Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Imai, Hisashi*; Yamashita, Ryo*; Shiozaki, Isao*; Urano, Kazuhiko*; Kasa, Hiroyoshi*; Maruyama, Yoshio*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Maekawa, Keisuke
JAEA-Research 2009-001, 116 Pages, 2009/03
Evaluation of long-term geological evolution and its impact on groundwater flow is one of the major themes within the frame of Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project. For the purpose of development of a groundwater flow modeling methodology considering the effects of long-term geological evolution, following three items were studied: (1) Upgrade of SMS (Sequential Modeling System of geo-environmental evolution impact on groundwater flow) which was developed in 2006 FY; (2) Groundwater flow simulation under more realistic conditions of geological structures and hydrogeological conditions; and (3) Sensitivity study of geo-environmental evolution impacts on groundwater flow. The studies showed following suggestive results. (1) Development of a precise time step setting enabled to narrow the gaps in simulated head between time steps in which the model configuration used to deformed. (2) Several aspects have been found from studies on impact factors such as deposition on pore pressure, recharge rate and difference in density of saline groundwater. For evaluation of pore pressure induced by deposition, it is necessary to model the porosity and permeability variation considering the exceed pore pressure change. The setting of recharge rate during the Ice Age influence the characteristics of groundwater flow in coastal and hilly areas. The density of groundwater is not so influential as topological potential factors, however it is effective for the characteristics of groundwater flow in coastal area and intrusion of recharge water from ground surface. (3) The sensitivity study on faulting characteristics indicated that the two types of fault configuration and the hydraulic conductivity setting considered are not influential on the nature of groundwater flow above the depth of 500 m.
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sato, Haruo; Tanai, Kenji; Inagaki, Manabu; Sawada, Atsushi; Niinuma, Hiroaki; Ishii, Eiichi; Maekawa, Keisuke; Tomura, Goji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-002, 156 Pages, 2009/05
The research and development plan for geological investigation, engineering technology and safety assessment during the drilling of a shaft down to intermediate depth are summarized according to the Midterm Plan till 2009 Fiscal year of JAEA. This report describes subject, current status and programme in the "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities). Furthermore regarding R&D plan in next Midterm Plan of JAEA, preliminary ideas are summarized.
Numakura, Masahiko; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Suzuki, Shinichi; Kobayashi, Toru*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro; Madden, P. A.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Research 2009-003, 26 Pages, 2009/04
We investigated the mixing behavior of molten TbCl in LiCl-KCl eutectuic melt by MD simulation. Also, simulation of molten YCl
in LiCl-KCl eutectuic melt by MD simulation. Also, simulation of molten YCl and LaCl
and LaCl systems were performed to elucidate the difference of the structural change by the difference in cation size (Y
systems were performed to elucidate the difference of the structural change by the difference in cation size (Y
 Tb
Tb
 La
La ). The coordination number of the molten pure YCl
). The coordination number of the molten pure YCl , TbCl
, TbCl and LaCl
and LaCl are mainly 6, 7 and 8 respectively. We consider that, in the molten pure state, the coordination number is influenced by the cation size. However, independent of cation size, the molten MCl
are mainly 6, 7 and 8 respectively. We consider that, in the molten pure state, the coordination number is influenced by the cation size. However, independent of cation size, the molten MCl tend to be formed the stable 6-fold structure by the mixing with LiCl-KCl eutectic. And, MD simulations on MCl
tend to be formed the stable 6-fold structure by the mixing with LiCl-KCl eutectic. And, MD simulations on MCl -LiCl and MCl
-LiCl and MCl -KCl systems revealed that the mixing effect was different between LiCl and KCl.
-KCl systems revealed that the mixing effect was different between LiCl and KCl.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2009-004, 165 Pages, 2009/05
Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) project aims at improvement of the reliability of technologies for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes. In investigation during construction of the underground facilities, the updating and check of the validity of initial stress estimations made during surface-based investigations is one of the main issues. Thus, three boreholes were made from the niche (GL-140 m) of ventilation shaft, and a three-dimensional evaluation of the initial stress in Koetoi Formation was done by the method called hydraulic fracturing technique and the analysis of the borehole breakout. Moreover, the direction of the maximum horizontal principal stress had been found to be east/west in general. However, the present test showed that the direction was 25 or 43 degrees counterclockwise from east/west.
Sasaki, Yuji; Sugo, Yumi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Takaumi
JAEA-Research 2009-005, 24 Pages, 2009/05
As a separation step of an innovative chemical separation process (ARTIST process) for treatment of spent nuclear fuel, the condition to extract TRU using TODGA was studied. TODGA has strong affinity with trivalent and tetravalent actinides. The oxidation state of Np and Pu can be changed quantitatively to Np(IV) and Pu(III) using ascorbic acid. After extraction of TRU, it is important to know the appropriate condition of stripping TRU from the organic phase. Tetramethyl-diglycolamide (TMDGA) has high affinity with An(III) and An(IV) in the aqueous phase. The chemical separation flow-sheet for actinides and Sr was designed. The flow rate of aqueous and organic phases, and stage number of mixer-settler were determined in order to obtain the optimum condition for TRU and Sr separations. The TRU extraction process was discussed from the viewpoints of the amount of metal oxide, heat generation and radioactivities.
Morita, Koji*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Suzuki, Toru; Yamano, Hidemasa
JAEA-Research 2009-006, 51 Pages, 2009/05
It is important to make a reasonable evaluation of coolability of debris bed with decay heat source in assessing post accident heat removal of a liquid metal cooled fast reactor. In general, the coolability of fuel debris depends on coolant convection, boiling and debris bed movement. In the present study, to understand fundamental characteristics of debris movement, self-leveling behavior caused by the coolant boiling was investigated experimentally using simulant materials. The present experiments employed depressurization boiling of water to simulate void distribution in a debris bed, which consists of solid particles of alumina. A rough estimation model of self-leveling occurrence was proposed and compared with the experimental results. Its extrapolation to reactor accident conditions was also discussed. In addition, solid-liquid flow experiments, which are relevant to debris bed movement behaviors, were analyzed to verify the validity of multiphase flow models employed in a safety analysis code. In the present verification study, basic validity of the code was demonstrated by analyzing experiments of water-column sloshing with solid particles.
Tatematsu, Kenji; Kawasaki, Hirotsugu; Nemoto, Masahiro; Murakami, Masakazu
JAEA-Research 2009-007, 46 Pages, 2009/06
In this study, we showed an energy demand and supply scenario toward the year 2100 in Japan, which underlies JAEA's "Nuclear Energy Vision 2100" published in October 2008. This energy demand and supply scenario aims at the coexistence of the reduction of the carbon dioxide emission and the energy security through reduction of the fossil fuel usage, positive electrification and the nuclear energy usage. We reduce the ratio of the fossil fuel in the primary energy supply to about 1/3 and extend the share of renewable and nuclear energy to 70% from current 15%. As a result, the carbon dioxide emission is reduced to current 10%, and it developed that the half was the contribution of the nuclear energy.
Kunimoto, Eiji; Shibata, Taiju; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Eto, Motokuni*; Shiozawa, Shusaku; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Maruyama, Tadashi*; Oku, Tatsuo*
JAEA-Research 2009-008, 28 Pages, 2009/06
The VHTR is being focused and developed internationally. In Japan, the HTTR of the JAEA is in operation, and research and development for the development of commercial HTGRs are carried out. Nuclear graphites are used for core components of the HTGRs and expansion of irradiation data is necessary when enough irradiation data are not established, because the graphite components in the HTGRs are used at severer condition than that in the HTTR. The necessary database can be established by expansion of existing irradiation data with appropriate interpolation and extrapolation methods. This paper shows the reasonable interpolation and extrapolation method for IG-110 graphite which is used for the HTTR and a major candidate for the VHTR. The interpolation and extrapolation method was developed so as to be general by using the irradiation data of the other graphites. As a result, irradiation properties of the IG-110 graphite were successfully expanded to the VHTR condition for the first time and the irradiation properties being necessary for the design could be developed.
Shiwaku, Hideaki; Mitsui, Takaya; Tozawa, Kazukiyo*
JAEA-Research 2009-009, 60 Pages, 2009/07
The liquid nitrogen circulation cooling device for a double crystal monochromator was introduced, and the multi-crystal switching system was developed on the JAEA dedicated beamline "BL11XU" at SPring-8. The multi-crystal switching system has features to be able to exchange crystals in cryogenic temperature and in a vacuum at any time. By this system, it is available to use high flux X-rays energy range of 6 to 70 keV.
Yokoyama, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2009-010, 42 Pages, 2009/07
A Common User Data Model, CUDM, has been developed for the purpose of benchmark calculations between APOLLO3 and MARBLE code systems. The CUDM was designed for core calculation benchmark problems with 3-dimensional Cartesian, 3-D XYZ, geometry. Based on the CUDM, a prototype system for a benchmark calculation, CUDM-benchmark, was also developed. In order to evaluate pertinence of CUDM, the CUDM-benchmark was applied to benchmark problems proposed by T. Takeda, G. Chiba and I. Zmijarevic. In addition, a detailed benchmark calculation for Chiba benchmark was performed. In this application, it was found that the results by IDT and SNT solvers agreed well with the reference results by Monte-Carlo code. In addition, model effects such as quadrature set effect, 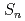 order effect and mesh size effect were systematically evaluated.
order effect and mesh size effect were systematically evaluated.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2009-011, 155 Pages, 2009/07
This report summarizes performances of core exit thermocouples (CETs) observed in 12 ROSA/LSTF tests which include ten small-break loss-of-coolant accident (SBLOCA) tests and two abnormal transient tests as an additional report to the OECD/NEA ROSA Project Test 6-1 report. The contents of this report are prepared to a task group which was set up to review and consolidate background knowledge of CET application to PWR accident management (AM) measures in April 2008 in the Working Group of Analysis and Management of Accident (WGAMA) at OECD/NEA. These tests cover wide ranges of test conditions such as size and location of break, primary pressure, core power, reflux water fall-back and operator actions. CET performances relative to the core temperature history are studied in each test, and general performances of CET are summarized focusing on the time delay and slow and low temperature excursion.
Chiba, Go
JAEA-Research 2009-012, 43 Pages, 2009/07
In order to evaluate applicability of a neutron transport simulation code system CBG to shielding problems, calculations are performed with CBG for the Kobayashi benchmark problem which has been proposed for validations of neutron shielding calculations. In fully-absorbed shielding problems, it is shown that angular quadrature sets which have limitations on the angular order result in large discrepancy to the reference solutions in neutron flux due to the ray effect and that angular quadrature sets which have no limitations on the order reproduce well the reference neutron flux. In partly-absorbed shielding problems, it is shown that the high-order Tri_DP T
T set reproduces well the reference neutron flux. In addition, a multi-step S
set reproduces well the reference neutron flux. In addition, a multi-step S method is proposed, and it is shown that it can drastically reduce calculation time without losing calculation accuracy.
method is proposed, and it is shown that it can drastically reduce calculation time without losing calculation accuracy.
Kobayashi, Yasushi; Yamada, Tsutomu; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Nishida, Takahiro*; Hironaga, Michihiko*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Daisuke*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-013, 70 Pages, 2009/06
Cementitious materials will be used to ensure construction and operational safety and work efficiency in a deep geological repository. The low alkaline cement has been developed to reduce uncertainties due to hyper alkaline for the long-term safety performance of the repository system. Functions of cementitious material required in each phase of repository construction, operation and closure were summarized in a separate report entitled "Application Study on Low Alkaline Cementitious Materials for Deep Geological Repository of High Level Radioactive Wastes (Phase I) "In this report, properties of low alkaline cement/concrete which have been developed both at home and abroad, and recipes of the low alkaline concrete taken account of application to the repository component have been investigated. Fresh and hardened properties of the low alkaline cement are equivalent to the OPC and the low alkaline cement has an advantage over OPC in terms of leaching resistance. The HFSC developed by JAEA, which belongs to a pozzolanic type low alkaline cement will be able to apply to the shotcrete and the lining concrete by choosing an adequate recipe. Clarification of influences of the chemical composition of groundwater on leachate properties of the hydrates, examination of pH measurement of cement leachate, evaluation of corrosion behavior of rebar embedded in the HFSC concrete are raised as open questions for future activities.
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2009-014, 18 Pages, 2009/07
Distribution model were established to estimate an effect of substitution reaction of Ra in calcite. To apply this model, number of reactive layers is required. It was reported to be 21 based on an experimental results. In the present study, distribution coefficient for substitution reaction (Kcp) for pore water of H-12 were estimated and release rate of 4n+2 series nuclide was calculated. Values of Kcp for types of pore water were estimated with mole amount of Ca in solid phase and solution and partition coefficient. Estimated Kcp are smaller than Kd of Ra in bentonite. Kd is empirical parameter shows all distribution reactions, including the effect of Kcp. Therefore, Kd  Kcp is reasonable. It was assumed that Kd included an effect of substitution reaction. As a result, similar trend of
Kcp is reasonable. It was assumed that Kd included an effect of substitution reaction. As a result, similar trend of  Th was shown for
Th was shown for  Ra. Half life of
Ra. Half life of  Ra (T1/2=1600 years) is significantly short and therefore behavior of it depends on radiation equilibrium with
Ra (T1/2=1600 years) is significantly short and therefore behavior of it depends on radiation equilibrium with  Th (T1/2=770000 years).
Th (T1/2=770000 years).
Horiguchi, Hironori; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kishi, Toshiaki; Otake, Shinichi*; Kumada, Hiroaki*
JAEA-Research 2009-015, 38 Pages, 2009/07
The boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) has been conducted at JRR-4. There is an increased number of cases due to the expansion of application against head and neck cancer and skin cancer. Therefore, the BNCT requires the establishment of procedure to perform more cases in a day. The determination of boron concentration in blood is important to determine the prescribed dose given to a patient. Currently, prompt  ray analysis (PGA) is applied to the determination of boron concentration. But the PGA is not applied to more than three times BNCT a day. Therefore, swiftness and precision method by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) is studied. Using BSH for Boron standard of the ICP-AES, we enabled to analyze accurately without an intricate sample preparation. The measurement precision of the ICP-AES was within 5% by the correction factor based on the PGA. We established the method of swiftness determination of boron concentration in blood for BNCT.
ray analysis (PGA) is applied to the determination of boron concentration. But the PGA is not applied to more than three times BNCT a day. Therefore, swiftness and precision method by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) is studied. Using BSH for Boron standard of the ICP-AES, we enabled to analyze accurately without an intricate sample preparation. The measurement precision of the ICP-AES was within 5% by the correction factor based on the PGA. We established the method of swiftness determination of boron concentration in blood for BNCT.
Hayashi, Katsuhiko; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Hiramoto, Masayuki*; Mizutani, Kazuhiko*; Morita, Atsushi*
JAEA-Research 2009-016, 127 Pages, 2009/08
"Study on configuration of analytical domain of the multi tunnels model" and "Remainders on an elasto-plastic FEM (Finite Element Method) analysis" in case of the full width of pillar become plastic on simplified model" are studied as "The study on the enhanced reliability of elasto-plastic FEM". In addition, "The effect of rock support and consolidation of the host rock to control the plastic region" was conducted as "The study on the mechanical stability of tunnels". As the results, it was seen that the analytical domain should be assigned 3-5W (W: width of multi tunnels) for a horizontal side from the endmost tunnel and 3-4W for below of the tunnels. It was found reasonable and proper on the elasto-plastic FEM analysis that the analysis domain must be large enough not to have plastic deformation in all analysis of domains under the condition in which the full width of pillar has plastic deformation. It was also found that the ground support suppresses the plasticity domain as the ground support effect. It was acknowledged that the auxiliary construction method by improvement of the ground has the suppression effect of the plasticity domain applying to the multi tunnels.
Yuki, Kazuhisa*; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Nakanishi, Shigeyuki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Yamano, Hidemasa
JAEA-Research 2009-017, 55 Pages, 2009/08
At Tohoku University, 1/15 scale and 1/7 scale flow tests are being performed in order to clarify an unsteady flow structure in the cold leg piping and to investigate the scale effect. In FY2007, the 1/15 scale test was carried out using a double elbow geometry. It was confirmed that there existed a separation along the inner wall of the 1st elbow and a large swirling flow in the 2nd elbow. Furthermore, the unsteady flow formed in and/or behind the separation region was transported downstream and flows into the center area of the 2nd elbow. At JAEA, a numerical analytical evaluation method is being developed to evaluate the feasibility of the reactor design. In FY2007, numerical analyses for the 1/15 scale test were performed using the commercial thermal-hydraulics code FLUENT. The analyses showed that the trend of calculated velocity distributions was in good agreement with the visualization test results.
Morita, Koji*; Ryu, P.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Sato, Ikken
JAEA-Research 2009-018, 52 Pages, 2009/09
Dynamic behaviors of solid-particle dominant multiphase flows were investigated to model the mobility of core materials in a low-energy disrupted core of a liquid metal fast reactor. Two series of experiments were performed, that is dam-break experiments and bubble visualization experiments. Verification of fluid-dynamics models used in the fast reactor safety analysis code SIMMER-III was also conducted based on the numerical simulations of these experiments. The experimental analyses show that SIMMER-III can, to some extent, represent effects of solid particle interaction on multiphase flow behaviors by adjusting model parameters of the particle jamming model. Further improvement of SIMMER-III with more generalized models is necessary to appropriately simulate interactions between solid particles in a wider range of flow conditions.
Abe, Hironobu; Hatakeyama, Nobuya; Yamazaki, Masanao; Okuzono, Akihiko*; Sakai, Tetsuo*; Inoue, Masahiro*
JAEA-Research 2009-019, 192 Pages, 2020/02
Construction of the underground facility is on going at the Horonobe Underground Research Center, a division of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The facility is consisted of three shafts and horizontal drifts at the completion of construction and it is excavated in geological environment with methane gas, so it is important to secure the workers and visitors security in case of fire in the underground. However, it is known that the fire gas such as methane shows a complicated behavior by drift effect and so on and very difficult to predict its behavior, even if under enforced ventilation. In order to construct new prediction method of the fire gas behavior, the model scaled experiments were conducted by using the basic model which consists of shafts and drifts. As a results, fundamental data of the fire gas behavior was grasped and complicated behavior of the fire gas such as three-dimensional backflow and main flow inversion phenomena at the underground structure were ascertained. A new fire gas behavior analysis system has been designed and a prototype system has been programmed which is able to simulate the phenomena noted above. Coupling analysis method is adapted to the system, which consists of mainly one-dimensional ventilation network analysis and simplified computational fluid dynamics program named M-CFD. To minimize calculation time, M-CFD was designed as two-dimensional calculation with simulators multi area analysis system. Using the prototype system, several experimented models representing typical behavior of fire gas have been simulated for model scaled experiments. The system qualitatively reappeared the phenomena such as back flow or main flow inversion, and most of calculations completed in expected time. This indicates appropriateness of the prototype system, but some upgrade such as heat conductivity analysis in the wall rock mass transfer calculation, user friendly interface system and others will be required.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Hirano, Toru; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2009-020, 36 Pages, 2009/08
On the radioactive waste disposal, the long-term mechanical stability of tunnel was required. Therefore, we have been developing the method evaluating the stability. This report describes the works in the FY2008. Chapter 1 is the overview. Chapter 2 is the result of long-term creep test on Tage tuff. The strain was increasing at very low speed and the strain rate was decreasing following elapsed time to the powers of -0.9. This behavior is likely to short-term creep. In Chapter 3, the control program was extended to conduct the generalized relaxation test along any relaxation pattern. Then, that test of Toki granite was carried out successfully. The parameters in the variable-compliance-type constitutive equation for Toki granite were deduced. In Chapter 4, parameter-obtaining methods for the constitutive equation were reviewed and criticized. In the final part, an idea of new rock characterization where time-dependent behavior of rock is considered as the important factor was proposed.
Ezure, Toshiki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Tobita, Akira; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2009-021, 44 Pages, 2009/09
An compact sodium-cooled fast reactor has been investigated in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development Project. The compact-sizing may cause the cover gas entrainment (GE) at the free surface of reactor vessel. The prevention of gas entrainment is one of the significant thermal hydraulic issues. In the previous study, a water experiment in the 1/1.8 scale partial model was performed to check the adequacy of reactor design. From the result, it has been assured GE did not occur in the rated condition of reactor. However, there are the specific operating conditions with the low sodium level due to the thermal contraction concerning the cold startup or shutdown of reactor, where the sodium temperature is low. The objective of this study is to evaluate the onset condition of gas entrainment in those condition. The onset condition of GE was clarified in low liquid level. From the result, it was assured gas entrainment did not occur with the doubled D/P geometry.
Kusano, Tomohiro; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Umeda, Koji; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Saito, Tatsuo; Yasue, Kenichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Yamada, Kunimi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-022, 47 Pages, 2009/09
The Japanese islands are located in the tectonically active Circum-Pacific Mobile Belt. As a result, Japan has a high frequency of earthquakes and eruptions. Special consideration is given to the long-term stability of the geological environment, taking into account volcanism, faulting, uplift, denudation, climatic change and sea-level change in Japan. Development of research/prediction technologies for geotectonic events has been carried out to evaluate the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. In fiscal year 2007, we carried out the following researches, to confirm existence of the phenomena that have influences on geological disposal system (e.g., active faulting, volcanism), and to develop the investigation techniques to reconstruct the history of these phenomena. For studies of faulting and seismic activity, we developed the investigation techniques to research distribution of crush zone, process of faulting, activity, and so on. For volcanological and geothermal studies, we developed a technique for detecting crustal magma and/or geothermal fluid in deep underground. For studies of uplift/denudation and climatic/sea-level changes, we extracted investigation techniques for landform developments and uplift rate with river terraces.
Takei, Hayanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Yano, Yoshiharu*; Ogawa, Yujiro*; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Research 2009-023, 114 Pages, 2009/09
Frequent beam trips as experienced in existing high power proton accelerators may cause thermal fatigue problems in ADS components which may lead to degradation of their structural integrity and reduction of their lifetime. Thermal transient analyses were performed to investigate the effects of beam trips on the reactor components. Our results indicated that the acceptable frequency of beam trips ranged from 50 to 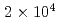 times per year depending on the beam trip duration. In order to consider measures to reduce the frequency of beam trips on the high power accelerator for ADS, we compared the acceptable frequency of beam trips with the operation data of existing accelerators. The result of this comparison showed that the beam trip frequency for durations of 10 seconds or less was within the acceptable level, while that exceeding five minutes should be reduced to about 1/30 to satisfy the thermal stress conditions.
times per year depending on the beam trip duration. In order to consider measures to reduce the frequency of beam trips on the high power accelerator for ADS, we compared the acceptable frequency of beam trips with the operation data of existing accelerators. The result of this comparison showed that the beam trip frequency for durations of 10 seconds or less was within the acceptable level, while that exceeding five minutes should be reduced to about 1/30 to satisfy the thermal stress conditions.
Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Kurata, Yuji; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Research 2009-024, 83 Pages, 2009/09
It is supposed that the Accelerator Driven System (ADS) is safer than other critical systems such as Fast Reactors since the ADS is driven by the external neutron source in the subcritical state. In this study, the investigation to confirm the possibility of Core Disruptive Accident (CDA) for the ADS was performed by Level 1 PSA and detailed safety analyses. Abnormal events for the ADS were sorted by Level 1 PSA and calculation cases for the safety analysis were discussed. Based on these results, safety analyses for Unprotected Transient Over Power (UTOP) and Unprotected Loss of Flow (ULOF) were carried out. These results showed that there were hardly possibilities of CDA for the ADS. In the beyond design basis accidents (UTOP and ULOF), it was considered that the creep rupture of the clad tube would happen. However, the frequency of the accidents was exceedingly small. It was concluded that the ADS had very little possibility of CDA or the re-criticality accident.
Okano, Yasushi; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Naganuma, Masayuki; Okubo, Tsutomu; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; Nishimura, Satoshi*
JAEA-Research 2009-025, 105 Pages, 2009/10
A metal fuel core has specific features on high heavy metal density, hard neutron spectrum, and efficient neutron utilization. Enlarged applicable design envelops would improve core performances and features: higher breeding ratio, compacted reactor core, and, smaller amount of Pu-fissile inventory. A joint study on "Reactor Core and Fuel Design of Metal Fuel Core of Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor" by Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry has been conducted during Japanese fiscal years of 2007 and 2008. This report shows the results on (1) the study on applicable design ranges of metal fuel specifications, (2) the study on conceptual core designs for high breeding ratio, and (3) the safety study on metal fuel core designed in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Kenji; Tobita, Akira; Kamide, Hideki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
JAEA-Research 2009-026, 160 Pages, 2009/10
Thermal stratification after a scram is one of main thermal loads of a reactor vessel in sodium cooled fast reactor. Water experiments using an 1/10th scaled model were carried out for an advanced loop type sodium cooled reactor. The reactor vessel is highly compact and has an upper inner structure (UIS), which has a slit in radial direction for fuel handling. The jet from core outlet goes through the UIS slit and makes asymmetric and locally high velocity field in the reactor upper plenum. Steep temperature distribution across the stratification interface and temperature fluctuations were found near the UIS slit. It was revealed that they were resulted from the impingement of the jet through the slit at the interface. Parameter experiments showed the characteristics of thermal stratification interface.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Choi, J. H.*; Hirano, Toru; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2009-027, 48 Pages, 2009/10
On the radioactive waste disposal, the long-term mechanical stability of tunnel was required. Therefore, we have been developing the method evaluating the stability. This report describes the works in the FY2008. Chapter 1 is the overview. In Chapter 2 we performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of single crystal quartz, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. After applying stress the surface of contacted area of quartz was observed by microscope and found traces of dissolution and reprecipitation. We managed two types of experiment; a closed solution experiment and a flow-through experiment. We discussed the Si dissolution rate based on the experimental results measured by ICP-AES. Fundamental mechanism of time-dependent creep and stress relaxation for crystalline rocks was discussed in Chapter 3 based on a concept of mechano-chemical coupling phenomena (as treated in Chapter 2) at micro-crack tips.
Nakatani, Takayoshi; Ishitoya, Kimihide; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Kurosawa, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Research 2009-028, 47 Pages, 2009/10
This study was carried out the evaluation of exposure dose on "Less-likely Scenarios" according to "Basic Policy for Safety Regulation Concerning Land Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (Interim Report)" (In July 2007, the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan). When the evaluation modeling was constructed, "Evaluation scenario" and "Fluctuating parameter" were simplified "Physical, chemical change of the disposal system according to the climatic variation and the tectonic movement" that was the event foreseen happening in the future to "Release coefficient from the disposal facilities of the nuclide", "Distribution coefficient of the natural barrier", "Velocity of the underground water", and "Distance of the transfer path". As the result, exposure doses in all cases for "Less-likely scenarios" were less than 300  Sv/y (standard exposure dose of "Less-likely Scenarios").
Sv/y (standard exposure dose of "Less-likely Scenarios").
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2009-029, 49 Pages, 2009/10
For applying Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is very important to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). Then, the spectra of natural uranium are measured using LIBS, 165 atomic spectra and 381 single ion spectra were identified.
Hazama, Taira
JAEA-Research 2009-030, 61 Pages, 2009/10
Accuracy in k-infinity and reaction rates is compared between APOLLO2 and SLAROM-UF on a fast reactor infinite pin cell model. In the 1st reference level calculation, APOLLO2 and SLAROM-UF agree with the reference value of k-infinity obtained by a continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation within 50 pcm. However, larger errors are observed in a particular reaction rate and energy range. A major problem common to both codes is in the cross section library of  Pu in the unresolved energy range. In the 2nd reference level calculation, which is based on the ECCO 1968 group structure, both results of k-infinity agree with the reference value within 100 pcm. The resonance overlap effect is observed by several percents in cross sections of heavy nuclides. In the standard level calculation based on the APOLLO2 library creation methodology, a discrepancy appears by more than 300 pcm. SLAROM-UF original standard level calculation is the best among the standard level calculations.
Pu in the unresolved energy range. In the 2nd reference level calculation, which is based on the ECCO 1968 group structure, both results of k-infinity agree with the reference value within 100 pcm. The resonance overlap effect is observed by several percents in cross sections of heavy nuclides. In the standard level calculation based on the APOLLO2 library creation methodology, a discrepancy appears by more than 300 pcm. SLAROM-UF original standard level calculation is the best among the standard level calculations.
Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Yamada, Atsuo*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2009-031, 58 Pages, 2009/11
JAEA is advancing the geo-scientific research at the Mizunami Underground Laboratory. In this project, the purpose of rock mechanics investigations is to understand the rock mechanical conditions deep underground and to construct a rock mechanical model of this site. This report describes the rock mechanics results from MIZ-1 borehole investigations. A brief summary is shown as follows. The rock mechanical properties are consistent with the results of similar investigations in the nearby Shobasama site. The AE/DRA and ASR stress measurement give very low confidence results due to very small deformation during drilling. The DSCA and hydraulic fracturing stress measurement show that the horizontal, maximum principal stress is oriented to NW-SE. About 600(m) depth, the in situ stress state is reverse fault type. But below it, the stress state changed to a wrench or normal fault type. In consideration of the investigations and geological model, we proposed a rock mechanical model.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sano, Michiaki; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2009-032, 68 Pages, 2009/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project is planned to extend over a period 20 years. The investigations will be conducted in 3 phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction Phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). This report summarizes the results of the investigations for the 2008 fiscal year (2008/2009), the 4th year of the Phase 2 investigations. The investigations, which are composed of "Geoscientific research" and "R&D on the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW)", were carried out according to "Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project Investigation Program for the 2008 Fiscal year". The results of these investigations, along with the results which were obtained in other departments of Japan Atomic Agency (JAEA), are properly offered to the implementations and the safety regulations. JAEA proceeded with the project in collaboration with experts from domestic and overseas research organisation.
Sugawara, Takanori; Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Nishihara, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2009-033, 102 Pages, 2009/11
In this study, the error analysis for transmutation systems was performed. As the transmutation system, Fast Reactor (FR) and Accelerator Driven System (ADS) were employed and the errors caused by the nuclear data for these systems were estimated by using the covariance data prepared in JENDL-3.3. The effect of MA-loaded critical experiments was also investigated by using the cross section adjustment procedure. It was considered that the MA-loaded critical experiment would be performed at Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) which has been planned its construction in the second phase of J-PARC project. The analysis results presented quantitatively that the errors caused by the nuclear data for these systems were improved by the MA-loaded experiments. The MA-loaded experiment is one of the most useful methods to improve the error caused by the nuclear data which relates to the reliability and the economic efficiency of the transmutation systems.
Takeda, Seiji; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nagasawa, Hirokazu; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Sekioka, Yasushi; Kanzaki, Yutaka; Sasaki, Toshihisa; Ochiai, Toru; Munakata, Masahiro; Tanaka, Tadao; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-034, 239 Pages, 2009/11
In safety assessment for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, it is of consequence to estimate the uncertainties due to the long-term frame associated with long-lived radionuclides and the expanded geological environment. The uncertainties result from heterogeneity intrinsic to engineered and natural barrier materials, insufficient understanding of phenomena occurring in the disposal system, erroneous method of measurement, and incomplete construction. It is possible to quantify or to reduce the uncertainties according to scientific and technological progress. We applied a deterministic and a Monte Carlo-based probabilistic method simulation techniques to the uncertainty analysis for performance of hypothetical geological disposal system for high level radioactive waste. This study provides the method to evaluate the effects of the uncertainties with respect to scenarios, models and parameters in engineering barrier system on radiological consequence. The results also help us to specify prioritized models and parameters to be further studied for long-term safety assessment.
Nakayama, Masashi; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Matsuda, Takeshi*; Noda, Masaru*; Iriya, Keishiro*; Takeda, Nobufumi*
JAEA-Research 2009-035, 70 Pages, 2009/11
In Horonobe Underground Research Center construction of underground facility began in 2005 and construction practicality test with HFSC (Highly Fly-ash contained Silica-fume Cement) is planned in a part of the gallery. Before HFSC will be placed in the gallery it is necessary to validate that HFSC has performance under the actual construction. The research results in 2007 were as follows. As corrosion behavior in HFSC, reinforced concrete specimen with HFSC 226 have been exposed to off-shore condition at in saline water and splashed zone and analyzed corrosion rate and chloride intrusion, and they were summarized. Service life time of HFSC reinforced concrete was assessed more than 50 years until cracking due to corrosion is generated. pH and components of solid and liquid phase which were made in 2002, and stored in water were analyzed. And cement paste of shotcrete which are made in 2006 were also analyzed. In this pH of shotcrete is lower than other in situ concrete since accelerating agent may act as decreasing factor of pH. The results obtained from this ten year's study were summarized on shotcerete, in situ concrete and grouting. Based on the summery, method of quality control, such as testing method, frequency, and standards so on, were investigated.
Nakayama, Masashi; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Noguchi, Akira; Miura, Norihiko*; Noda, Masaru*; Iriya, Keishiro*; Hitomi, Takashi*
JAEA-Research 2009-036, 49 Pages, 2009/11
In Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (Horonobe URL) Project, construction practicality test with HFSC (Highly Fly-ash contained Silica-fume Cement) is planned in a part of the gallery. It is necessary to validate that HFSC has performance under the actual construction, before HFSC is placed in the gallery. The main tasks in 2008 are follows; (1) suggestion of mix design for liner concrete of shaft in Horonobe URL, (2) investigation of long term pH changes in order to use for modeling, and (3) an experiment for interaction between HFSC and ground water around Horonobe URL. (1) 4 types of mix proportion are designed for ordinary concrete and high strength concrete which contains polypropylene fiber or not. As early age strength, 5N/mm is required because of concrete formwork. HFSC424 with low water binder ratio can fulfill this requirement in combination with super plasticizer. (2) pH and components of solid and liquid phase which were made in 2003, and stored in water were analyzed. And cement paste of shotcrete which are made in 2006 were also analyzed. In this pH of shotcrete is lower than other in situ concrete since accelerating agent may act as decreasing factor of pH. (3) An experiment which investigates dissolution of HFSC cement hydrates to ground water around Horonobe URL. According to the experiment, dissolving depth of HFSC is 4 times small comparing to Ordinary Portland Cement hydrates after 30th water exchange.
is required because of concrete formwork. HFSC424 with low water binder ratio can fulfill this requirement in combination with super plasticizer. (2) pH and components of solid and liquid phase which were made in 2003, and stored in water were analyzed. And cement paste of shotcrete which are made in 2006 were also analyzed. In this pH of shotcrete is lower than other in situ concrete since accelerating agent may act as decreasing factor of pH. (3) An experiment which investigates dissolution of HFSC cement hydrates to ground water around Horonobe URL. According to the experiment, dissolving depth of HFSC is 4 times small comparing to Ordinary Portland Cement hydrates after 30th water exchange.
Kitamura, Akira; Kirishima, Akira*; Saito, Takumi*; Shibutani, Sanae*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2009-037, 91 Pages, 2009/11
Within the scope of the JAEA thermodynamic database project for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU radioactive wastes, the selection of the thermodynamic data on the inorganic compounds and complexes of cobalt and nickel have been carried out. For cobalt, extensive literature survey has been performed and all the obtained literatures have been carefully reviewed to select the thermodynamic data. Selection of thermodynamic data of nickel has been based on a thermodynamic database published by the OECD/NEA, which has been carefully reviewed by the authors, and then thermodynamic data have been selected after surveying latest literatures. Based on the similarity of chemical properties between cobalt and nickel, complementary thermodynamic data of nickel and cobalt species expected under the geological disposal condition have been selected to complete the thermodynamic data set for the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive wastes.
Sakai, Ryutaro; Munakata, Masahiro; Ooka, Masao*; Kameya, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Research 2009-038, 38 Pages, 2009/11
In the safety assessment for a geological disposal of radioactive waste, it is important to develop a methodology and uncertainties of long-term estimation of regional groundwater flow system. The authors discussed the uncertainties of hydraulic conductivity as a significant hydrological parameter for regional groundwater flow analysis model. This study demonstrated that confining pressure change cased by uplift and subsidence and change of hydraulic gradients under the long-term geological and hydrological environmental change could possibly produce variations more than one order of magnitude in hydraulic conductivity of rock mass. It also clarified that the effect of water quality change on hydraulic conductivity is not negligible and that the replacement of fresh water and saline water cased by sea level change could predict to reduce hydraulic conductivities in rock mass 0.6 times from its present data in case of Horonobe site.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Suyama, Tadahiro
JAEA-Research 2009-039, 22 Pages, 2009/11
For the better understanding of phenomena caused by iron-bentonite(smectite) interactions, experimental samples conducted over a period of 10 years at room temperature with mixture of distilled water, iron and bentonite (an iron/bentonite mass ratio of 1) were analyzed to identify the alteration behavior of smectite. Major results are summarized below. (1)The color of bentonite changed to grey-green or grey-black with interaction of iron material. The pH and Eh values of solution after the experiment also changed to more alkaline and reducing (pH around 11.5, Eh -284 mV vs. SHE) comparing with the initial condition. (2)Results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, Scanning Electron Microphotograph (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microphotograph (TEM) observation suggested that no alteration was occurred and the initial Na-type smectite would be remained.
Kobayashi, Takuya; Togawa, Orihiko; Ito, Toshimichi; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Hayashi, Keisuke*; Shima, Shigeki*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; In, Teiji*
JAEA-Research 2009-040, 63 Pages, 2009/12
A spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant has the possibility of routine releases of liquid radioactive wastes from a discharge pipe to the off Shimokita region during its operations. Thus, for environmental safety, it is important to assess the migration processes of released radionuclides from the plant. Therefore, an ocean circulation prediction code and an oceanic radionuclides migration prediction code, which were developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency, has been improved to describe the migration behavior of radionuclides in the off Shimokita region. Parameters on characteristics and dynamics of particulate materials in seawater have also been obtained in the study area for the adjustment and verification of the oceanic radionuclides migration prediction code. This report summarizes the primary results of the study which was carried out at the off Shimokita region from FY2003 to 2008.
Fukaya, Yuji; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okubo, Tsutomu
JAEA-Research 2009-041, 86 Pages, 2009/12
The purpose of this research is to investigate spent fuel characteristics of High Conversion type core of FLWR (HC-FLWR). HC-FLWR is a new reactor concept and the spent fuel characteristics have been investigated comparing with other types of reactor. For the evaluation, the ORIGEN code was also used. The ORIGEN libraries for HC-FLWR were generated using the SWAT code. The decay heat and the radioactivity after a cooling time of 2 years and 4 years were evaluated. As a result, the decay heat and the radioactivity of FP nuclides from the HC-FLWR spent fuel are almost the same as those of LWRs and full-MOX-LWRs with the discharge burn-up of 45GWd/t, and the decay heat and the radioactivity of actinides are higher than others, because of its large amount of loaded Pu inventory and the Pu composition from the LWR spent fuel including large amount of  Pu. However, the Pu vector of the spent fuel is better than that of full-MOX-LWRs, because of the harder spectrum.
Pu. However, the Pu vector of the spent fuel is better than that of full-MOX-LWRs, because of the harder spectrum.
Shibata, Taiju; Eto, Motokuni*; Kunimoto, Eiji*; Shiozawa, Shusaku; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Oku, Tatsuo*; Maruyama, Tadashi*
JAEA-Research 2009-042, 119 Pages, 2010/01
For the design of the graphite components in the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the graphite structural design code for the HTTR etc. were applied. However, general standard systems for the High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) have not been established yet. The authors had studied on the technical issues which is necessary for the establishment of a general standard system for the graphite components in the HTGR. The results of the study were documented and discussed at a "Special committee on research on preparation for codes for graphite components in HTGR" at Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ). As a result, "Draft of Standard for Graphite Core Components in High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor" was established. In this draft standard, the graphite components are classified three categories (A, B and C) in the standpoints of safety functions and possibility of replacement. For the components in the each class, design standard, material and product standards, and in-service inspection and maintenance standard are determined. This draft standard is the first standard in the world which shows the concept of standard for the graphite core components in HTGR.
Kurosawa, Hideki; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Kosaka, Hideki*; Saito, Satoshi*; Ninomiya, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2009-043, 144 Pages, 2010/01
Research on the influence of fault activity on deep geological environments contributes to the reliability of geological disposal systems for HLW. In this study, preliminary test shows that measured value within 1 hour after measurement start is supposed to include hydrogen gas generated by rock fracturing during the drilling of sampling holes and that stored in surrounding disturbed rocks, though the monitoring from a hand-drilled hole is effective for a rapid measurement. We investigated the concentration of hydrogen gas emitted from the Yamasaki fault zone, in southeast Japan. In our survey, the points where high concentrations of hydrogen gas emission was detected were unevenly distributed along the active fault, and in the southeast portion of the study area where small earthquakes frequently occurred.
Nakatsuka, Noboru; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Sato, Haruo; Sugita, Yutaka; Nakayama, Masashi; Miyahara, Shigenori; Asano, Hidekazu*; Saito, Masahiko*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Hayashi, Hidero*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-044, 53 Pages, 2010/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Radioactive Waste Management Funding and Research Center (RWMC) effect an agreement about research and development of high level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal and carried out research and technological development about geological disposal technology. JAEA has been carried out the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project which is intended for sedimentary rock and the Project includes geoscientific research and geological disposal technology. RWMC carried out an investigation about full-scale demonstration of engineered barrier system (EBS) and operation technology for HLW disposal, under the contract with the Natural Resources and Energy Agency, Ministry of Economy, the Trade and Industry. The investigation aims to obtain the citizens' understanding of the geological disposal. This work includes the full-scale demonstration of operation technology in the Horonobe URL. This joint research is about engineering technology concerned with the work. In 2008 fiscal year (2008/2009), the master plan of the work was made, and a part of the device for transportation of engineered barrier was made, and it has begun the exhibition of full-scale bentonite block and overpack.
Yada, Hiroki; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Maeda, Junichi*
JAEA-Research 2009-045, 64 Pages, 2010/03
In case the electromagnetic pump in the primary sodium purification system of Monju trips up, the sodium flow in the system stops. If we restart the system without stopping the main primary sodium circuit system, the mixing piping structure which connects the branch flow from the purification system to the main flow is subjected to thermal transient load because the cold stagnant sodium is pushed out and the hot sodium from main flow follows. The aim of this study is to assess the fatigue damage of the mixing piping structure in the primary sodium purification system of Monju in case its electromagnetic pump trips up and then it is restarted with keeping plant operation. From the analysis results, we concluded that (1) the fatigue damages were mainly dependent on the temperature difference between the cold sodium at the initial stage and the hot sodium after restart, (2) the fatigue damages were considerably mitigated by preheating and (3) even the severest case allows more than 400 cycles of this events.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Murakami, Hiroshi; Masuda, Kenta; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Matsuda, Setsuro; Ichige, Satoru; Takahashi, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-046, 80 Pages, 2010/01
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H20 (2008) Japanese fiscal year.
Hyakutake, Toru*; Muto, Akinori*; Sasakura, Mariko*; Minowa, Hirotsugu*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Takahashi, Nobuo; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Ema, Akira; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Research 2009-047, 92 Pages, 2010/01
System decontamination has been generally carried out with the aim of reducing the amount of radioactive waste generated and minimizing human exposure to radiation released from nuclear fuel facilities. At the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, metal surfaces that are contaminated by uranium are dry decontaminated by using iodine heptafluoride (IF ) as a system decontaminator. In this dry decontamination technique, a chemical reaction occurs between the uranium compound attached to the metal surface and IF
) as a system decontaminator. In this dry decontamination technique, a chemical reaction occurs between the uranium compound attached to the metal surface and IF . Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination techniques is required. In the present study, the efficiency of a dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center.
. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination techniques is required. In the present study, the efficiency of a dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center.
Belitz, H. J.*; Althausen, B.*; Uehara, Kazuya; Amemiya, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Research 2009-048, 21 Pages, 2010/01
This probe has been developed to measure the ion temperature in the scrape-off-layer (SOL) of the tokamak boundary plasma. Since in the SOL plasma the ion temperature is usually larger than the electron temperature ions reach to the probe with the thermal speed without considering presheeth at the probe frontier. The probe with the cylindrical shape is placed at the parallel to the magnetic field lines. Important parameters of this probe are probe length L, the ratio of L to the radius a and the mean ion Larmor radius  r
r . The ion current density to the side and the end is double integrated and k is expressed analytically. When two probes with different length are placed to the parallel to the magnetic field k is estimated by the difference of the current and we can measure the temperature directly. The application examples to the SOL plasma of JFT-2M and TEXTOR are shown.
. The ion current density to the side and the end is double integrated and k is expressed analytically. When two probes with different length are placed to the parallel to the magnetic field k is estimated by the difference of the current and we can measure the temperature directly. The application examples to the SOL plasma of JFT-2M and TEXTOR are shown.
Uehara, Kazuya
JAEA-Research 2009-049, 11 Pages, 2010/01
The current drive generated by radio frequency waves is regarded as the momentum transfer from waves to resonant electrons through the Landau damping process. The conventional current drive theory is based on the quasi-linear diffusion using the Fokker-Planck equation to derive the deviation of the electron distribution function to cause the current and is not considered the momentum transfer. The momentum transfer is evaluated using a well-defined model of Landau damping and we derived the current drive theory considering the competition between the electron acceleration by the effective force acting on resonate electrons and the collision of particles. The deformed distribution function to yield the RF current is also formulated with a Boltzmann equation including a simple collision term.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*
JAEA-Research 2009-050, 57 Pages, 2010/01
It is important to understand EDZ in assessing performance of repository and designing of plug. It is known that it remains possible that the large-scale EDZ is generated due to strain localization from boring investigations and tunnel excavation analyses and rock properties changes with increase of depth. Excavation analysis of vertical shaft in sedimentary rock taken into account strain softening, depth variation of rock properties and the actual construction procedure had been done in order to understand EDZ of Horonobe URL. The large-scale EDZ due to strain localization was generated around the border between Koetoi formation and Wakkanai formation. From result obtained from excavation analysis, scale of EDZ obtained from excavation analysis is from 60 cm to 120 cm. And it was estimated that seismic velocity changed by 20 percent, elastic modulus changed by 30 percent and hydraulic conductivity changed by 0.1 m/s order.
Ono, Ayako; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Tobita, Akira
JAEA-Research 2009-051, 30 Pages, 2010/02
The main cooling system of Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) consists of two loops to reduce the plant construction cost. In the design of JSFR, sodium coolant velocity is beyond 9 m/s in the primary hot leg pipe with large-diameter. The maximum Reynolds number in the piping reaches 4.2 10
10 . The hot leg pipe having an elbow with curvature ratio of r/D = 1.0, so-called "short elbow", which enables a compact reactor vessel. Under such a system condition, the flow-induced vibration (FIV) is concerned at the short elbow. It is significant to obtain the knowledge of the fluctuation intensity and spectra of velocity and pressure fluctuations in order to grasp the mechanism of the FIV. In this study, water experiments were conducted. Two types of 1/8 scaled elbows with different curvature ratio, r/D = 1.0, 1.5, were used to investigate the influence of curvature on velocity fluctuation at the elbow. The velocity fields in the elbows were measured using a high speed PIV method. Unsteady behavior of secondary flow at the elbow outlet and separation flow at the inner wall of elbow were observed in the two types of elbows. It was found that the growth of secondary flow correlated with the flow fluctuation near the inside wall of the elbow.
. The hot leg pipe having an elbow with curvature ratio of r/D = 1.0, so-called "short elbow", which enables a compact reactor vessel. Under such a system condition, the flow-induced vibration (FIV) is concerned at the short elbow. It is significant to obtain the knowledge of the fluctuation intensity and spectra of velocity and pressure fluctuations in order to grasp the mechanism of the FIV. In this study, water experiments were conducted. Two types of 1/8 scaled elbows with different curvature ratio, r/D = 1.0, 1.5, were used to investigate the influence of curvature on velocity fluctuation at the elbow. The velocity fields in the elbows were measured using a high speed PIV method. Unsteady behavior of secondary flow at the elbow outlet and separation flow at the inner wall of elbow were observed in the two types of elbows. It was found that the growth of secondary flow correlated with the flow fluctuation near the inside wall of the elbow.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2009-052, 30 Pages, 2010/02
We have investigated propagation characteristics of the laser ablation plume produced from CeO sample to optimize experimental conditions for isotope analysis for low-decontaminated TRU fuel. Vertical flow velocity and horizontal expansion velocity of the plume were evaluated with optical TOF measurement and Doppler splitting measurement. These measurements revealed that (1) the ionic plume in vacuum consists of two components having vertical velocities of 4.7 km/s and 9.3 km/s whereas the atomic plume has a single component having velocity of 3.5 km/s, and (2) these velocities for particles in various excited states are almost the same, (3) horizontal velocity is about 20% slower than the vertical one, (4) plume expansion in gas environment is described with a drag model, (5) under an optimum condition for isotope analysis, plume expansion is almost stopped and an ionization degree is significantly decreased.
sample to optimize experimental conditions for isotope analysis for low-decontaminated TRU fuel. Vertical flow velocity and horizontal expansion velocity of the plume were evaluated with optical TOF measurement and Doppler splitting measurement. These measurements revealed that (1) the ionic plume in vacuum consists of two components having vertical velocities of 4.7 km/s and 9.3 km/s whereas the atomic plume has a single component having velocity of 3.5 km/s, and (2) these velocities for particles in various excited states are almost the same, (3) horizontal velocity is about 20% slower than the vertical one, (4) plume expansion in gas environment is described with a drag model, (5) under an optimum condition for isotope analysis, plume expansion is almost stopped and an ionization degree is significantly decreased.
Hasegawa, Ken
JAEA-Research 2009-053, 29 Pages, 2010/02
We measured the magnetic susceptibility of boring cores obtained from the Regional Hydrological Study Project to interpret the aeromagnetic survey data which was carried out in Tono area with about 40 km square surrounding Tono Geoscience Center. The result of measurements indicates that the magnetic susceptibility of the Toki Granite is not distributed uniformly and the maximum value becomes two orders in magnitude larger than its minimum value.
Hasegawa, Ken
JAEA-Research 2009-054, 53 Pages, 2010/02
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performing the geoscientific research project, the "Regional Hydrogeological Study" (RHS) Project began in 1992. The study site for this project is located in an area that includes the Tono Geoscience Center (TGC), Toki City, Gifu Prefecture. This project is intended for the development of an understanding of the geological environment and development of analytical techniques and methods for systematic geological studies. As one of the RHS Project, TGC approached the defining of geological structures with an aeromagnetic survey. The target is the low magnetic anomaly area known as the Ryoke belt. The fundamental data processing such as data compilation and diurnal correction were done, and the datum correction were also done by means of the "equivalent source" method. Final data shows the magnetic anomaly which may be caused by the Toki granite. To make clear the cause of this anomaly, magnetic susceptibility measurement of rock samples of the Toki granite from some boreholes were done. The results of this measurement indicated that the Toki granite is divided into two zones from the view point of magnetic susceptibility, one zone has relatively high magnetic susceptibility (2 10
10 (SI)), another has quite low magnetic susceptibility (5
(SI)), another has quite low magnetic susceptibility (5 10
10 (SI)). Forward modeling using this result gave the 3-D model of the Toki granite which has relatively high magnetic susceptibility, and this model can almost explain the result of the aeromagnetic survey. Final data shows also additional magnetic anomalies, one may be caused by the normal remanent magnetization of the Hachiya and Nakamura formation above the Kani basin, another one may be caused by unknown intrusive rock above the Mino sedimentary complex rock area. Our approach shows that an aeromagnetic survey can be used to define geological structures for low magnetic anomaly areas such as the Ryoke belt.
(SI)). Forward modeling using this result gave the 3-D model of the Toki granite which has relatively high magnetic susceptibility, and this model can almost explain the result of the aeromagnetic survey. Final data shows also additional magnetic anomalies, one may be caused by the normal remanent magnetization of the Hachiya and Nakamura formation above the Kani basin, another one may be caused by unknown intrusive rock above the Mino sedimentary complex rock area. Our approach shows that an aeromagnetic survey can be used to define geological structures for low magnetic anomaly areas such as the Ryoke belt.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-055, 145 Pages, 2010/02
This report summarizes studies that were carried out with the aim of assessing and systemizing the technology used for the investigation and analysis of the deep underground geological environment in relation to the disposal of radioactive waste. The main studies were: (1) a study on the research and development (R&D) topics proven to have practical application for the investigation, analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment, and, (2) a study on leading edge technology that can provide the advanced technical basis for the investigation, analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment. The principal results obtained from the studies are as follows: Regarding the R&D topics (1, above), the specific investigations, measurements, numerical and chemical analyses were reviewed with respect to engineering technology and the geological environment in this year. Based on the results of the review, topics requiring collaboration research in overlapping research fields, including safety assessment, were identified. Also, the near field concept (NFC) was reconsidered in terms of both the generic model and for crystalline rock. Regarding advanced technology (2, above), based on the objectives of the JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) research project, the study was implemented considering previous R&D results and detailed research result at the research site and thus an assessment of the need for advanced technical basis for investigation and analysis. This study contributed to the R&D development and its practical application.
Hayashi, Katsuhiko; Kishi, Hirokazu; Kabayashi, Yasushi*; Takebe, Atsuji*; Fujiyama, Tetsuo*; Hiramoto, Masayuki*; Mizutani, Kazuhiko*; Morita, Atsushi*
JAEA-Research 2009-056, 86 Pages, 2010/02
In this study, the effect of constitutive models such as strain softening of rock masses for EDZ, and the stress relief ratio used for multi tunnels analysis were conducted. As the result, it is necessary to confirm mechanical behavior of in situ rock and it is important to choose suitable constitutive models, and it is possible for all tunnels in multi tunnels model to have same stress relief ratio.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2009-057, 188 Pages, 2010/02
A series of break size parameter tests (SB-PV-07 and SB-PV-08) were conducted at the Large Scale Test Facility of ROSA-V Program to have an insight into effects of accident management action on core cooling during a simulated vessel top break loss-of-coolant accident with a total failure assumption on the high pressure injection (HPI) system at a pressurized water reactor (PWR). Typical phenomena of vessel top break with break sizes between 1.0 and 0.1% cold leg break equivalent were clarified including upper head water level transients related to steam discharge, coolant mass inventory related to core heat-up, performance of core exit thermocouple (CET)and three-dimensional steam flows in core and core exit. Both operator actions of HPI recovery in the 1.0% top break and steam generator depressurization in the 0.1% top break resulted in immediate recovery of core cooling when these were initiated by CET heat-up at 623 K.
Hayashi, Katsuhiko; Kishi, Hirokazu; Kabayashi, Yasushi*; Takebe, Atsuji*; Okubo, Seisuke*
JAEA-Research 2009-058, 106 Pages, 2010/02
In this study, experimental studies on the strength recovery, the generalized stress relaxation behavior and the tensile strength were conducted using samples obtained from the Wakkanai-formation shale. As the results, the strength recovery has time-dependent characteristics. It was founded that the generalized stress relaxation behavior depends on the draining conditions. Furthermore, regarding the tensile strength, complete stress-strain curve under uniaxial tensile strength conditions was gotten and it was found that there is small residual strength. The results of uniaxial tensile strength in this year are almost same as the minimum value of splitting tensile strength test results.
Isogai, Takeshi*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Research 2009-059, 28 Pages, 2010/02
Porewater model of bentonite is important to evaluate the behavior of radionuclides and corrosion of overpack material for performance assessment of geologic disposal of high level radioactive waste. In the present study, as a matter of consideration for applicability of porewater model to the actual geological environment, experiments of bentonite-water interactions using groundwater sampled from Horonobe underground laboratory were conducted. In order to test the applicability of model, comparison between the data obtained by experiments and modeling results by porewater model based on chemical equilibrium was performed.
Shimo, Michito*; Kumamoto, So*; Ito, Akira*; Karasaki, Kenji*; Sawada, Atsushi; Oda, Yoshihiro; Sato, Hisashi
JAEA-Research 2009-060, 70 Pages, 2010/03
It is important for safety assessment of HLW geological disposal to evaluate groundwater flow and mass transport in deep underground appropriately. Though it is considered that the mass transport in sedimentary rock occurs in pores between grains mainly, fractures of sedimentary rock can be main paths. In this study the following three tasks were carried out: (1) laboratory hydraulic and tracer experiments using the rock cores of Wakkanai formation, (2) a study on the tracer test and sampling technique for the larger scale, (3) a study on the reduction technique of uncertainty of the hydrogeological models using data from surface-based investigation. On the block scale tracer test technique, the sampling technique using wire saw and tracer test technique using block samples were suggested. As for the reduction technique of uncertainty of the hydrogeological model, availability of the information other than pressure data, such as the temperature and salinity and all, were presented.
Nakano, Yoshihiro; Fukaya, Yuji; Akie, Hiroshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao
JAEA-Research 2009-061, 92 Pages, 2010/03
A series of research on a high conversion type innovative water reactor for flexible fuel cycle (FLWR) has been conducted. This FLWR is a boiling water reactor (BWR) with a tight triangular fuel rod lattice and the uranium plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel. FLWR is designed for two types of cores to be developed in succession. The preceding core is a high conversion type FLWR (HC-FLWR) and the other core is Reduced Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) of which the conversion ratio is more than 1.0. Three design studies and a senario study on HC-FLWR are presented in this report. The first design study is for a representative core. The second one is for a transition core from HC-FLWR to RMWR. In the transition core, both assemblies for HC-FLWR and RMWR exist. The third one is for a core to recycle minor actinides (MAs). Regarding to the scenario study, based on design results of the representative core, effective plutonium utilization in future LWR was considered within general framework.
Sekioka, Yasushi*; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2009-062, 68 Pages, 2010/03
In safety assessment for geological disposal, release of radionuclides from vitrified waste is dependent on dissolution rate of glass matrix. It is assumed that the alteration and dissolution of glass in an engineered barrier system proceeds by a mechanism not related by the chemical affinity for dissolution reaction of glass matrix. Recent studies indicate that the glass dissolution rate is likely to decrease as time passed, but scientific basis on the dissolution process has not been necessarily understood. We estimate uncertainty of the glass dissolution rate represented by not only a model of constant dissolution rate but also a model of decreasing dissolution rate. In order to estimate the parameter uncertainty of the glass dissolution rate, we carried out the statistical analysis of the appropriate release rate data of boron for a hypothetical condition of disposal system, based on investigating the relation between published data of glass dissolution and those experimental conditions. As a result of the model of constant dissolution rate, the uncertainty of the glass dissolution rate is estimated to be a variance with about 3 orders and logarithmic mean of 0.004 g/m /day. The glass dissolution rate by the decreasing model changes in the range of 10
/day. The glass dissolution rate by the decreasing model changes in the range of 10 to 10
to 10 g/m
g/m /day by 1000 years and is lower than the minimum value estimated by the model of constant dissolution rate. The result indicates that the difference of two models may lead to large variance of the glass dissolution rate in safety assessment.
/day by 1000 years and is lower than the minimum value estimated by the model of constant dissolution rate. The result indicates that the difference of two models may lead to large variance of the glass dissolution rate in safety assessment.
Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Sone, Tomoyuki; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Ishitoya, Kimihide; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Shimoda, Satoko*; Kurosawa, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Research 2009-063, 80 Pages, 2010/03
The purpose of this study was to assess exposure dose of "Likely Scenarios" and "Less-likely Scenarios" on sub-surface disposal. They were two of "Classification of three types scenarios" in "Basic Policy for Safety Regulation Concerning Land Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (Interim Report)" formulated by the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan. Selection of the assessed scenarios, development of the assessment tool and preliminary exposure dose assessment were conducted. Maximum exposure doses for "Likely Scenarios" and "Less-likely Scenarios" were less than each standard dose value in the Interim Report (Likely Scenarios: 10 Sv/y, Less-likely Scenarios: 300
Sv/y, Less-likely Scenarios: 300 Sv/y).
Sv/y).
Nakatani, Takayoshi; Ishitoya, Kimihide; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Sone, Tomoyuki; Shimada, Hidemitsu*; Nakai, Kunihiro*
JAEA-Research 2009-064, 104 Pages, 2010/03
The purpose of this study was to assess exposure dose of "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios" on sub-surface disposal. It was one of "Classification of three types scenarios" in "Basic Policy for Safety Regulation Concerning Land Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (Interim Report)" formulated by the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan. Selection of the assessed scenarios, development of the assessment tool and preliminary exposure dose assessment were conducted. Exposure dose of "Well water drinking scenario" was the highest in the assessed scenarios. This scenario assumed that the groundwater in Excavation Disturbed Zone (EDZ) was directly used as drinking water without any dilution. Although this was very conservative condition and the result exceeded 10 mSv/y, it was under the upper limit of standard dose value (10 100 mSv/y) in the Interim Report for "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios".
100 mSv/y) in the Interim Report for "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios".
Saito, Yuya; Tanai, Kenji; Takaji, Kazuhiko*; Shigeno, Yoshimasa*; Shimogochi, Takafumi*
JAEA-Research 2009-065, 76 Pages, 2010/03
The 3-D mechanical coupled analysis technique for the long term mechanical behavior of near field is developed. The object of analysis is extended to the disposal gallery and the near field rock, in addition to the buffer material and the overpack for previous one. The analysis model is developed with a degradation model of concrete support and modeling of the near field rock with the valuable- compliance-type constitutive equation. The remaining problems of current study are related to; (1) mechanical property and modeling of backfill material, (2) adopting a degradation model of concrete support in the prototype model, (3) examining the effect of analytical model mesh and time step for the 3-D mechanical coupled analysis. We conducted the one-dimensional consolidation test for the backfill material. The backfill material shows a similar behavior to that of buffer material. And the prototype model is developed adopting a degradation model for a concrete support and examining the effect of the model mesh and time step.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2009-066, 18 Pages, 2010/03
It has been known that carbon steel can be passivated in high pH environment and sometimes be attacked by localized corrosion such as pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion. If carbon steel overpack is attacked by localized corrosion, it is possible that the overpack may be penetrated in a short term, since the propagation rate of localized corrosion is larger than that of general corrosion in general. It has been known that the pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion are initiated in the presence of aggressive species for passive film represented by chloride ion. In repository environment, it is possible that the pH in groundwater containing chloride ion such as seawater type groundwater is raised by a contact with the cement material in concrete structures constructed around the engineered barrier system and then pitting corrosion or crevice corrosion is caused on the carbon steel overpacks. In this study, the propagation behavior of pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion was examined by immersion tests under air equilibrium condition using artificial groundwater at Horonobe as an example of seawater-type groundwater. As the results, the pitting factor (ratio of the maximum corrosion depth and average corrosion depth) were within the literature data obtained in neutral and alkaline water and in various natural water environments. The maximum corrosion depth of carbon steel overpack was predicted by extreme value statistical analysis of the experimental data, and it was confirmed that the predicted corrosion depths were not over the values calculated from current empirical models for propagation of pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion in every cases.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2009-067, 29 Pages, 2010/03
Since the propagation rate of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is generally larger than that of other corrosion mode without cracking, it is difficult to avoid the penetration due to SCC by designing the corrosion allowance. Therefore, it is important to clarify the possibility of SCC initiation or conditions where SCC is possible to be occurred. It has been known that copper and copper alloys are susceptible to SCC in ammonia environment depending on the conditions. In this study, the SCC susceptibility of oxygen free copper was investigated in ammonia solution and groundwater containing ammonium ion under oxidizing condition by slow strain rate technique. As the results, no SCC was observed both in 0.05M and 0.1M NH OH solution. In Horonobe groundwater containing ammonium ion, brittle fracture surface and cracks were observed at -144mV vs. SCE. The morphologies of the SCC were not only intergranular type but also transgranular type and transgranular cracks branched from intergranular crack. In these test conditions, corrosion products were strongly adhered to the specimen surface and inside of the cracks. This indicates that the SCC was caused by tarnish rupture mechanism. In buffer material saturated with Horonobe groundwater, mechanical properties such as maximum stress and fracture strain were comparable with those in silicon oil, and no distinct cracks due to SCC were detected on the specimens.
OH solution. In Horonobe groundwater containing ammonium ion, brittle fracture surface and cracks were observed at -144mV vs. SCE. The morphologies of the SCC were not only intergranular type but also transgranular type and transgranular cracks branched from intergranular crack. In these test conditions, corrosion products were strongly adhered to the specimen surface and inside of the cracks. This indicates that the SCC was caused by tarnish rupture mechanism. In buffer material saturated with Horonobe groundwater, mechanical properties such as maximum stress and fracture strain were comparable with those in silicon oil, and no distinct cracks due to SCC were detected on the specimens.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Naito, Morimasa
JAEA-Research 2009-068, 31 Pages, 2010/03
Corrosion of metal is an interaction between the material and the environment, so that the corrosion behavior of carbon steel overpack might be affected by not only the environmental factors but also the material factors. In this study, the effect of general impurities in carbon steel such as C, Si, Mn, P and S on the electrochemical behavior and the corrosion rate were studied using carbonate aqueous solution and synthetic seawater. The experimental results were summarized as follows; (1) The effect of the impurities on the critical passivation current density,  and the passive current density,
and the passive current density,  were small in 0.01M carbonate aqueous solution at pH10. (2) Breakdown of passive film and increase in anodic dissolution were observed in the tests for high Si condition of 0.73% and 0.97%. (3) In buffer material saturated with 0.01M carbonate aqueous solution, no passivation was observed and the effect of impurities on the anodic polarization behavior was small. (4) The corrosion rate of carbon steel in seawater was increased with the concentration of impurities. Among the impurity elements, the effects of P and Mn were relatively large. (5) It was inferred that the increase in corrosion rates in synthetic seawater by the addition of Si, Mn and P was promoted by the activation of hydrogen evolution reaction as a cathodic reaction.
were small in 0.01M carbonate aqueous solution at pH10. (2) Breakdown of passive film and increase in anodic dissolution were observed in the tests for high Si condition of 0.73% and 0.97%. (3) In buffer material saturated with 0.01M carbonate aqueous solution, no passivation was observed and the effect of impurities on the anodic polarization behavior was small. (4) The corrosion rate of carbon steel in seawater was increased with the concentration of impurities. Among the impurity elements, the effects of P and Mn were relatively large. (5) It was inferred that the increase in corrosion rates in synthetic seawater by the addition of Si, Mn and P was promoted by the activation of hydrogen evolution reaction as a cathodic reaction.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Ochs, M.*; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2009-069, 83 Pages, 2010/03
This report presents the prototype model/database for integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD2009) in bentonite systems as basis for performance assessment (PA) of geological disposal. The sorption model is based on a relatively simple 1-site surface complexation/diffuse layer model in combination with 1-site ion exchange model. The model parameters for surface chemistry/sorption are evaluated based on existing datasets for Na-montmorillonite, which covers key geochemical conditions, in consistent way. The diffusion model based on homogeneous pore structure and electrical double layer theory was developed and coupled with batch-based sorption model, then was validated by using data in compacted montmorillonite. The sorption and diffusion models were also tested by applying data in bentonite systems. The model and related parameters developed for key radionuclides such as Cs, Np(V), Ni, Am, etc. are integrated to ISD2009 database, which could be useful in future PA exercise.
Matsumoto, Kazuhiro; Tanai, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2009-070, 47 Pages, 2010/03
The buffer that will be used as a component of the engineered barriers system swells when saturated by groundwater. As a result of this swelling, buffer may penetrate into the surrounding rock zone through open fractures. It sustained for extremely long periods of time, the buffer extrusion could lead to reduction of buffer density, which may in turn degrade the assumed performance. In this report, the viscosity of bentonite was measured as one of the parameter of diffusion model. In addition, the simulation analysis was carried out to confirm the applicability of diffusion model.
Kuno, Yoshio; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Research 2009-071, 65 Pages, 2010/03
To evaluate colloidal effects on radionuclide (RN) migration through a fractured rock, sensitivity analyses were conducted by considering the properties of groundwater colloids. Distribution coefficient for the mobile colloids Kd (m
(m /kg) and colloid concentration M (kg/m
/kg) and colloid concentration M (kg/m ) are important parameters since the product of them (Kd
) are important parameters since the product of them (Kd M) indicates the colloidal effects on RN migration, which is noticeably enhanced in the case of Kd
M) indicates the colloidal effects on RN migration, which is noticeably enhanced in the case of Kd M
M  1. Furthermore, colloid migration was simulated by taking into account colloid filtration by the fracture surfaces. Filtered colloids tend to increase with increasing the filter coefficient
1. Furthermore, colloid migration was simulated by taking into account colloid filtration by the fracture surfaces. Filtered colloids tend to increase with increasing the filter coefficient  (1/m). Breakthrough of RNs shows a peak curve since RNs sorbed on the filtered colloids increase and mobile RNs decrease with time. RN distribution to the filtered colloids could have a sufficient impact on RN migration by reducing mobile concentration in the fracture.
(1/m). Breakthrough of RNs shows a peak curve since RNs sorbed on the filtered colloids increase and mobile RNs decrease with time. RN distribution to the filtered colloids could have a sufficient impact on RN migration by reducing mobile concentration in the fracture.
Kusano, Tomohiro; Asamori, Koichi; Kurosawa, Hideki; Tanikawa, Shinichi; Ninomiya, Atsushi; Negi, Tateyuki; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yasue, Kenichi; Yamada, Kunimi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-072, 72 Pages, 2010/03
The Japanese islands are located in the tectonically active Circum-Pacific Mobile Belt. As a result, Japan has a high frequency of earthquakes and eruptions. Special consideration is given to the long-term stability of the geological environment, taking into account volcanism, faulting, uplift, denudation, climatic change and sea-level change in Japan. Development of research/prediction technologies for geotectonic events has been carried out to evaluate the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. In fiscal year 2008, we carried out the following researches. For studies on faulting and seismic activity, we developed investigation techniques for evolutional history and activity of fault, and carried out case studies for development of effective assessment model in the fault zones. For volcanological and geothermal studies, we provided an integrated approach for detecting crustal magma and/or geothermal fluid in deep underground using geophysical and geochemical data. For the general evaluation study on uplift/denudation and climatic/sea-level change, we arranged investigation techniques for reconstruction of paleo-topography and paleo-climate, and to establish a simulation model for landform development. For studies on the long-term stability of the geological environments, we developed simulation techniques for groundwater flow related by crustal movement.