coefficient. The gap between the coefficient from the test and reference (or estimation) might result from the affection of grain boundaries.
Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Umeda, Koji; Sasao, Eiji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Saito, Tatsuo; Yasue, Kenichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Mashima, Hidehisa*; Shimada, Koji; Yamada, Kunimi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-062, 61 Pages, 2008/07
The Japanese islands are located in the tectonically active Circum-Pacific Mobile Belt. As a result, Japan has a high frequency of earthquakes and eruptions. Special consideration is given to the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. Development of research/prediction technologies for geotectonic events has been carried out to evaluate the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. During fiscal year 2006, we carried out the following researches, to confirm existence of the phenomena that have influences on geological disposal system, and to develop the research techniques to reconstruct the history of these phenomena. For studies of active faulting and seismic activity, we reviewed the existing techniques to research past activities and distribution of active faults (migration, extension, development process of a deformation zone). For volcanological and geothermal studies, we extracted a technique for detecting crustal magma and/or geothermal fluid in deep underground using geophysical and geochemical data, and models assessing the likelihood of future volcanism and its influence on geological environment. For studies of uplift/denudation and climatic/sea-level change, we constructed conceptual models such as landform development model.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Takehiro; Sugita, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2008-063, 37 Pages, 2008/09
As part of the research and development program on geological disposal of HLW, the Horonobe Underground Research Center, a division of the JAEA, is implementing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Horonobe URL Project) with the aim of investigating sedimentary rock formations. According to the research plan described in the Midterm Plan of JAEA, geological investigations are to be carried out during the drilling of a shaft down to intermediate depth, while research and development in the areas of engineering technology and safety assessment are to be promoted by collaboration with other research organizations. The results of the R&D activities will be systematized as a "knowledge base" that supports a wide range of arguments related to the safety of geological disposal. The Horonobe URL Project is planned to extend over a period of 20 years. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" and "Phase 3: Operation phase". This report summarizes the investigation program for the 2008 fiscal year (2008/2009), the 4th year of the Phase 2 investigations. In the 2008 fiscal year, investigations in "geoscientific research" and "research and development on geological disposal technology" are continuously carried out. Construction of the underground facilities is ongoing at Ventilation Shaft and Access Shaft (East). Pre-boring around Ventilation Shaft is also carried out Regarding the surface facilities, construction of the International Communication House will be started.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi; Hayakawa, Masao*; Nagashima, Nobuo*
JAEA-Research 2008-064, 118 Pages, 2008/08
This report describes a result of the research conducted by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency and the National Institute for Materials Science under contract with JNES that was concerned with a multi-scale analysis of plastic deformation behavior at the crack tip of SCC. In this research, analyses of the plastic deformation behavior and microstructure around the crack tip were performed in a nano-order scale. The hardness measured in nano, meso and macro scales was employed as a common index of the strength, and the essential data necessary to understand the SCC propagation behavior were acquired and analyzed that are mainly a size of plastic deformation region and a microstructural information in the region, e.g. data of crystallografy, microscopic deformation and dislocations at the inside of grains and grain boundaries.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-065, 51 Pages, 2008/08
This report describes the results of the works in the fiscal year 2007. In Chapter 1, we described the overview and background of this study. In Chapter 2, the result of continuing creep test of Tage tuff which was started from the fiscal year 1997 was described. Although there was some annual variability, the precious data were obtained. In Chapter 3, the control program for the generalized relaxation test was developed. The generalized relaxation test of Toki granite was conducted in order to get basically data. In Chapter 4, the extended constitutive equation of variable compliance was analytically discussed. Using the data obtained in Chapter 3, the parameters of Toki granite of the constitutive equation were obtained and numerical simulation was conducted.
Kurosaki, Yukio*; Yamachi, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-066, 168 Pages, 2008/09
Mizunami underground research laboratory planned to excavate to 1000 m depth and now under construction. One of the most serious problems in a greatly deeper shaft is "TAKANUKE" collapse caused by slip movement of large discontinuities. In this report, we have conducted numerical studies using finite difference method in order to throw an objective light on a mechanism of TAKANUKE collapse. These studies show two different stress states in upper and lower side of large discontinuities. In order to evaluate a possibility of TAKANUKE collapse during MIZUNAMI main shaft sinking, we have conducted a particle body analysis as well. A fault with a high strike up to 79 degree, discovered in survey boring at MIZUNAMI site, has a low potential of TAKANUKE collapse during shaft sinking.
Sato, Hisashi; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2008-067, 32 Pages, 2008/09
A parallel plate fracture model is used for the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal in crystalline rocks, such as granitic rocks. However, it is known that an effect of heterogeneously distributing fracture aperture onto the hydraulic property is different from the transport property used for the parallel plate model. Therefore, in order to investigate influences of heterogeneity of aperture distribution to the hydraulic and mass transport properties used for parallel plate model, aperture distribution and tracer concentration distribution data measured by optical method has been examined to understand the relationship between fracture transmissivity and transport aperture. The numerical simulation based on darcy flow shows 1.6 times larger flow rate than the data obtained from the hydraulic test. This result is one of precious evidence supported by quantitatively measured aperture data to demonstrate the inconsistency of the assumption of "local cubic law".
Yamazaki, Masanao; Yamaguchi, Takehiro; Funaki, Hironori; Fujikawa, Daisuke; Tsusaka, Kimikazu
JAEA-Research 2008-068, 45 Pages, 2008/09
This report summarizes the measurement plan during construction of the underground facility based on the design in advance and the observational construction program for feedback measurements data into design and construction on subsequent steps. This report also describes about design and construction management program for contractor of underground facilities.
 11 boreholes and update of the rock mechanical model around the Horonobe URL construction area
11 boreholes and update of the rock mechanical model around the Horonobe URL construction areaSanada, Hiroyuki; Niunoya, Sumio*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-069, 57 Pages, 2008/09
The investigations of Horonobe URL (Underground Research Laboratory) project is subjected of the siliceous rocks in Horonobe-cho Teshio-gun Hokkaido. This research report shows the result of the rock mechanical investigations which have been carried out from 2004 to 2005 as a part of the project. The objectives of the rock mechanical investigation are follows to obtain the data which were necessary for construction design of URL and to confirm the distribution of rock mechanical properties in URL construction area. Considered result acquired from this investigation, when we tried to update the rock mechanical model, there was no point of main policy change in the model.
Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Takehiro
JAEA-Research 2008-070, 38 Pages, 2008/09
In the 2007 fiscal year, investigations in "geoscientific research" is continuously carried out. Investigations in "research and development on geological disposal technology" is also continuously carried out. Construction of the underground facilities is ongoing at Ventilation Shaft and East Shaft. Pre-boring around Ventilation Shaft is also carried out. Regarding the surface facilities, construction of the Public Information House and preparation of the exhibits are still continuing and will be completed in May 2007. Public Information House will be scheduled to open in this summer. A detailed design will be drawn up for the International Communication House.
Matsuo, Koichi*; Kishimoto, Munemaru*; Makuuchi, Ayumu*; Teshima, Minoru*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Niunoya, Sumio*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-071, 44 Pages, 2008/09
Correlation between resistivity in rock mass and groundwater quality is shown from the results of investigation such as borings and geophysical exploration. Electrical resistivity survey had been done to understand impact on behavior of groundwater by construction of underground research laboratory. This paper shows distribution of resistivity around underground research laboratory obtained from electrical resistivity survey.
Yokoyama, Yutaka*; Mitsui, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Rieko; Taniguchi, Naoki; Asano, Hidekazu*; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2008-072, 232 Pages, 2008/10
It is possible that the corrosion resistance at the overpack welds is different from that at base metal due to the differences of material properties. In this study, corrosion behavior of welded joint for carbon steel was compared with base metal using the specimens taken from welded joint model fabricated by TIG (Tungsten Arc Welding, GTAW), MAG (Gas Metal Arc Welding, GMAW) and EBW (Electron Beam Welding) respectively. The results of these corrosion tests indicated that the corrosion resistance to general corrosion, pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion at welded metal of TIG and MAG was inferior to base metal. No deterioration of corrosion resistance was observed in any corrosion modes for EBW, which does not need filler material. Neither the base metals nor the welds is not susceptible to SCC under the carbonate concentration near that of the disposal environment.
Ueno, Kenichi; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Suyama, Tadahiro
JAEA-Research 2008-073, 25 Pages, 2008/10
The iron-bentonite interaction was assessed no significant effect for long term stability of buffer material. But recently, smectite alteration for non-swelling mineral such as berthierin at iron-rich environment was reported. This report wraps up the recent study and assess for the effect of iron-bentonite interaction for long term stability of buffer materials. In this report processes for candidate under repository condition were considered following three phenomena, ion-type changing from Na -type bentonite to Fe
-type bentonite to Fe -type, mineralogical alteration for non-swelling minerals and cementation caused by corrosion products.
-type, mineralogical alteration for non-swelling minerals and cementation caused by corrosion products.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2008-074, 72 Pages, 2008/09
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project is planned to extend over a period of 20 years. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction Phase"(investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase"(research in the underground facilities). This report summarizes the results of the investigations for the 2007 fiscal year (2007/2008), the 3rd year of the Phase 2 investigations. The investigations, which are composed of "Geoscientific research" and "R&D on the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW)", were carried out according to "Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project Investigation Program for the 2007 Fiscal Year". The results of these investigations, along with the results which were obtained in other departments of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), are properly offered to the implementations and the safety regulations. JAEA proceeded with the project in, collaboration with experts from domestic and overseas research organization.
Futagami, Satoshi; Hayafune, Hiroki; Sato, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Research 2008-075, 94 Pages, 2008/10
Based on the comprehensive evaluation in FS, straight double-wall tube SG was recommended as reference design. But straight double-wall tube SG has many technical issues. Alternative SG was designed by the objects as shown bellow. "safety performance is equal to reference design", "property protection performance is equal to reference design", "economically acceptable", "based on common technology with reference design", To design alternative SG with prevention of tube failure propagation, design options to resist the wastage by sodium-water reaction were evaluated from the point of view of property protection performance. And, candidates for alternative SG were proposed with combination of design options. By comparative evaluation of alternative SG by view of technical issues and adoption time, "Protective wall tube SG", "Coated wall tube SG" with resistance to tube wastage, and "Short length double wall tube SG" with low difficulty were elected.
Shibata, Takemasa; Tamura, Koji; Ogura, Koichi
JAEA-Research 2008-076, 13 Pages, 2008/10
Cross sections of symmetric charge transfer are calculated for ytterbium, lutetium and samarium. Symmetric charge transfer of lanthanoide elements in most cases has two main reaction paths, that is, resonant and non-resonant paths due to open 4f shells inside 6s electrons. At low impact energy, charge transfer cross sections are small because only resonant path is possible. On the other hand, the charge transfer of ytterbium, lutetium and samarium has only resonant path. Therefore the charge transfer cross sections of these atoms decrease monotonically with the impact energy. The cross sections of ytterbium and samarium are 203  and 224
and 224  at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu, respectively. These values are larger than the cross sections of many lantanoid elements such as dysprosium. The cross section of lutetium is 65
at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu, respectively. These values are larger than the cross sections of many lantanoid elements such as dysprosium. The cross section of lutetium is 65  at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu. This value is small due to d-electron transfer.
at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu. This value is small due to d-electron transfer.
Yamauchi, Hiroki; Ishii, Yoshinobu*; Igawa, Naoki; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Utsumi, Wataru
JAEA-Research 2008-077, 28 Pages, 2008/10
The neutron powder diffractometer, HRPD, can provide high-resolution data that meet the many users' needs until now. On the other hand, the demand of high-efficiency is growing in the recent years. In order to improve the source intensity and measurement efficiency, the authors tried to develop asymmetric reflection-type Ge monochromators. The mosaic crystals (20 in the horizontal direction) were cut at an angle of 40
in the horizontal direction) were cut at an angle of 40  relative to the Ge,3,3,1 reflecting planes. The diffraction results of standard Si samples reveal that peak intensities by the asymmetric type are improved 1.2 times larger than those by the existing symmetric type, but integrated intensities are almost comparable each other. For mosaic crystals, asymmetric reflections in compression geometry intensify the current density, but reflectivity is always less than that in symmetric reflections, and thus the suppression of the reflectivity just cancels out the enhancement of the current density.
relative to the Ge,3,3,1 reflecting planes. The diffraction results of standard Si samples reveal that peak intensities by the asymmetric type are improved 1.2 times larger than those by the existing symmetric type, but integrated intensities are almost comparable each other. For mosaic crystals, asymmetric reflections in compression geometry intensify the current density, but reflectivity is always less than that in symmetric reflections, and thus the suppression of the reflectivity just cancels out the enhancement of the current density.
 concentration at extraction section
concentration at extraction sectionNakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Koizumi, Tsutomu
JAEA-Research 2008-078, 24 Pages, 2008/10
Concerning the advanced aqueous reprocessing system, we have been investigating a simplified solvent extraction process using TBP as an extractant for U, Pu and Np co-recovery. The experiment was conducted with low HNO concentration in the feed solution and high HNO
concentration in the feed solution and high HNO concentration in the scrubbing solution, which was expected to bring a high HNO
concentration in the scrubbing solution, which was expected to bring a high HNO concentration into the extraction section and the efficient Np oxidation and extraction in this section. This experiment had been conducted with the dissolver solution of "JOYO" Mk-I and Mk-II irradiated MOX fuel. The Pu valence was adjusted to Pu(IV) by bubbling NOx gas into the feed solution. It was attempted to oxidize Np(V) to Np(VI) in the extraction section by adjusting HNO
concentration into the extraction section and the efficient Np oxidation and extraction in this section. This experiment had been conducted with the dissolver solution of "JOYO" Mk-I and Mk-II irradiated MOX fuel. The Pu valence was adjusted to Pu(IV) by bubbling NOx gas into the feed solution. It was attempted to oxidize Np(V) to Np(VI) in the extraction section by adjusting HNO concentration of the feed and scrubbing solutions to 3.9M and 10M, respectively. After operation, the Np leakage to the raffinate could be kept under 6.3%. The decontamination factor of total-
concentration of the feed and scrubbing solutions to 3.9M and 10M, respectively. After operation, the Np leakage to the raffinate could be kept under 6.3%. The decontamination factor of total- was 5.1
was 5.1 10
10 in this experiment.
in this experiment.
Tetsu, Keiichi*; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2008-079, 30 Pages, 2008/10
For the safety assessment of HLW geological disposal system, the homogeneous parallel plate model is usually applied as one of the nuclide migration evaluation models. The transmissivity and the fracture aperture as an average characteristic is one of important parameters in the parallel-plate model. However, the natural fractures have complex characteristics such as infilling of gauge, branching and roughness of fracture surface. The methodology how to justify those parameter values is one of the important issues. In this study, 50cm scale of the rock block includes single natural fracture was excavated from Kamaishi in-situ experiment site and observed a fracture by grinding the rock surface iteratively. A series of the digital image data of the fracture was obtained in 500 grinding sections, perpendicular to fracture profile. The coordinate of fracture topography was measured in interval of 1mm at each section, and the fracture data was obtained about 250,000 data points.
Hattori, Shuji*; Inoue, Fumitaka*; Kurachi, Hiroaki*; Watashi, Katsumi; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Hashimoto, Takashi; Yada, Hiroki
JAEA-Research 2008-080, 45 Pages, 2009/02
Research on cavitation erosion in liquid metal is very important to confirm the safety of fast breeder reactor using sodium coolant. In this study, a cavitation erosion test apparatus was developed to carry out the erosion tests in low-temperature liquid metals. Cavitation erosion tests were carried out in liquid lead-bismuth alloy and in deionized water. We discuss the effect of liquid parameters and temperature effects on the erosion rate. We reach to the following conclusions. The erosion rate was evaluated in terms of a relative temperature which was defined as the percentage between freezing and boiling points. At 14  C relative temperature, the erosion rate is 10 times in lead-bismuth alloy, and 2 to 5 times in sodium, compared with that in deionized water. The erosion rate can be evaluated as a function of material density and sound velocity. Finally, the temperature dependence was discussed in term of liquid vapor pressure.
C relative temperature, the erosion rate is 10 times in lead-bismuth alloy, and 2 to 5 times in sodium, compared with that in deionized water. The erosion rate can be evaluated as a function of material density and sound velocity. Finally, the temperature dependence was discussed in term of liquid vapor pressure.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2008-081, 16 Pages, 2008/11
For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is very important to investigate the analytical method to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium and plutonium. Experiments using gadolinium as simulated sample, in which several 100 ppm of copper was contained, were performed and the analytical performance was estimated. The spectrum was decomposed into each peak of some spectra component on Gd and Cu. And the result, intensity of Cu component intermingled in Gd was determined quantitatively. In order to evaluate the linearity in the impurity analysis, the experiments with various concentration of Cu were carried out. The detection limit was determined to be about 70 ppm from the equivalent noise level which was estimated from the standard deviation in wavelength. The results curried out under the other laser conditions (intensity and wavelength) ware also evaluated.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Murakami, Hiroshi; Masuda, Kenta; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Matsuda, Setsuro; Ichige, Satoru; Takahashi, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-082, 84 Pages, 2008/11
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H19 (2007) fiscal year, which are (1) treatment and packaging of TRU waste including applicability of calcination for unpacking and sorting of wastes, characterization and inspection methodology of TRU waste, (2) mechanical assessment for the near-field structure including model development and preparation, introduction of hostrock creep model and coupling analysis of deformation of hostrock and engineered barrier. (3) performance assessment of the disposal system including data acquisition and preparation on radionuclides migration, cementitious material alteration, bentonite and hostrock alteration with alkaline solution and nitrate effect, and (4) alternative technology development including decomposition of nitrate.
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yoshida, Eiichi
JAEA-Research 2008-083, 25 Pages, 2008/11
In case of the tube failure in the steam generator of the sodium cooled fast breeder reactor, its adjoined tubes are rapidly heated up by the chemical reaction between sodium and water/steam. And it is known that the tubes have the damage called "wastage" by the disclosure steam jet. This research is a fundamental study based on the metallography about temperature estimation of the damaged tubes at the sodium-water reaction for being reflected in establishment of the mechanism theory analysis technique of the behavior. In the examination, the material which gave the rapid thermal history which imitated sodium-water reaction was produced. And it was investigated whether the thermal history (i.e. maximum temperature and the holding time) of the samples could be presumed from the metallurgical examination of the samples.
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Nakama, Shigeo; Yamada, Atsuo*; Hirano, Toru; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2008-084, 35 Pages, 2008/11
To establish a scientific and technical basis of geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, Japanese Atomic Energy Agency is advancing the geo-scientific research project of Mizunami Underground laboratory (MIU) in crystalline rock environment at Tono Geo-science Center. At MIU, the geo-scientific research is planned to be carried out in three Phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase, Construction Phase and Operation Phase. Currently, the Project is under the Construction Phase. This report presents the following results about rock mechanics studies conducted in the 2006 fiscal year, (1) The boring investigation for rock mechanics, from the connection gallery opened on G.L.-100m, (2) The advanced study for determination of three dimensional distributions of the initial rock stress, (3) The advanced study to evaluation of rock-stress using boring cores, (4) The basic study on crystalline rock for evaluation of long-term behavior.
Osawa, Hideaki; Ota, Kunio; Hama, Katsuhiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Shinji; Amano, Kenji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Miyamoto, Tetsuo; Toyoda, Gakuji; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-085, 742 Pages, 2008/11
This report shows the results the project for the establishment of comprehensive site characterization technology, entrusted from Natural Resources and Energy Agency, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Natural Resources and Energy Agency in 2007.
Ishizaka, Kaoru*; Tanaka, Masaru*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Sato, Kazuhiko; Koga, Osamu
JAEA-Research 2008-086, 64 Pages, 2008/12
In this study, to discuss the appropriate Risk Communication (RC) method on the uranium mining sites reclamation, comparative investigation of RC cases which concern the siting of solid waste management facilities and nuclear facilities, and questionnaire survey on the risk perception of landfill were conducted. As a result of comparative investigation, information disclosure and supplement are important factor to obtain public trust on the siting plan and developer. As assumption of the public participation, it is necessary the safety assurance of the siting plan and regional development plan cover a long period. As a result of questionnaire survey, it was shown that the almost people worried about health and the environmental impact of radioactive waste; moreover, there are a lot of ratios of the peoples who felt a dangerous and scary sensuously.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2008-087, 148 Pages, 2008/10
This report presents major results observed in LOCA test (SB-CL-09) conducted at the ROSA/LSTF test facility simulating 10% cold leg break in a 4-loop Westinghouse-type PWR. Following are found in this test with an assumption of high pressure injection system. (1) The relatively large break size resulted in pressure inverse within 2 minutes between the primary and steam generator secondary sides. (2) During a loop-seal clearing (LSC) process started at about 1 minutes after the break, the core water level was suppressed to almost lower end and then it recovered to the middle core height. The water level remained at the middle height was due to remained water levels in the SG U-tube inlet sides which were higher than their outlet sides. (3) Significant core heat-up was observed above the water level at the middle height and core power was tripped off at 111s. (4) The effects of fall-back water from the intact loop hot leg was observed by the local core cooling.
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Kunimaru, Takanori; Shibano, Kazunori
JAEA-Research 2008-088, 78 Pages, 2009/01
Spectral analyses of the groundwater pressure data which has been monitored in the boreholes; HDB-3, 6, 7 and 8, were carried out to estimate formation properties and remove the components of response to atmospheric pressure fluctuation and earth tide from time series. The results revealed that groundwater pressure at the all intervals responds to atmospheric pressure but does not respond to earth tide at all above the resolution of measurements. Specific storage, vertical hydraulic conductivity and shear modulus were estimated from the response to atmospheric loading and compared with the data obtained in the laboratory experiments.
Chiba, Go; Okumura, Keisuke
JAEA-Research 2008-089, 48 Pages, 2008/11
Integral test for various evaluated nuclear data files has been carried out in order to support the development of JENDL-4. Integral test and sensitivity analysis have been done for the copper, tungsten, iron, beryllium and deuterium nuclear data, and beneficial information for the nuclear data evaluation for those nuclides has been obtained. In addition, another integral test for light water solution systems, plutonium aging effect and low enriched-uranium solution systems has been carried out, and beneficial information also have been obtained.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-090, 52 Pages, 2008/11
This report describes the results of the works in the fiscal year 2007. In Chapter 1, we described the overview and background of this study. In Chapter 2 a reaction theory of pressure dissolution of quartz was proposed and by using a homogenization analysis the dissolution of quartz in bentonite was simulated by a modified diffusion model. In Chapter 3 CLSM was used to acquire clearly focused three-dimensional images of granite specimens of Mizunami underground lab for stress relaxation tests, and observed the change of micro-scale structure including the mineral configuration under applying compression stress. The local strain distributions suggest that a shearing mode is dominant in the granite samples. In Chapter 4 a strong discontinuity concept is introduced in the micro-scale problem of the multi-scale homogenization analysis, and Toki granite sample problems were solved.
Zukeran, Atsushi*; Chiba, Go; Otsuka, Naohiko*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Takano, Hideki*
JAEA-Research 2008-091, 162 Pages, 2009/02
Uncertainty of Doppler reactivity is theoretically formulated and then uncertainties of self-shielding factor and its temperature gradient due to errors of resonance parameters were evaluated from NJOY output. Sensitivity analysis was made for  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu and
Pu and  Pu of JENDL-3.3 based on JFS-3 70 group structure. Resultant sensitivity coefficients are provided for the uncertainty evaluation of Doppler reactivity.
Pu of JENDL-3.3 based on JFS-3 70 group structure. Resultant sensitivity coefficients are provided for the uncertainty evaluation of Doppler reactivity.
Ishitoya, Kimihide; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Takase, Toshio*; Kurosawa, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Research 2008-092, 64 Pages, 2008/12
In this study, some scenarios for safety assessments were developed. According to each developed scenario, the parameters were set up for dose calculation. Calculated results were analyzed and summarized from the viewpoints of effects of radionuclide migration parameters such as release coefficient, distribution coefficient, ground water velocity and migration distance. Dose more than 10  Sv/y was calculated in some cases. Increase of ground water velocity or decrease of distribution coefficient caused by sea water inflow into migration path influenced slightly on the dose excess. In case of rapid change of the parameters, severe influences on the dose excess were observed. But, it wasn't thought that this rapid change would happen actually. On the other hand, in case of linear assumption of parameter change from 10,000 y to 100,000 y, dose less than 10
Sv/y was calculated in some cases. Increase of ground water velocity or decrease of distribution coefficient caused by sea water inflow into migration path influenced slightly on the dose excess. In case of rapid change of the parameters, severe influences on the dose excess were observed. But, it wasn't thought that this rapid change would happen actually. On the other hand, in case of linear assumption of parameter change from 10,000 y to 100,000 y, dose less than 10  Sv/y was calculated.
Sv/y was calculated.
Ezure, Toshiki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Kamide, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2008-093, 34 Pages, 2008/12
Concerning the vortex cavitation in the sodium-cooled fast reactor, basic experiments were performed. The effects of pressure and viscosity on the inception of vortex cavitations were examined in a basic water experiments. As the results, it appeared that the onset value of cavitation coefficient became higher with the increase of the pressure. In addition, it also appeared that the onset value of cavitation coefficient became higher with lower viscosity. However, this difference of onset value for the viscosity became smaller with the increase pressure, and was negligible with the same pressure in the real reactor.
Hato, Shinji; Homma, Toshimitsu
JAEA-Research 2008-094, 95 Pages, 2009/02
The atmospheric diffusion experiments were implemented by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) around Mount Tsukuba in 1989 and 1990, and the tracer gas concentration were monitored. In this study, the Gauss Plume Model and RAMS/HYPACT that are meteorological forecast code and atmospheric diffusion code with detailed physical law are made a comparison between monitored concentration. In conclusion, the Gauss Plume Model is better than RAM/HYPACT even complex topography if the release is around release point and short estimation. This reason is difference of wind between RAMS and observation.
Kuji, Masayoshi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Hara, Masato; Minamide, Masashi*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Takeuchi, Shinji; Sato, Toshinori*; Asai, Hideaki
JAEA-Research 2008-095, 54 Pages, 2009/01
A large amount of water inflow is frequently generated during the excavation of an underground cavern, such as road and railway tunnels, underground electric facilities etc. The reduction of water inflow is sometimes quite important for the reduction of cost for the water treatment and pumping during the construction of an underground cavern. The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) is currently being constructed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. During its excavation, a large amount of water inflow into the shafts has been increasing and affecting the project progress. Therefore, a field experiment of post-excavation grouting around the Ventilation Shaft in a sedimentary formation carried out to confirm the effect of existing grouting technology for sedimentary formations in MIU project. The result shows that the applied methods in this field experiment are effective to prevent water inflow. This report describes the summary of the field experiment and the knowledge obtained through the experiment.
Ueta, Shohei; Tobita, Tsutomu*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Tomimoto, Hiroshi; Kozawa, Takayuki; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Masayuki
JAEA-Research 2008-096, 34 Pages, 2009/01
The temperature monitors for fuel blocks in high temperature gas reactors during operation are being developed. The temperature monitors consist of alloy wires, with various melting points, sealed in quarts capsules. The temperature can be evaluated in the range from 600 to 1400  C with 22 types of the temperature monitors. The temperature monitors have been irradiated by the capsule in JMTR, and then, PIEs such as X-ray radiograph and EPMA have been carried out. As the results of the PIE, it was estimated that the temperature monitors can be used up to 90 days at 1100
C with 22 types of the temperature monitors. The temperature monitors have been irradiated by the capsule in JMTR, and then, PIEs such as X-ray radiograph and EPMA have been carried out. As the results of the PIE, it was estimated that the temperature monitors can be used up to 90 days at 1100  C, or up to 50 days at 1300
C, or up to 50 days at 1300 1350
1350  C.
C.
Matsumoto, Kazuhiro; Iijima, Kazuki; Tanai, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2008-097, 64 Pages, 2009/02
In the geological disposal of High Level Radioactive Waste (HLW), buffer material composed of engineered barriers system is expected to play important roles for the post-closure safety, for example, retardation of radionuclide migration. After overpack is breached, vitrified waste is considered to be dissolved by groundwater, followed by radionuclide dissolution into the groundwater and migration through the buffer material, as a reference scenario of safety assessment. It is also concerned about that bentonite colloids generated from the buffer may sorb radionuclides released from the buffer and consequently facilitate the radionuclide migration due to forming stable pseudo-colloids. In this study, erosion experiments of bentonite were carried out under the flow condition simulating groundwater flow and the generation rate of bentonite colloid from buffer materials is also discussed.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Takeuchi, Shinji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Mizuno, Takashi; Oyama, Takuya
JAEA-Research 2008-098, 116 Pages, 2009/02
The excavation and pumping of water from the shafts of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project were halted on October 2005 due to fluoride and boron concentrations in the discharge water that exceeded the Japanese Environmental Standards for discharge into rivers. The numerical simulations indicate that predicted volume of inflow water into the shafts would be considerably greater as the shaft sinking advances. Consequently, JAEA decided to carry out pilot borehole investigations from the bottom of the two shafts to acquire information for increasing the capacity of the water treatment facility, planning for the grouting and reconsideration of the facility design by obtaining information on the geological environment. Based on the pilot borehole investigations, information on the geological environment to a depth of around 500 mbGL was obtained and synthesized.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-099, 171 Pages, 2009/03
In this year, the following studies were carried out with the aim of systemizing the technology on the investigation and analysis to understand the deep underground geological environment in relation to the radioactive waste disposal. (1) The study on the research and development (R&D) subjects which turned to the practical investigation and analysis of deep underground geological environment. (2) The study on the advanced technical basis for the investigation and analysis of deep underground geological environment. The results obtained from the studies are as follows: Regarding (1), the specific investigations, measurements, numerical and chemical analyses were performed particularly for research subjects: (a) the repository design and engineering technology and (b) geological environment. Based on the results on (1), (c) tasks of collaboration research on niche area between the research fields, including the safety assessment field, were selected. Also subject's items of the NFC (Near Field Concept) redefinition were discussed. Regarding (2), based on the extraction tasks of JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) research project, the study was implemented with applying previous R&D results and detailed research at the research field was carried out. This study contributed to the R&D development for its practical application.
 accelerator for ITER NB system
accelerator for ITER NB systemKashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2008-100, 82 Pages, 2009/02
In a neutral beam (NB) system for heating and current drive of ITER, detailed designs of a multi aperture five stage accelerator to produce 1 MeV 40 A D and 870 keV 46 A H
and 870 keV 46 A H ion beams are ongoing. However, it was expected that the shinethrough power from 870 keV H
ion beams are ongoing. However, it was expected that the shinethrough power from 870 keV H beam was above tolerable level for the maximum plasma density prior to any H mode. Therefore, it was required to reduce the beam energy to 500 keV with maintaining high beam current. The objective of this study is to identify necessary modifications from the original five stage accelerator to a three stage accelerator to produce 500 keV H
beam was above tolerable level for the maximum plasma density prior to any H mode. Therefore, it was required to reduce the beam energy to 500 keV with maintaining high beam current. The objective of this study is to identify necessary modifications from the original five stage accelerator to a three stage accelerator to produce 500 keV H ion beam. The physics design of the three stage accelerator was carried out based on a beam optics study in a 2D beam analysis, a beamlet steering design in a 3D multi beamlets analysis and gas density / stripping loss of negative ions in a 3D gas analysis. Finally, the items for necessary modification were summarized.
ion beam. The physics design of the three stage accelerator was carried out based on a beam optics study in a 2D beam analysis, a beamlet steering design in a 3D multi beamlets analysis and gas density / stripping loss of negative ions in a 3D gas analysis. Finally, the items for necessary modification were summarized.
Shimo, Michito*; Kumamoto, So*; Karasaki, Kenji*; Sato, Hisashi; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2008-101, 70 Pages, 2009/03
It is important for safety assessment of HLW geological disposal to evaluate groundwater flow and mass transport in deep underground. The fractures might dominate flow and transport even though it is soft sedimentary rocks. In this study the following three tasks were carried out. Firstly, non-sorbing tracer experiments were carried out. The obtained breakthrough curve was interpreted and mass transport parameters, such as longitudinal dispersivity, matrix diffusion coefficient, transport aperture, were obtained. Secondary, several cases mass transport simulations using single fracture model that the hydraulic aperture, transport aperture, and porosity is different were performed to study on the influence that a difference of the aperture and porosity gives a mass transport in the fractured sedimentary rocks. Finally, groundwater flow was simulated to estimate the flow direction and recharge from the surface using the temperature distribution data obtained in Horonobe boreholes.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Teshima, Minoru*; Kishimoto, Munemaru*; Matsuo, Koichi*
JAEA-Research 2008-102, 58 Pages, 2009/03
The present document is to report the result of geophysical survey by electric survey around a site proposed for the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project at Horonobe-cho, Hokkaido by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This Electric survey using pole-pole array in Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Area was the second survey. Resistivity distribution near surface was about 20 ohm-m and it become to about 2 ohm-m as the depth increasing. Resistivity distribution was good agreement with existing survey results and existing electrical resistivity log data. By comparing resistivity model with hydrology model, it was confirmed that resistivity reflected the density of salinity. The range and distribution trends of apparent resistivity in this year were similar to the results of last year. It is thought that the data in which reproducibility is high is acquired in this survey. The influence on the underground water flow by construction is not admitted now.
Tamura, Junji*; Kido, Hiroko*; Hato, Shinji; Homma, Toshimitsu
JAEA-Research 2008-103, 94 Pages, 2009/03
The plume models are used in probabilistic accident consequence assessment (PCA) codes due to cost and time savings. The PCA code, OSCAAR developed by JAERI (Present; JAEA) uses the puff model to calculate atmospheric transport and dispersion. In order to investigate uncertainties involved with the structure of the atmospheric dispersion/deposition model in OSCAAR, we have introduced the more sophisticated computer codes that included regional meteorological model RAMS and atmospheric transport model HYPACT, and comparative analyses between OSCAAR and RAMS/HYPACT have been performed. In this study, model verification of OSCAAR and RAMS/HYPACT was conducted using data of long term atmospheric diffusion experiments, which were carried out in Tokai-mura, Ibaraki-ken. The predictions by models and the results of the atmospheric diffusion experiments indicated relatively good agreements. And it was shown that model performance of OSCAAR was the same degree as it of RAMS/HYPACT.
Masuda, Kenta; Oda, Chie; Nakanishi, Hiroshi*; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Takase, Toshio*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Fujita, Hideki*; Negishi, Kumi*; Honda, Akira
JAEA-Research 2008-104, 194 Pages, 2009/03
Saline groundwater contains high concentrations of chloride ions, which possibly elevate the pH of cement pore water by reacting with hydrogarnet and producing Friedel's salt. Calcium aluminate hydrates and portlandite, which can be found in hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC), were immersed in a sodium chloride solution, which had concentrations similar to those found in seawater.
Sato, Hisashi; Takasu, Tamio*; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2008-105, 24 Pages, 2009/03
In coastal area, the density difference between seawater and freshwater causes seawater intrusion under the freshwater. The methodology to evaluate saltwater distribution due to density driven flow might be crucial for bringing forward the radioactive waste disposal project. Although the extensive verification studies of the model for the salt water wedge have been reported, verification issue is still under the discussion. The saline concentration distribution in transition zone of salt water and fresh water was not evaluated, quantitatively. In order to obtain verification data of a numerical code that consider saltwater density distribution, we developed the quantitative measurement method by optical method for Mini-MACRO. And, quantitative concentration distribution data of saltwater wedge could be obtained. As a result, we showed that the width of the transition zone was narrower than the Henry's semi analytical result by quantitative data.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Hayashi, Katsuhiko; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Hiramoto, Masayuki*
JAEA-Research 2008-106, 91 Pages, 2009/02
It is generally known that the rock has the properties of strength recovery by elapse of time around the tunnel inside sedimentary rock with ground support due to inner pressure and ground pressure. The properties of strength recovery must be taken into account of the estimation about cavity shape stability or the long-term dynamical behavior of closed disposal ground. Our research study is focusing on the properties of strength recovery, generalized relaxation behavior and the characteristics of tensile strength by experiments using boring cores obtained from the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory so as to improve the modeling for future stage.
Izaki, Kenji; Ino, Kazuo*; Mizuniwa, Harumi
JAEA-Research 2008-107, 46 Pages, 2009/03
The contamination control has been carried out by alpha-ray measurement in facilities where handling plutonium like the MOX fuel manufacturing facility and the reprocessing facility, etc. In the case of alpha-ray measurement, it is necessary to consider the influence of radon progeny that is natural radionuclide. The influence of radon progeny has been decreased by pulse height discrimination technique using the semiconductor detector as needed. However, the semiconductor detector has potentially significant problems such as the durability and noise susceptibility. Therefore the accuracy of pulse height discrimination by the ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector was confirmed as alternative to the semiconductor detector. This report shows the accuracy of pulse height discrimination technique using the ZnS(Ag) scintillation detector and evaluates the adaptability to contamination control equipments.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2008-108, 58 Pages, 2009/02
Immersion tests of carbon steel were performed in compacted bentonite simulating the buffer material for 10 years duration, and corrosion products formed on the coupon surface were observed and analyzed by various methods. And then, the stability and dissolution/precipitation behavior of corrosion products were discussed from the view point of thermodynamics. The results of this study are summarized as follows; (1) In the case of the test in 80  C, black or dark gray corrosion product was formed on the coupons, and it was tightly adhered to the surface. By contrast, in lower temperature of 50
C, black or dark gray corrosion product was formed on the coupons, and it was tightly adhered to the surface. By contrast, in lower temperature of 50  C, no tight corrosion product was observed on the coupon surface. (2) Ferrous carbonate corrosion products such as siderite, FeCO
C, no tight corrosion product was observed on the coupon surface. (2) Ferrous carbonate corrosion products such as siderite, FeCO or Fe
or Fe (OH)
(OH) CO
CO were identified as the crystallized corrosion products in seawater type test solutions. In the test result in dilute test solution, magnetite, (Fe
were identified as the crystallized corrosion products in seawater type test solutions. In the test result in dilute test solution, magnetite, (Fe O
O ) was identified and no carbonate compounds were found. The presence of these compounds was agreed with thermo dynamical aspects assuming the test conditions. (3) Ca, S, Si and Al were detected in corrosion products layer besides Fe, and their distribution patterns were dependent on the experimental conditions. (4) It was indicated that the corrosion rate of carbon steel in compacted bentonite was correlated to the behavior of dissolution/precipitation of the corrosion products. (5) A conceptual model of the corrosion propagation behavior of carbon steel in compacted bentonite was proposed with reference to the existing corrosion models.
) was identified and no carbonate compounds were found. The presence of these compounds was agreed with thermo dynamical aspects assuming the test conditions. (3) Ca, S, Si and Al were detected in corrosion products layer besides Fe, and their distribution patterns were dependent on the experimental conditions. (4) It was indicated that the corrosion rate of carbon steel in compacted bentonite was correlated to the behavior of dissolution/precipitation of the corrosion products. (5) A conceptual model of the corrosion propagation behavior of carbon steel in compacted bentonite was proposed with reference to the existing corrosion models.
Mihara, Morihiro; Torii, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Research 2008-109, 46 Pages, 2009/03
Low-alkaline cement using pozzolans is under consideration as a possible filling and structural material in geological disposal for long-lived radioactive waste. Silica fume and high-volume fly ash are used to develop the low-alkaline cement which is named as HFSC, High-volume Fly ash Cement. In this study, pore structure and diffusivity of chloride ion in HFSC pastes were investigated in order to understand the fundamental transport properties of ions.
Suzuki, Hideaki; Kimura, Makoto; Fujita, Tomoo
JAEA-Research 2008-110, 29 Pages, 2009/02
It is necessary to consider the disturbance around the tunnel caused by the excavation of the realistic numerical simulation regarding the long-term behavior of near-filed after of engineered barrier system. In this paper, it is presented the preliminary analysis for Excavation Disturbed Zone (EDZ) around the horizontal drift at GL.-140m on Horonobe URL project. The coupled analysis, in which the hydraulic disturbance was considered, aiming principally at changes of the geochemical properties in the ground water with excavation was carried out. As a result, changes the pH in the ground water occurred, and it was showed these changes were caused by the gasification of the carbon dioxide in the ground water with enlarging the unsaturated zone, which is reaching up to about 5 meters long from the surface on the drift tunnel.
Oi, Takao; Inagaki, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebashi, Takeshi
JAEA-Research 2008-111, 32 Pages, 2009/03
A demonstration of the usefulness of the systematic approach to evaluate the importance of concerns affecting the geological disposal of radioactive wastes.
Kobayashi, Yasushi; Yamada, Tsutomu; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Nishida, Takahiro*; Hironaga, Michihiko*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Daisuke*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-112, 43 Pages, 2009/03
In deep geological repository, use of cementitious material for rock support, lining, and grouting is essential for construction and operation and possibly raises in groundwater pH due to leachate from the cements. Since this hyperalkaline condition may lead to degradation of barriers, there is concern that it gives significant impact on long-term safety performance of the repository system. Because of these backgrounds, developments of low alkaline cement have been conducted both at home and abroad. JAEA is now planning to conduct an in-situ test for shotcreting using low alkaline cement at the Horonobe URL. On the other hand, CRIEPI has studied and developed cementitious materials for disposal of radioactive wastes. This joint research report summarizes requirements and expected performance of cementitious materials in repository taking account of surrounding conditions in each stage of the repository program so as to reflect them to further development of the low alkaline cement.
Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Naganawa, Hirochika; Nagano, Tetsushi; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Shimojo, Kojiro; Matsubara, Tatsuo; Mita, Yutaka; Taki, Tomihiro; Murata, Masato
JAEA-Research 2008-113, 27 Pages, 2009/03
An effective mass processing equipment using solvent extraction method, named "emulsion flow extractor," is the most promising apparatus for removal and recovery of uranium from liquid waste originated from decontamination of uranium-contaminated fluoride waste in the uranium conversion test facility and of used gas centrifuges in the uranium enrichment facility at Ningyo-toge environmental engineering center. Prior to application of the emulsion flow extractor for actual uranium-containing liquid waste, properties of some phosphorous extractants for extraction and separation of uranium and constituents from simulated liquid wastes were examined through batch tests. These preliminary tests revealed that D2EHPA would be a promising candidate for extractant used for treatment of the actual uranium-containing liquid wastes, and that the extractants with a surfactant like AOT would not be useful.
Inagaki, Manabu; Ebina, Takanori*
JAEA-Research 2008-114, 36 Pages, 2009/03
In arrangement of the premise of the total performance evaluation of the disposal system, it is important to build the "reference total performance evaluation concept" based on consideration of more realistic design situation, and consideration of the performance evaluation based on the safety function. Extract the scenario on changing some condition becomes easy with those "reference total performance evaluation concept". I can think the methodology which treats change in the disposal condition as perturbation to the condition put in order doesn't damage a existence concepts, and is also effective in step-by-step development of evaluation. Therefore I can think the method to put a flow of information on a system of existence in order by FepMatrix with the investigation/design-disposal condition-structure of the safety function is useful.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Schooneveld, E.*; Rhodes, N.*
JAEA-Research 2008-115, 33 Pages, 2009/03
A compact two-dimensional neutron detector was developed for iBIX instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The specifications required for the detector were a spatial resolution of less than 1 mm, a detector efficiency of more than 50% for thermal neutrons, a  sensitivity of less than 10
sensitivity of less than 10 , detector coverage of around 15
, detector coverage of around 15 15 cm
15 cm with least dead area, compactness, modularity, and a pulse pair resolution of less than 2
with least dead area, compactness, modularity, and a pulse pair resolution of less than 2  s. The detector components were studied in detail and optimized for the purpose. The compact prototype detector that has a neutron sensitive area of 13.3
s. The detector components were studied in detail and optimized for the purpose. The compact prototype detector that has a neutron sensitive area of 13.3 13.3 cm
13.3 cm was made and feasibility of the detector was demonstrated successfully in the experiments at the ISIS pulsed neutron source.
was made and feasibility of the detector was demonstrated successfully in the experiments at the ISIS pulsed neutron source.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Tsutsui, Noriaki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Schooneveld, E. M.*; Rhodes, N. J.*
JAEA-Research 2008-116, 26 Pages, 2009/03
New ZnS scintillator, light reflector and digital signal processing modules were developed to upgrade the Japanese ENGIN-X type linear scintillation neutron detector. The developed ZnS/ B
B O
O scintillator improved detector efficiency by a factor 1.2 for neutrons with a wavelength of 1
scintillator improved detector efficiency by a factor 1.2 for neutrons with a wavelength of 1  whilst the detector maintained similar
whilst the detector maintained similar  sensitivity and multi-count ratio compared to the present AST (4:1) scintillator. The paint coating less light reflector was developed with an aluminum reflector with etched surface. The detector implemented with this reflector exhibited similar detector performances with paint coating reflectors, confirming feasibility of the reflector with long-term stability. The digital signal-processing module incorporating photon-counting method was successfully developed. The fully digitalized photon counting system improved a temperature stability of neutron counts significantly comparing to the present analogue system.
sensitivity and multi-count ratio compared to the present AST (4:1) scintillator. The paint coating less light reflector was developed with an aluminum reflector with etched surface. The detector implemented with this reflector exhibited similar detector performances with paint coating reflectors, confirming feasibility of the reflector with long-term stability. The digital signal-processing module incorporating photon-counting method was successfully developed. The fully digitalized photon counting system improved a temperature stability of neutron counts significantly comparing to the present analogue system.
Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Inagaki, Manabu; Koo, Shigeru*; Shibata, Masahiro; Itazu, Toru; Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Research 2008-117, 36 Pages, 2009/03
It is considered that it is possible to avoid the effect of the uplift and denudation process on geological disposal system by siting and a repository design. However, since the uplift/denudation continues far into the future, it is important to enhance the confidence of the methodology to evaluate such an effect, based on the understanding of geohistorical information and potential impact on the disposal system. This paper presents an evolution pattern of the geological environment and the influence analysis in terms of system performance affected by the uplift and denudation process based on the relevant conceptual models for groundwater scenarios of the disposal system for a hypothetical sedimentary rock. As a result, it is indicated that the conceptual model is capable to identify a specific combination of patterns of system evolution of the geological environment in terms of features on the uplift and denudation process, and also provides technical basis for setting up parameters of nuclide migration model and the subsequent influence analysis. Consequently, it is also indicated that the evaluation methodology applied in this study is valuable to evaluate the uplift/denudation phenomena with specific geological environment, and the results obtained by the analysis could be valuable information for site investigation and/or the prediction of a future change trend for the uplift/denudation.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2008-118, 33 Pages, 2009/03
In general, copper is thermodynamically stable under anaerobic condition, so that corrosion due to water reduction can not occurr on copper. However, in the presence of sulfide, copper loses its thermodynamical stability and corrodes as copper sulfide, and is susceptible to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) depending on environmental condition. In this study, slow strain rate tests (SSRT) were performed in synthetic sea water containing sodium sulfide and the effect of electrode potential and the difference of material grade were examined. The results were summarized as follows; (1) The SCC susceptibilities at the electrode potentials of +100 mV and +300 mV above Ecorr (corrosion potential in anaerobic condition) were lower than that at a level of Ecorr. In case of Ecorr +700 mV, the SCC susceptibilities became larger than those in Ecorr +100 mV and Ecorr +300 mV. (2) In comparison of oxygen free copper and phosphorous deoxidized copper, the former tended to be allowed to crack initiation more readily, but the mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation were almost equal in both materials. (3) In order to apply the SSRT with buffer material, a test column attached to a specimen was developed. As the result of SSRT of phosphorous deoxidized copper using the column, no SCC was observed in 0.001 M - Na S at -420 mV vs SCE, which is the rest potential under anaerobic condition (nitrogen atmosphere) in buffer material.
S at -420 mV vs SCE, which is the rest potential under anaerobic condition (nitrogen atmosphere) in buffer material.
Kawamura, Makoto; Ebashi, Takeshi; Makino, Hitoshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Oi, Takao
JAEA-Research 2008-119, 32 Pages, 2009/03
Uplift, subsidence, denudation, and sedimentation are phenomena over long-term in a regional scale. It is difficult to ignore the impacts of those phenomena on a disposal system completely in long-term. Therefore, type and extent of the impacts on geological and disposal environmental conditions, and disposal systems need to be evaluated quantitatively in order to develop perturbation scenarios. JAEA has been developing a systematic methodology to develop perturbation scenarios based on the appropriate understanding of those phenomena. The variety of the change of geological environment and evolution pattern of the environment, which are caused by the variation of the uplift, subsidence, denudation, sedimentation phenomena and those rates, are understood by arranging the information in the framework of the thermal-hydrological-mechanical-chemical-geometrical (T-H-M-C-G) system, and the impacts of those environmental change to the performance of the repository system are also examined by using the T-H-M-C-G system. In this study, firstly, the potential changes of the geological environment were identified by examination of possible combinations of the uplift/denudation and subsidence/ sedimentation. The effects of the initial environmental condition are also considered. Geohistorical information and Modern analogue theory should be used in this stage. This procedure is essential to set up the scenarios regarding uplift/denudation and subsidence/sedimentation, to clarify the trend and/or range of the change of the geological environmental conditions. Then, the phenomena which give the large impacts to a disposal system were extracted based on the T-H-M-C-G system. By applying the developed framework which deals with the impacts on the HLW disposal system realistic view and builds evaluation scenarios and models based on step wise manner, we acquired the prospect that realistic uplift and denudation scenario could be built to this examination procedure.
Mizuno, Takatoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Research 2008-120, 19 Pages, 2009/03
In an accelerator for a N-NBI, there are several processes of secondary-particle production such as the collision of H ions with H
ions with H gas, extraction of H
gas, extraction of H ions from beam plasma, and secondary-electron emission. The secondary particles cause heat load to the NBI components. It is necessary to analyze behavior of them in the accelerator. In this report, the secondary-particle behavior in MAMuG type MeV accelerator at JAEA has been analyzed by EAMCC. In the result, it is clarified that about 40% of H
ions from beam plasma, and secondary-electron emission. The secondary particles cause heat load to the NBI components. It is necessary to analyze behavior of them in the accelerator. In this report, the secondary-particle behavior in MAMuG type MeV accelerator at JAEA has been analyzed by EAMCC. In the result, it is clarified that about 40% of H ions extracted from the ion source were lost by the stripping process in the MeV accelerator. More than 90% of the heat load to the intermediate grids was caused by collision of the electrons. A comparison of results obtained from experiments and present analyses showed different tendency in the currents flowing into the 2nd and the 3rd intermediate grids. This is supposed due to H
ions extracted from the ion source were lost by the stripping process in the MeV accelerator. More than 90% of the heat load to the intermediate grids was caused by collision of the electrons. A comparison of results obtained from experiments and present analyses showed different tendency in the currents flowing into the 2nd and the 3rd intermediate grids. This is supposed due to H ions extracted from beam plasma as a possible cause of the difference.
ions extracted from beam plasma as a possible cause of the difference.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Inoue, Takashi; DeEsch, H.*; Svensson, L.*
JAEA-Research 2008-121, 26 Pages, 2009/03
For the ITER NBI, two accelerator concepts have been proposed. One is the SINGAP (single gap single aperture) developed at CEA Cadarache and the other is the MAMuG (Multi aperture multi gap) developed at JAEA. In order to assess the performance of the SINGAP and the MAMuG concepts at the same test facility under the same diagnostics, a collaborative test was performed between JAEA and CEA Cadarache under an ITER task agreement. For this purpose, the SINGAP accelerator was installed at the MTF of JAEA. From the viewpoint of voltage holding, maximum beam current and electron acceleration, the MAMuG showed better performance than the SINGAP, and it has been decided to choose the MAMuG as the baseline accelerator for the ITER NBI.
Sakai, Ryutaro; Munakata, Masahiro; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2008-122, 18 Pages, 2009/03
It is important to evaluate effect on the groundwater flow system by the natural phenomena in the safety assessment of geological disposal of radioactive waste through a survey of recent scientific informations. In this report we study about the scenario of sea level change effecting on the groundwater flow system which is very important for a safety of disposal facility in costal area. As a result, this study show that the non-current paleo-fresh water at present is possible to start to discharge at sea floor in the next glacial period by denudation of marine-clay sediments and to grow stagnant again in the next interglacial period by deposition of marine-clay sediments. Therefore it is important to predict the scenario considering the denudation and deposition correlated with transgression and regression that could affect the change of groundwater flow characteristics during the glacial and interglacial period.
Oyaizu, Makoto; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
JAEA-Research 2008-123, 25 Pages, 2009/03
For the safety issue of fusion reactors, several studies have been performed to reveal the tritium permeation behavior in F82H, one of low-activation ferritic steels, as a potential structural material of blanket. These studies were performed with the use of pure hydrogen isotope gas for inlet side and vacuum for outlet side, although these in the blanket system are different. Therefore in the present study, it is subjected to reveal the tritium permeation from feed gas composed from tritiated water vapor diluted by helium to purge gas composed from helium, as a simulation of HCSB blanket. The temperature dependence and tritiated water vapor partial pressure dependence experiments were performed. As the results, tritium permeation looked limited by diffusion, it is implied that one or some of the surface reactions could be different, and suggested that the existence of water could result in the formation of oxide layer which have a possibility to work as tritium permeation barrier.
Shibata, Takemasa; Ogura, Koichi
JAEA-Research 2008-124, 12 Pages, 2009/03
The metastable states' population of neodymium atoms produced by electron beam heating was measured with the laser induced fluorescence method. The atomic excitation temperature derived from the metastable state distribution decreased to about 1500K with increasing deposition rate. This atomic excitation temperature is about three times higher than that of gadolinium atoms produced by electron beam heating. Near the evaporation surface the collisional relaxation of neodymium and gadolinium atoms occurs through inelastic collisions between fine structures. The gadolinium and neodymium atoms have ten valence electrons of 4f 5d6s
5d6s and six valence electrons of 4f
and six valence electrons of 4f 6s
6s , respectively. The orbital radius of 5d electron is relatively larger than that of 4f electron. Low collisional relaxation of neodymium is considered to be due to small orbital radius of 4f electron and no existence of 5d electron.
, respectively. The orbital radius of 5d electron is relatively larger than that of 4f electron. Low collisional relaxation of neodymium is considered to be due to small orbital radius of 4f electron and no existence of 5d electron.
Iwatsuki, Jin; Noguchi, Hiroki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kubo, Shinji; Sakaba, Nariaki; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
JAEA-Research 2008-125, 60 Pages, 2009/03
Preliminary design study was carried out on the hydrogen production demonstration plant of IS process for thermochemical hydrogen production. In the pilot test, hydrogen production will be examined under prototypical condition using an apparatus made of industrial materials, which is driven by the sensible heat of helium gas heated by an electric heater that simulates the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). Tentative system condition was defined considering the HTTR specification and the experience on the construction and the operation of the mock-up test facility of steam reformer. The process condition and the system flow diagram were discussed to meet the system condition. Based on the defined process condition, types of the main components were discussed taking the corrosion resistance of the structural materials into consideration. Applicable rules and regulations were also surveyed regarding the plant construction and operation.
Seno, Shoji*; Kunimaru, Takanori; Nakajima, Makoto*; Toida, Masaru*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Sohail, A. R.*
JAEA-Research 2008-126, 120 Pages, 2009/12
At first, to exclude the influences of working of nature such as tide and atmospheric pressure from the source data, an analysis with Bayesian model was progressed. As the result of the estimation of these influences calculated by BAYTAP-G (Bayesian Tidal Analysis Program Grouping Model), it was found that the influence of the atmospheric pressure was comparatively large and that of tide was comparatively small.